- Choosing the Right Variety
- Climate
- Soil Conditions
- Personal Preference
- Selecting the Ideal Location
- Sunlight
- Soil Conditions
- Protection
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Azaleas
- Choosing the Right Location
- Preparing the Planting Hole
- Planting the Azalea
- Watering and Mulching
- Regular Care and Maintenance
- Watering and Fertilizing
- Watering
- Fertilizing
- Pruning and Shaping
- Protecting from Pests and Diseases
- Winter Care and Maintenance
- 1. Mulching
- 2. Watering
- 3. Protecting from Frost
- 4. Pruning
- 5. Fertilization
- 6. Preventing Winterburn
- 7. Snow Removal
- Q&A:
- When is the best time to plant azaleas?
- What type of soil is best for azaleas?
- Can azaleas tolerate full sun?
- How often should I water azaleas?
- Should I prune my azaleas?
- How can I fertilize my azaleas?
- Video: Azalea Care in Pots , Save Dying Azaleas ! How to care for Azaleas ! Azalea potting and fertilizing
Azaleas are beautiful flowering plants that can add color and vibrancy to any garden or indoor space. With thousands of varieties to choose from, azaleas offer a wide range of colors, shapes, and sizes, making them a popular choice among gardeners and plant enthusiasts.
When it comes to planting and caring for azaleas at home, there are a few key tips to keep in mind. First, it’s important to choose the right location for your azaleas. These plants thrive in partial shade, so finding a spot that offers some protection from direct sunlight is ideal. Additionally, azaleas prefer well-draining soil that is slightly acidic, so adding organic matter or peat moss to the planting hole can help create the right conditions for them to thrive.
It’s also important to water azaleas regularly, especially during the growing season. These plants have shallow roots, so they require consistent moisture to stay healthy. However, it’s important to avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot and other issues. Using a soaker hose or drip irrigation system can help ensure that your azaleas receive the right amount of water without soaking the leaves or flowers.
In terms of fertilizing azaleas, it’s best to use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer specifically designed for acid-loving plants. This will provide the necessary nutrients without causing excessive growth or burn the roots. Applying the fertilizer in early spring, just before the new growth begins, and again in early summer can help promote healthy growth and abundant blooms.
In conclusion, planting and caring for azaleas at home can be a rewarding experience. By choosing the right location, providing adequate water and nutrients, and maintaining a balanced environment, you can enjoy the beauty of these stunning plants for years to come.
Choosing the Right Variety
When it comes to choosing the right variety of azaleas for your home garden, there are a few factors to consider. The specific variety of azalea you choose will depend on factors such as your climate, soil conditions, and personal preference.
Climate
Azaleas are typically divided into two main categories: evergreen and deciduous. Evergreen azaleas are best suited for warmer climates, as they can tolerate heat and direct sunlight. Deciduous azaleas, on the other hand, are more cold hardy and can withstand colder temperatures. Consider your local climate when selecting the variety of azalea to ensure it will thrive in your area.
Soil Conditions

Azaleas prefer acidic soil with a pH between 4.5 and 6.0. Before planting azaleas, test your soil’s pH levels and amend it if necessary. You can lower soil pH by adding elemental sulfur or organic matter such as peat moss. Additionally, azaleas prefer well-draining soil, so ensure that your planting site has good drainage.
