- What is Yellowberry and its cultivation?
- Cultivation
- Propagation
- Harvesting
- Uses
- Properties and benefits of Yellowberry
- Different varieties of Yellowberry
- 1. Golden Delicious
- 2. Granny Smith
- 3. Red Delicious
- 4. Fuji
- 5. Gala
- How to grow Yellowberry at home?
- 1. Choose the right variety
- 2. Find a suitable location
- 3. Prepare the soil
- 4. Planting
- 5. Watering
- 6. Fertilizing
- 7. Pruning
- 8. Pest and disease control
- Best soil and climate for Yellowberry
- Soil Requirements:
- Climate Requirements:
- Sunlight Requirements:
- Caring for Yellowberry plants
- Watering
- Fertilizing
- Pruning
- Weeding
- Pest and Disease Control
- Harvesting
- Pests and diseases affecting Yellowberry plants
- Pests
- Diseases
- Harvesting and storing Yellowberries
- Harvesting
- Storage
- Questions and Answers:
- What is yellowberry?
- How do you cultivate yellowberries?
- What are the properties of yellowberries?
- Are there different varieties of yellowberries?
- How do you know when yellowberries are ripe?
- Can yellowberries be used for cooking?
- Do yellowberries have any health benefits?
- Videos: 9 Types of Berry Bushes to grow in your Garden
Yellowberry, also known as Barbados cherry or Acerola, is a small tropical fruit tree that is native to the Caribbean and Central and South America. It is widely cultivated for its tart and juicy fruits, which are rich in Vitamin C and have a distinctive yellow color. The Yellowberry tree is easy to grow and can be found in many tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
One of the main properties of Yellowberry is its high concentration of Vitamin C. In fact, Yellowberry contains more Vitamin C than citrus fruits like oranges and lemons. This makes it a popular fruit for boosting the immune system and preventing colds and flu. Additionally, Yellowberry is rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body against free radical damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
There are several varieties of Yellowberry, each with its own unique flavor and characteristics. Some varieties have a sweet and tangy taste, while others have a more sour and acidic flavor. The most common varieties include the Florida Sweet, the Barbados Cherry, and the Manoa Sweet. These varieties can range in color from light yellow to deep red, depending on their ripeness.
Fun Fact: Yellowberry is often used to make jams, jellies, and fruit juices, and is also a popular ingredient in desserts and cocktails.
What is Yellowberry and its cultivation?
Yellowberry is a type of berry that is known for its vibrant yellow color and sweet flavor. It is native to regions with a cool climate, such as northern Europe and parts of North America. Yellowberry plants belong to the genus Rubus, which also includes raspberries and blackberries.
Cultivation
Yellowberry plants are typically cultivated in home gardens and small-scale farms due to their delicate nature. Here are some key points to consider when cultivating Yellowberry:
- Climate: Yellowberry plants thrive in cool climates with mild summers and cold winters.
- Soil: They prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter.
- Sunlight: Yellowberry plants require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight each day.
- Watering: They need consistent moisture, but overwatering should be avoided to prevent root rot.
- Pruning: Regular pruning helps maintain the health and shape of the plants.
Propagation
Yellowberry plants can be propagated through various methods, including:
- Seeds: The berries contain small seeds, which can be collected, dried, and planted to grow new plants.
- Division: Mature Yellowberry plants can be divided into smaller sections and replanted.
- Cuttings: Stem cuttings can be taken from healthy plants and rooted to produce new plants.
Harvesting

Ripe Yellowberries are typically ready for harvest in the late summer or early fall, depending on the location and climate. They should be picked when fully yellow and easily detach from the plant. It is recommended to harvest the berries in the morning when they are cool and firm.
