- Importance of Pruning in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
- Promotes New Growth
- Controls Plant Density
- Improves Airflow
- Facilitates Harvesting
- Maintains Plant Health
- Conclusion
- Understanding the Growth Cycle of Remontant Raspberry Plants
- 1. Dormant Stage
- 2. Bud Swell
- 3. Vegetative Growth
- 4. Flowering
- 5. Fruit Development
- 6. Harvest
- Conclusion
- Pruning Methods for Stimulating Early Fruit Production
- 1. Winter Pruning
- 2. Thinning
- 3. Tipping
- 4. Suckering
- 5. Pruning Frequency
- 6. Training and Support
- Timing of Pruning in Remontant Raspberry Varieties
- Pruning in the Dormant Season
- Summer Pruning
- Conclusion
- Recommended Tools for Pruning Remontant Raspberry Plants
- Avoiding Common Pruning Mistakes in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
- 1. Pruning at the wrong time
- 2. Over-pruning
- 3. Pruning too aggressively
- 4. Neglecting the removal of suckers
- 5. Failing to sanitize tools
- 6. Not considering the plant’s growth habit
- Pruning Techniques for Maintaining Plant Health and Vigor
- Introduction
- Pruning Basics
- Specific Pruning Techniques
- Renovation Pruning
- Fruit-Bearing Cane Pruning
- Thinning Pruning
- Conclusion
- Consulting Experts and Resources for Pruning guidance in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
- Question-answer:
- What are remontant raspberry varieties?
- Why is early fruit production important in raspberries?
- What are some pruning techniques for early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties?
- How does removing the first flower buds help with early fruit production?
- What is selective thinning of canes?
- Why is heading back the canes important for early fruit production?
- Are there any other factors that can help with early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties?
- Video: Pruning Raspberries – Why? How? When? (2020)
Raspberry plants are known for their delicious fruit and their ability to produce multiple crops throughout the growing season. Remontant raspberry varieties, in particular, are highly desirable for their ability to bear fruit in both the early and late seasons. However, in order to maximize fruit production, proper pruning techniques must be employed.
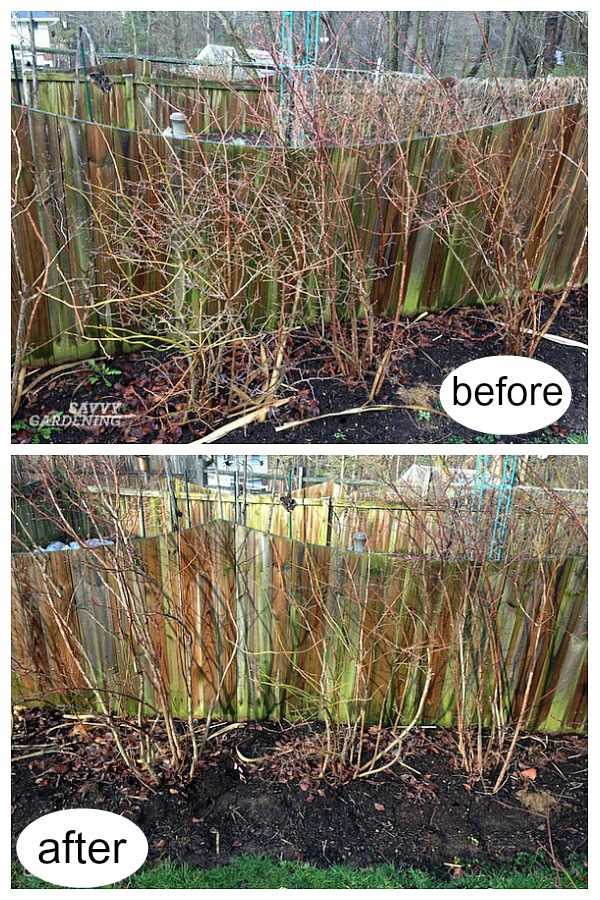
The first step in pruning remontant raspberry plants is to remove any dead or damaged canes. This allows the plant to direct its energy towards the healthy canes, ultimately leading to higher fruit yields. It is also important to thin out the remaining canes, leaving only a few of the strongest and healthiest canes. This helps to ensure that the plant can support the weight of the fruit and allows for better air circulation, reducing the risk of disease.
