- Identifying the Weevil Infestation
- Physical Appearance
- Damage Symptoms
- Life Cycle
- Monitoring Methods
- Conclusion
- Potential Damage Caused by Weevils
- 1. Yield Loss
- 2. Quality Reduction
- 3. Secondary Infections
- 4. Economic Impact
- 5. Psychological Stress
- Methods of Controlling Weevil Populations
- Biological Control Agents for Weevils
- Ladybugs
- Parasitic Wasps
- Nematodes
- Predatory Insects
- Chemical Control Options for Weevils
- 1. Insecticides
- 2. Pheromone Traps
- 3. Biological Control
- 4. Integrated Pest Management
- 5. Resistance Management
- Preventive Measures to Avoid Weevil Infestations
- Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Weevils
- 1. Cultural Controls
- 2. Biological Controls
- 3. Mechanical Controls
- 4. Chemical Controls
- 5. Monitoring and Early Detection
- Question-answer:
- How do I know if my strawberries have a weevil infestation?
- What kind of damage do weevils cause to strawberries?
- What are some effective control methods to get rid of weevils on strawberries?
- Are there any organic methods to control weevils on strawberries?
- How can I prevent weevils from infesting my strawberry plants?
- Can weevils spread diseases to strawberry plants?
- When is the best time to apply insecticides for weevil control?
- Video: Pesticide Companies Don’t Want You to Know These Secrets | Complete Guide to Organic Pest Control
Strawberries are a beloved fruit cherished for their sweet and juicy taste. However, a common garden pest known as the weevil can wreak havoc on these delicate berries. Weevils are small beetles that feed on the leaves and fruit of strawberry plants, causing damage and decreasing the quality of the harvest.
To effectively control and prevent weevil infestations on strawberries, it’s important to understand their life cycle and habits. Weevils lay their eggs on the strawberry plants, and once hatched, the larvae feed on the leaves and berries. They then pupate in the soil, emerging as adults to continue the cycle. This makes it crucial to target both the adult weevils and their eggs to prevent future infestations.
There are several methods that can be employed to control and prevent weevil infestations on strawberries. One effective approach is the use of insecticidal sprays. These sprays contain chemicals that specifically target weevils, killing them on contact. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions on the product label and apply the spray when the weevils are most active, typically in the early morning or late evening.
In addition to insecticidal sprays, physical barriers can also be used to prevent weevils from reaching the strawberry plants. These barriers can include mesh screens or row covers that are placed over the plants to keep the weevils out. Regularly inspecting the plants and removing any weevils or eggs that are found can also help control the population.
Tip: Practicing good garden hygiene, such as removing plant debris and keeping the area around the strawberry plants clean and weed-free, can also help prevent weevil infestations. Weevils are attracted to decaying organic matter and weeds, so maintaining a clean garden environment can discourage their presence.
By employing a combination of these control and prevention methods, gardeners can effectively manage and reduce weevil infestations on their strawberry plants. This not only protects the health and quality of the berries, but also ensures a bountiful harvest for strawberry lovers to enjoy.
Identifying the Weevil Infestation
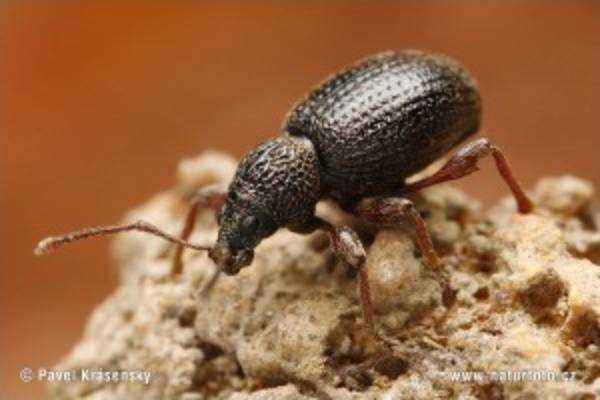
Identifying a weevil infestation on strawberries is crucial in order to effectively control and prevent further damage. Weevils are small beetles that belong to the Curculionidae family. There are several common species of weevils that attack strawberries, including the strawberry root weevil (Otiorhynchus ovatus) and the black vine weevil (Otiorhynchus sulcatus).
