- Choosing the Right Time
- Preparing the Soil
- Step 1: Choose the Right Location
- Step 2: Remove Weeds and Debris
- Step 3: Test and Amend the Soil
- Step 4: Create Raised Beds or Mounds
- Step 5: Fertilizer Application
- Step 6: Till the Soil
- Step 7: Final Soil Preparation
- Selecting the Strawberry Varieties
- 1. Climate
- 2. Day Length
- 3. Taste and Texture
- 4. Disease Resistance
- 5. Yield and Fruit Size
- 6. Harvesting Period
- Planting the Strawberries
- Providing Adequate Watering
- Managing Pests and Diseases
- Pests
- Diseases
- Fertilizing the Plants
- 1. Soil Testing
- 2. Organic Fertilizers
- 3. Balanced Fertilizer
- 4. Timing
- 5. Application Rates
- 6. Application Method
- 7. Mulching
- 8. Regular Maintenance
- 9. Avoid Chemical Fertilizers
- Harvesting and Storing Strawberries
- 1. Harvesting:
- 2. Storing:
- 3. Enjoying:
- Question-answer:
- When is the best time to plant strawberries in open ground?
- How do I prepare the soil before planting strawberries?
- Can I grow strawberries in containers?
- What is the ideal spacing for strawberry plants?
- How often should I water my strawberry plants?
- Video: The Best Way to Propagate Strawberries
Autumn is the perfect time to start thinking about planting and caring for strawberries in open ground. The cooler temperatures and increased moisture create the ideal conditions for establishing strong and healthy strawberry plants. By following a few simple steps, you can ensure a bountiful harvest of delicious strawberries next summer.
Choosing the Right Variety
When it comes to strawberries, there are many different varieties to choose from. Some are better suited for certain regions or growing conditions, while others may have specific flavor profiles or characteristics. It’s important to do some research and select a strawberry variety that will thrive in your specific area. Popular choices include ‘Eversweet’, ‘Albion’, and ‘Chandler’.
Preparing the Soil
Before planting your strawberries, it’s important to prepare the soil properly. Strawberries prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Start by removing any weeds or grass from the planting area. Then, loosen the soil with a garden fork or tiller. Work in a generous amount of compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil’s fertility and structure.
Planting the Strawberries
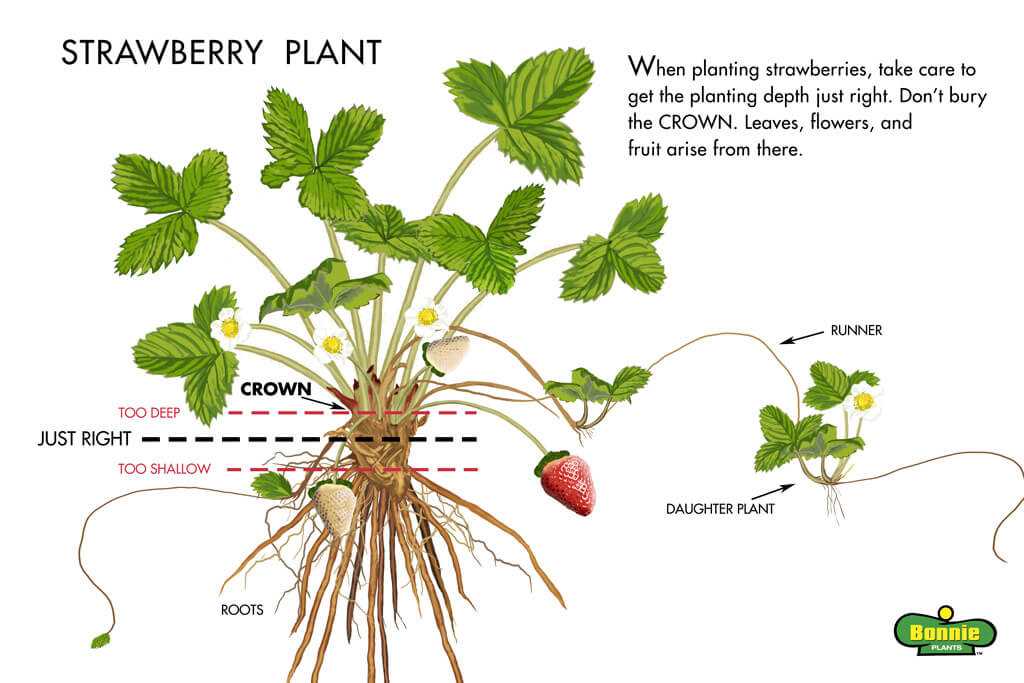
Once the soil is prepared, it’s time to plant the strawberries. Dig a hole for each plant, making sure it is large enough to accommodate the roots without bending or crowding them. Place the plant in the hole, spreading out the roots and ensuring that the crown (the point where the roots meet the stem) is level with the surrounding soil. Fill in the hole with soil, gently firming it around the plant.