Another important aspect of pruning remontant raspberries is the timing of the cuts. It is recommended to prune in early spring, before new growth begins. This allows the plant to focus its energy on producing new canes and fruit, rather than healing the wounds from pruning. Additionally, pruning in early spring helps to remove any canes that may have been damaged by winter weather.
In conclusion, proper pruning techniques are essential for maximizing fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties. By removing dead or damaged canes, thinning out the remaining canes, and pruning at the right time, gardeners can ensure a bountiful harvest of delicious raspberries throughout the growing season.
Importance of Pruning in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
Pruning plays a crucial role in the cultivation of remontant raspberry varieties. It is an essential practice that not only helps maintain the health and productivity of the plants but also promotes early fruit production.
Promotes New Growth
Pruning stimulates the growth of new canes in remontant raspberries. By removing old and dead canes, the plant’s energy is directed towards the development of new shoots. These new canes are vigorous and more productive, resulting in increased fruit yields.
Controls Plant Density
Pruning helps control the density of remontant raspberry plants. By removing excess canes, the plants have more space to grow and receive adequate sunlight and air circulation. This prevents overcrowding and reduces the risk of diseases and pest infestations.
Improves Airflow
A well-pruned remontant raspberry plant allows for better airflow, reducing the chances of fungal diseases. Proper airflow also helps in the pollination process, ensuring better fruit set and quality. Pruning opens up the canopy, allowing sunlight to reach all parts of the plant and promoting uniform ripening of the fruits.
Facilitates Harvesting
Pruning helps in the efficient harvesting of remontant raspberries. By removing unnecessary canes and limiting the height and spread of the plants, the fruits become more accessible and easy to harvest. Pruning also reduces the risk of fruit damage during harvesting operations.
Maintains Plant Health
Regular pruning helps maintain the overall health of remontant raspberry plants. By removing diseased, damaged, or weak canes, the risk of spreading diseases is minimized. Pruning also helps in the early detection of any abnormal growth or pest infestations, allowing for prompt action to be taken to prevent further damage.
Conclusion
Pruning is a critical practice in remontant raspberry cultivation. It promotes new growth, controls plant density, improves airflow, facilitates harvesting, and maintains plant health. By implementing proper pruning techniques, growers can ensure healthy and productive plants, leading to early fruit production and higher yields.
Understanding the Growth Cycle of Remontant Raspberry Plants
Raspberry plants, specifically remontant raspberry varieties, are popular among growers due to their ability to produce fruit multiple times throughout the growing season. Understanding the growth cycle of these plants is essential in implementing proper pruning techniques to maximize early fruit production.
1. Dormant Stage
The growth cycle of remontant raspberry plants begins in the dormant stage, which typically occurs during the winter months. During this stage, the plants go through a period of rest and do not show any visible signs of growth. It is important to note that the exact timing of the dormant stage may vary depending on the specific variety and climate conditions.
2. Bud Swell
As the winter months come to an end and temperatures begin to rise, remontant raspberry plants enter the bud swell stage. During this stage, the buds on the canes start to swell and show signs of growth. This is an exciting phase for growers as it indicates the approach of the growing season.
3. Vegetative Growth
After the bud swell stage, remontant raspberry plants enter a phase of vigorous vegetative growth. New shoots emerge from the canes and leaves start to develop. This stage is crucial for establishing a strong plant structure and optimizing photosynthesis, which contribute to fruit production later in the season.
4. Flowering

Once the vegetative growth stage is complete, remontant raspberry plants transition into the flowering stage. During this stage, the plant produces flower buds that eventually open into blossoms. The timing and duration of the flowering stage may vary depending on the specific variety, environmental conditions, and cultural practices.
5. Fruit Development
After successful pollination and fertilization, the flowers of remontant raspberry plants develop into fruits. This stage is characterized by the growth and maturation of the fruit, which undergoes various color changes as it reaches its optimal ripeness. The duration of fruit development may vary depending on the variety and growing conditions.
