- Selecting the Wrong Rootstock
- Factors to Consider
- Consulting Experts
- Neglecting Proper Site Preparation
- Factors to Consider
- Site Preparation Steps
- Conclusion
- Failing to Choose the Right Scion
- 1. Know your desired apple variety
- 2. Consider grafting compatibility
- 3. Select healthy scionwood
- 4. Consider the age of scionwood
- 5. Collect scionwood at the right time
- 6. Label and store scionwood properly
- Poor Grafting Techniques
- Lack of Pruning and Training
- Inadequate Pest and Disease Prevention
- Pest Prevention
- Disease Prevention
- Conclusion
- Improper Irrigation and Fertilization
- Harvesting at the Wrong Time
- Question-answer:
- What are some mistakes to avoid when grafting apple trees in autumn?
- Why is it important to avoid using old or weak rootstocks for apple tree grafting?
- What can happen if the cambium layers are not properly aligned when grafting apple trees?
- What tools are suitable for grafting apple trees?
- What care and protection should be provided for grafted apple trees?
- Video: New technique of grafting apples with watermelon to get more apples
If you’re an apple tree enthusiast, autumn is an exciting time to think about grafting and harvesting. Grafting allows you to create new apple varieties by combining different tree parts, while harvesting provides the delicious fruits of your labor. However, to ensure a successful grafting and bountiful harvest, it’s important to avoid some common autumn mistakes.
1. Timing is key: Grafting should be done during the dormant season of the apple tree, which typically falls in late autumn or early spring. It’s crucial to avoid grafting too early or too late, as it can result in poor graft union formation or unsuccessful bud development. Take note of your local climate and the specific apple tree variety you are working with to determine the optimal timing.
2. Choose the right rootstock: The success of your grafting project heavily depends on selecting the appropriate rootstock. The rootstock should be compatible with the scion (the top portion of the grafted tree), ensuring a strong and healthy union. Consider factors such as disease resistance, soil adaptability, and desired tree size when choosing the rootstock.
Pro Tip: Consult with local experts or nurseries to get advice on the most suitable rootstock for your area and specific grafting goals.
3. Prune properly: Before you start grafting, make sure to prune the apple tree correctly. Remove crossing branches, dead wood, and any diseased or damaged parts. Pruning helps improve air circulation and light penetration, promoting the health and productivity of the tree. Additionally, pruning allows you to create a suitable framework for grafting by selecting strong and well-positioned branches.
4. Adequate support and protection: Once you have successfully grafted your apple tree, ensure it is properly supported and protected. Provide stakes or ties to prevent the newly grafted tree from being damaged by winds or other external factors. Consider using protective materials such as tree guards or netting to safeguard against pests and animals that may harm both the grafted tree and the eventual harvest.
By avoiding these autumn mistakes, you can increase your chances of successful apple tree grafting and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious apples. Remember to plan and prepare adequately, seeking advice from experts if needed, to ensure the best possible results.
Selecting the Wrong Rootstock
When it comes to grafting apple trees, selecting the right rootstock is crucial for the success of your project. The rootstock determines many important factors such as the size, vigor, and disease resistance of the tree, as well as its adaptability to different soil types and climate conditions.
One of the biggest mistakes that novice grafters make is selecting the wrong rootstock for their desired outcome. This can result in stunted growth, poor fruit production, or even the death of the tree.
Factors to Consider


Before choosing a rootstock for your apple tree grafting project, consider the following factors:
- Growth Habit: Different rootstocks produce trees with varying sizes and shapes. Some rootstocks promote dwarf or semi-dwarf trees, which are ideal for small spaces or container gardening. Others produce standard-sized or vigorous trees suitable for larger orchards.
- Disease Resistance: The rootstock can affect the tree’s resistance to certain pests and diseases, such as apple scab or fire blight. It’s important to choose a rootstock that is resistant to prevalent diseases in your area to ensure a healthy and productive tree.
- Soil Adaptability: Consider the soil type and pH levels in your planting area. Certain rootstocks are better suited for specific soil conditions, such as heavy clay or sandy soils. Choose a rootstock that will thrive in your soil to maximize tree health and growth.
- Climate Adaptability: Different rootstocks have varying levels of cold hardiness or heat tolerance. Select a rootstock that can withstand the temperature extremes of your region to prevent winter damage or heat stress.
Consulting Experts

If you’re unsure about which rootstock to choose for your apple tree grafting project, it’s always a good idea to consult with local horticultural experts or experienced orchardists. They can provide valuable advice based on your specific location and growing conditions.
Additionally, there are various resources available online or in gardening books that provide detailed information on different apple rootstocks and their characteristics. Take the time to research and gather as much knowledge as possible to make an informed decision.