Personal Preference
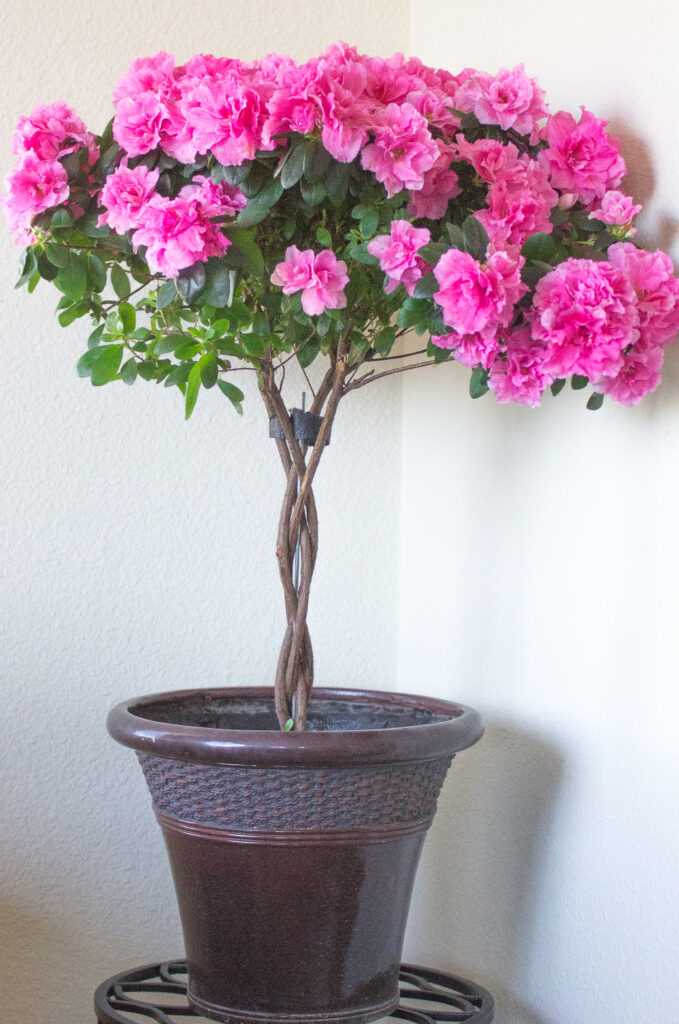

When choosing the right variety of azaleas, consider your personal preference in terms of flower color, size, and fragrance. Azaleas come in a wide range of colors, including shades of pink, white, red, and purple. Some varieties may have larger blooms, while others may be more compact in size. Some azalea varieties also have a strong fragrance, which can add to the overall appeal of your garden.
| Variety | Climate | Flower Color | Size | Fragrance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encore Azaleas | Both evergreen and deciduous varieties available | Various colors | Medium | Some varieties have a mild fragrance |
| Girard’s Pleasant White | Both evergreen and deciduous varieties available | White | Medium | No fragrance |
| Pink Ruffle Azalea | Evergreen | Pink | Medium | No fragrance |
These are just a few examples of azalea varieties available. Research different varieties and consult with local nurseries to find the best variety that suits your preferences and growing conditions.
Selecting the Ideal Location
Choosing the right location is crucial for the successful growth and blooming of azaleas. The ideal location will provide the necessary sunlight, soil conditions, and protection from harsh elements.
Sunlight
Azaleas thrive in partial shade, which means they need some direct sunlight but also benefit from protection during the hottest hours of the day. Look for a spot that receives morning sun and afternoon shade, such as under a deciduous tree or on the east side of a building.
Soil Conditions
Azaleas prefer moist, well-drained soil that is slightly acidic. Before planting, test the soil pH to ensure it falls between 5.0 and 6.0. If the soil is too alkaline, you may need to amend it with organic matter or sulfur to lower the pH.
Additionally, make sure the soil is loose and friable, as azaleas have shallow roots. If the soil is heavy and clay-like, consider incorporating organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to improve drainage.