Physical Appearance

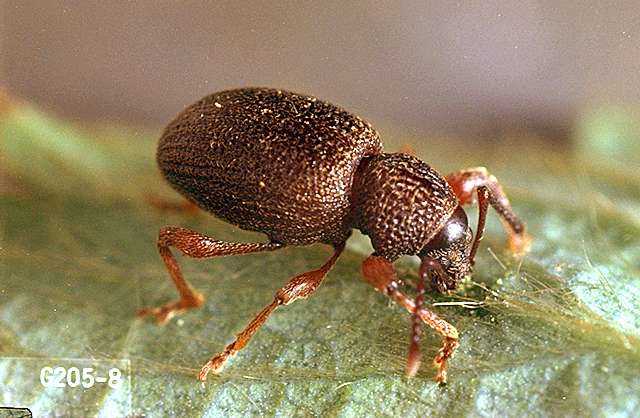
Weevils have a distinct oval-shaped body with a hardened exoskeleton. They typically measure between 4 to 8 millimeters in length. These beetles are usually dark brown or black in color, making them easily recognizable. Weevils have a characteristic snout-like extension on their head that they use to bore into fruits and plants.
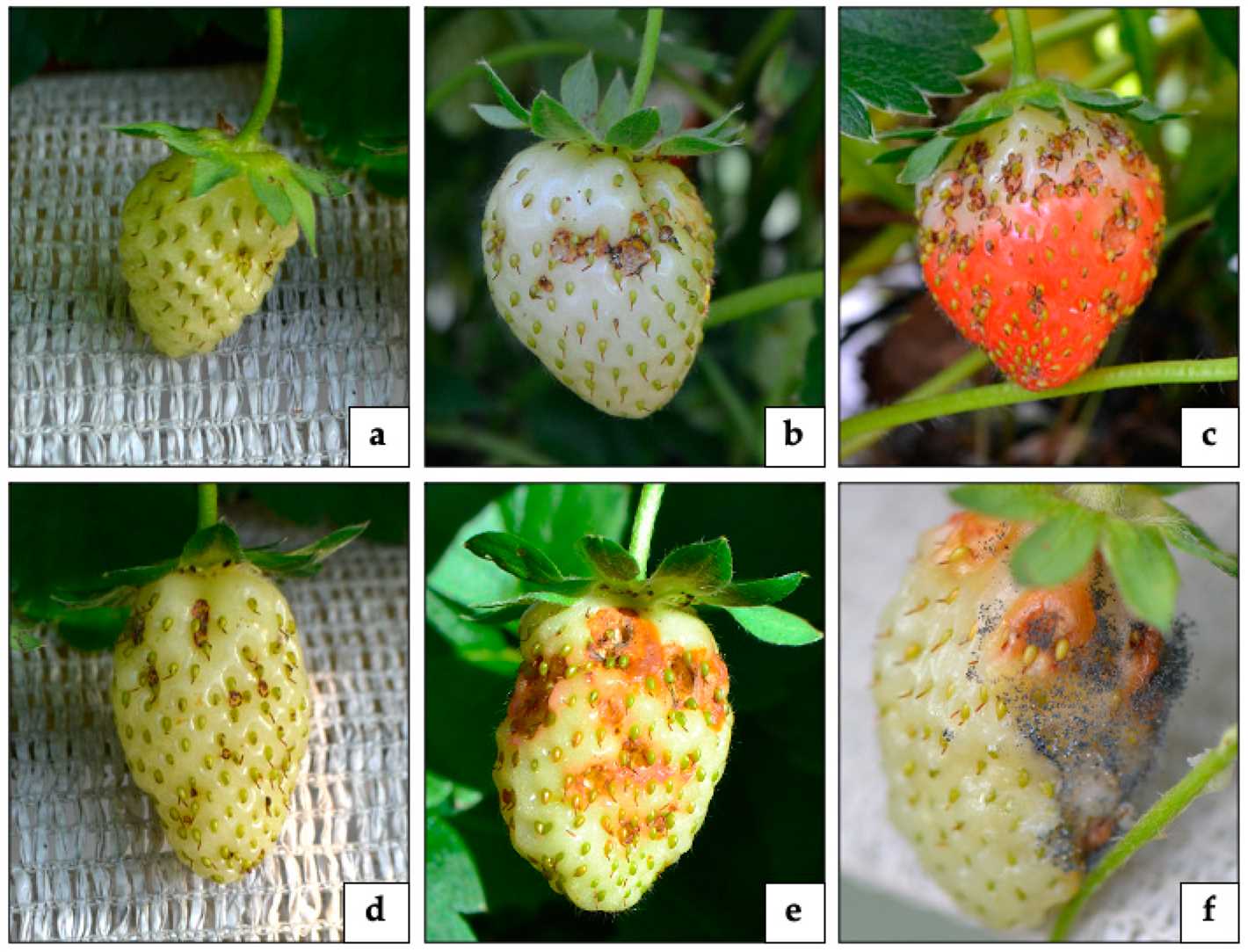
Damage Symptoms
When strawberries are infested with weevils, they exhibit various signs of damage. Some common symptoms include:
- Presence of small holes or punctures on the strawberry surface
- Brown discoloration or decay around the feeding sites
- Wilting or stunted growth of strawberry plants
- Visible damage on the leaves, stems, or crowns of the plants
Life Cycle
The life cycle of weevils consists of several stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Understanding their life cycle can help identify the appropriate control measures. Weevils typically lay their eggs in the soil near strawberry plants. The eggs hatch into larva, which then feed on the roots of the plants. Once fully grown, the larva pupate and emerge as adult weevils.