Caring for Your Strawberries
After planting, it’s important to provide proper care for your strawberries. Water the plants thoroughly after planting, and continue to water regularly throughout the autumn. Mulching around the plants with straw or shredded leaves can help conserve moisture and suppress weed growth. Be sure to remove any weeds that do appear, as they can compete with the strawberries for nutrients and water.
By taking the time to properly plant and care for strawberries in autumn, you can set yourself up for a successful harvest next summer. With the right variety selection, soil preparation, and ongoing care, you can enjoy the sweet taste of homegrown strawberries straight from your own backyard.
Choosing the Right Time
When it comes to planting strawberries in open ground, choosing the right time is crucial for their successful growth and yield.
Autumn is generally the best time to plant strawberries in open ground, as it allows the plants to establish themselves before the winter months and ensures a strong start for the following spring. The exact timing can vary depending on your location and climate, but it is generally recommended to plant strawberries from late August to mid-September.
Here are a few factors to consider when choosing the right time for planting strawberries:
- Climate: Consider the average temperatures and climate conditions in your area. Strawberries prefer cool temperatures and can be sensitive to extreme heat or frost. Planting them in autumn allows them to establish roots before the winter cold sets in.
- Sunlight: Choose a time when the days are still long enough to provide ample sunlight for the strawberries. Sunlight is crucial for the plants to produce energy through photosynthesis and develop healthy fruits.
- Soil conditions: Consider the moisture levels and soil temperature in your garden. Ideally, the soil should be well-drained and slightly acidic, with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Avoid planting strawberries in waterlogged or compacted soil.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines and may vary depending on your specific location and climate. It’s always a good idea to consult with local gardening experts or extension services for the most accurate planting recommendations.
Preparing the Soil
Before planting strawberries in autumn, it is important to prepare the soil properly. This will ensure that the plants have the best possible start and will result in a higher yield of delicious berries.
Step 1: Choose the Right Location
Strawberries prefer well-draining soil and full sun exposure for at least 6 to 8 hours a day. Choose a location in your garden that meets these requirements to ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Step 2: Remove Weeds and Debris
Prior to planting, remove any weeds, grass, or debris from the area where you plan to grow strawberries. Weeds can compete with the strawberry plants for nutrients and water, so it is important to eliminate them before planting.
Step 3: Test and Amend the Soil
It is a good idea to test the soil to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Strawberries prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If the pH is too high, you can amend the soil by adding sulfur or peat moss to lower it.
In addition to pH adjustment, you may also need to add organic matter to improve the soil structure. Compost or well-rotted manure can be mixed into the top 6 to 8 inches of soil to provide nutrients and improve drainage.
Step 4: Create Raised Beds or Mounds

Strawberries benefit from raised beds or mounds, as they improve drainage and promote better root development. Create raised beds by forming soil into long, narrow mounds that are about 8 inches high and 2 feet wide.
Step 5: Fertilizer Application
Before planting, it is recommended to apply a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 or 14-14-14 formulation, according to the package instructions. This will provide the plants with the necessary nutrients to support healthy growth.
Step 6: Till the Soil
To further prepare the soil, use a garden tiller or a hand tool like a garden fork to loosen and aerate it. This will help improve drainage and make it easier for the strawberry roots to penetrate the soil.
