- Autumn Grafting: A Comprehensive Guide
- Timing
- Process
- Compatible Grafting Combinations
- Understanding the Timing for Autumn Grafting
- Factors Affecting Timing
- Optimal Timing
- Conclusion
- The Grafting Process: Step-by-Step
- Step 1: Gather Your Materials
- Step 2: Prepare the Scion and Rootstock
- Step 3: Join the Scion and Rootstock
- Step 4: Protect the Graft
- Step 5: Monitor and Care for the Graft
- Step 6: Remove Supports
- Step 7: Maintain and Prune
- Choosing the Right Grafting Combinations for Autumn
- 1. Compatibility
- 2. Disease Resistance
- 3. Climate Adaptability
- 4. Desired Traits
- 5. Rootstock Vigor
- Identifying Compatible Grafting Techniques
- 1. Genetic Compatibility
- 2. Similar Growth Habits
- 3. Tissue Compatibility
- 4. Disease Resistance
- 5. Compatibility Testing
- Pruning and Preparing the Bud for Autumn Grafting
- Enhancing Graft Success: Tips and Tricks
- 1. Selecting Compatible Combinations
- 2. Proper Timing
- 3. Surface Preparation
- 4. Proper Technique
- 5. Securing the Graft
- 6. Providing Optimal Conditions
- 7. Monitoring and Care
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Autumn Grafting
- Protecting and Caring for Your Grafted Plants in Autumn
- Selecting a Suitable Location
- Providing Adequate Watering
- Protecting from Frost
- Monitoring for Pests and Diseases
- Applying Mulch
- Winterizing Your Grafted Plants
- Question-answer:
- When is the best time to do autumn grafting with a bud?
- What is the process of autumn grafting with a bud?
- Can I graft different types of plants together in autumn?
- What are some compatible grafting combinations for autumn grafting with a bud?
- What are some tips for a successful autumn grafting with a bud?
- Video: Grafting Fruit Trees | The best grafting techniques for Apples, Pears and other fruit trees
Grafting is a horticultural technique that allows gardeners and farmers to propagate plants and trees by joining together compatible parts to create a new plant with desired characteristics. Autumn is an ideal time for grafting, as the plants are preparing for dormancy, making them more receptive to the process. Grafting with a bud, a specific type of grafting, is a popular method used by many gardeners to achieve successful results.
Timing is crucial when it comes to autumn grafting with a bud. It is important to choose the right moment when the plants are still actively growing but have entered a period of reduced vigor. This usually occurs in late summer or early autumn when the days start to shorten, and temperatures begin to cool. Grafting during this period allows the plants to establish themselves before going into dormancy, increasing the chances of success.
The process of grafting with a bud involves removing a small segment of a plant with a dormant bud and attaching it to a compatible rootstock. The bud serves as the graft’s growing point, and once the graft is successfully joined, it will grow into a new shoot or branch. It is important to choose compatible grafting combinations, ensuring that the plants have similar growth habits and are from the same genus or species. This increases the chances of a successful graft and the development of a healthy, vigorous plant.
Grafting with a bud offers many advantages. It allows gardeners to improve the overall health and vigor of plants, to create unique hybrids with desirable traits, and to propagate plants that are difficult or slow to propagate through other methods. With proper timing, meticulous attention to detail during the grafting process, and careful selection of compatible grafting combinations, autumn grafting with a bud can lead to successful results, allowing gardeners to expand their plant collection and achieve their desired gardening goals.