Uses
Yellowberries can be enjoyed fresh, added to various dishes, or used to make jams, jellies, and desserts. They are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthy addition to any diet.
| Varieties | Description |
|---|---|
| Sunshine Yellowberry | A popular variety known for its large size and intense sweetness. |
| Golden Nugget | Produces smaller berries with a tangy flavor, often used in baking. |
| Lemon Splash | Known for its unique citrusy taste and yellow-green color. |
Properties and benefits of Yellowberry
- Rich in antioxidants: Yellowberries are highly packed with antioxidants, which help protect the body against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- High in Vitamin C: Yellowberries are an excellent source of Vitamin C, which is an essential nutrient for maintaining a healthy immune system and promoting collagen synthesis.
- Source of dietary fiber: Yellowberries are a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps prevent constipation.
- Contains minerals: Yellowberries contain important minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and manganese, which are essential for various bodily functions including nerve function, heart health, and bone development.
- Low in calories: Yellowberries are low in calories, making them a perfect snack for those who are watching their calorie intake.
- Natural energy booster: Yellowberries are a great source of natural energy due to their carbohydrate content and low glycemic index, providing a sustained release of energy without causing blood sugar spikes.
Moreover, Yellowberries are known for their deliciously sweet and tangy flavor, making them a popular choice for desserts, smoothies, salads, and jams. With their vibrant yellow color, they also add a visually appealing touch to various dishes.
So whether you enjoy them fresh or incorporate them into your favorite recipes, Yellowberries can be a tasty and nutritious addition to your diet.
Different varieties of Yellowberry
Yellowberry is a popular fruit that comes in various varieties. Each variety has its own unique characteristics and flavor profiles. Here are some of the different varieties of Yellowberry:
1. Golden Delicious
The Golden Delicious variety of Yellowberry is known for its sweet and crisp flavor. It has a bright yellow skin and a creamy white flesh. This variety is often used for eating fresh or in salads.
2. Granny Smith
The Granny Smith variety of Yellowberry is famous for its tart and tangy taste. It has a vibrant green skin and a firm, juicy flesh. This variety is commonly used for baking and cooking due to its ability to retain its shape and flavor.
3. Red Delicious

The Red Delicious variety of Yellowberry is recognized for its deep red skin and mildly sweet flavor. It has a firm and crunchy texture. This variety is often enjoyed as a fresh snack or used in baking recipes.
4. Fuji
The Fuji variety of Yellowberry originates from Japan and is known for its sweet and juicy characteristics. It has a reddish-green skin and a crispy flesh. This variety is commonly used for eating fresh and in desserts.
5. Gala
The Gala variety of Yellowberry is known for its firm and sweet taste. It has a yellow-orange skin with red stripes and a crisp white flesh. This variety is often used for eating fresh or in salads.
These are just a few examples of the many different varieties of Yellowberry available. Each variety offers a unique taste experience, making Yellowberry a versatile fruit enjoyed in various culinary applications.
How to grow Yellowberry at home?
Growing Yellowberry at home is relatively easy and requires minimal space and care. Here are some steps you can follow to successfully cultivate Yellowberry plants:
1. Choose the right variety
There are several Yellowberry varieties available, each with its own unique characteristics. Consider factors such as taste, size, and disease resistance when choosing the variety that suits your preferences.
2. Find a suitable location
Yellowberry plants thrive in full sun, so choose a spot in your garden or balcony that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Make sure the location has well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging.
3. Prepare the soil
Before planting, prepare the soil by removing any weeds or grass. Yellowberries prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. If your soil is too alkaline, you can add sulfur or compost to lower the pH.
4. Planting
Plant Yellowberry seeds or seedlings according to the recommended spacing mentioned on the seed packet or plant tag. Dig a hole large enough to accommodate the root ball and make sure the plant is positioned at the same depth as it was in its container.
5. Watering
Yellowberry plants require regular watering, especially during hot and dry periods. Water deeply once or twice a week, ensuring the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering, as it can increase the risk of diseases.
6. Fertilizing
Apply a balanced fertilizer or compost around the base of the plant in early spring and mid-summer to provide essential nutrients. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the correct dosage.