By avoiding the mistake of selecting the wrong rootstock, you can increase the chances of a successful grafting project and enjoy abundant harvests from your apple trees for years to come.
Neglecting Proper Site Preparation

One common mistake in apple tree grafting and harvesting is neglecting proper site preparation. Before planting or grafting apple trees, it is crucial to ensure that the site is suitable for their growth and development. Failure to prepare the site properly can result in poor tree health, limited yields, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Factors to Consider
When preparing the site for apple tree grafting or planting, several factors should be taken into account:
- Soil Quality: Apple trees thrive in well-drained soils with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. Test the soil to assess its fertility and pH level. Amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve its structure and fertility.
- Sunlight: Apple trees require at least six hours of direct sunlight per day to produce healthy fruit. Choose a site that receives ample sunlight throughout the day.
- Space: Adequate space is essential for apple tree growth. Make sure the site provides enough room for the mature size of the tree, including both the height and the spread of the branches.
- Wind Protection: Strong winds can damage apple tree branches and reduce fruit production. Consider planting the trees in a location that is sheltered from strong winds, such as near a building or a natural windbreak.
Site Preparation Steps
Proper site preparation for apple tree grafting or planting involves the following steps:
- Clear the Area: Remove any existing vegetation, such as grass or weeds, from the planting area. This helps reduce competition for nutrients and reduces the risk of pests and diseases.
- Soil Testing and Amendment: Test the soil for pH and nutrient levels. Based on the results, amend the soil with any necessary amendments, such as lime to adjust pH or fertilizer to provide essential nutrients.
- Prepare the Planting Hole: Dig a planting hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the apple tree’s root system. Loosen the soil at the bottom of the hole to encourage root penetration.
- Backfill and Water: Fill the planting hole with soil, ensuring that the tree is planted at the same depth it was in its nursery container. Water the tree thoroughly after planting to settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots.
- Mulch: Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of the tree. This helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Stake and Protect: If necessary, stake the tree to provide support and protect it from strong winds. Use tree guards or wraps to prevent damage from rodents and other animals.
Conclusion
Proper site preparation is fundamental for successful apple tree grafting and harvesting. By considering factors such as soil quality, sunlight, space, and wind protection, and following the necessary site preparation steps, you can create an ideal environment for your apple trees to thrive and produce abundant fruit.
Failing to Choose the Right Scion

Choosing the right scion is crucial for successful apple tree grafting and eventual harvest. The scion is the piece of the desired apple variety that will be grafted onto the rootstock. Failing to choose the right scion can result in poor grafting success and a lack of desired fruit quality.
1. Know your desired apple variety
Before choosing a scion, it is important to know the specific apple variety you desire. Research the characteristics, flavor, and growth habits of the variety to ensure it aligns with your expectations.
2. Consider grafting compatibility
Not all apple varieties are compatible for grafting with each other. Some varieties may have natural genetic barriers that prevent successful grafting. Research the compatibility of the desired variety with the rootstock you plan to use.
3. Select healthy scionwood
When choosing scionwood, make sure it is healthy and free from any signs of disease or damage. Look for scionwood that has well-developed buds and is approximately ¼ to ½ inch in diameter. Avoid scionwood that appears weak or has signs of discoloration.
4. Consider the age of scionwood
The age of scionwood can also affect grafting success. Generally, using scionwood that is one-year-old is recommended, as it tends to have the best success rate. However, some apple varieties may require younger or older scionwood for optimal grafting results.
5. Collect scionwood at the right time
Timing is important when collecting scionwood. It is recommended to collect scionwood during the dormant season, preferably in late winter or early spring before bud break. Collect scionwood from healthy, well-maintained trees to increase the chances of success.
6. Label and store scionwood properly
After collecting scionwood, label it with the variety name and other relevant information to ensure proper identification. Store the scionwood in a cool, dark, and humid environment to prevent drying out. Consider wrapping the scionwood in a damp paper towel or storing it in a plastic bag to maintain moisture.
By taking the time to choose the right scion for your apple tree grafting project, you can increase the likelihood of successful grafting and enjoy abundant harvests of your desired apple variety.
Poor Grafting Techniques
Incorrect Alignment: One of the most common mistakes in grafting apple trees is improper alignment of the scion and rootstock. It is crucial to ensure that the cambium layers of both the scion and rootstock are perfectly aligned in order to achieve a successful graft.
Inadequate Contact: Insufficient contact between the scion and rootstock can lead to graft failure. It is important to make sure that the scion is firmly and securely attached to the rootstock, with good surface contact and minimal gaps.