Autumn Grafting: A Comprehensive Guide
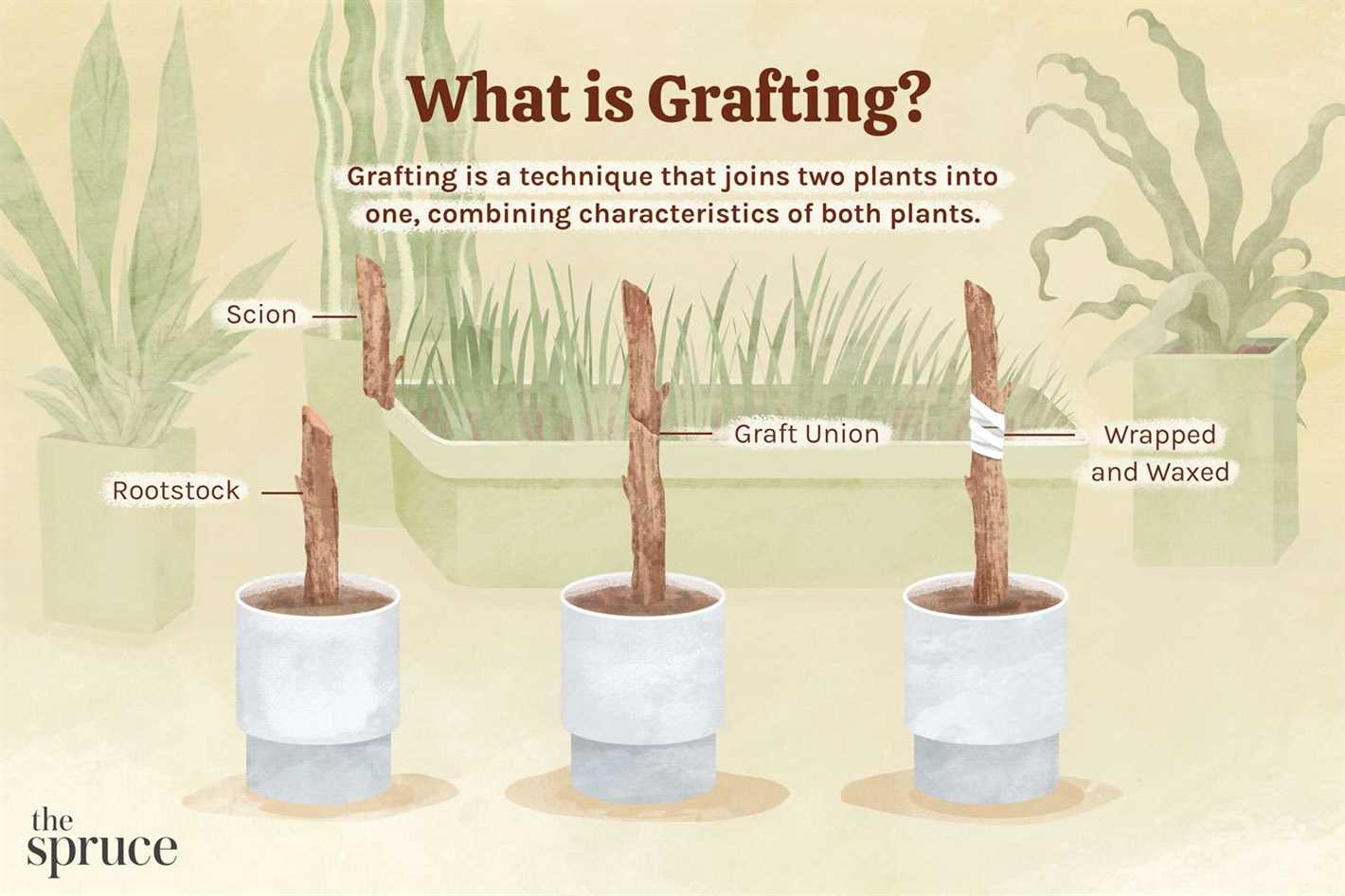
Grafting is a fascinating technique used by horticulturists to combine two different plants into one, resulting in the growth of a new plant that has the desirable characteristics of both. Autumn grafting, in particular, is a popular method due to the favorable conditions that this season offers for successful grafting.
Timing
Timing is crucial when it comes to autumn grafting. It is generally recommended to start the process in late summer or early fall, when the plants are still actively growing and the temperatures are starting to cool down. This allows the grafted plant to establish itself before winter.
Process
The process of autumn grafting involves joining a bud from one plant, known as the scion, with the rootstock of another plant. Here are the steps involved:
- Select healthy plants: Choose a healthy scion with the desired characteristics and a compatible rootstock that works well with the scion.
- Prepare the scion: Take a dormant bud from the scion and trim away any excess leaves or stems.
- Prepare the rootstock: Make a clean cut on the rootstock to create a suitable area for grafting.