7. Pruning
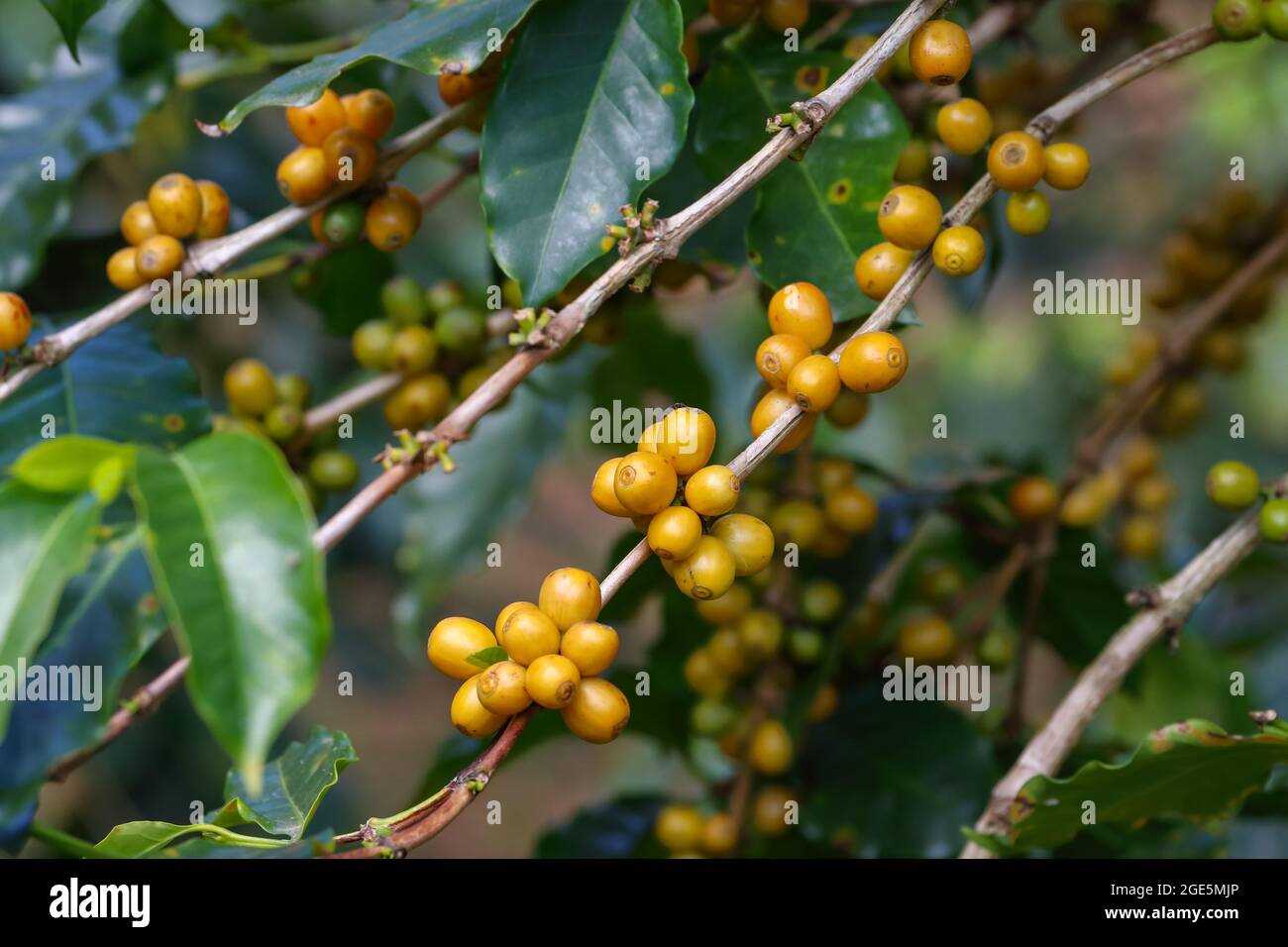
Prune Yellowberry plants to remove any dead or damaged branches and to maintain an open, airy structure. This helps improve air circulation and reduces the risk of diseases. Pruning can be done in late winter or early spring.
