- How to Plant Gooseberries, Blackcurrants, and Redcurrants in Spring
- 1. Choose the Right Location
- 2. Prepare the Soil
- 3. Dig the Planting Hole
- 4. Planting the Bush
- 5. Watering and Mulching
- 6. Fertilizing
- 7. Pruning
- 8. Pests and Diseases
- Choosing the Right Variety
- Consider Local Climate
- Determine Preferred Taste and Use
- Consider Disease Resistance
- Consult Local Nurseries and Garden Centers
- Site and Soil Preparation
- 1. Location
- 2. Soil Type
- 3. Soil Preparation
- 4. Soil Testing
- 5. Fertilizer Application
- 6. Drainage
- 7. Mulching
- Planting Gooseberries
- 1. Choose the Right Location
- 2. Prepare the Soil
- 3. Dig Planting Holes
- 4. Plant the Gooseberry Bush
- 5. Mulch and Water
- 6. Prune and Train
- Planting Blackcurrants
- 1. Choosing a Suitable Location
- 2. Preparing the Soil
- 3. Planting
- 4. Spacing
- 5. Watering and Mulching
- 6. Pruning
- 7. Fertilizing
- Planting Redcurrants
- 1. Choosing a Variety
- 2. Site Selection
- 3. Soil Preparation
- 4. Planting
- 5. Watering and Mulching
- 6. Pruning
- 7. Fertilizing
- 8. Harvesting
- Proper Watering and Mulching
- Watering
- Mulching
- Fertilizing and Pruning
- 1. Fertilizing:
- 2. Pruning:
- 3. Maintenance:
- Pest and Disease Control
- 1. Aphids
- 2. Gooseberry sawfly
- 3. Currant blister aphid
- 4. Powdery mildew
- Question-answer:
- When is the best time to plant gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
- Are gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants easy to grow?
- What type of soil is best for planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
- How far apart should gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants be planted?
- Do gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants require regular pruning?
- What are some common pests and diseases that affect gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
- Video: GOOSEBERRIES – HOW TO PLANT AND GROW THEM
If you’re thinking about planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, or redcurrants this spring, there are a few tips that can help ensure success. These delicious berries are not only tasty, but they are also packed with health benefits. Planting them in the right way will give you a bountiful harvest and ensure the plants thrive for years to come.
Choose the right location: Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants prefer a sunny spot with well-draining soil. They can tolerate some shade, but they will produce more fruit if they receive at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. Make sure the soil is rich in organic matter and has a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5.
Prepare the soil: Before planting, it’s important to prepare the soil properly. Remove any weeds or grass and dig a hole that is twice the size of the root ball. Mix in some compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil’s fertility. This will provide the plants with the nutrients they need to grow strong and produce abundant berries.
Planting the bushes: When planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, or redcurrants, make sure the crown of the plant is level with the soil surface. Space the bushes about 3-4 feet apart to allow for air circulation and easy harvesting. Water the plants thoroughly after planting and add a layer of mulch around the base to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Care and maintenance: Once your berry bushes are planted, it’s important to provide them with proper care and maintenance. Water the plants regularly, especially during dry periods, and keep an eye out for any signs of pests or diseases. Prune the bushes in late winter or early spring to promote new growth and remove any dead or damaged branches. Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring to give the plants a boost of nutrients.
By following these tips, you can enjoy a successful harvest of gooseberries, blackcurrants, or redcurrants in your garden this spring. These berries are not only delicious to eat fresh or use in recipes, but they also make excellent additions to jams, jellies, and desserts. Get ready to enjoy the sweet rewards of your hard work!
How to Plant Gooseberries, Blackcurrants, and Redcurrants in Spring
If you’re planning to plant gooseberries, blackcurrants, or redcurrants in your garden this spring, here are some tips to ensure their successful growth:
1. Choose the Right Location
These berry bushes thrive in full sun or partially shaded areas, so select a spot in your garden that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Ensure the soil is well-drained and rich in organic matter for optimal growth.