6. Harvest
The final stage of the growth cycle is the harvest stage, where growers can finally reap the rewards of their efforts. Remontant raspberry plants produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season, allowing for multiple harvesting periods. It is important to monitor the fruits closely and harvest them at their peak ripeness to ensure the best flavor and quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the growth cycle of remontant raspberry plants is crucial for implementing effective pruning techniques and maximizing early fruit production. By recognizing the different stages of growth, growers can optimize their cultural practices and ensure a successful harvest season.
Pruning Methods for Stimulating Early Fruit Production
Pruning is an essential practice in promoting early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties. By selectively removing certain parts of the plant, we can encourage the development of new growth, increase airflow and sunlight penetration, and maximize fruit set and ripening. Here are several pruning techniques that can help stimulate early fruit production:
1. Winter Pruning

Winter pruning, done during the dormant season, is one of the most important and effective techniques for promoting early fruit production. It involves the removal of old and weak canes to make room for new growth. By eliminating excess canes, the plant’s energy can be redirected towards the production of new buds and fruit.
2. Thinning
Thinning refers to the selective removal of excess canes and branches. This technique allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, reducing the risk of disease and promoting fruit ripening. Remove any canes that are overcrowded or crossing each other, as well as any weak or damaged canes.
3. Tipping
Tipping involves the removal of the top portion of the new canes, usually around 10 to 12 inches from the tip. This technique stimulates lateral bud development and branching, resulting in increased fruit production. Tipping can be done during the dormant season or after fruiting.
4. Suckering
Suckering is the removal of suckers or shoots that emerge from the base of the plant. These suckers can divert energy away from the main canes and reduce fruit production. Regularly remove suckers to ensure that all the plant’s resources are focused on fruit development.
5. Pruning Frequency
Regular pruning is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of raspberry plants. Conduct pruning annually, preferably during the winter or early spring before new growth begins. This allows the plant to allocate resources more efficiently and promotes early fruit production.
6. Training and Support
Proper training and support structures, such as trellises or wires, can also influence early fruit production. By training the canes to grow vertically and providing support, we can optimize sunlight exposure, increase airflow, and improve overall fruit quality and production.
Remember to always use clean and sharp pruning tools to minimize the risk of disease transmission. Additionally, monitor the plants regularly for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to control them. By implementing these pruning methods, you can effectively stimulate early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties.
Timing of Pruning in Remontant Raspberry Varieties
Pruning is an essential practice in the cultivation of remontant raspberry varieties, as it helps to promote early fruit production and maintain the health and vigor of the plants. However, the timing of pruning plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results.
Pruning in the Dormant Season
The dormant season is typically the best time to prune remontant raspberry varieties. This is usually during late winter or early spring when the plants are still in their dormant state. Pruning during this period allows the plants to recover quickly and promote new growth before the onset of the growing season.
Remove Dead and Diseased Canes: Start by removing any dead or diseased canes. These canes can harbor pathogens and reduce the overall health of the plant. Cut them back to ground level to prevent the spread of diseases.
Thin Out Canes: Next, thin out the remaining canes to create better air circulation and light penetration. Remove weak or thin canes, as well as those that are crossing or crowded. Aim for about 6-8 of the healthiest and strongest canes per plant.
Prune to Desired Height: Trim the remaining canes to the desired height. This is usually done at 4-5 feet to make harvesting easier, but can vary depending on personal preference and the specific variety.
Summer Pruning
In addition to pruning during the dormant season, some remontant raspberry varieties may benefit from summer pruning. Summer pruning involves removing the tips of the canes after they have finished bearing fruit. This can help promote the development of lateral branches and encourage a second round of fruiting later in the season.
Wait for Fruit Harvest: Allow the canes to bear fruit during the main summer harvest period before considering summer pruning. This ensures that the plants have had the opportunity to produce a maximum amount of fruit during their primary fruiting cycle.
Prune After Harvest: After the main fruit harvest is complete, prune the canes by cutting off the top one-third of the cane. This stimulates the formation of lateral branches, which can then bear fruit in the later part of the season.
