- Understanding Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- What are viral diseases in indoor plants?
- How do viral diseases spread in indoor plants?
- What are the common symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants?
- How to prevent and manage viral diseases in indoor plants?
- In summary
- Symptoms of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- 1. Stunted Growth
- 2. Leaf Mottling
- 3. Distorted Leaves
- 4. Yellowing or Chlorosis
- 5. Necrotic Spots
- 6. Streaks or Rings
- 7. Leaf Drop
- Common Types of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- Causes and Spread of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- Causes of Viral Diseases
- Spread of Viral Diseases
- Preventing the Spread of Viral Diseases
- Diagnosing Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- Preventing Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- 1. Start with healthy plants
- 2. Practice good hygiene
- 3. Remove infected plants
- 4. Avoid overwatering
- 5. Control pests
- 6. Maintain good air circulation
- 7. Use virus-free planting materials
- 8. Educate yourself
- Treating Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
- 1. Prevention is key
- 2. Sanitation
- 3. Control vectors
- 4. Proper plant care
- Q&A:
- What are viral diseases of indoor plants?
- What are some common symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants?
- How can I prevent viral diseases from infecting my indoor plants?
- Are there any treatments available for viral diseases in indoor plants?
- Can viral diseases in indoor plants be transmitted to outdoor plants?
- What are some common insect vectors that transmit viral diseases to indoor plants?
- Video: Part 1: Concept of diseases in plants # microbiology# plant symptoms# Genes & Genus
Welcome to Part 1 of our comprehensive guide on viral diseases of indoor plants. In this series, we will explore the different types of viruses that can affect indoor plants, their symptoms, and possible treatment options. Viral diseases are a common problem for indoor plant enthusiasts, as they can cause significant damage to the overall health and appearance of plants. It is essential to be aware of these diseases and take preventative measures to ensure the well-being of your indoor plants.
Viruses are tiny infectious agents that can only replicate inside the cells of living organisms. They can infect a wide range of plant species and are often transmitted through various means, such as insects, contaminated tools, or infected plant material. Once a virus infects a plant, it can cause a variety of symptoms, including stunted growth, yellowing or mottled leaves, leaf distortion, and reduced crop yield. Some viral diseases may even lead to the death of the infected plant.
One of the most common viral diseases of indoor plants is Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). This virus affects a wide range of plant species, not just tomatoes, and is often spread by thrips, tiny insects that feed on plant sap. TSWV can cause wilting, necrotic spots on leaves, and deformed flowers and fruits. It is crucial to control the population of thrips and remove any infected plants to prevent the spread of TSWV.
Another significant viral disease is Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV). This virus affects a variety of plants, including tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and ornamental plants. CMV is transmitted through aphids, which carry the virus from plant to plant as they feed. Symptoms of CMV include mottled or mosaic-like patterns on the leaves, stunted growth, and deformed fruits. Controlling aphid populations and removing infected plants are essential steps in managing CMV.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of our comprehensive guide on viral diseases of indoor plants, where we will continue to explore other common viral diseases and their management strategies.
Understanding Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
Indoor plants are a popular choice for both decorative and functional purposes. However, just like outdoor plants, indoor plants are also susceptible to viral diseases. Understanding these diseases is essential for ensuring the health and longevity of your indoor plants.
What are viral diseases in indoor plants?
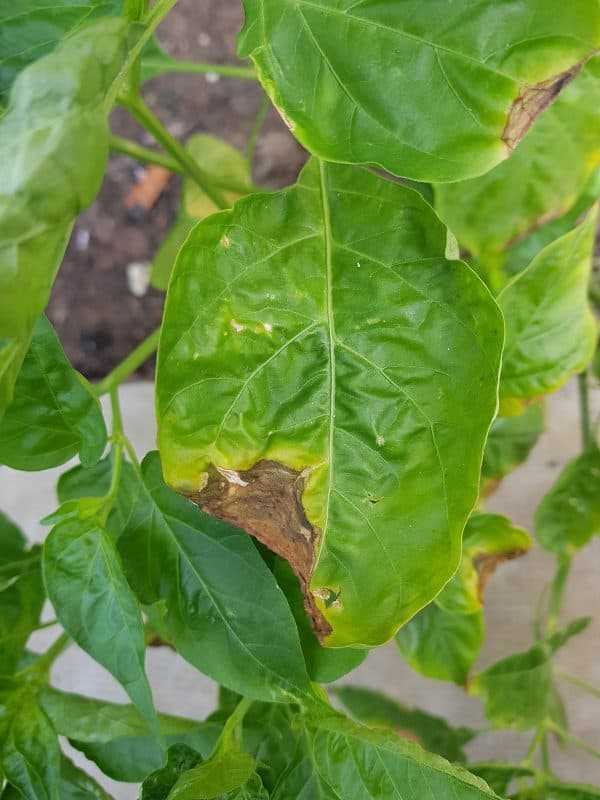

Viral diseases in indoor plants are caused by plant viruses, which are non-living infectious agents. These viruses can infect a wide range of plants, leading to various symptoms and damages. It is important to note that viral diseases cannot be cured with traditional methods, such as fungicides or bactericides, as they specifically target fungi and bacteria, not viruses.