- Join the scion and rootstock: Insert the bud of the scion into the prepared area of the rootstock and secure it with grafting tape or a grafting clip.
- Provide proper care: Keep the grafted plant in a controlled environment, providing adequate moisture, light, and protection from extreme temperatures.
- Monitor the graft: Regularly check the grafting site for any signs of infection or failure and take necessary actions to prevent any issues.
Compatible Grafting Combinations
Successful grafting depends on selecting compatible combinations of scions and rootstocks. Here are some commonly used combinations for autumn grafting:
| Scion | Rootstock |
|---|---|
| Apple | M9, MM 106 |
| Pear | Quince A or C |
| Peach | St. Julian A |
| Plum | Myrobalan |
These combinations have been found to have a high success rate and produce healthy, productive plants.
In conclusion, autumn grafting is a rewarding technique that allows plant enthusiasts and horticulturists to create new, unique plants. By following the proper timing, utilizing the correct process, and selecting compatible grafting combinations, successful autumn grafting can be achieved, resulting in the growth of thriving plants with desired characteristics.
Understanding the Timing for Autumn Grafting
Grafting in autumn can be a successful technique for propagating plants. However, timing is crucial for a successful graft. Understanding the optimal timing for autumn grafting is essential to ensure the best chances of success.
Factors Affecting Timing
Several factors influence the timing for autumn grafting:
- Plant Dormancy: Grafting is most successful when the scion, the plant part being grafted, is dormant. It is crucial to select scions that have entered winter dormancy to promote successful union with the rootstock.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature and moisture levels play a vital role in successful grafting. Autumn is the ideal time for grafting as it provides cooler temperatures and higher moisture levels that promote healing and growth.
- Grafting Compatibility: It is essential to choose grafting combinations that are compatible. Some plants may have specific seasonal requirements or may be more amenable to grafting at certain times of the year.
Optimal Timing
The optimal timing for autumn grafting can vary depending on the specific plant and local climate conditions. In general, late summer to early autumn is considered the best time for most grafting activities.
Here are a few guidelines for determining the optimal timing for autumn grafting:
- Observe Plant Dormancy: Monitor the target plant and wait for signs of dormancy, such as leaf drop or stem dieback. This indicates that the plant is entering its dormant phase, making it ready for grafting.
- Check Local Weather Patterns: Research the average temperature and moisture levels in your area during late summer to early autumn. Choose a time when the conditions are favorable for grafting.
- Consult Plant-Specific Recommendations: Some plants have specific timing requirements for grafting. Consult reliable sources or seek advice from experienced gardeners or horticulturists familiar with the specific plant you are working with.
Conclusion
Understanding the timing for autumn grafting is crucial for successful plant propagation. By considering plant dormancy, environmental conditions, and grafting compatibility, you can determine the optimal timing for your grafting activities. Late summer to early autumn is generally the best time for most grafting projects. However, it is always important to observe the specific requirements of the plants you are working with and seek expert advice when needed.
The Grafting Process: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Gather Your Materials
Before you begin the grafting process, make sure you have all the necessary materials:
- Scion wood: the part of the bud that will be grafted onto the rootstock
- Rootstock: the plant onto which the scion will be grafted
- Grafting knife: a sharp, clean knife for making precise cuts
- Pruning shears: for trimming the scion wood and rootstock
- Grafting tape or parafilm: to secure the graft and protect it from drying out
Step 2: Prepare the Scion and Rootstock
Trim the scion wood and rootstock to the desired size. It is important to match the diameter of the scion and rootstock for a successful graft. Make a slanting cut on both the scion wood and rootstock, ensuring that the cambium layers are aligned.
Step 3: Join the Scion and Rootstock
Place the scion onto the rootstock, aligning the cambium layers. Hold the graft firmly in place and wrap grafting tape or parafilm around the graft, starting below the graft union and extending above it. The tape should be tight enough to hold the graft in place but not too tight to restrict growth.
Step 4: Protect the Graft
To prevent the graft from drying out and to provide extra protection, apply grafting wax or sealant to the top and exposed sides of the graft. This will help to seal the graft and reduce the risk of infection.