Step 7: Final Soil Preparation
Finally, rake the soil surface to level it out and remove any large clumps or rocks. This will provide a smooth surface for planting the strawberry plants.
By following these steps to prepare the soil, you will create an ideal growing environment for your strawberries, giving them a strong foundation for healthy growth and a bountiful harvest.
Selecting the Strawberry Varieties
When it comes to selecting the right strawberry varieties, there are several factors to consider. The climate, soil conditions, and personal preferences all play a role in choosing the best strawberry plants for your garden. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
1. Climate
First and foremost, consider the climate in your area. Different strawberry varieties have different temperature and moisture requirements. Some varieties are more suitable for colder climates, while others thrive in warmer regions. Research the specific climate requirements of each variety to ensure you choose plants that will thrive in your area.
2. Day Length
Another important factor to consider is the day length requirement of the strawberry varieties. Some varieties are classified as day-neutral and can produce fruit regardless of the day length. Others are classified as short-day or long-day varieties, meaning they require specific day lengths to initiate blooming and fruiting. Choose the variety that matches the day length in your region for best results.
3. Taste and Texture
Taste and texture are subjective qualities, but they are important considerations when choosing strawberry varieties. Some varieties are known for their sweet flavor, while others may have a more tart taste. Texture can also vary, with some varieties being softer and juicier, while others are firmer and more suitable for baking. Consider your personal taste preferences and how you plan to use the strawberries when making your selection.
4. Disease Resistance

Strawberry plants are susceptible to various diseases, such as powdery mildew, verticillium wilt, and gray mold. Look for varieties that have good disease resistance to minimize the risk of plant damage and fruit loss. Consult with local gardening experts or extension services to determine which varieties are recommended for disease-prone areas.
5. Yield and Fruit Size
Consider the yield and fruit size of different strawberry varieties. Some plants produce larger fruits, while others are known for their high yield. If you have limited space, you may prefer a variety that produces smaller fruits but in greater quantities. On the other hand, if you value larger berries, choose a variety that is known for its size.
6. Harvesting Period
Lastly, consider the harvesting period of the strawberry varieties. Some varieties have an early, intermediate, or late ripening period. By selecting a combination of varieties with different ripening times, you can enjoy fresh strawberries for a longer period throughout the growing season.
Remember to do thorough research on each variety before making a decision. By considering these factors and selecting the right strawberry varieties for your specific conditions and preferences, you can ensure a successful and enjoyable strawberry garden.
Planting the Strawberries
Before planting strawberries, it is important to choose a suitable location with well-draining soil and adequate sunlight. Here are the steps to plant strawberries in the open ground:
- Prepare the soil: Start by preparing the soil by removing any weeds and grass from the area. It is recommended to dig the soil to a depth of about 8 inches and add organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil’s fertility and drainage.
- Choose the right varieties: Select strawberries varieties that are suitable for your climate and growing conditions. Consider factors such as disease resistance, yield, and flavor.
- Planting: Dig small holes in the prepared soil, ensuring they are wide and deep enough to accommodate the strawberry plants’ root system. Space the holes about 12-18 inches apart, allowing enough room for the plants to spread. Place one strawberry plant in each hole and cover the roots with soil, making sure the crown is level with the soil surface.
- Watering: After planting, water the strawberry plants thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots. Avoid over-watering, as it may lead to root rot. Provide regular watering as needed to keep the soil evenly moist.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around the plants to suppress weed growth, retain moisture, and maintain even soil temperatures.
- Staking: If you are growing tall varieties of strawberries, consider staking or trellising the plants to keep them upright and prevent the fruit from touching the ground.
- Fertilizing: Strawberry plants benefit from regular fertilization. Apply a balanced fertilizer once or twice during the growing season, following the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates.
- Pruning: Regularly remove any yellowing or diseased leaves from the strawberry plants. Also, trim off runners or daughter plants to maintain the desired spacing between plants.
By following these steps, you can successfully plant strawberries in the open ground, ensuring healthy growth and bountiful fruit harvests. Remember to provide proper care and attention throughout the season to enhance the plants’ productivity and longevity.