Protection
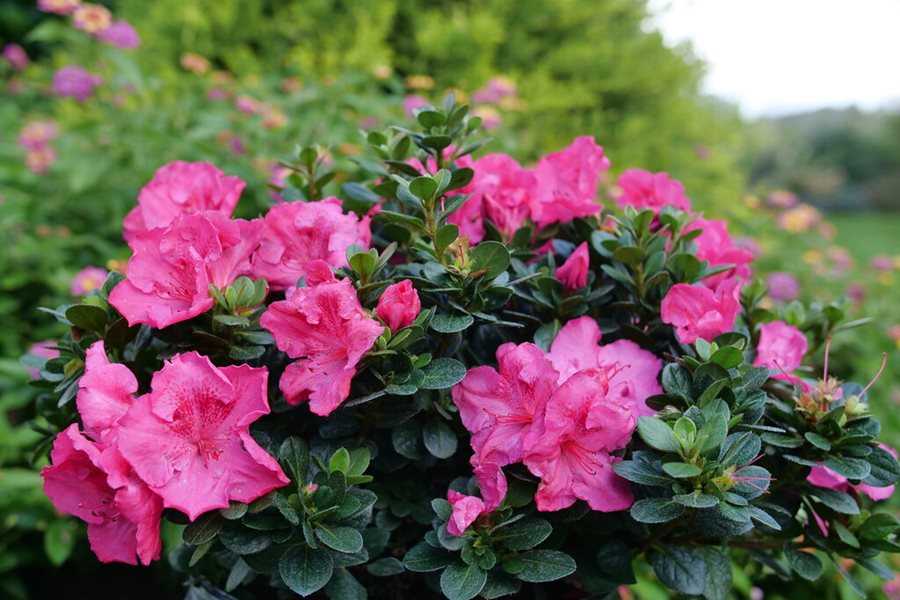

Azaleas are vulnerable to harsh winds and extreme temperatures. Look for a location that provides some natural protection, such as a windbreak or existing trees and shrubs. Avoid planting azaleas in low-lying areas where cold air may accumulate during winter months.
| Factors | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Sunlight | Partial shade with morning sun and afternoon shade |
| Soil Conditions | Moist, well-drained, slightly acidic (pH 5.0-6.0) |
| Protection | From harsh winds and extreme temperatures |
By selecting the ideal location for your azaleas, you will provide them with the best conditions for healthy growth and abundant blooming.
Preparing the Soil
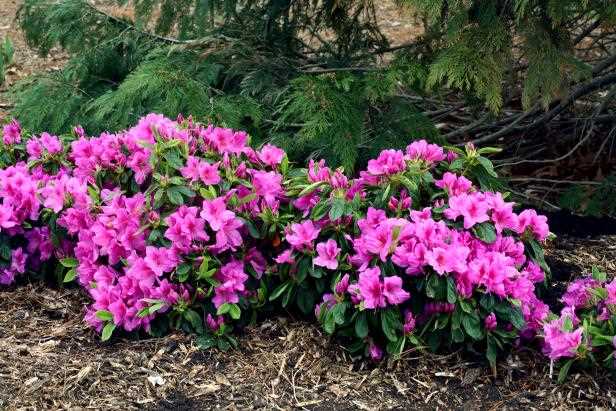

Before planting azaleas, it is important to prepare the soil to create an optimal growing environment for these beautiful flowering plants. Here are some steps to follow:
- Test the soil: Start by testing the pH level of your soil. Azaleas prefer acidic soil with a pH between 4.5 and 6.0. You can use a home soil testing kit or send a sample to a local agricultural extension service for analysis.
- Amend the soil: If the pH level is too high, you will need to lower it by adding amendments. Sphagnum peat moss, elemental sulfur, or iron sulfate can be added to help acidify the soil. Follow the instructions on the packaging for the correct amounts to use.
- Improve drainage: Azaleas prefer well-draining soil, so if your soil is heavy or clayey, you will need to improve its drainage. Adding organic matter such as compost, leaf mold, or pine bark to the soil can help loosen it and improve drainage.
- Remove weeds and debris: Before planting, remove any weeds, rocks, or debris from the planting area. This will help prevent competition for nutrients and ensure that the azaleas have a clean and healthy environment to grow in.
- Prepare the planting hole: Dig a hole that is twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball of the azalea plant. Loosen the soil in the planting hole and mix in some organic matter to help the plant establish its roots.
By taking these steps to prepare the soil, you will create an ideal growing environment for your azaleas. This will help ensure that they thrive and produce beautiful blooms for years to come.
Planting Azaleas
Azaleas are beautiful flowering shrubs that can bring vibrant colors to any garden or landscape. They are relatively easy to plant and care for, but it’s important to follow a few key steps to ensure their success.
Choosing the Right Location
Azaleas thrive in well-draining soil and prefer partial sun to shade. When choosing a location for planting, look for an area with dappled sunlight or some shade during the hottest part of the day. Avoid planting them in direct, full sunlight, as this can scorch their leaves.
It’s also important to consider the soil conditions in the chosen location. Azaleas prefer acidic soil with a pH level between 5.0 and 6.0. You may need to amend the soil with organic matter or use a specific azalea soil mix to ensure the proper pH balance.