Monitoring Methods

Regular monitoring of strawberry plants is essential for early detection of weevil infestations. There are several methods that can be used to monitor the presence of weevils:
- Visual inspection: Carefully examine the strawberry plants and fruits for any signs of weevil infestation, such as holes or feeding damage.
- Sticky traps: Place sticky traps near the plants to catch adult weevils. This can help estimate the population density of weevils in the area.
- Soil sampling: Collect soil samples from the root zone of strawberry plants and inspect them for weevil eggs or larvae.
Conclusion
Identifying a weevil infestation on strawberries is crucial for effective control and prevention. By understanding the physical appearance, damage symptoms, and life cycle of weevils, growers can implement appropriate monitoring methods and take necessary actions to mitigate the infestation.
Potential Damage Caused by Weevils

Weevils are small beetles that can cause significant damage to strawberry crops if left uncontrolled. These pests primarily target the ripe and developing fruit, feeding on the exterior and burrowing into the flesh. Here are some potential damages caused by weevils:
1. Yield Loss
Weevils can cause a substantial decrease in crop yield as they feed on the strawberries. By damaging the fruit, they render it unmarketable and unfit for consumption. The extent of yield loss depends on the severity of the infestation and the effectiveness of control measures.
2. Quality Reduction
Weevil infestations can result in a decline in fruit quality. The feeding activity of these pests can lead to deformities, discoloration, and softening of the strawberries. This reduces the market value and consumer appeal of the affected produce.
3. Secondary Infections
When weevils tunnel into the strawberries, they create entry points for pathogens and fungi. These opportunistic organisms can infect the damaged fruit, causing further decay and spoilage. The presence of secondary infections can worsen the overall damage caused by weevils.
4. Economic Impact
The economic impact of weevil damage extends beyond immediate yield loss and reduced quality. Farmers may incur additional expenses in controlling and preventing weevil infestations through the use of pesticides or other management practices. Additionally, decreased marketable yield and lower product quality may result in financial losses for growers.
5. Psychological Stress
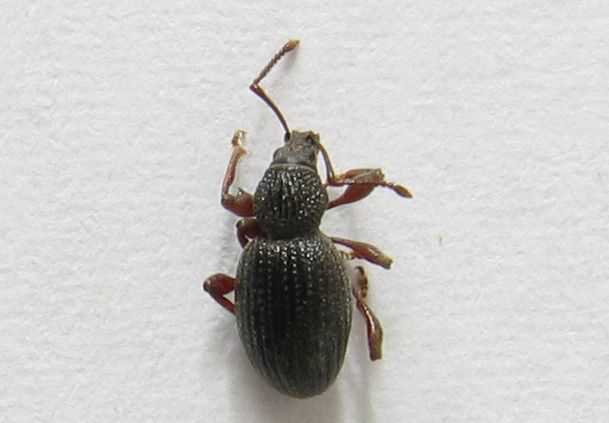

Weevil infestations can cause psychological stress for farmers who rely on strawberry crops as a source of income. The presence of these pests and the potential damage they can cause can create anxiety and uncertainty regarding the success of their harvests. Effective control and prevention methods are essential in reducing such stress.
In conclusion, weevils pose a significant threat to strawberry crops, causing yield loss, quality reduction, secondary infections, economic impact, and psychological stress. Implementing effective control and prevention measures is crucial for minimizing the potential damage caused by these pests.
Methods of Controlling Weevil Populations
- Sanitation: Keeping the strawberry planting area free from weeds and debris can help minimize weevil populations. Weevils are attracted to areas with high amounts of organic matter, so keeping the area clean can deter them from establishing a population.
- Trapping: Placing sticky traps or pheromone traps around the strawberry plants can help capture adult weevils. These traps can be effective in reducing the overall population and monitoring the level of infestation.
- Hand-picking: If the weevil population is low, hand-picking the pests off the plants can be an effective method of control. This method is time-consuming but can be necessary for small gardens or if chemical control is not desired.