2. Prepare the Soil

Prior to planting, prepare the soil by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris. Loosen the soil with a garden fork or tiller to a depth of around 12 inches. Incorporate organic matter such as compost or aged manure to improve soil fertility.
3. Dig the Planting Hole
Dig a hole that is slightly larger and deeper than the container in which the plant is currently growing. Gently remove the plant from its container, taking care not to disturb the roots too much.
4. Planting the Bush
Place the plant in the hole, making sure that the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above the ground surface. Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the plant to eliminate any air pockets.
5. Watering and Mulching
After planting, water the bush thoroughly to ensure proper establishment. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of the plant to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth.
6. Fertilizing
During the first year of growth, apply a balanced organic fertilizer to provide essential nutrients. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and timing. In subsequent years, fertilize the bushes annually in early spring.
7. Pruning
Prune the bushes in late winter or early spring to promote healthy growth and improve fruit production. Remove any dead, damaged, or diseased branches. Thin out the center of the bush to increase airflow and sunlight penetration.
8. Pests and Diseases
Keep an eye out for common pests and diseases that can affect these berry bushes, such as aphids, powdery mildew, or leaf spot. Take appropriate measures, such as using organic insecticides or fungicides, to control and prevent infestations.
Following these tips will help ensure the successful planting and growth of your gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants in spring. With proper care, you’ll be able to enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious berries in the years to come.
Choosing the Right Variety
When it comes to planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants in the spring, it is important to choose the right variety for your garden. The variety you select will depend on several factors, including your location, climate, and personal preferences.
Consider Local Climate
Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants thrive in cool temperate climates, making them suitable for many regions. However, it is important to consider your specific local climate when choosing a variety. Some varieties are more cold-hardy than others and can withstand frost and freezing temperatures better.
Research the average winter temperatures and frost dates in your area, and select a variety that is known to tolerate those conditions. This will ensure that your plants have the best chance of surviving the winter and producing an abundant harvest.
Determine Preferred Taste and Use
Another factor to consider when choosing a variety is the taste and intended use of the fruit. Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants come in a range of flavors, from sweet to tart. Consider whether you prefer to eat the berries fresh, make jams and jellies, or use them in baking.
Some varieties are better suited for fresh eating, while others are more suitable for cooking or preserving. Research the flavor profiles of different varieties and choose one that aligns with your taste preferences and intended use.
Consider Disease Resistance
Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants are susceptible to certain diseases and pests. When selecting a variety, consider its disease resistance in order to minimize the risk of plant damage and ensure a successful harvest.
Look for varieties that are resistant to common diseases such as powdery mildew, leaf spot, and aphids. Choosing disease-resistant varieties can help reduce the need for chemical treatments and make maintenance easier.
Consult Local Nurseries and Garden Centers
If you’re unsure which variety to choose, don’t hesitate to consult with local nurseries and garden centers. They are often knowledgeable about the varieties that perform well in your area and can provide valuable advice and recommendations.
Take advantage of their expertise and ask questions about specific varieties’ characteristics, adaptability, and care requirements. This way, you can make an informed decision and select the perfect variety for your garden.
Site and Soil Preparation
Before planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants in the spring, it is important to prepare your site and soil properly to ensure healthy growth and maximum fruit production. Here are some tips to help you with site and soil preparation:
1. Location
Choose a sunny or partially shaded location for your berry bushes. They need at least 6 hours of sunlight per day to thrive. Avoid areas with strong winds or frost pockets, as cold temperatures can damage the plants.
2. Soil Type
Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. They can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including clay and sandy soils. However, the pH level of the soil should be slightly acidic to neutral, ideally between 6.0 and 7.0.
3. Soil Preparation
Start by clearing the area of any weeds, grass, or debris. Dig over the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches, breaking up any clumps and removing any stones or roots. Incorporate organic matter, such as well-rotted compost or manure, into the soil to improve its structure and fertility.