Preparing the Planting Hole
Before planting your azalea, dig a hole that is twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball. Loosen the soil around the hole to help the roots establish and spread more easily.
You can also add some organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to the hole to improve the soil’s drainage and fertility. Mix it well with the existing soil to create a nutrient-rich bed for your azalea.
Planting the Azalea
Remove the azalea from its container and gently loosen the roots if they appear root-bound. Place the root ball in the hole, making sure that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding soil.
Backfill the hole with the soil mixture, ensuring that there are no air pockets around the roots. Gently tamp down the soil to secure the azalea in place.
Watering and Mulching
After planting, give your azalea a good watering to settle the soil and help the roots establish. Water it deeply and regularly, especially during dry spells or hot weather.
Applying a layer of mulch around the base of the plant can help conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use organic mulch, such as pine straw or wood chips, and apply it to a depth of 2-3 inches.
Regular Care and Maintenance
Azaleas require regular care to keep them healthy and blooming. Prune them after they finish flowering to maintain their shape and remove any dead or crossing branches.
Feed your azaleas with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants. Follow the product instructions for application rates and frequency.
Monitor your azaleas for any signs of pests or diseases, such as aphids, lacebugs, or powdery mildew. Treat any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
With proper planting and care, your azaleas can provide years of beauty and enjoyment in your garden or landscape.
Watering and Fertilizing
Proper watering and fertilization are essential for the health and growth of azaleas. Here are some tips on how to water and fertilize your azaleas:
Watering
- Water your azaleas regularly, especially during dry spells. Azaleas prefer moist but well-drained soil. The frequency of watering will depend on the weather conditions and the moisture level of the soil.
- Avoid overwatering as it can lead to root rot. To check if your azaleas need watering, stick your finger a few inches into the soil. If it feels dry, it’s time to water.
- Use a soaker hose or a drip irrigation system to provide a slow, even watering to the roots. Avoid overhead watering as it can lead to foliar diseases.
- Mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture and prevent weed growth. Mulch also helps to regulate the soil temperature.
Fertilizing
- Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer specifically formulated for acid-loving plants like azaleas. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for proper application rates.
- Apply the fertilizer in early spring before the new growth starts. Avoid fertilizing in late fall or winter as it may stimulate new growth that can be susceptible to frost damage.
- Spread the fertilizer evenly around the base of the plant, taking care not to get it on the leaves or stems.
- Water the fertilizer into the soil thoroughly after application to ensure proper absorption.
- Monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiency or excess. Yellowing leaves with green veins may indicate an iron deficiency, while leaf burn or stunted growth may indicate overfertilization.
Remember, proper watering and fertilization practices can help your azaleas thrive and produce beautiful blooms. Regular observation and adjustment of your watering and fertilizing routine will ensure that your azaleas stay healthy and vibrant.
Pruning and Shaping
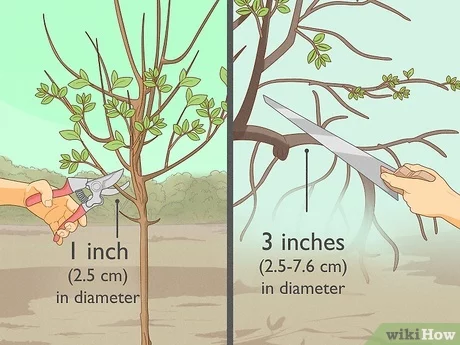
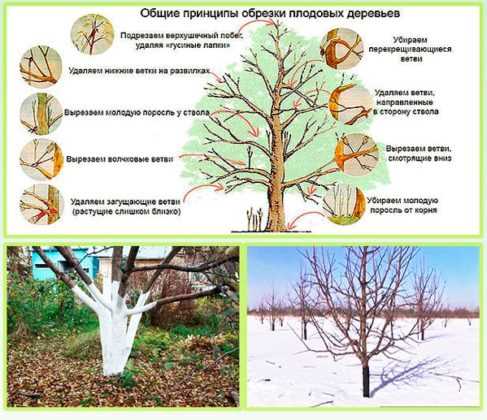
Pruning is an essential part of maintaining the health and appearance of your azaleas. Regular pruning helps to promote bushier growth, control the size of the plant, and encourage more blooms. Here are some tips for pruning and shaping your azaleas:
- Timing: The best time to prune azaleas is immediately after they finish blooming, usually in the spring. Pruning at this time allows the plant to recover and set new buds for the following year’s blooms.