Step 5: Monitor and Care for the Graft
After grafting, it is important to monitor the graft closely for signs of successful union. Keep the grafts moist and in a protected environment, such as a greenhouse or shaded area. Provide adequate water and nutrients to promote healthy growth.
Step 6: Remove Supports
Once the graft has successfully taken and new growth is evident, it is safe to remove the grafting tape or parafilm. Carefully cut away the tape or film, ensuring not to damage the graft union.
Step 7: Maintain and Prune
Maintain the grafted plant by pruning any unwanted shoots or branches. Regularly monitor the health of the graft and make necessary adjustments as needed to promote optimal growth.
Following these steps will increase your chances of successful grafting and allow you to enjoy the benefits of a well-grafted plant.
Choosing the Right Grafting Combinations for Autumn
Grafting combinations play a crucial role in the success of the grafting process. It is important to choose compatible combinations to ensure a healthy and productive graft. Here are some factors to consider when selecting the right grafting combinations for autumn:
1. Compatibility
When choosing grafting combinations, it is essential to consider the compatibility between the scion and rootstock. Choose varieties that are closely related or from the same species to increase the chances of a successful graft. This will ensure that the graft union is strong and the two parts can grow together successfully.
2. Disease Resistance
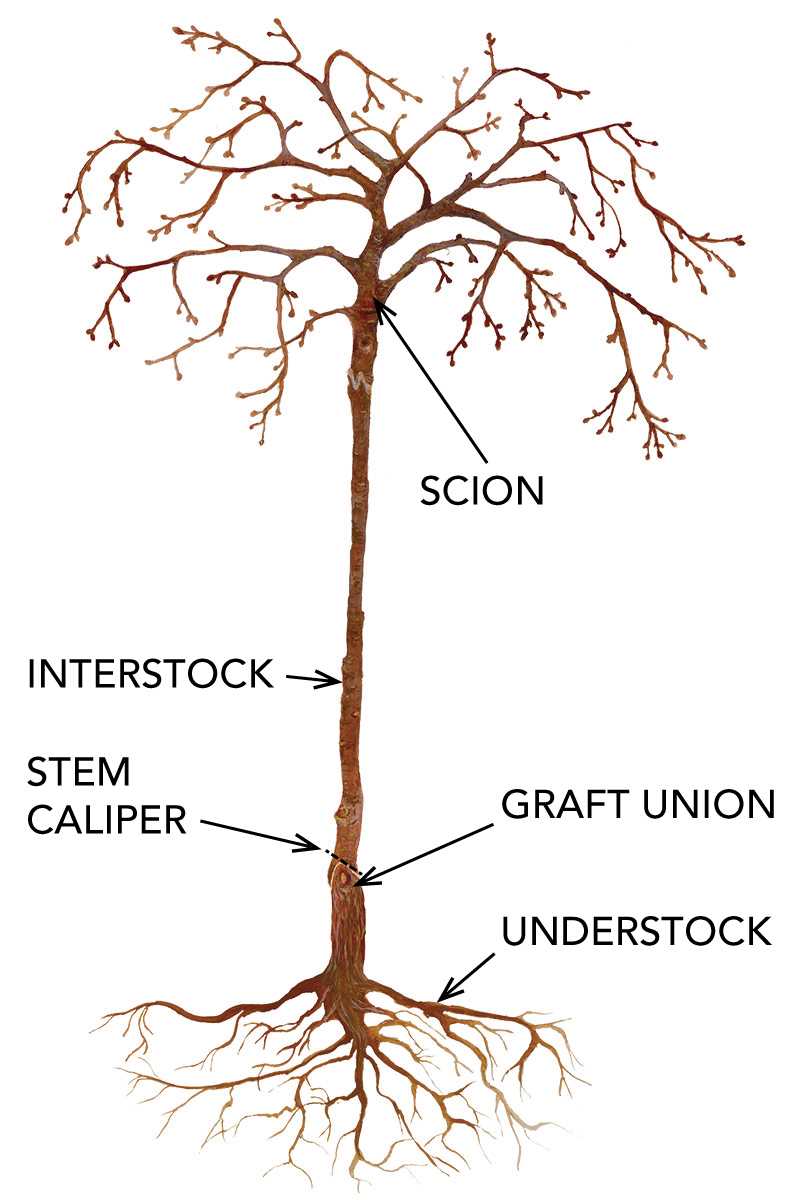
Another factor to consider is the disease resistance of the rootstock. Select rootstocks that are resistant to common diseases in your area to minimize the risk of graft failure due to disease. This will also help to ensure that the grafted plant remains healthy and productive throughout the growing season.