How do viral diseases spread in indoor plants?
Viral diseases in indoor plants can spread through various mechanisms, including direct contact, insect vectors, or contaminated tools and equipment. Direct contact occurs when healthy plants come into contact with infected plants or plant materials, promoting the transfer of the virus. Insect vectors, such as aphids or whiteflies, can transmit viruses from infected plants to healthy ones while feeding on plant sap. Additionally, tools and equipment used in gardening activities can harbor viral particles, leading to indirect transmission between plants.
What are the common symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants?
The symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants can vary depending on the specific virus and the affected plant species. However, some common symptoms include stunted growth, yellowing or mottling of leaves, leaf curling, distorted or discolored flowers, and overall decline in plant vigor. It is important to closely monitor your indoor plants for any signs of viral diseases to take timely action and prevent further spread.
How to prevent and manage viral diseases in indoor plants?
Preventing and managing viral diseases in indoor plants requires a combination of good gardening practices and proper measures. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Start with healthy plants from reputable sources to minimize the risk of introducing infected plants.
- Isolate new plants for a period of time to observe any potential symptoms of viral diseases before introducing them to the rest of your indoor plants.
- Practice good hygiene by regularly cleaning and disinfecting gardening tools and equipment to prevent cross-contamination.
- Monitor your indoor plants regularly for any signs of viral diseases and take immediate action if necessary, such as removing and destroying infected plants.
- Utilize insect control methods to prevent the transmission of viruses by insect vectors.
- Consider using virus-resistant plant varieties, if available, to reduce the risk of viral infections.
In summary
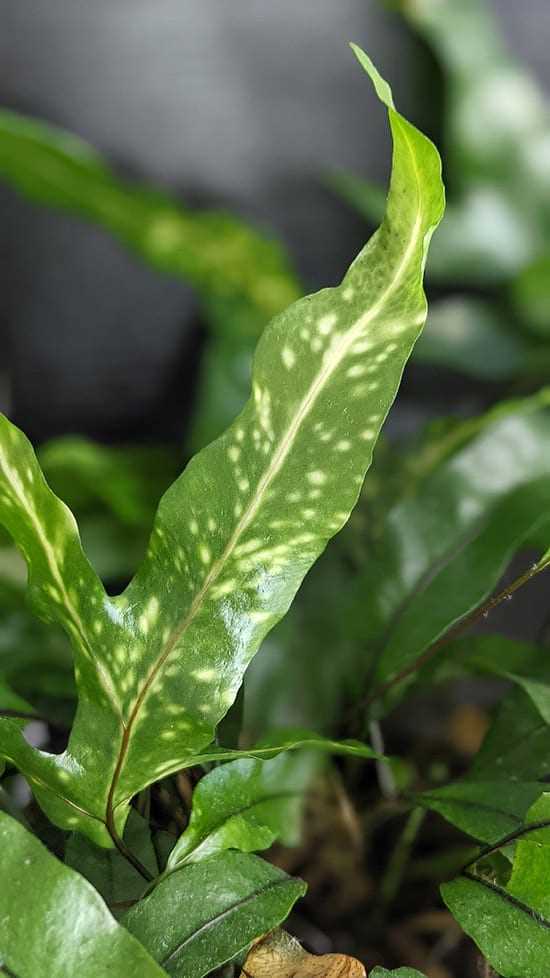

Understanding viral diseases in indoor plants is crucial for their successful cultivation. By being aware of how these diseases spread, recognizing their symptoms, and implementing preventative measures, you can ensure the well-being of your indoor plants and minimize the risk of viral infections.
Symptoms of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
Viral diseases can have a significant impact on the health and appearance of indoor plants. It is important for plant owners to be able to recognize the symptoms of viral infections in order to take appropriate action. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
1. Stunted Growth
One of the first signs of a viral infection in indoor plants is stunted growth. Infected plants may fail to grow to their full potential, with leaves and stems appearing smaller and less developed than usual.
2. Leaf Mottling
Mottled leaves, which display patches or streaks of different colors, are a common symptom of viral diseases in indoor plants. The mottling can be asymmetrical and may vary in intensity.