- Biological control: Introducing natural enemies of weevils, such as beneficial nematodes or predatory insects, can help reduce their populations. These biological control agents can be purchased and released in the strawberry planting area.
- Chemical control: If the weevil infestation is severe, chemical insecticides can be used as a control method. It is important to choose an insecticide that is labeled for use on strawberries and follow the instructions carefully to ensure proper application and minimize harm to beneficial insects.
Biological Control Agents for Weevils
Weevils are a common pest in strawberry crops, causing damage to the fruit and reducing yield. While chemical pesticides can be effective in controlling weevils, they can also have negative impacts on the environment and human health. Biological control agents offer an alternative and sustainable method for managing weevil populations.
Ladybugs
Ladybugs, also known as ladybirds or lady beetles, are often considered beneficial insects due to their voracious appetite for small pests such as aphids, mites, and weevil larvae. Adult ladybugs and their larvae feed on weevils, reducing their population and preventing further damage to the strawberries.
Parasitic Wasps
Parasitic wasps, such as Trichogramma wasps, are natural enemies of weevils. These tiny wasps lay their eggs inside weevil eggs or larvae. When the wasp eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the weevil eggs or larvae, ultimately killing them. Introducing parasitic wasps into the strawberry fields can help control the weevil population.
Nematodes
Nematodes are microscopic worms that are known to parasitize and kill weevil larvae. There are specific nematode species, such as Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and Steinernema carpocapsae, that are effective in controlling weevils. These nematodes can be applied to the soil in strawberry fields, where they will seek out weevil larvae and infect them, ultimately causing their death.
Predatory Insects
Various predatory insects, such as ground beetles and rove beetles, are natural enemies of weevils. These insects prey on weevil adults and larvae, helping to reduce their population. Creating a diverse and balanced ecosystem in strawberry fields that supports the presence of these predatory insects can aid in controlling weevil populations.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of biological control agents can vary depending on various factors such as the specific weevil species, environmental conditions, and the presence of alternative food sources for the beneficial insects. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with agricultural experts or entomologists to determine the most suitable biological control strategies for managing weevils in strawberry crops.
Chemical Control Options for Weevils
Weevils can cause significant damage to strawberry crops, leading to reduced yields and quality. Chemical control methods can be an effective way to manage weevils and mitigate their impact. Here are some commonly used chemical control options for weevils in strawberry production:
1. Insecticides
Insecticides are the most common chemical control option for weevils. They can be applied as sprays or granules to target adult weevils or their larvae. Some commonly used insecticides include:
- Pyrethroids: Pyrethroid insecticides are effective against adult weevils. They act by disrupting the insect’s nervous system, leading to paralysis and death.
- Organophosphates: Organophosphate insecticides work by inhibiting the activity of enzymes in the weevil’s nervous system, ultimately causing paralysis and death.
- Neonicotinoids: Neonicotinoid insecticides are systemic, meaning they are taken up by the plant and can kill weevils when they feed on the treated plants.
It is important to carefully read and follow the instructions on the insecticide label to ensure proper and safe application.
2. Pheromone Traps
Pheromone traps are another chemical control option that can help detect and monitor weevil populations. These traps use synthetic chemicals that mimic the scent of female weevils to attract and trap males. By monitoring the number of captured weevils, growers can determine the severity of the infestation and take appropriate control measures.
3. Biological Control
While not a chemical control option, biological control methods can also be used to manage weevil populations. Predatory insects such as parasitic wasps and nematodes can be introduced into the crop to prey on weevils and their larvae. This can help reduce weevil numbers without the use of chemical pesticides.
4. Integrated Pest Management
An integrated pest management (IPM) approach combines various control methods to effectively manage weevil populations. This may include a combination of chemical controls, biological controls, cultural practices, and monitoring techniques. By using multiple strategies, growers can reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and minimize the impact on beneficial insects and the environment.
5. Resistance Management
Continuous and excessive use of the same insecticide can lead to the development of weevil populations resistant to that particular chemical. To prevent resistance, it is important to rotate the use of different insecticides with different modes of action. This helps ensure that weevils are not able to adapt and survive the chemical treatments.
Remember, when using chemical control options for weevils, it is crucial to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and adhere to proper safety precautions to protect yourself, the crop, and the environment.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Weevil Infestations
The following preventive measures can help avoid weevil infestations in strawberry crops:
Clean and inspect: Regularly clean the strawberry fields and remove any fallen leaves, fruits, or debris that may provide a breeding ground for weevils. Inspect the plants for signs of weevil damage, including chewed leaves, boreholes, and stunted growth.