Providing Adequate Watering
Watering is an essential part of caring for strawberry plants, especially in the autumn season. Adequate watering ensures the plants receive the necessary moisture to grow and develop, leading to healthy and productive plants.
Here are some tips for providing adequate watering for your strawberry plants:
- Consistency: Aim to water the plants consistently to keep the soil evenly moist. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to rotting of the roots, but also make sure the plants do not dry out.
- Timing: Water the plants in the early morning or late evening, when the temperatures are cooler. This helps to minimize evaporation and allows the plants to absorb the moisture more effectively.
- Root zone: Focus the watering around the root zone of the plants. This is where the majority of the roots are located, and it ensures that the water reaches the plants’ roots more efficiently.
- Drip irrigation: Consider using drip irrigation or a soaker hose system to water your strawberry plants. These methods deliver water directly to the root zone, reducing water loss through evaporation and keeping the foliage dry, which can help prevent diseases.
In addition to regular watering, it is also important to monitor the moisture levels of the soil. Stick your finger into the soil near the plants to check if it feels dry or moist. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water again.
Remember to adjust your watering schedule based on the weather conditions. During periods of heavy rainfall, you may need to reduce or even stop watering temporarily to prevent overwatering and waterlogged soil.
| Signs of inadequate watering: | Signs of overwatering: |
|---|---|
|
|
By providing adequate watering for your strawberry plants, you are setting them up for success in the autumn season. Remember to pay attention to their moisture needs and adjust your watering routine accordingly, and you will be rewarded with healthy, thriving plants and a bountiful strawberry harvest.
Managing Pests and Diseases

Strawberry plants are susceptible to a number of pests and diseases that can affect their growth and productivity. It is important to effectively manage these issues to ensure the health of your plants and the quality of your berries. Here are some common pests and diseases that can affect strawberries, along with some strategies for managing them:
Pests
- Strawberry Root Weevil: These insects feed on the roots of strawberry plants, causing stunted growth and decreased fruit production. To manage them, regularly inspect the plants for signs of damage and apply a suitable insecticide.
- Spider Mites: Spider mites can cause yellowing of leaves and fine webbing between branches. To control spider mites, keep the plants well watered and free from dust. If an infestation occurs, apply a miticide or insecticidal soap.
- Slugs and Snails: Slugs and snails can eat through leaves and fruits, damaging the plants. To control them, keep the area around the plants free from debris and apply crushed eggshells or diatomaceous earth as a barrier.
- Aphids: Aphids suck the sap from the leaves, causing distortion and stunted growth. To manage aphids, regularly inspect the plants and remove any affected leaves or stems. You can also introduce natural predators like ladybugs to control the population.
Diseases
- Gray Mold (Botrytis Fruit Rot): Gray mold can cause the berries to rot and become covered in a fuzzy gray mold. To prevent this disease, ensure good air circulation around the plants, remove any infected berries immediately, and avoid overhead watering.
- Leaf Spot: Leaf spot causes dark spots on leaves, leading to yellowing and defoliation. To manage leaf spot, remove infected leaves and apply a fungicide if necessary. Avoid overcrowding the plants to improve air circulation.
- Verticillium Wilt: Verticillium wilt causes wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth in strawberry plants. To manage this disease, plant resistant varieties, practice crop rotation, and remove and destroy infected plants.
- Powdery Mildew: Powdery mildew appears as a white powdery coating on leaves and can stunt plant growth. To manage powdery mildew, ensure good air circulation, remove infected leaves, and apply a fungicide if necessary.
Regularly monitoring your strawberry plants for pests and diseases, practicing good sanitation, and taking appropriate measures will help ensure the health and productivity of your strawberry crop.
Fertilizing the Plants

Proper fertilization is essential for the healthy growth of strawberry plants and to ensure a bountiful harvest. Here are some important points to consider when fertilizing strawberries:
1. Soil Testing
Before applying any fertilizers, it is important to conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels and pH of the soil. This will help you identify any deficiencies or imbalances in the soil that need to be addressed.
2. Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are the preferred choice for strawberry plants as they are slow-release and provide a steady supply of nutrients over time. Compost, well-rotted manure, and worm castings are excellent choices for organic fertilizers.
3. Balanced Fertilizer
Strawberries require a balanced fertilizer that provides adequate amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (N-P-K). Look for a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of 10-10-10 or a similar balanced ratio.
4. Timing
Apply fertilizer to strawberry plants in early spring before new growth emerges. Avoid fertilizing in late summer or early fall as this can stimulate new growth that may be susceptible to frost damage.
5. Application Rates
Follow the recommended application rates provided on the fertilizer packaging. Over-fertilizing can cause excessive vegetative growth and reduced fruit yield.
6. Application Method
Apply the fertilizer evenly around the base of the plants, avoiding direct contact with the leaves and crowns. Water the plants immediately after fertilizing to help the nutrients reach the root zone.
7. Mulching
After applying the fertilizer, mulch around the strawberry plants with straw or pine needles. This will help retain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and provide additional organic matter as the mulch breaks down.
8. Regular Maintenance
Throughout the growing season, monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. Adjust the fertilization schedule or rates as needed to ensure optimal plant health.
9. Avoid Chemical Fertilizers

Avoid using chemical fertilizers that can be harmful to the environment and may leach into groundwater. Organic fertilizers provide a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to nourishing strawberry plants.
By following these fertilization guidelines, you can help ensure that your strawberry plants receive the nutrients they need for vigorous growth, strong root development, and abundant fruit production.
Harvesting and Storing Strawberries
Harvesting ripe strawberries is an exciting and rewarding task. It is important to pick them at the right time to enjoy their full flavor and sweetness. Here are some tips and techniques for harvesting and storing strawberries:
1. Harvesting:
- Check your strawberries daily, as they can ripen quickly.
- Pick the strawberries when they are fully ripe, bright red, and have a glossy appearance.
- Gently grasp the stem just above the fruit and pull it upwards. This helps avoid damaging the plant.
- Do not pick unripe or green strawberries, as they will not ripen off the plant.
- Remove any spoiled or damaged berries to prevent the spread of disease.
- It is best to harvest strawberries in the morning when they are cool and firm.
2. Storing:
- Only store fresh, undamaged strawberries.
- Keep strawberries refrigerated to prolong their freshness.
- Do not wash strawberries before storing, as moisture can make them spoil faster.
- Place the strawberries in a shallow bowl or container lined with paper towels to absorb excess moisture.
- If you have a large quantity of strawberries, avoid stacking them on top of each other, as it can cause bruising.
- To freeze strawberries, wash and dry them thoroughly, then place them in a single layer on a baking sheet and freeze. Once frozen, transfer them to a freezer-safe bag or container.
3. Enjoying:

- Strawberries are best enjoyed fresh within a couple of days after harvesting.
- To serve strawberries, rinse them gently under cool water and remove the stems.
- Strawberries can be enjoyed on their own, added to salads, used in cakes and pastries, or made into preserves and jams.
By following these simple steps, you can ensure that your harvested strawberries stay fresh and delicious, allowing you to enjoy their delightful flavor throughout the season.
Question-answer:
When is the best time to plant strawberries in open ground?
The best time to plant strawberries in open ground is in autumn.
How do I prepare the soil before planting strawberries?
Before planting strawberries, it is important to prepare the soil by removing any weeds, loosening it with a fork, and adding compost or well-rotted manure to improve its fertility.
Can I grow strawberries in containers?
Yes, strawberries can be grown in containers. It is important to choose a container that is at least 8 inches deep and has drainage holes. Use a good quality potting mix and provide regular watering and fertilization.
What is the ideal spacing for strawberry plants?
The ideal spacing for strawberry plants is about 12 inches apart, with a distance of 24 inches between rows. This allows the plants to have enough room to grow and spread properly.
How often should I water my strawberry plants?
Strawberry plants should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods. It is important to keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged, as this can cause root rot. Aim to provide approximately 1 inch of water per week.