4. Soil Testing
It is advisable to test your soil before planting to determine its pH level and nutrient content. You can do this by purchasing a soil testing kit or by sending a soil sample to a testing laboratory. The results will help you determine if any amendments are needed to optimize the soil conditions for your berry bushes.
5. Fertilizer Application
If the soil test indicates nutrient deficiencies, you can apply a balanced fertilizer or specific amendments, such as bone meal for phosphorus or sulphate of potash for potassium. Follow the package instructions for application rates and timing, as excessive fertilizer can harm the plants.
6. Drainage
Ensure proper drainage by incorporating organic matter into the soil and creating raised beds or mounds if necessary. Berry bushes do not like wet feet, so water should drain away quickly to prevent root rot or other water-related issues.
7. Mulching
After planting, apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the bushes to help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. This can be in the form of well-rotted compost, straw, woodchips, or bark.
By following these tips for site and soil preparation, you can create an ideal growing environment for your gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants, setting them up for healthy growth and a bountiful harvest.
Planting Gooseberries
To ensure the successful growth of your gooseberries, it’s important to properly plant them in the spring. Here are some tips to help you get started:
1. Choose the Right Location
Gooseberries require a location that receives full sun or partial shade. Choose a spot in your garden that has well-draining soil and is sheltered from strong winds. Avoid planting gooseberries in areas where other plants susceptible to powdery mildew are growing, as gooseberries are prone to this fungal disease.
2. Prepare the Soil
Before planting, prepare the soil by removing any weeds or grass and turning it over with a garden fork or spade. Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil to improve drainage and enrich its nutrient content.
3. Dig Planting Holes
Dig planting holes that are wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots of the gooseberry plant. Space the holes at least 4-5 feet apart to allow for adequate air circulation and sunlight penetration between plants.
4. Plant the Gooseberry Bush
Place the gooseberry bush in the center of the planting hole, ensuring that the top of the rootball is level with the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the roots. Water the plant thoroughly after planting to settle the soil and remove any air pockets.
5. Mulch and Water
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around the base of the gooseberry bush. This will help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Water the plant regularly, especially during dry spells, to keep the soil evenly moist.
6. Prune and Train
In the first year after planting, prune the gooseberry bush by removing any damaged or crossing branches. Train the remaining branches to an open-centered form to allow for good air circulation and sun exposure. Regular pruning in subsequent years will help maintain the bush’s shape and increase fruit production.
By following these planting tips, you’ll be on your way to growing healthy and productive gooseberry plants in your garden.
Planting Blackcurrants
If you’re considering planting blackcurrants in your garden, there are a few key steps to follow to ensure their successful growth and development. Here are some tips to help you get started:
1. Choosing a Suitable Location
Blackcurrants prefer to grow in full sun or partial shade. It’s important to select a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day. The soil should be well-draining and rich in organic matter. Avoid planting in areas with heavy clay soil that tends to retain water.
2. Preparing the Soil
Prior to planting, prepare the soil by removing any weeds and incorporating organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure. This will help improve the soil structure, drainage, and nutrient content, creating an ideal environment for blackcurrant plants.
3. Planting
Plant blackcurrant bushes in early spring or late autumn when the soil is moist but not waterlogged. Dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the plant. Place the plant in the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is at ground level. Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the plant’s base.
4. Spacing
Give blackcurrant bushes plenty of room to grow by spacing them approximately 1.2-1.5 meters apart. This will allow air circulation and prevent overcrowding, reducing the risk of disease and improving the overall health of the plants.
5. Watering and Mulching
Water newly planted blackcurrants thoroughly and regularly during dry periods to ensure they establish strong root systems. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plants to help conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature.