3. Climate Adaptability
Consider the climate conditions in your area and choose grafting combinations that are well-adapted to those conditions. Different varieties have different temperature and moisture requirements, so choose combinations that can thrive in your local climate. This will increase the chances of a successful graft and ensure that the grafted plant can withstand the autumn weather.
4. Desired Traits
Think about the desired traits that you want in your grafted plants. Do you want a certain flavor, size, or color? Choose scions that have the desired traits and then select compatible rootstocks to graft them onto. This will allow you to create plants with the desired qualities and ensure a successful graft.
5. Rootstock Vigor
Consider the vigor of the rootstock when choosing grafting combinations. Some rootstocks have more vigorous growth and can provide better support for the scion. This is especially important for grafts done in autumn when the plant needs to establish itself before winter arrives. Choosing a rootstock with good vigor will help the grafted plant to grow and establish quickly.
By considering these factors and choosing the right grafting combinations for autumn, you can increase the chances of a successful graft and enjoy healthy, productive plants in your garden.
Identifying Compatible Grafting Techniques
Grafting is a technique used to combine the tissues of two different plants in order to create a new plant with desirable characteristics. However, not all plants are compatible for grafting, and it is important to choose the right combination of scion and rootstock for successful grafting. Here are some key factors to consider when identifying compatible grafting techniques:
1. Genetic Compatibility
One of the primary factors to consider is the genetic compatibility between the scion and rootstock. Plants that are closely related are more likely to be compatible for grafting. For example, you can graft different varieties of apple trees onto each other because they are closely related. On the other hand, grafting an apple tree onto a peach tree would likely be unsuccessful due to their genetic differences.
2. Similar Growth Habits
Plants with similar growth habits are more likely to be compatible for grafting. This is because their growth patterns and requirements are more likely to align. For example, grafting a climbing rose onto a climbing rose rootstock would be a compatible combination, as both plants have a similar growth habit. However, grafting a climbing rose onto a shrub rose rootstock may not be successful due to their differing growth habits.
3. Tissue Compatibility
It is important to consider the compatibility of the tissues of the scion and rootstock. The cambium layer, the actively dividing tissue responsible for the growth of new cells, must be aligned for successful grafting. If the cambium layers do not align properly, the graft may not take. Additionally, it is important to consider the compatibility of the vascular tissues, which are responsible for transporting water and nutrients throughout the plant.
4. Disease Resistance
Choosing a rootstock that is resistant to common diseases and pests can help increase the success rate of grafting. By grafting a scion onto a disease-resistant rootstock, you can benefit from the desirable characteristics of the scion while providing the plant with increased resistance to common threats.
5. Compatibility Testing
If you are unsure about the compatibility of a specific grafting combination, you can perform compatibility testing. This involves making a small incision and inserting a piece of the scion into the rootstock. If the graft takes and shows signs of growth, it is likely that the combination is compatible. If the graft fails to take or shows signs of rejection, it may be necessary to try a different combination.
By considering these factors and performing compatibility testing when necessary, you can increase the chances of successful grafting and create new plants with the desired characteristics.
Pruning and Preparing the Bud for Autumn Grafting
Before embarking on the autumn grafting process, it is important to properly prune and prepare the bud to ensure a successful graft. Here are the steps to take:
- Selecting the Bud: Choose a healthy and well-developed bud from the desired variety that you wish to graft onto the rootstock. The bud should be located on a suitable branch, ideally from the current season’s growth.
- Pruning the Bud: Use a sharp and clean grafting knife to carefully remove the bud from its original branch. Make a clean, smooth, and slanting cut just below the bud, leaving a small portion of the bark intact. This will serve as the handle for the bud during the grafting process.