3. Distorted Leaves
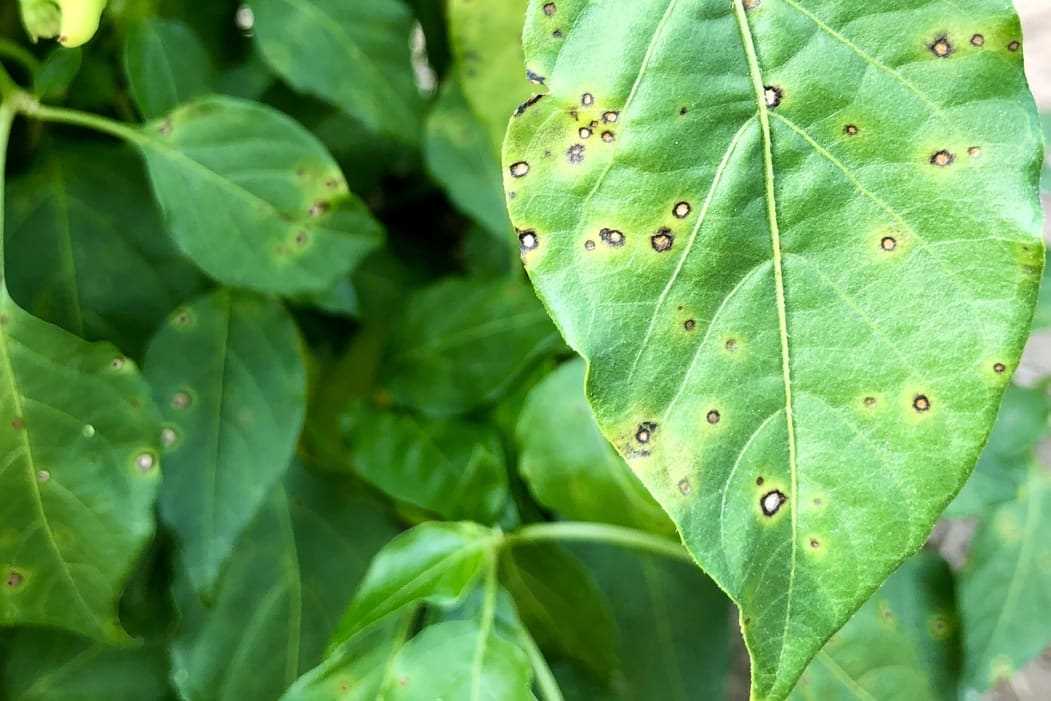
Viral infections can cause leaves to become distorted, with abnormal shapes and sizes. The edges of the leaves may be curled, or the overall leaf shape may be twisted or puckered.
4. Yellowing or Chlorosis

Yellowing of the leaves, also known as chlorosis, is another common symptom of viral diseases in indoor plants. Infected leaves may turn pale yellow or develop irregular yellow patches.
5. Necrotic Spots
Infected plants may develop necrotic spots, which are areas of dead tissue on the leaves or stems. These spots can vary in size, shape, and color, ranging from small brown lesions to large black patches.
6. Streaks or Rings
Some viral infections in indoor plants can cause the development of characteristic streaks or rings on the leaves. These patterns can be symmetrical or asymmetrical and may be of varying colors.
7. Leaf Drop
In severe cases of viral infection, indoor plants may experience leaf drop. Infected leaves may become weak and easily detach from the plant, leading to a loss of foliage.
It is important to note that many of these symptoms can also be caused by other factors such as nutrient deficiencies, pests, or environmental stress. To confirm whether a plant is infected with a virus, laboratory testing may be required. If a viral infection is suspected, it is best to isolate the affected plant and seek professional advice.
Common Types of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
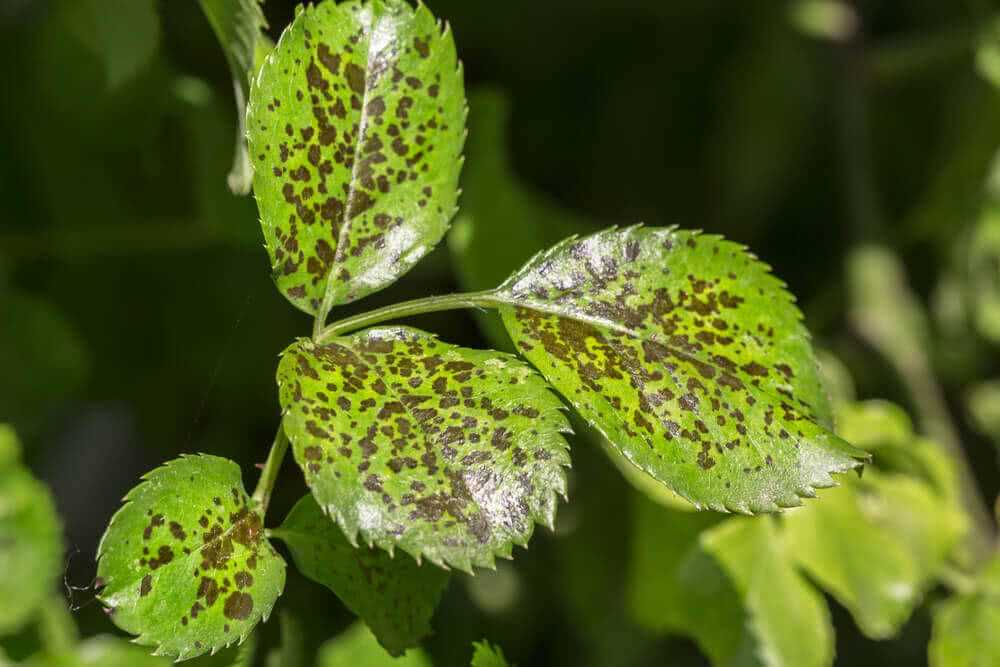

Indoor plants are susceptible to various viral diseases that can cause significant damage to their health and overall appearance. Here are some of the most common types of viral diseases that affect indoor plants:
Mosaic Viruses: Mosaic viruses are a group of viruses that cause mosaic-like patterns or mottling on the leaves of infected plants. The affected leaves may display various colors such as yellow, green, and brown, and the patterns can range from random spots to streaks or swirls. Some examples of mosaic viruses include cucumber mosaic virus and tobacco mosaic virus.