Conclusion
Timing is crucial when it comes to pruning remontant raspberry varieties. Pruning during the dormant season helps to improve plant vigor and promote early fruit production, while summer pruning can encourage a second round of fruiting. By following the proper timing and techniques for pruning, growers can maximize the yield and quality of their remontant raspberry crops.
Recommended Tools for Pruning Remontant Raspberry Plants
Proper tools are essential for successful pruning of remontant raspberry plants. Here are some recommended tools that can help you achieve desired results:
- Pruning shears: Invest in a good pair of pruning shears with sharp blades. These shears will make it easier to make clean cuts and minimize damage to the plants.
- Lopping shears: Lopping shears are larger, more powerful pruning tools that are useful for cutting thicker canes or branches. These shears can handle canes up to 1 inch in diameter and are ideal for removing older wood.
- Hand saw: A hand saw is useful for cutting larger canes or branches that are too thick for pruning shears or lopping shears. Look for a saw with a sharp and durable blade that can make clean cuts without causing excessive damage to the plants.
- Gloves: Wear a good pair of gardening gloves to protect your hands from thorns and prickles while pruning. Choose gloves that fit well and provide sufficient dexterity.
- Protective eyewear: It’s a good idea to wear protective eyewear while pruning to protect your eyes from flying debris and potential injury.
- Sanitizing solution: A sanitizing solution, such as a mixture of water and household bleach, is essential for sanitizing your pruning tools between cuts. This helps prevent the spread of diseases and ensures the health of your plants.
Having the right tools at your disposal will make the pruning process more efficient and effective. Ensure that your tools are clean, sharp, and well-maintained for the best results.
Avoiding Common Pruning Mistakes in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
Proper pruning is essential for maximizing the fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties. However, it is common for growers to make mistakes that can negatively impact the health and productivity of the plants. Here are some common pruning mistakes to avoid:
1. Pruning at the wrong time
Timing is crucial when it comes to pruning remontant raspberries. Pruning should be done during the dormant season, typically from late winter to early spring. Pruning too early can expose the plants to frost damage, while pruning too late can delay bud break and flowering.
2. Over-pruning
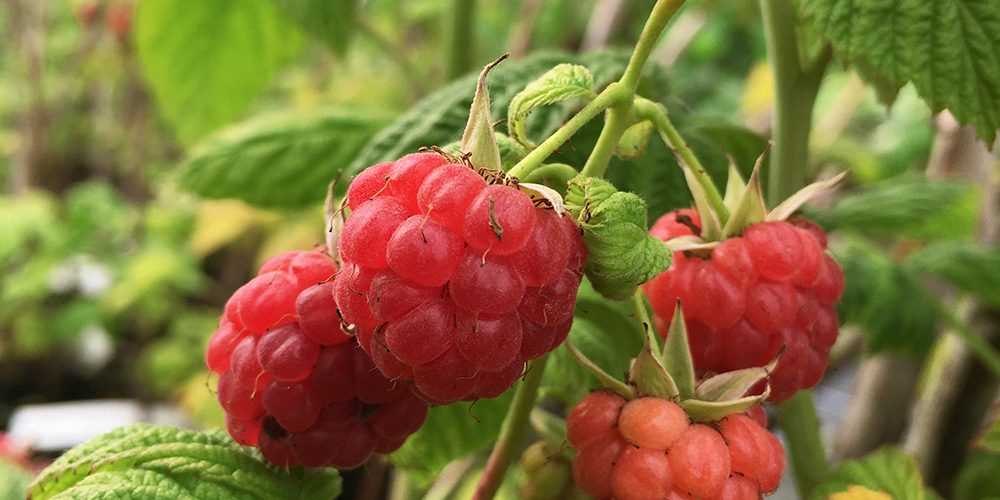

While some pruning is necessary to stimulate new growth and remove dead or diseased canes, over-pruning can be detrimental to remontant raspberries. Excessive pruning can reduce the number of fruit-bearing canes and weaken the overall structure of the plant. It is important to strike a balance between pruning and maintaining the plant’s vigor.
3. Pruning too aggressively
Aggressive pruning, such as cutting the canes down to the ground, is not recommended for remontant raspberries. These varieties produce fruit on both new and old canes, so removing all the canes can result in a significant reduction in fruit production. It is best to selectively prune and remove only the dead, weak, or crowded canes.