- Tools: Use sharp and clean pruning shears or loppers to make clean cuts. This helps prevent the spread of diseases and promotes faster healing.
- Remove dead and diseased branches: Start by removing any dead, damaged, or diseased branches. Cut them back to a healthy section of the branch, making sure to dispose of the removed material properly to prevent the spread of diseases.
- Thinning: To promote air circulation and reduce the risk of diseases, thin out dense areas by selectively removing some of the older and weaker branches. This will also stimulate new growth and improve the overall shape of the plant.
- Size control: If your azaleas are getting too large or unruly, you can prune them back to the desired size and shape. Trim the branches back to a lateral bud or a healthy side branch. However, avoid cutting into the older woody stems as they may not produce new growth easily.
- Shape: Azaleas can be pruned to maintain a natural shape or shaped into a specific form, such as a ball, mound, or hedge. Use handheld pruning shears to carefully trim the outer foliage to achieve the desired shape. Step back occasionally to check the overall balance and symmetry.
Remember, it’s important to not over-prune your azaleas, as this can stress the plant and reduce its ability to produce flowers. Always maintain a balance between pruning for shape and allowing the plant to grow naturally.
If you’re unsure about how to prune your azaleas or want to avoid any mistakes, consider consulting a professional gardener or horticulturist for guidance.
Protecting from Pests and Diseases
- Keep a close eye on pests: Azaleas are susceptible to various pests such as aphids, lace bugs, and spider mites. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of infestation, such as discolored leaves, distorted growth, or fine webbing. If you notice any pests, take prompt action to control them.
- Natural pest control methods: Whenever possible, use natural methods to control pests on your azaleas. Some options include introducing beneficial insects such as ladybugs or lacewings, spraying neem oil or insecticidal soap, or using companion planting techniques to deter pests.
- Preventive measures: To minimize the risk of pest infestations, maintain good hygiene in your garden. Regularly remove fallen leaves and other debris that can harbor pests. Also, avoid over-fertilizing your azaleas as this can attract pests. Instead, follow a balanced fertilization schedule.
- Be cautious with chemicals: If natural methods are not effective in controlling pests, you may need to resort to chemical pesticides. However, exercise caution when using these products. Read and follow the instructions carefully, wear protective clothing, and apply only as directed. Avoid spraying pesticides on windy days or when bees and other beneficial insects are active.
Preventing diseases:
- Choose disease-resistant varieties: When selecting azaleas for your garden, opt for varieties that are known for their resistance to common diseases such as powdery mildew or root rot. This can significantly reduce the risk of your plants getting infected.
- Proper watering: Overwatering can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases, while underwatering can stress the plants and make them more susceptible to diseases. Therefore, it’s crucial to maintain a consistent watering schedule and provide sufficient moisture without creating waterlogged conditions.
- Avoid overhead watering: Wetting the foliage of azaleas can predispose them to diseases. Instead, water the plants at their base to keep the foliage dry. Consider using soaker hoses or drip irrigation for efficient and targeted watering.
- Clean tools and equipment: Diseases can spread through contaminated tools, so it’s essential to clean your gardening equipment regularly. Disinfect pruning shears, shovels, and other tools with a solution of bleach or rubbing alcohol before using them on your azaleas.
Regular monitoring: Keep a watchful eye on your azaleas throughout the growing season. Look out for any signs of diseases, such as spots or discoloration on the leaves, wilting, or stunted growth. Promptly address any issues to prevent diseases from spreading to other plants.
Please remember: This HTML is a simplified version and may not contain all the necessary tags for a fully functional webpage.
Winter Care and Maintenance

Winter care is crucial for the health and survival of azaleas. Here are some tips to help you properly care for your azaleas during the winter months:
1. Mulching
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as pine straw or wood chips, around the base of your azaleas. Mulching helps insulate the roots, protect them from extreme cold temperatures, and retain moisture in the soil.