Ring Spot Viruses: Ring spot viruses cause ring-shaped markings on the leaves of infected plants. These markings can be light or dark in color and can be found on both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves. Ring spot viruses can affect a wide range of indoor plants, including ferns, begonias, and philodendrons.
Leaf Curl Viruses: Leaf curl viruses cause the curling and distortion of the leaves of infected plants. The affected leaves may also exhibit a leathery texture and a reduced size. Leaf curl viruses can affect a variety of indoor plants, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
Necrotic Spot Viruses: Necrotic spot viruses cause the development of necrotic or dead spots on the leaves of infected plants. These spots can vary in shape and color, and they often have a brown or black center surrounded by a yellow or brown halo. Necrotic spot viruses can affect many indoor plants, including orchids, African violets, and begonias.
Yellowing Viruses: Yellowing viruses cause the yellowing and wilting of the leaves of infected plants. The affected leaves may also exhibit stunted growth and a general decline in overall health. Yellowing viruses can affect a wide range of indoor plants, including roses, citrus trees, and ferns.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the viral diseases that can affect indoor plants. Diagnosing and treating viral diseases in indoor plants can be challenging, and it’s often best to consult with a plant expert or horticulturist for proper identification and control measures.
Causes and Spread of Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants

Indoor plants are susceptible to various viral diseases, which can significantly impact their health and appearance. Understanding the causes and spread of these diseases is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Causes of Viral Diseases
Viral diseases in indoor plants are primarily caused by plant viruses. These viruses are microscopic pathogens that can infect a wide range of plant species. They typically enter the plant through wounds or natural openings, such as stomata.
Plant viruses can be transmitted through various means, including:
- Infected plant material: Using infected plant materials, such as cuttings or seeds, can introduce viruses into healthy plants.
- Insect vectors: Many plant viruses are transmitted by insects, such as aphids, whiteflies, and leafhoppers. These insects feed on infected plants and carry the viruses to healthy plants.
- Contaminated tools: Using contaminated tools, such as pruning shears or scissors, can transfer viruses from infected plants to healthy plants.
- Contaminated soil or water: Some viruses can persist in the soil or water, infecting plants that come in contact with them.
- Airborne transmission: Certain viruses can be transmitted through the air, especially in enclosed spaces with poor ventilation.
Spread of Viral Diseases
Once a plant is infected with a virus, the virus can spread within the plant through its vascular system, reaching different parts of the plant, including leaves, stems, and roots. As the virus replicates, it can cause various symptoms, such as leaf chlorosis, mottling, stunting, and curling.
Viral diseases can also spread from one plant to another through different mechanisms:
- Direct contact: Infected plants in close proximity to healthy plants can transmit viruses through physical contact.
- Vector transmission: Insects that act as vectors can transmit viruses from infected plants to healthy plants as they feed.
- Seed transmission: Some plant viruses can be transmitted through seeds, leading to the infection of new plants.
- Grafting or budding: Viruses can be transmitted through grafting or budding when infected plant tissues are joined with healthy plants.
Preventing the Spread of Viral Diseases
Preventing the spread of viral diseases in indoor plants is crucial for maintaining healthy plants. Here are some preventive measures:
- Use virus-free plant material: Start with healthy plants or certified virus-free plant materials.
- Inspect and quarantine new plants: Check new plants for any signs of viral diseases before introducing them to your indoor garden. Quarantine new plants for a period to ensure they are free from viruses.
- Practice good hygiene: Clean and sterilize your gardening tools regularly to prevent the spread of viruses.