Poor Wound Preparation: Neglecting to properly prepare the grafting wounds can result in a weak and unsuccessful graft. The scion and rootstock should be clean and free of any debris or blemishes. The wounds should be carefully cut and aligned to maximize contact and facilitate healing.
Inappropriate Grafting Tools: Using dull or improper grafting tools can make the grafting process more challenging and increase the risk of failure. It is important to use sharp, clean, and suitable tools for making precise cuts and facilitating a successful graft.
Inadequate Aftercare: After grafting, it is crucial to provide proper care and attention to the graft site to ensure successful healing and integration. This includes protecting the graft from extreme temperatures, pests, and diseases, as well as providing adequate irrigation and nutrition.
Lack of Pruning and Training
- Proper pruning and training are essential for maintaining the health and productivity of apple trees.
- Without regular pruning, apple trees can become overcrowded and develop weak, tangled branches.
- Pruning helps open up the tree canopy, allowing sunlight and air to reach all parts of the tree.
- This promotes good fruit development and helps prevent diseases by reducing moisture and increasing airflow.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when it comes to pruning and training apple trees:
- Delaying pruning: Waiting too long to prune apple trees can result in excessive growth and poor fruit production. Pruning should be done during the dormant season, before new growth begins.
- Overpruning: While it’s important to remove dead, damaged, or diseased branches, excessive pruning can weaken the tree and reduce fruit production. It’s important to strike a balance between removing unnecessary growth and preserving the overall structure of the tree.
- Improper cuts: Make sure to use sharp, clean tools to make proper pruning cuts. Avoid leaving stubs or making cuts too close to the trunk, as this can invite pests and diseases.
- Ignoring training: Training young apple trees involves properly shaping their growth and guiding the branches to establish a strong framework. Neglecting this step can lead to a disorganized and unproductive tree.
Overall, regular pruning and training can help ensure healthy, productive apple trees with abundant harvests.
Inadequate Pest and Disease Prevention
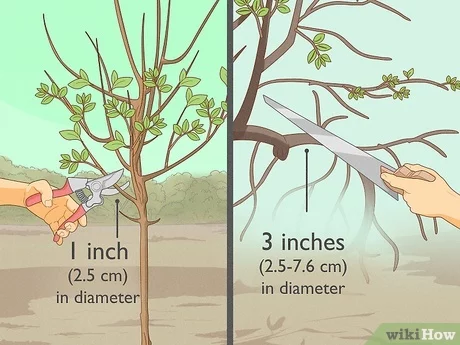
Pest and disease prevention plays a crucial role in the cultivation and maintenance of apple trees. Failure to implement adequate preventive measures can lead to significant damage to your trees and a decrease in overall fruit yield.
Pest Prevention
One common mistake is neglecting to monitor and control common tree pests such as aphids, apple maggots, and codling moths. These pests can cause serious damage to both the foliage and fruit of apple trees.
To prevent infestations, it is essential to regularly inspect your trees for signs of pests and take appropriate action. This may involve using organic or chemical insecticides, applying sticky traps, or using pheromone dispensers to disrupt mating patterns.
It is also important to maintain good hygiene practices in your orchard. Clean up fallen leaves and fruit promptly, as they can harbor pests and diseases. Regularly prune your trees to remove any dead or diseased wood, as this can attract pests.
Disease Prevention
Apple trees are susceptible to several diseases, including apple scab, powdery mildew, and fire blight. These diseases can weaken the tree, reduce fruit production, and even lead to tree death if left untreated.
To prevent diseases, make sure to select disease-resistant apple tree varieties for grafting. Properly space your trees to ensure adequate airflow and sunlight penetration, as this can help prevent the growth and spread of fungal spores.
Regularly inspect your trees for signs of disease, such as leaf discoloration, powdery growth, or cankers on branches. If you spot any signs, promptly prune and remove the affected branches or apply appropriate fungicides or bactericides to control the spread of the disease.
Remember to always follow the recommended application rates and safety guidelines when using any chemical treatments.
Conclusion
Preventing pests and diseases is vital for maintaining healthy and productive apple trees. By implementing proper preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of damage and ensure a bountiful apple harvest.
Improper Irrigation and Fertilization

When it comes to maintaining the health and productivity of your apple trees, proper irrigation and fertilization are crucial. However, many gardeners make mistakes in these areas, leading to poor growth and limited fruit production. Here are some common errors to avoid:
- Overwatering: Excess water can suffocate the roots and create a breeding ground for fungal diseases. Avoid overwatering by allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings and using a well-draining soil mix.