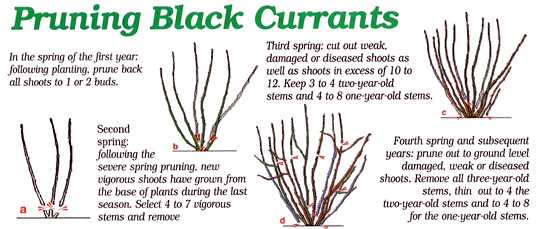
6. Pruning
Once blackcurrant bushes are established, it’s important to prune them annually to maintain their shape, promote air circulation, and encourage fruit production. Prune during the dormant season, removing any dead, damaged, or crossing branches.
7. Fertilizing

Blackcurrant plants benefit from regular fertilization to support their growth and fruit production. Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring and again in early summer following the manufacturer’s instructions.
By following these planting tips, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious blackcurrants in your own garden.
Planting Redcurrants
Redcurrants are a delicious and versatile fruit that can be grown in your garden. Here are some tips for successfully planting redcurrants in the spring:
1. Choosing a Variety
Before planting redcurrants, it’s important to choose a variety that suits your needs. There are different redcurrant varieties available, each with its own characteristics including size, taste, and disease resistance. Research the different varieties and select the one that best meets your preferences.
2. Site Selection
Redcurrants prefer a sunny or partially shaded location that is sheltered from strong winds. The soil should be well-drained and rich in organic matter. It’s also important to ensure there is enough space for the redcurrant bushes to grow, as they can reach a height of up to 4 feet.
3. Soil Preparation
Prepare the soil before planting by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris. Test the pH of the soil and adjust it if necessary. Redcurrants prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH of around 6.0 to 6.5. If the soil is too acidic, add lime to raise the pH. If it’s too alkaline, add sulfur or peat moss to lower the pH.
4. Planting
Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots of the redcurrant plant. Place the plant in the hole, making sure that the buds are level with the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots. Water the plant thoroughly after planting to help settle the soil.
5. Watering and Mulching
Redcurrants require consistent moisture, especially during dry periods. Water the plants regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plants to help retain moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature.
6. Pruning
Pruning is an important part of redcurrant plant care. Prune the plants in late winter or early spring to remove any dead, damaged, or diseased wood. This will help improve air circulation and promote healthy growth. Also, prune to shape the plant and maintain its size.
7. Fertilizing
Redcurrants benefit from regular fertilization. Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring when the buds begin to swell. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dosage and application method. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth and reduced fruit production.
8. Harvesting
Redcurrants are ready to be harvested when they are fully ripe and have a bright red color. Gently remove the berries from the stems, taking care not to damage the plant. Use the harvested redcurrants fresh or preserve them by making jams, jellies, or sauces.
By following these tips, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious redcurrants from your garden.
Proper Watering and Mulching
Watering and mulching are essential aspects of successfully planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. Properly watering your plants and mulching them helps to conserve moisture, control weeds, and maintain proper soil temperature, promoting healthy growth and fruit production.