- Control insect vectors: Use insecticides or natural predators to control insect vectors and reduce the chances of viral transmission.
- Proper plant care: Healthy plants are less susceptible to viral diseases. Provide optimal growing conditions, including proper watering, adequate light, and appropriate fertilization.
- Isolate infected plants: Remove and isolate any infected plants to prevent the spread of viruses to healthy plants.
By understanding the causes and spread of viral diseases in indoor plants, and implementing appropriate preventive measures, you can minimize the impact of these diseases and maintain a healthy indoor garden.
Diagnosing Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
Diagnosing viral diseases in indoor plants can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those caused by other factors such as nutrient deficiencies or fungal infections. However, there are a few key indicators that can help identify viral diseases:
- Mosaic patterns on leaves: One of the most common signs of viral diseases in indoor plants is the presence of mosaic patterns on the leaves. These patterns may consist of irregular spots, streaks, or mottled areas of discoloration.
- Stunted growth: Another characteristic symptom of viral diseases in indoor plants is stunted growth. Infected plants may fail to reach their full potential size and exhibit overall reduced growth compared to healthy plants.
- Leaf distortion: Viral diseases can cause significant distortion in the leaves of indoor plants. This can manifest as curling, cupping, or twisting of the leaves. The leaves may also appear deformed or misshapen.
- Necrotic spots or rings: Some viral diseases can lead to the formation of necrotic spots or rings on the leaves of indoor plants. These spots are often brownish or black and can vary in size and shape. They may also be surrounded by a yellow halo.
If you suspect that your indoor plant is infected with a viral disease, it is important to take action promptly to prevent the spread of the virus to other plants. Here are some steps you can take:
- Isolate the infected plant: Move the infected plant away from other healthy plants to prevent the spread of the virus. Place it in a separate room or area until the disease is properly diagnosed and treated.
- Consult a plant disease specialist: If you are unsure about the diagnosis or need assistance in treating the viral disease, it is recommended to consult a plant disease specialist or an agricultural extension service for guidance.
- Implement proper sanitation practices: Viral diseases can spread through contaminated tools, pots, or soil. Clean and disinfect your gardening tools and containers regularly to minimize the risk of transmission.
- Consider plant removal: In severe cases where the virus has extensively infected the plant and there is little chance of recovery, it may be necessary to remove and destroy the infected plant to prevent further spread.
Diagnosing viral diseases in indoor plants can be challenging, but with careful observation and timely action, you can help prevent the spread of the virus and protect your other plants from infection.
Preventing Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
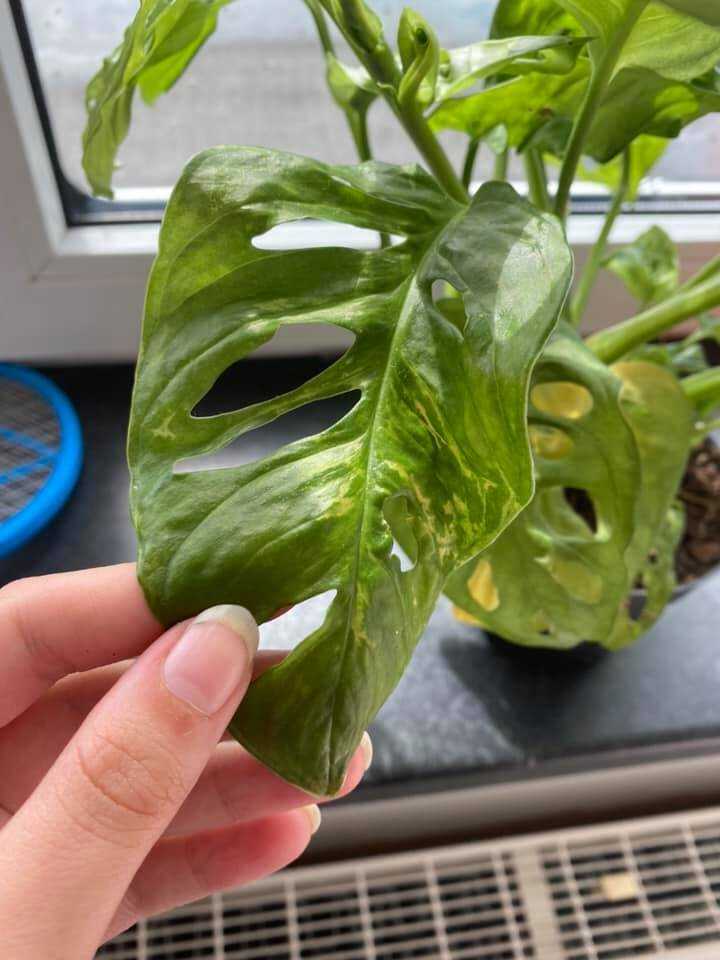

Preventing viral diseases in indoor plants is crucial to maintaining the health and vitality of your plants. Viral diseases can spread quickly and have devastating effects on your indoor garden. Here are some steps you can take to prevent viral diseases from infecting your indoor plants:
1. Start with healthy plants
When introducing new plants to your indoor garden, make sure they are healthy and free from any signs of disease. Inspect the leaves, stems, and roots for any abnormalities or discoloration. Quarantine newly acquired plants for a few weeks to ensure they are not carrying any diseases that may spread to your other plants.