Rotate crops: Practice crop rotation by planting strawberries in different areas each year. Weevils can overwinter in the soil, so planting strawberries in the same location year after year can increase the risk of infestation.
Use physical barriers: Install physical barriers such as row covers or nets to protect the strawberry plants from adult weevils. Ensure that the barriers are properly secured to prevent weevils from accessing the plants.
Implement trap crops: Plant trap crops around the strawberry fields to attract weevils away from the main crop. Remove and destroy the trap crops regularly to eliminate the weevils.
Prune and discard: Regularly prune and discard any infested or damaged parts of the strawberry plants. This can help prevent weevils from spreading and reproducing.
Monitor and scout: Regularly monitor the strawberry plants for weevil activity. Scouting involves inspecting the plants, especially during the early morning or evening hours when weevils are most active. Use sticky traps or pheromone traps to monitor adult weevils.
Practice sanitation: Maintain proper sanitation practices in and around the strawberry fields. Remove weeds and keep the area clean from excess plant debris, as these can attract and harbor weevils.
Use natural predators: Introduce natural predators of weevils, such as parasitic wasps or predatory beetles, into the strawberry fields. These natural predators can help control weevil populations.
Apply organic insecticides: If preventive measures fail and weevil infestation becomes severe, consider using organic insecticides labeled for use on strawberries. Follow the instructions carefully and apply the insecticides at the recommended rates and timing to minimize environmental impact.
By implementing these preventive measures, strawberry growers can reduce the risk of weevil infestations and protect their crops from damage.
Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Weevils
Weevils are a common pest that can cause significant damage to strawberry crops. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies combine various methods to effectively control and prevent weevil infestations.
1. Cultural Controls

- Plant resistant varieties: Choose strawberry varieties that are less susceptible to weevil damage.
- Crop rotation: Rotate strawberry crops with non-host plants to disrupt the weevil life cycle.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infested plants and debris to prevent the spread of weevils.
2. Biological Controls
- Encourage natural predators: Attract beneficial insects such as predaceous beetles and parasitic wasps to control weevil populations.
- Release beneficial organisms: Introduce microbial pesticides or beneficial nematodes to specifically target weevils.
3. Mechanical Controls
- Handpicking: Inspect plants regularly and manually remove adult weevils and larvae.
- Trapping: Set up sticky traps or pheromone traps to monitor and catch adult weevils.
4. Chemical Controls

- Insecticides: Use insecticides as a last resort and only if necessary. Follow label instructions and consider the potential impact on beneficial insects.
5. Monitoring and Early Detection

- Regular monitoring: Check plants for signs of weevil activity, such as feeding damage or adult presence.
- Early detection: Detect and address weevil infestations early to prevent widespread damage.
Remember, implementing a combination of these IPM strategies is often the most effective approach to managing weevil populations in strawberry crops. Consult with local agricultural extension services or pest management professionals for specific recommendations and guidance.
Question-answer:
How do I know if my strawberries have a weevil infestation?
You can check for weevil infestation by examining the strawberries closely. Look for small holes or tunnels in the strawberries, as well as larvae or adult weevils on or near the fruit.
What kind of damage do weevils cause to strawberries?
Weevils can cause significant damage to strawberries by feeding on the fruit. They create small holes or tunnels, which can make the strawberries unappealing and inedible.
What are some effective control methods to get rid of weevils on strawberries?
There are several effective control methods to get rid of weevils on strawberries. These include removing and destroying infested fruit, applying insecticides, using sticky traps, practicing good weed control, and introducing natural predators.
Are there any organic methods to control weevils on strawberries?
Yes, there are organic methods to control weevils on strawberries. These include handpicking the weevils, using neem oil or diatomaceous earth as a natural insecticide, introducing beneficial nematodes, and maintaining proper sanitation practices in the garden.
How can I prevent weevils from infesting my strawberry plants?
You can prevent weevils from infesting your strawberry plants by practicing regular inspection and removing any infested fruit or plants. It is also important to maintain proper weed control, as weevils can hide and breed in weeds. Additionally, introducing natural predators, such as birds or beneficial insects, can help keep weevil populations in check.
Can weevils spread diseases to strawberry plants?
Weevils do not typically spread diseases to strawberry plants. However, their feeding can weaken the plants and make them more susceptible to other pests and diseases. It is important to control weevil populations to prevent damage to the plants.
When is the best time to apply insecticides for weevil control?
The best time to apply insecticides for weevil control is early in the morning or late in the evening, when the weevils are most active. It is important to follow the instructions on the insecticide label and use it according to the recommended dosage.