2. Watering
Water your azaleas thoroughly before the first freeze of the winter. During winter, azaleas still need some moisture, so be sure to check the soil’s moisture levels periodically. Water the plants if the soil feels dry to the touch.
3. Protecting from Frost
If frost is forecasted, protect your azaleas by covering them with a frost cloth or bedsheet. Ensure the cover reaches the ground around the plant to provide insulation. Remove the cover during the day to allow sunlight and airflow.
4. Pruning
Avoid pruning your azaleas in late fall or winter, as this may stimulate new growth that can be damaged by freezing temperatures. Instead, wait until spring when the threat of frost has passed to prune any overgrown or dead branches.
5. Fertilization
Avoid fertilizing your azaleas during winter, as it can encourage new growth that can be damaged by cold weather. Resume fertilization in early spring when the plants start actively growing.
6. Preventing Winterburn
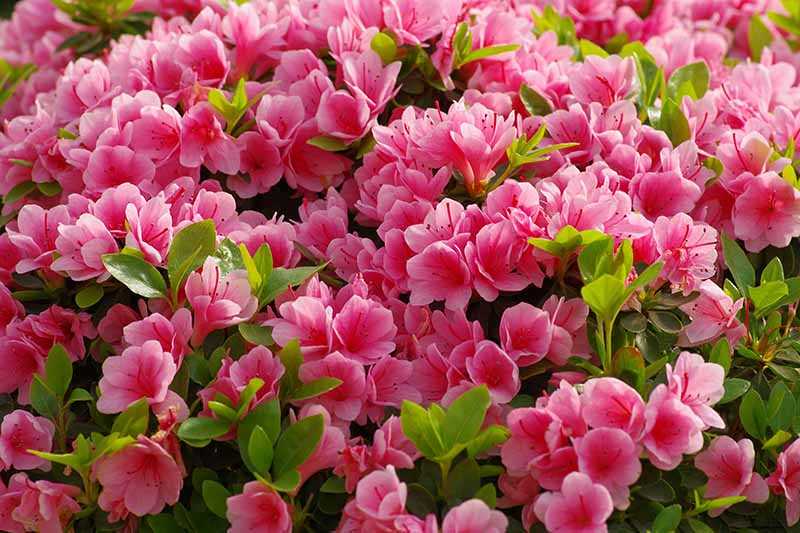

Protect your azaleas from winterburn, which occurs when the leaves lose water faster than the roots can absorb it. To prevent this, spray an antidesiccant on the foliage before winter sets in. This waxy coating helps retain moisture and protect the leaves from drying out.
7. Snow Removal
If heavy snowfall accumulates on your azaleas, gently brush off the snow to prevent branches from breaking or getting weighed down. Avoid shaking the plant as it can cause damage.
By following these winter care and maintenance tips, you can help your azaleas survive the cold weather and ensure they thrive when spring arrives.
Q&A:
When is the best time to plant azaleas?
The best time to plant azaleas is in the early spring or fall when the weather is cool. This allows the plant to establish its roots before the hot summer months.
What type of soil is best for azaleas?
Azaleas prefer acidic soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 6.0. They also thrive in well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter.
Can azaleas tolerate full sun?
Azaleas prefer partial shade or filtered sunlight. While they can tolerate some morning sun, they are susceptible to sunburn and damage in full sun conditions.
How often should I water azaleas?
Azaleas require regular watering, especially during dry spells. It is important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, as azaleas do not tolerate soggy conditions. Water deeply and thoroughly, allowing the water to reach the root zone.
Should I prune my azaleas?
Pruning azaleas can help maintain their shape and encourage more blooms. The best time to prune azaleas is in the spring after flowering. Remove any dead or diseased branches and thin out crowded areas to improve air circulation.
How can I fertilize my azaleas?
Azaleas benefit from regular fertilization in the spring and early summer. Use a slow-release, acid-loving fertilizer specifically formulated for azaleas. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as this can cause damage to the plant. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the recommended dosage.
Video:
Azalea Care in Pots , Save Dying Azaleas ! How to care for Azaleas ! Azalea potting and fertilizing