8. Pest and disease control
Yellowberries are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, regular monitoring is important to detect and control any issues early on. Keep an eye out for common pests such as aphids, spider mites, and fruit worms.
Following these steps and providing proper care will help you successfully grow delicious Yellowberries at home. Enjoy your bountiful harvest!
Best soil and climate for Yellowberry
The Yellowberry plant thrives in specific soil and climate conditions that are optimal for its cultivation. Here are the best soil and climate requirements for Yellowberry:
Soil Requirements:
- The soil should be well-draining and loamy.
- A pH level between 6.0 and 6.5 is considered ideal for Yellowberry.
- The soil should be rich in organic matter, which helps in retaining moisture.
- Sandy or clayey soils should be avoided as they can hinder proper root development and drainage.
Climate Requirements:
- Yellowberry requires a temperate climate with moderate winters and warm summers.
- The plant thrives in regions with a minimum average temperature of 15°C (59°F) during the growing season.
- Areas with a frost-free period of at least 150-180 days are conducive to Yellowberry cultivation.
Sunlight Requirements:
Yellowberry plants require full sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours a day. They cannot tolerate excessive shade, as it may inhibit flower and fruit development.
It is essential to ensure that the soil and climate conditions are suitable for Yellowberry cultivation to maximize yield and quality. Adequate care and attention to these requirements will result in healthy Yellowberry plants and bountiful harvests.
Caring for Yellowberry plants
Watering
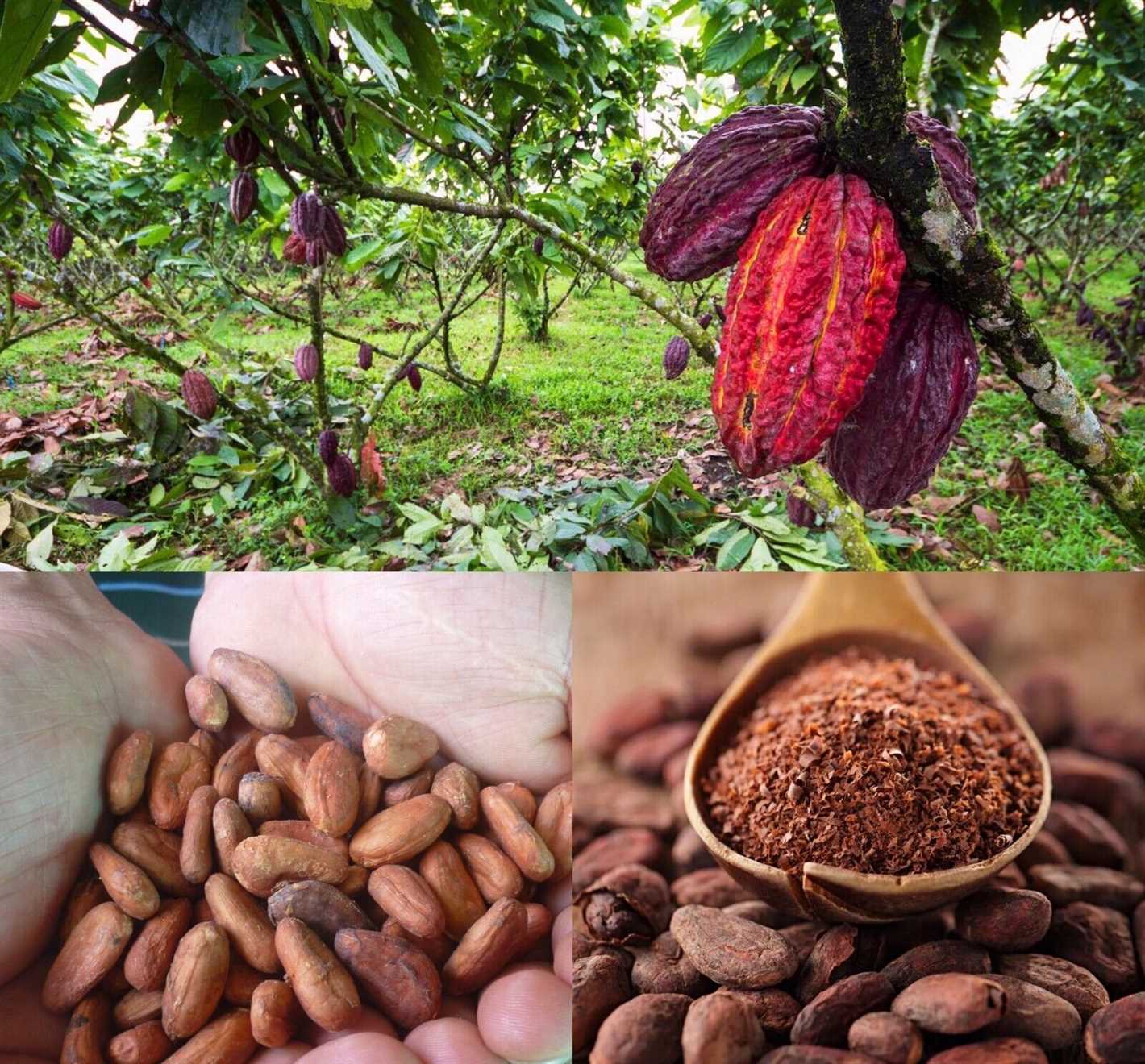

Yellowberry plants require regular watering to ensure their proper growth and fruit production. The soil around the plants should be kept evenly moist, but not waterlogged. To check moisture levels, insert your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. If it feels dry at that depth, it’s time to water. Deep watering once or twice a week is usually sufficient, but adjust the frequency based on weather conditions and the plant’s needs.
Fertilizing