- Underwatering: On the other hand, inadequate watering can result in stressed trees and smaller, less flavorful fruits. Be sure to provide enough water, especially during dry spells, to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Improper watering technique: Watering just at the surface can encourage shallow root growth, making the tree more susceptible to drought and diseases. Instead, apply water deeply and evenly to encourage the roots to grow deeper into the soil.
- Using the wrong fertilizer: Apple trees have specific nutrient requirements, and using the wrong type or ratio of fertilizer can lead to imbalances and deficiencies. Test your soil to determine its nutrient needs, and choose a fertilizer formulated for fruit trees.
- Applying fertilizer at the wrong time: Timing is crucial when it comes to fertilizing apple trees. Applying fertilizer too early or too late in the season can result in inefficient uptake or nutrient leaching. Follow the recommended guidelines for your specific variety and region.
- Overfertilizing: While a certain amount of fertilizer is necessary for healthy growth, overdoing it can cause excessive vegetative growth at the expense of fruit production. Use fertilizers sparingly and in accordance with the tree’s needs.
- Neglecting organic matter: Improving the soil’s organic matter content is essential for proper nutrient retention and moisture regulation. Add compost or well-rotted manure to the soil regularly to enrich its fertility and structure.
- Ignoring pH levels: Apple trees prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0-7.0), and extreme pH levels can hinder nutrient availability. Test your soil’s pH regularly and adjust it if necessary using organic amendments.
By avoiding these irrigation and fertilization mistakes, you can ensure the health and abundant harvest of your apple trees. Take the time to understand their specific needs and provide them with the right care, and you’ll be rewarded with delicious fruits year after year.
Harvesting at the Wrong Time

One common mistake when it comes to apple tree grafting and harvesting is not timing the harvest correctly. Harvesting at the wrong time can result in apples that are underripe or overripe, making them less flavorful and less likely to store well.
Understanding the Harvest Window
Apple trees have a specific time window during which their fruit is ready to be harvested. This window can vary depending on the variety of apple tree and the local climate. It is important to understand and identify the signs of ripeness specific to your apple tree variety.
Generally, apples are ready for harvest when they have reached their full size and color, and when they are easy to detach from the tree with a gentle twist or tug. The fruit should feel firm to the touch and have a slight give when gently pressed.
The Consequences of Harvesting Too Early
If you harvest apples too early, they may be underripe and lacking in flavor. Underripe apples will have a starchy taste and lack the desirable sweetness that fully ripe apples possess. Additionally, underripe apples are unlikely to store well and may spoil quickly.
The Consequences of Harvesting Too Late
On the other hand, if you wait too long to harvest your apples, they may become overripe. Overripe apples will have a mealy texture and may have started to rot or develop mold. These apples are not pleasant to eat and are best used for making apple products like cider or applesauce.
Best Practices
To avoid harvesting at the wrong time, it is helpful to keep track of the estimated harvest time for your apple tree variety. You can consult gardening references or online resources to find this information. Additionally, you can perform regular checks on your apples as they approach the estimated harvest window to assess their ripeness.
When harvesting apples, use a gentle twisting motion to detach them from the tree. Avoid pulling or tugging forcefully, as this can cause damage to the fruit or the tree itself. Handle the apples with care to prevent bruising, which can increase the likelihood of spoilage.
By harvesting your apples at the right time, you can ensure that they are at their peak flavor and have the best chance of storing well. This allows you to enjoy the fruits of your labor throughout the autumn and beyond.
Question-answer:
What are some mistakes to avoid when grafting apple trees in autumn?
Some mistakes to avoid when grafting apple trees in autumn include using old or weak rootstocks, not properly aligning the cambium layers when grafting, using incorrect tools for grafting, grafting in unsuitable weather conditions, and not providing proper care and protection for the grafted trees.
Why is it important to avoid using old or weak rootstocks for apple tree grafting?
Using old or weak rootstocks for apple tree grafting can result in poor growth and weak, unhealthy trees. It is important to use healthy and vigorous rootstocks to ensure the success of the grafting process.
What can happen if the cambium layers are not properly aligned when grafting apple trees?
If the cambium layers are not properly aligned when grafting apple trees, the graft may not take and the tree may not establish a strong connection between the scion and the rootstock. This can result in graft failure and the death of the grafted tree.
What tools are suitable for grafting apple trees?
Suitable tools for grafting apple trees include sharp grafting knives or pruning shears for making clean and precise cuts, grafting tape or rubber bands for securing the graft, and grafting wax or sealing compound to protect the graft and prevent infection.
What care and protection should be provided for grafted apple trees?
Grafted apple trees should be provided with proper watering, fertilization, and protection from pests and diseases. It is also important to provide support for the grafted tree, such as staking or tying it to a trellis, to ensure its stability and proper growth.