- Trimming the Bud: Trim the bud’s leaves, keeping only a small portion of the petiole intact. Remove any excess foliage or stems that may hinder the grafting process.
- Protecting the Bud: To prevent the bud from drying out, it is important to immediately coat the cut portion of the bud with a grafting wax or sealant. This will help retain moisture and protect the bud from infection.
Once the bud has been pruned and prepared, it is ready to be grafted onto the rootstock. Ensure that the bud is handled with care and kept moist until it is time for grafting.
Enhancing Graft Success: Tips and Tricks
When it comes to grafting, there are several tips and tricks that can help enhance the success rate of your grafts. These techniques can improve the compatibility between the scion and rootstock, promote proper healing, and reduce the risk of graft failure.
1. Selecting Compatible Combinations
Choosing compatible grafting combinations is crucial for a successful graft. Make sure that the scion and rootstock are from the same species or, in some cases, closely related species. This will increase the chances of a successful union and reduce the risk of graft rejection.
2. Proper Timing
The timing of grafting plays a significant role in the success of the graft. Grafting should be done during the dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring. This is when the plants are less active, and the graft can heal more effectively. Avoid grafting during periods of extreme temperatures or when the plants are stressed, as this can hinder the healing process.
3. Surface Preparation
Before grafting, it is essential to prepare the surfaces of the scion and rootstock. Clean both surfaces by removing any dirt, debris, or diseased tissue. This will ensure a clean union and prevent the introduction of pathogens that can cause graft failure.
4. Proper Technique
Using the correct grafting technique is vital for a successful graft. Make sure to match the diameter of the scion and rootstock to create proper contact between the two. Use a sharp and clean grafting knife to make a clean, sloping cut on both the scion and rootstock. This will create a larger surface area for the union and improve the chances of successful healing.
5. Securing the Graft
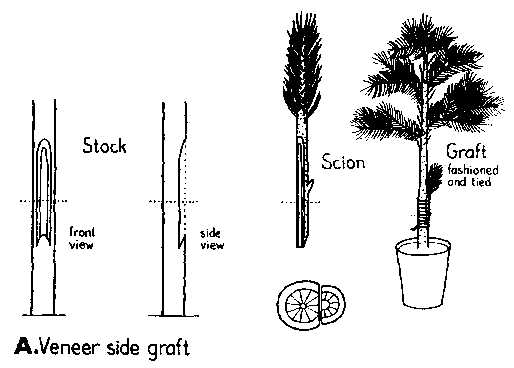
Securing the graft is crucial to keep the scion and rootstock in place and promote successful healing. Use grafting tape or clips to tightly secure the graft. This will prevent movement and ensure proper contact between the two parts.
6. Providing Optimal Conditions
Creating optimal conditions for the graft can significantly improve its success rate. Keeping the graft in a protected, shaded area can reduce stress and provide a more favorable environment for healing. Maintaining proper humidity and moisture levels is also essential for graft survival.
7. Monitoring and Care
After grafting, it is important to monitor the graft regularly and provide appropriate care. Check for any signs of infection or graft failure, such as discoloration or wilting. Adjust the support or protection as needed. Additionally, providing supplementary nutrients or growth-promoting substances can help enhance graft success and accelerate healing.
By following these tips and tricks, you can greatly increase the chances of a successful graft and enjoy the benefits of your carefully selected combinations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Autumn Grafting
When it comes to autumn grafting, there are a few common mistakes that beginners often make. By being aware of these mistakes, you can increase your chances of success and avoid some frustrating pitfalls. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
- Poor timing: One of the biggest mistakes in autumn grafting is not grafting at the right time. It’s important to graft when the scion wood is dormant and the rootstock is still active. Waiting too long into the autumn season can result in failure to take or weak grafts.
- Incorrect bud selection: Choosing the right bud for grafting is crucial. Make sure you select a bud that is plump and healthy. Avoid using buds that are damaged or discolored as they are less likely to take.
- Improper technique: Another mistake to avoid is using improper grafting techniques. It’s important to make clean and precise cuts on both the scion wood and the rootstock. Avoid cutting too deeply or at the wrong angle, as this can hinder successful grafting.