Yellowberry plants benefit from regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and abundant fruiting. Before planting, incorporate a balanced fertilizer into the soil according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Once the plants are established, apply a slow-release fertilizer every spring to provide a steady supply of nutrients throughout the growing season. Additionally, you can supplement with a liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during active growth.
Pruning
Pruning helps maintain the shape, size, and health of Yellowberry plants. It also improves air circulation, reduces disease risk, and enhances fruit production. Prune in late winter or early spring before new growth starts. Start by removing any dead, damaged, or diseased branches. Then, thin out overcrowded growth and prune back to encourage branching and fruiting. You can also remove any suckers or unwanted shoots near the base of the plant.
Weeding
Weeds can compete with Yellowberry plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Regular weeding is necessary to keep the planting area free of weeds. Use a hoe or hand tools to carefully remove weeds around the plants, taking care not to damage the shallow roots. Applying a layer of mulch around the base of the plants can help suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture.
Pest and Disease Control
Yellowberry plants are generally resistant to common pests and diseases. However, keeping an eye out for any signs of damage or infestation is important. Inspect the plants regularly and take appropriate action at the first sign of trouble. This may involve removing affected leaves or using organic methods to control pests, such as handpicking or spraying with neem oil.
Harvesting
Yellowberries are ready to harvest when they turn golden-yellow and have a slightly soft texture. Gently twist or cut the berries from the plant, taking care not to damage the surrounding fruit or branches. Harvesting should be done in the morning when the berries are cool and fresh. After harvesting, store the Yellowberries in a cool, dry place or consume them immediately for the best flavor.
Pests and diseases affecting Yellowberry plants

Yellowberry plants are generally quite hardy and resistant to pests and diseases. However, there are some common issues that can affect their growth and productivity.