2. Practice good hygiene
Good hygiene is essential in preventing the spread of viral diseases. Wash your hands and use clean tools before handling your indoor plants. Avoid touching healthy plants after handling diseased plants, as this can transfer viral particles. Disinfect your tools regularly to prevent the transmission of diseases.
3. Remove infected plants
If you notice any signs of viral infection, such as distorted leaves, stunted growth, or yellowing, remove the infected plants immediately. Isolate them from your healthy plants to prevent further spread of the disease. Dispose of the infected plants properly to ensure the virus is not transferred to other plants or the environment.
4. Avoid overwatering
Overwatering can weaken the plants’ immune systems, making them more susceptible to viral infections. Make sure to water your plants appropriately, allowing the soil to dry out between waterings. Avoid excessive moisture, as it can create an ideal environment for the growth and spread of viruses.
5. Control pests
Pests, such as aphids and whiteflies, can transmit viral diseases from one plant to another. Regularly inspect your indoor plants for signs of pests and take appropriate measures to control them. Use natural or chemical methods to eliminate pests and prevent them from spreading diseases.
6. Maintain good air circulation
Proper air circulation in your indoor garden can help reduce the risk of viral diseases. Ensure that your plants are not overcrowded and there is enough space between them. Use fans or open windows to promote air movement and prevent the buildup of stagnant air, which can facilitate disease transmission.
7. Use virus-free planting materials
When propagating new plants, use virus-free planting materials to minimize the risk of introducing viral diseases. Purchase seeds, cuttings, or bulbs from reputable sources that guarantee their plants are virus-free. This will greatly reduce the chances of introducing viruses into your indoor garden.
8. Educate yourself
Stay informed about common viral diseases that affect indoor plants and their symptoms. Educate yourself on how to identify and prevent viral infections in your plants. Regularly read articles, attend workshops, or seek advice from experts to stay up to date with the latest information on viral diseases and their prevention.
By following these preventive measures, you can greatly reduce the risk of viral diseases infecting your indoor plants. Regular monitoring and prompt action are crucial in maintaining a healthy indoor garden.
Treating Viral Diseases in Indoor Plants