Watering
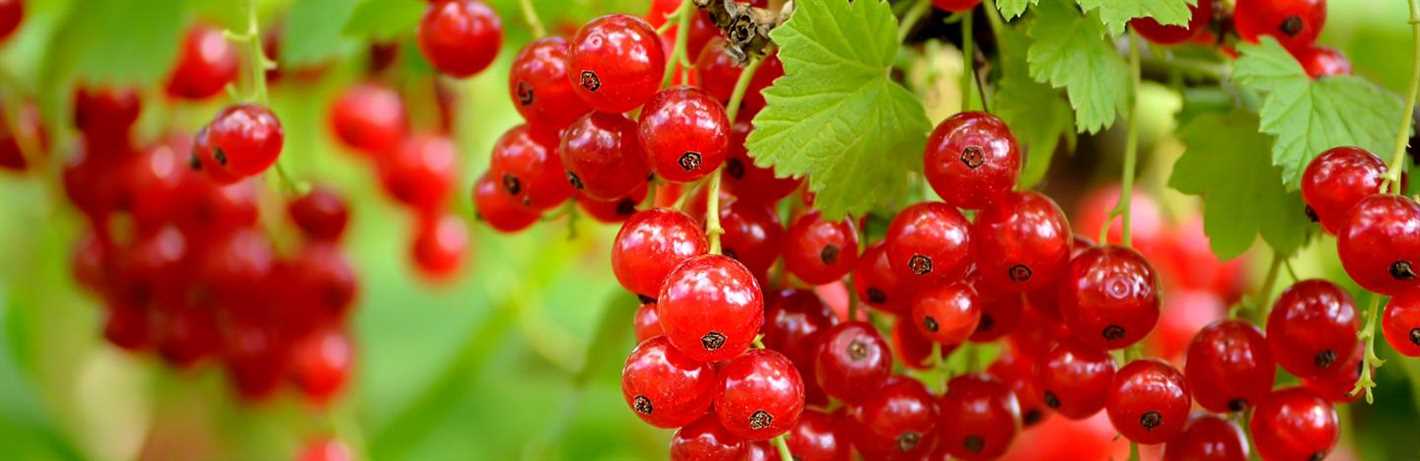

During the first growing season, it is crucial to provide adequate water to establish the plants’ root systems. Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants require about 1 inch (2.5 cm) of water each week. However, the exact amount may vary depending on the weather conditions and soil moisture levels.
- Water the plants deeply, allowing the water to penetrate the soil and reach the root zone.
- Ensure the water is evenly distributed around the plants.
- Water the plants in the morning or evening to minimize water loss due to evaporation.
- Monitor the soil moisture regularly, especially during hot or dry periods.
- Adjust the watering schedule accordingly to prevent overwatering or underwatering.
Mulching
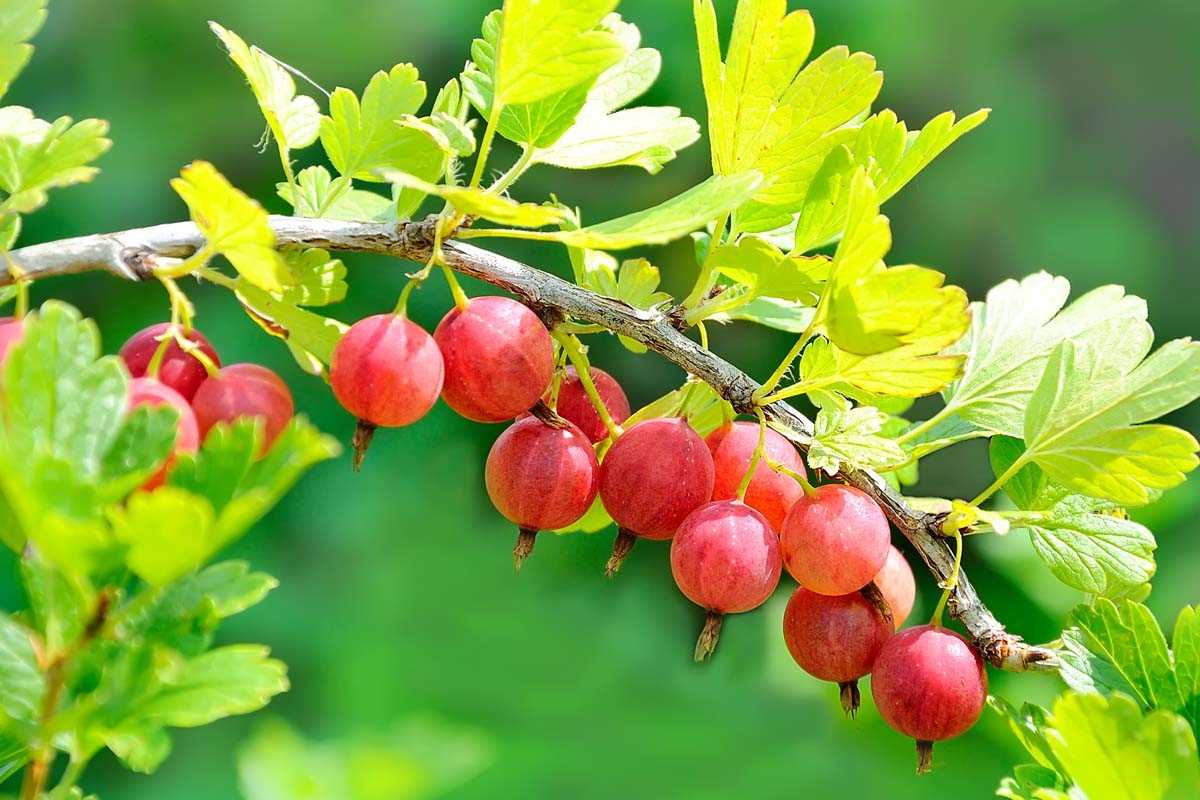

Mulching is an effective technique to suppress weeds, conserve moisture, and improve soil structure. Use organic mulch such as wood chips, straw, or compost around the berry plants.