4. Neglecting the removal of suckers
Suckers, which are new shoots that emerge from the base of the plant, should be regularly removed to prevent overcrowding and competition among the canes. Neglecting to remove suckers can lead to reduced light penetration, increased disease susceptibility, and a decrease in fruit quality and yield.
5. Failing to sanitize tools
Pruning tools should be properly sanitized between cuts to prevent the spread of diseases and pests. Using dirty tools can transmit pathogens from one plant to another, potentially causing infections and weakening the overall health of the plants. Sanitize your tools with a 10% bleach solution or rubbing alcohol before and after each cut.
6. Not considering the plant’s growth habit
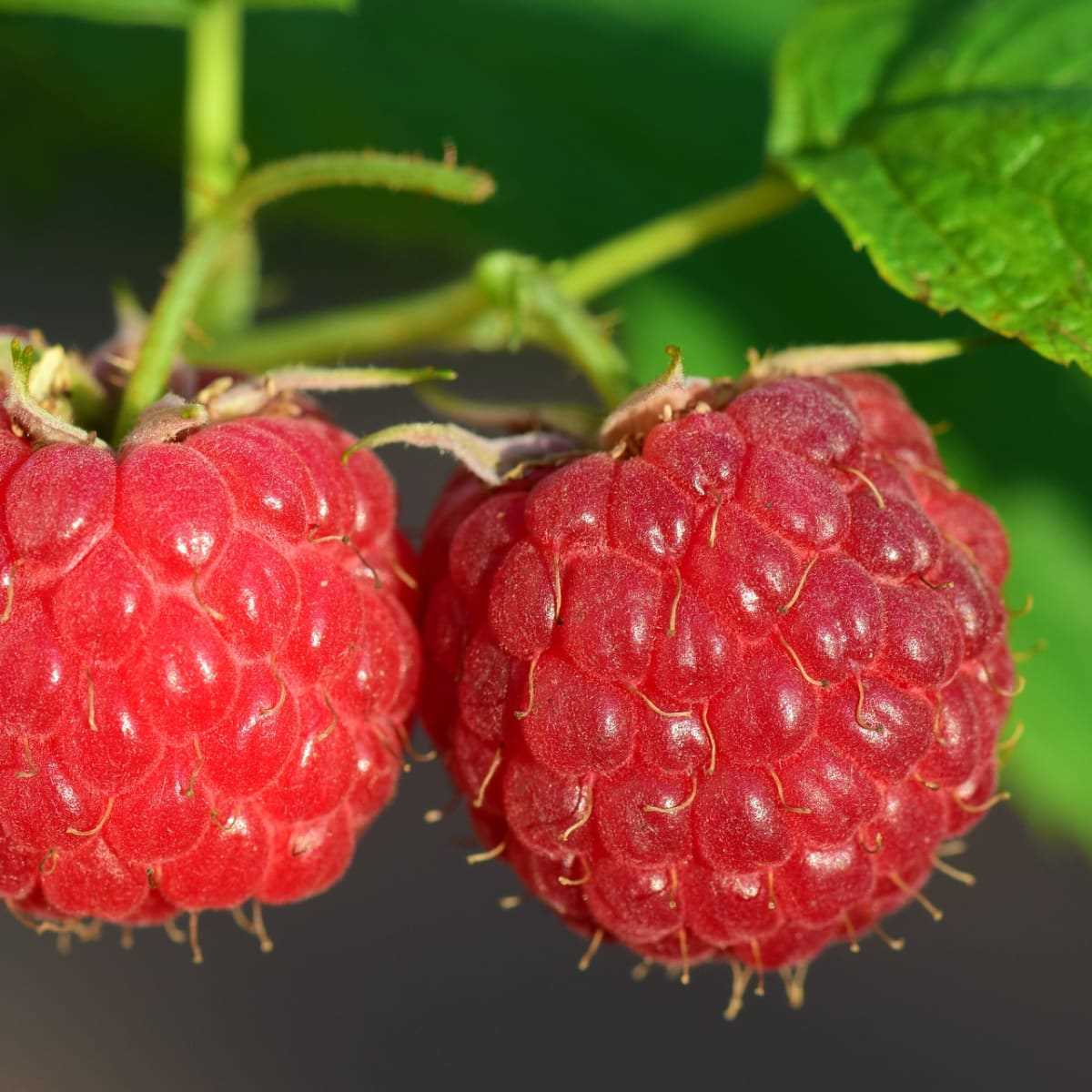

Each remontant raspberry variety has its own specific growth habit, which should be taken into consideration when pruning. Some varieties have a more upright growth habit, while others may have a more sprawling or spreading growth habit. Understanding the growth habit will help you determine the best pruning techniques to maintain a balanced and productive plant.