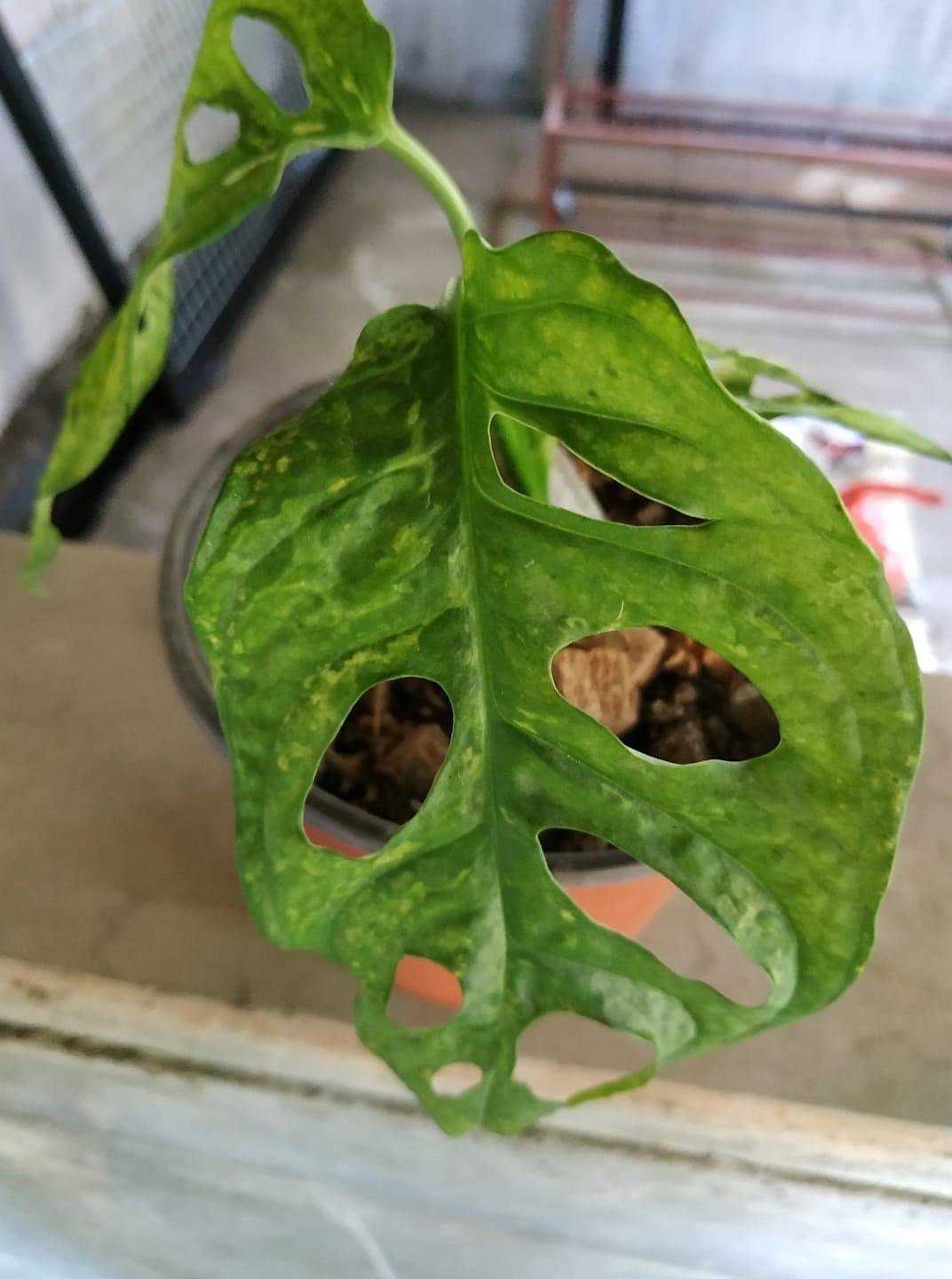

Viral diseases can be a major threat to the health and vitality of indoor plants. Once a plant is infected with a virus, there is no cure. However, there are steps you can take to manage and control viral diseases in your indoor plants.
1. Prevention is key
The best way to deal with viral diseases is to prevent them from happening in the first place. Here are a few prevention measures you can take:
- Quarantine: Before introducing a new plant into your indoor environment, quarantine it for a few weeks to monitor for any signs of viral infection.
- Clean tools: Use clean tools when working with plants to prevent the spread of viruses. Clean your tools with a disinfectant solution between plants.
- Avoid open wounds: Be careful not to damage your plants, as open wounds provide an entry point for viruses.
2. Sanitation
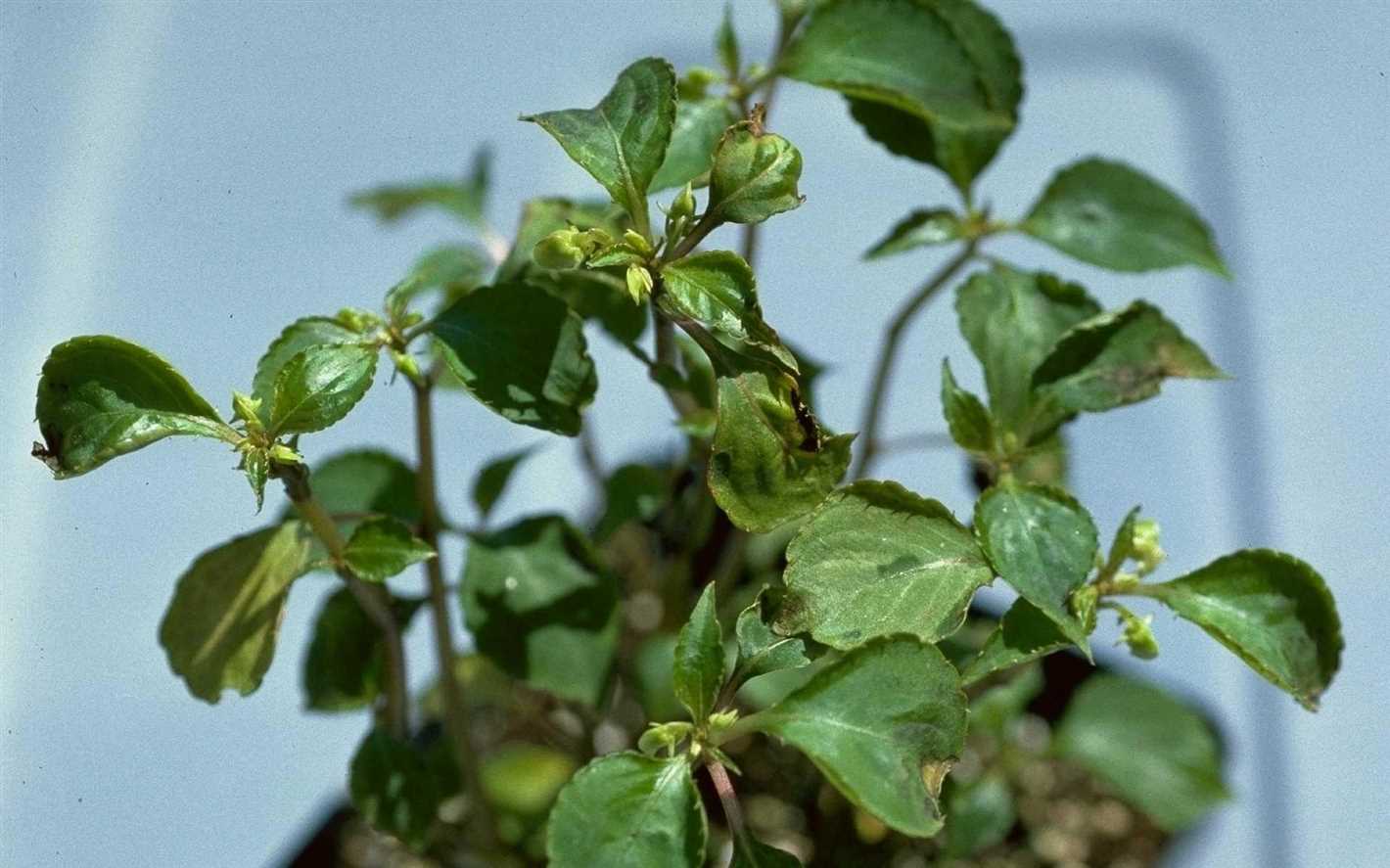

Good sanitation practices can help reduce the spread of viral diseases. Here are some tips:
- Remove infected plants: If you notice any signs of viral infection, immediately remove the infected plants to prevent the virus from spreading.
- Wash hands: Wash your hands thoroughly after handling infected plants to avoid carrying the virus to other plants.
- Clean the environment: Regularly clean and disinfect the environment to minimize the risk of viruses surviving and spreading.
3. Control vectors
Viral diseases are often transmitted by insects or other vectors. Controlling these vectors can help prevent the spread of viruses. Here are some methods:
- Pest control: Implement effective pest control measures to reduce the population of vectors that can transmit viruses.
- Physical barriers: Use physical barriers, such as screens or nets, to prevent insects from coming in contact with your plants.
- Natural predators: Introduce natural predators, like beneficial insects, that feed on vectors, helping to control their population.
4. Proper plant care
Providing optimal care for your indoor plants can help strengthen their immune systems and make them more resistant to viral infections. Here are some care tips:
- Healthy environment: Ensure your plants have proper lighting, temperature, humidity, and ventilation for their specific needs.
- Nutrient balance: Provide the right balance of nutrients to support the overall health and vigor of your plants.
- Regular inspection: Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of viral infection, and take immediate action if you notice any symptoms.