- Apply a layer of mulch around the plants, leaving a gap around the base of the stems to prevent rot.
- The mulch layer should be around 2-4 inches (5-10 cm) deep.
- Replenish the mulch layer as needed to maintain the desired depth.
- Mulch should be spread in a circle about 2 feet (60 cm) in diameter around each plant.
- Avoid piling the mulch directly against the stems to prevent moisture-related diseases.
By following these watering and mulching practices, you can create optimal growing conditions for your gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. Remember to monitor the plants regularly and adjust your watering schedule as necessary to ensure their health and productivity.
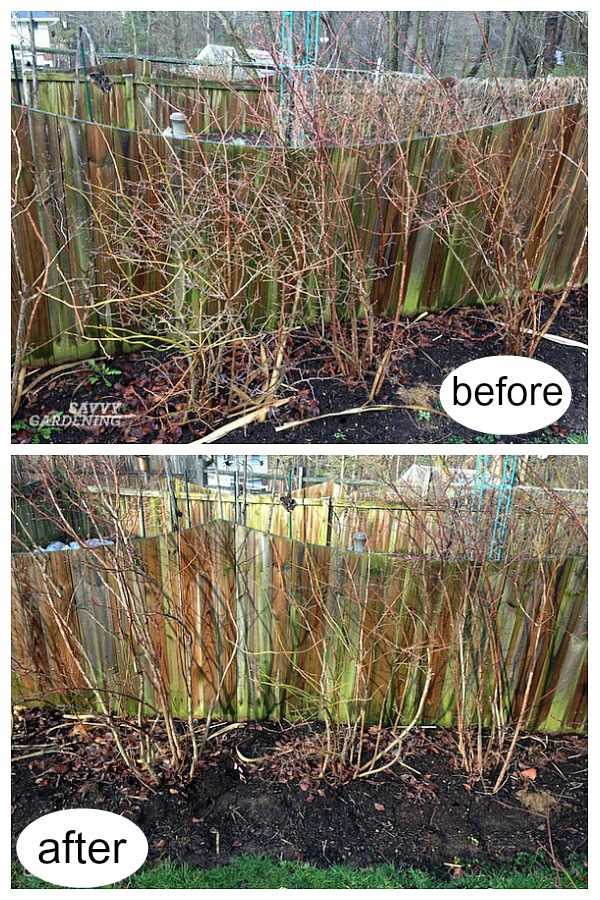
Fertilizing and Pruning
Fertilizing and pruning are important tasks for maintaining the health and productivity of gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. Here are some tips on how to properly fertilize and prune these plants:
1. Fertilizing:
It’s recommended to fertilize gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants in early spring, just before new growth begins. Use a balanced fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Spread the fertilizer evenly around the base of the plants, avoiding direct contact with the stems.