Pests
- Aphids: These small insects feed on the sap of the Yellowberry plants, causing the leaves to curl and become distorted. Regular inspection and the use of insecticidal soap can help control aphid infestations.
- Spider mites: These tiny pests often appear in hot and dry conditions, sucking the sap from the leaves and causing yellowing and browning. Spraying the plants with water and keeping the humidity high can help deter spider mites.
- Caterpillars: Some caterpillars, such as the yellow-striped armyworm, can feed on the leaves of Yellowberry plants. Handpicking and using organic insecticides are effective methods of control.
Diseases
- Fungal diseases: Yellowberry plants can be susceptible to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and gray mold. Regular pruning to improve air circulation and applying fungicides can help prevent and manage fungal infections.
- Root rot: Overwatering or poorly-drained soil can lead to root rot, causing the Yellowberry plants’ roots to become black and mushy. Proper watering practices and improving soil drainage can prevent root rot.
- Bacterial diseases: Bacterial infections, such as bacterial leaf spot, can cause dark spots on the leaves of Yellowberry plants. Removing infected leaves and applying copper-based fungicides can help control bacterial diseases.
It is important to regularly inspect Yellowberry plants for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to prevent and manage them. Maintaining good plant health and providing the right growing conditions can also help reduce the risk of pest and disease problems.
Harvesting and storing Yellowberries
Harvesting
Yellowberries are typically harvested when they are fully ripe and have turned a bright yellow color. It is important to choose berries that are plump and have a glossy appearance. This indicates that they are at their peak of ripeness and flavor.
To harvest yellowberries, gently grasp the stem of the berry and twist it off the plant. Be careful not to exert too much pressure as this can damage the berry. It is important to handle the berries with care to prevent bruising or squishing.
Storage
After harvesting yellowberries, it is important to store them properly to maintain their freshness and flavor. Yellowberries are delicate and should be handled with care.
One option for storing yellowberries is to place them in a shallow container, such as a tray or a baking sheet, lined with paper towels. This will help absorb any excess moisture and prevent the berries from becoming mushy.
Yellowberries should be stored in the refrigerator, ideally in the crisper drawer, at a temperature between 32-40°F (0-4°C). They can be stored for up to 5-7 days, but it is recommended to consume them as soon as possible for the best flavor and texture.
It is important to avoid washing yellowberries before storing them, as the moisture can cause them to spoil more quickly. Instead, rinse them gently just before consumption to remove any dirt or debris.
If you have excess yellowberries that you are unable to consume before they start to spoil, you can freeze them for later use. Simply rinse and dry the berries, then spread them out on a baking sheet and place in the freezer. Once frozen, transfer the berries to a freezer-safe container or bag. Yellowberries can be stored in the freezer for up to 6 months.
Questions and Answers:
What is yellowberry?
Yellowberry is a type of berry that belongs to the Vaccinium family. It is similar to blueberries and cranberries in terms of taste and appearance.
How do you cultivate yellowberries?
Yellowberries are typically cultivated by planting the seeds or transplanting the seedlings in well-drained soil. They require a sunny location and regular watering.
What are the properties of yellowberries?
Yellowberries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They are known for their anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties.
Are there different varieties of yellowberries?
Yes, there are several varieties of yellowberries, including Earlyblaze, Sparkleberry, and Honeybee. Each variety has its own unique flavor profile and ripening time.
How do you know when yellowberries are ripe?
Yellowberries are ripe when they turn a golden-yellow color and are slightly soft to the touch. They should easily come off the plant when gently pulled.
Can yellowberries be used for cooking?
Yes, yellowberries can be used in various recipes, including pies, jams, sauces, and even salads. They add a sweet and tangy flavor to dishes.
Do yellowberries have any health benefits?
Yes, yellowberries are packed with nutrients and have several health benefits. They can help improve digestion, boost the immune system, and protect against certain diseases.