By avoiding these common pruning mistakes, you can ensure the optimal growth, health, and fruit production of your remontant raspberry plants.
Pruning Techniques for Maintaining Plant Health and Vigor
Introduction
Pruning is an essential practice in maintaining the health and vigor of remontant raspberry varieties. By selectively removing certain parts of the plant, pruning promotes better air circulation, light penetration, and overall plant growth. The proper pruning techniques can enhance fruit production, prevent diseases, and ensure the longevity of the raspberry plants.
Pruning Basics
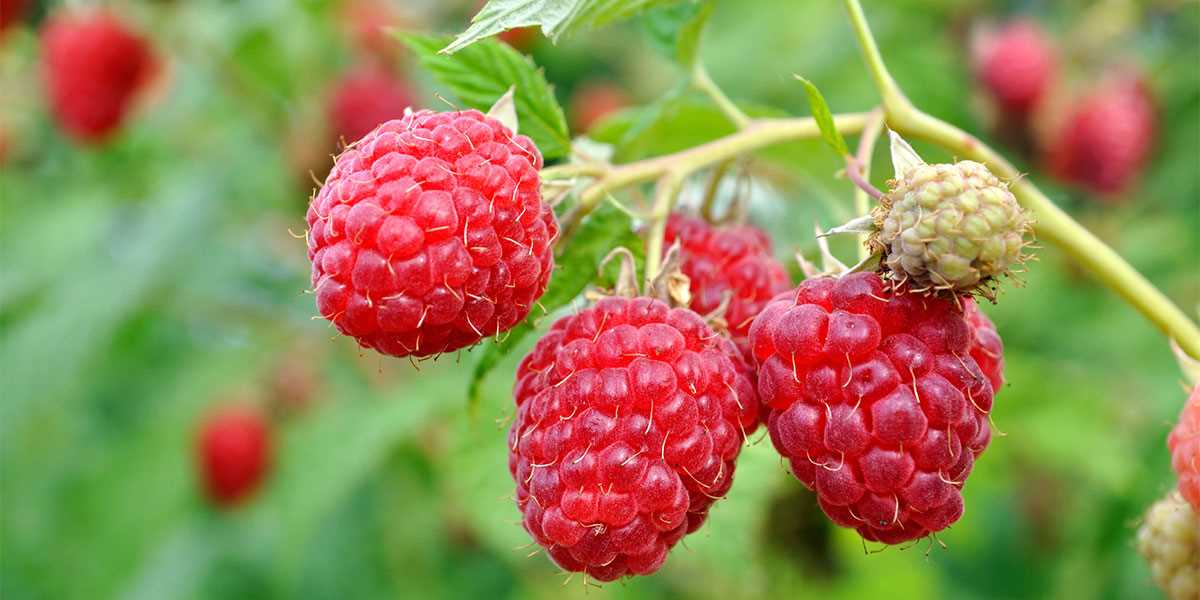

When pruning remontant raspberry varieties, it is crucial to follow a few basic guidelines:
- Prune during the dormant period, typically in late winter or early spring before new growth starts.
- Use sharp, clean pruning tools to make precise cuts and minimize the spread of disease.
- Remove any dead, damaged, or diseased canes to prevent the spread of infections.
- Thin out overcrowded canes to promote better airflow and light penetration.