Remember, prevention and early detection are key in managing viral diseases in indoor plants. By implementing these strategies, you can minimize the risk of viral infections and keep your indoor plants healthy and thriving.
Q&A:
What are viral diseases of indoor plants?
Viral diseases of indoor plants are infections caused by viruses that affect the health and growth of the plants. These viruses can be transmitted through various means such as contaminated tools, insect vectors, or even through the air.
What are some common symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants?
Some common symptoms of viral diseases in indoor plants include stunted growth, yellowing or mottling of leaves, curling or distortion of leaves, and formation of spots or speckles on the leaves. Other symptoms may include wilting, necrosis, or a general decline in overall plant health.
How can I prevent viral diseases from infecting my indoor plants?
Preventing viral diseases in indoor plants can be done through a combination of different measures. This includes practicing good hygiene by disinfecting tools and pots, avoiding the use of contaminated materials, and regularly monitoring plants for any signs of infection. Additionally, it is important to quarantine any new plants before introducing them to your existing collection to minimize the risk of spreading diseases.
Are there any treatments available for viral diseases in indoor plants?
Unfortunately, there are no specific treatments available for viral diseases in indoor plants. Once a plant is infected with a virus, there is no cure. The best course of action is to remove and destroy the infected plant to prevent the spread of the virus to other plants.
Can viral diseases in indoor plants be transmitted to outdoor plants?
Yes, viral diseases in indoor plants can be transmitted to outdoor plants. This can occur through various means such as insect vectors, windblown particles, or by bringing infected plants outdoors. It is important to practice caution and proper hygiene to prevent the spread of viruses between indoor and outdoor plants.
What are some common insect vectors that transmit viral diseases to indoor plants?
Some common insect vectors that can transmit viral diseases to indoor plants include aphids, whiteflies, thrips, and mealybugs. These insects feed on the sap of the plants and can introduce viruses into the plant’s system while feeding. Regular inspection and control of these insect pests can help reduce the spread of viral diseases.
Video:
Part 1: Concept of diseases in plants # microbiology# plant symptoms# Genes & Genus