- Insufficient support: Providing proper support for the graft is essential. The union between the scion wood and the rootstock needs to be secure and stable. Using grafting tape or a similar material to hold the two parts together can help prevent movement and ensure a successful graft.
- Failure to protect the graft: After grafting, it’s important to protect the graft from extreme temperatures, pests, and diseases. Applying a grafting wax or sealant can help protect the graft from drying out and prevent infections.
- Not monitoring progress: Finally, failing to monitor the progress of your grafts can lead to missed opportunities to correct any issues. Regularly check the graft site for signs of growth or problems, and make any necessary adjustments as needed.
Avoiding these common mistakes can greatly increase your chances of successful autumn grafting. By paying attention to timing, bud selection, technique, support, protection, and progress monitoring, you can increase your chances of achieving healthy and thriving grafts.
Protecting and Caring for Your Grafted Plants in Autumn
Grafting is a delicate process that requires proper care and protection, especially during the autumn season. By following a few key steps, you can ensure the success of your grafted plants throughout the colder months.
Selecting a Suitable Location
When choosing a location for your grafted plants, it is important to consider factors such as sunlight, wind exposure, and temperature fluctuations. Look for areas with ample sunlight to promote healthy growth and avoid locations prone to strong winds that could damage the grafted union. Additionally, try to select a spot that offers some protection against extreme temperature swings, as these can negatively impact the grafted plants.
Providing Adequate Watering
Proper watering is crucial for the health of grafted plants, especially during the autumn season. Monitor soil moisture regularly and water as needed to keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Remember that the cold weather can cause the soil to dry out more slowly, so be mindful of this when determining watering frequency.
Protecting from Frost
Frost can be particularly damaging to grafted plants, as it can harm both the scion and rootstock. To protect against frost, consider using frost blankets or horticultural fleece to cover your grafted plants overnight. These materials can provide insulation and help maintain a more stable temperature, reducing the risk of damage from frost.
Monitoring for Pests and Diseases

Pests and diseases can pose a threat to grafted plants, especially during the autumn season when many insects and pathogens are still active. Regularly inspect your grafted plants for any signs of pests or diseases, such as wilting, discoloration, or unusual growth. If any issues are detected, take appropriate measures to mitigate the problem, such as using organic insecticides or fungicides.
Applying Mulch
Applying a layer of mulch around the base of your grafted plants can offer many benefits. Mulch helps to retain moisture in the soil, regulate temperature, and reduce weed growth. Additionally, it can provide some insulation against cold weather and protect the grafted union from potential damage.
Winterizing Your Grafted Plants
Before the colder temperatures set in, it is important to prepare your grafted plants for winter. This may include pruning any dead or damaged branches, wrapping the graft union with tree tape or grafting wax for added protection, and applying a thick layer of mulch around the base. By taking these steps, you can help ensure the survival and success of your grafted plants throughout the winter season.
By following these guidelines and providing the necessary care and protection, you can enhance the chances of your grafted plants thriving in the autumn season. Remember to monitor your plants regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure their ongoing health and vitality.
Question-answer:
When is the best time to do autumn grafting with a bud?
The best time to do autumn grafting with a bud is when the bark separates easily from the wood, which is usually in late summer or early autumn.
What is the process of autumn grafting with a bud?
The process of autumn grafting with a bud involves selecting a healthy bud from the desired variety, making a T-shaped cut on the rootstock, and inserting the bud into the cut. The bud is then wrapped and sealed to protect it.
Can I graft different types of plants together in autumn?
Yes, it is possible to graft different types of plants together in autumn. However, it is important to choose compatible grafting combinations to increase the chances of a successful graft.
What are some compatible grafting combinations for autumn grafting with a bud?
Some compatible grafting combinations for autumn grafting with a bud include apple on apple, pear on pear, and plum on plum. It is important to choose varieties that are genetically similar to increase the chances of a successful graft.
What are some tips for a successful autumn grafting with a bud?
Some tips for a successful autumn grafting with a bud include selecting healthy buds and rootstocks, making clean cuts, securing the bud tightly, and protecting the graft from extreme weather conditions. It is also important to choose compatible grafting combinations and graft during the optimal time.