Specific Pruning Techniques
Renovation Pruning
Renovation pruning is a severe pruning technique that aims to rejuvenate the raspberry plants by removing all the canes to the ground level. This technique is typically done every 3-4 years to maintain plant health and vigor. Renovation pruning allows new canes to grow and produce fruit in the following season.
Fruit-Bearing Cane Pruning
For remontant raspberry varieties, it is important to distinguish between primocanes and floricanes. Primocanes are the new green canes that emerge from the ground each season, while floricanes are the canes that have already produced fruit. To maximize fruit production, it is recommended to prune the floricanes to the ground level after they have finished fruiting, leaving the primocanes intact for the next season.
Thinning Pruning
Thinning pruning involves selectively removing some of the canes in crowded areas to improve airflow and light penetration. This technique helps reduce the risk of diseases, such as powdery mildew and gray mold, as well as increases the quality and size of the remaining fruits. Remove the weakest and most crowded canes, leaving the strongest and healthiest ones to thrive.
Conclusion
Pruning is a vital aspect of maintaining plant health and vigor in remontant raspberry varieties. By following the proper pruning techniques, such as renovation pruning, fruit-bearing cane pruning, and thinning pruning, growers can ensure better fruit production, disease prevention, and long-term plant health. Regular pruning plays a crucial role in maximizing the yield and quality of remontant raspberries.
Consulting Experts and Resources for Pruning guidance in Remontant Raspberry Cultivation
Pruning is an essential practice in remontant raspberry cultivation to ensure optimal fruit production. To gain in-depth knowledge and guidance on pruning techniques specific to remontant raspberry varieties, it is highly beneficial to consult experts and utilize available resources. Here are some valuable sources that can provide expert advice and information:
- Agricultural Extension Services: Local agricultural extension offices and services can provide valuable guidance on pruning techniques tailored to your specific region or area. They often have experts who specialize in berry cultivation and can offer personalized recommendations.
- University Research and Cooperative Extensions: Many universities and cooperative extensions conduct research on berry cultivation, including pruning practices. Their websites and publications often provide detailed information on pruning techniques based on scientific studies and field trials.
- Online Forums and Communities: Participating in online forums and communities dedicated to berry cultivation and raspberry farming can connect you with experienced growers who can provide insights and tips on pruning techniques. Some popular online platforms include gardening forums, social media groups, and specialized farming communities.
- Books and Publications: Books and publications focusing on berry cultivation, raspberry farming, and pruning techniques can provide comprehensive information and step-by-step instructions. Look for reputable authors or publications that have been reviewed and recommended by experts in the field.
- Agricultural Workshops and Conferences: Attending workshops and conferences related to berry cultivation or raspberry farming can provide opportunities for hands-on learning and access to experts in pruning techniques. These events often feature seminars and demonstrations specifically focused on pruning and other cultivation practices.
Remember, when seeking expert advice and resources for pruning remontant raspberry varieties, it’s important to consider the specific characteristics and requirements of the variety you are cultivating. Consulting local experts familiar with your region’s conditions and utilizing reputable sources will help you make informed decisions and improve your pruning practices.
Question-answer:
What are remontant raspberry varieties?
Remontant raspberry varieties are types of raspberries that produce fruit multiple times throughout the growing season.
Why is early fruit production important in raspberries?
Early fruit production is important in raspberries because it allows growers to have a longer harvesting period and increases the potential for higher yields.
What are some pruning techniques for early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties?
Some pruning techniques for early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties include removing the first flower buds, selectively thinning canes, and heading back the canes to promote lateral shoot development.
How does removing the first flower buds help with early fruit production?
Removing the first flower buds helps with early fruit production by redirecting the plant’s energy towards the development of stronger canes and larger fruit later in the season.
What is selective thinning of canes?
Selective thinning of canes is the process of removing weaker or overcrowded canes to allow more sunlight, air circulation, and nutrients to reach the remaining canes, resulting in better fruit production.
Why is heading back the canes important for early fruit production?
Heading back the canes is important for early fruit production because it stimulates the growth of lateral shoots that will bear fruit earlier in the season.
Are there any other factors that can help with early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties?
Yes, providing proper irrigation, fertilization, and mulching can also contribute to early fruit production in remontant raspberry varieties.