- Lightly rake the fertilizer into the soil and water thoroughly to promote absorption.
- Repeat the fertilization process once or twice during the growing season, following the manufacturer’s guidelines for dosage and timing.
2. Pruning:
Pruning is essential for shaping the plants, removing dead or diseased wood, and promoting better airflow and sunlight penetration.
- Prune gooseberries and redcurrants in late winter or early spring, before new growth appears.
- Remove any dead, damaged, or crossing branches, as well as any suckers growing from the base of the plants.
- Thin out the center of the plant to improve air circulation and reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
- Blackcurrants should be pruned in late winter or early spring, but they require different treatment. Cut back all stems to around 5cm above the ground to encourage new growth and better fruit production.
3. Maintenance:
After fertilizing and pruning, it’s important to regularly monitor the plants for any signs of pests or diseases. Remove any weeds growing around the bushes, and ensure the plants receive adequate water, especially during dry periods.
By following these fertilizing and pruning tips, you can help ensure the healthy growth and fruitful harvest of your gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants.
Pest and Disease Control

Pests and diseases can pose a threat to gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants, but with proper care and attention, you can minimize the risks and maintain healthy plants. Here are some tips for pest and disease control:
1. Aphids
Aphids can cause damage to the leaves and stems of your plants. To control aphids:
- Regularly inspect your plants for signs of aphids.
- If you spot aphids, you can try using insecticidal soap or neem oil spray to control them.
- Encourage natural predators, such as ladybugs, lacewings, or parasitic wasps, as they feed on aphids.
2. Gooseberry sawfly
Gooseberry sawfly larvae can quickly defoliate your gooseberry plants. To control gooseberry sawflies:
- Inspect your plants regularly, especially the undersides of leaves, for signs of sawfly larvae.
- If you find the larvae, you can handpick and destroy them or prune affected branches.
- Encourage natural predators like birds or parasitic wasps to control sawflies.
3. Currant blister aphid
Currant blister aphids can cause small blisters on the leaves of currant plants. To control currant blister aphids:
- Regularly inspect your plants for signs of aphids and leaf blisters.
- If you spot aphids or leaf blisters, prune and destroy affected branches.
- Encourage natural predators, such as ladybugs or lacewings, to control aphids.
4. Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew can affect the leaves and fruits of gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. To control powdery mildew:
- Avoid overcrowding your plants to improve air circulation.
- Water your plants at the base, rather than overhead, to keep the foliage dry.
- If powdery mildew appears, prune and destroy affected branches.
- Consider using fungicidal sprays approved for use on gooseberries and currants.
By taking proactive steps in pest and disease control, you can ensure the health and productivity of your gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants throughout the growing season.
Question-answer:
When is the best time to plant gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
The best time to plant gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants is in spring, when the soil has thawed and is workable.
Are gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants easy to grow?
Yes, gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants are generally easy to grow as long as they are planted in well-draining soil, receive adequate sunlight, and are properly cared for.
What type of soil is best for planting gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
Gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants thrive in loamy, well-draining soil with a pH level between 6 and 6.5. Adding organic matter, such as compost, can also improve the soil’s fertility.
How far apart should gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants be planted?
Gooseberries should be planted approximately 1.5-2 meters apart, while blackcurrants and redcurrants should be spaced about 1 meter apart. This allows enough room for the plants to grow and spread out.
Do gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants require regular pruning?
Yes, regular pruning is important for gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. Pruning helps to maintain the shape of the plants, encourages new growth, and improves air circulation. It is best to prune them in late winter or early spring before new growth appears.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants?
Some common pests that can affect gooseberries, blackcurrants, and redcurrants include aphids, gooseberry sawfly, and currant blister aphid. Diseases such as powdery mildew, leaf spot, and botrytis can also affect these plants. Regularly inspecting the plants and taking preventive measures, such as proper hygiene and using organic pest control methods, can help mitigate these issues.







