- Top 8 Benefits of Organic Fertilisers for Sustainable Agriculture
- Enhanced Soil Fertility
- 1. Nutrient-rich Composition
- 2. Beneficial Microorganisms
- 3. Soil Structure Improvement
- 4. Long-term Nutrient Supply
- 5. Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Soil Erosion
- Improved Nutrient Retention
- Healthier Plant Growth
- Non-Toxic and Safe
- Environmentally Friendly
- Reduced Chemical Use
- Non-toxic
- Improving Soil Quality
- Reduced Water Pollution
- Promoting Biodiversity
- Long-Term Soil Health
- 1. Nutrient Retention
- 2. Enhancing Soil Structure
- 3. Microbial Activity
- 4. Long-Term Sustainability
- Sustainable and Cost-Effective
- Environmental Sustainability
- Soil Health
- Economic Benefits
- Conclusion
- Q&A:
- What are organic fertilisers?
- Why are organic fertilisers beneficial for sustainable agriculture?
- What are the advantages of using organic fertilisers over synthetic fertilisers?
- Can organic fertilisers improve crop yields?
- Are there any disadvantages of using organic fertilisers?
- Can organic fertilisers reduce the environmental impact of agriculture?
- What other sustainable practices should be combined with the use of organic fertilisers?
- Video: Understanding Our Soil: The Nitrogen Cycle, Fixers, and Fertilizer
Organic fertilisers, derived from natural sources such as plants and animals, offer numerous benefits for sustainable agriculture. Unlike synthetic fertilisers, organic fertilisers provide essential nutrients to plants in a slow-release form, resulting in improved soil fertility and healthier crops.
One of the key advantages of organic fertilisers is their ability to enhance soil structure and increase its water-holding capacity. The organic matter present in these fertilisers helps to improve soil structure, making it more crumbly and easier to cultivate. This allows for better water infiltration and retention, reducing the risk of soil erosion and helping plants withstand drought conditions.
Furthermore, organic fertilisers are a sustainable choice for farmers as they promote biodiversity and protect the environment. Unlike chemical fertilisers, organic fertilisers do not contain harmful substances that can pollute water bodies or lead to the destruction of beneficial microorganisms in the soil. In fact, they can help to enrich the soil with beneficial microbes and earthworms, which contribute to nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
In addition to their environmental benefits, organic fertilisers also contribute to the quality and nutritional value of crops. They provide a wide range of trace minerals and micronutrients that are often lacking in synthetic fertilisers, resulting in healthier and more nutrient-dense produce. Organic farming practices that rely on these fertilisers also help to reduce the use of pesticides and herbicides, further enhancing food safety and reducing the risk of chemical residues.
In conclusion, the use of organic fertilisers in sustainable agriculture offers multiple benefits. These fertilisers improve soil structure, promote biodiversity, protect the environment, and enhance the nutritional value of crops. By choosing organic fertilisers, farmers can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to agriculture.
Top 8 Benefits of Organic Fertilisers for Sustainable Agriculture
Organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources such as plant and animal materials. They provide numerous benefits for sustainable agriculture, promoting soil health, and improving crop yield. Here are the top 8 benefits of using organic fertilisers:
Improved Soil Structure: Organic fertilisers improve the soil structure by increasing its ability to hold water and nutrients. This leads to better root development and healthier plants.
Long-Term Nutrient Supply: Organic fertilisers release nutrients slowly over time, providing a long-term supply of essential elements for plant growth. This helps minimize nutrient loss and ensures plants have a consistent supply of nutrients throughout their growth cycle.
Enhanced Soil Fertility: Organic fertilisers contain a wide range of macronutrients and micronutrients that enrich the soil and replenish nutrient levels. This improves the overall fertility of the soil and supports the growth of healthy, productive crops.
Environmentally Friendly: Organic fertilisers are made from natural materials and do not contain synthetic chemicals or pollutants. They reduce the risk of water and soil pollution, ensuring a more sustainable farming system.
Reduced Soil Erosion: Organic fertilisers help to reduce soil erosion by improving the soil structure and increasing its ability to hold water. This prevents runoff and protects the topsoil from being washed away during heavy rain or irrigation.
Carbon Sequestration: Organic fertilisers contribute to carbon sequestration in the soil. They contain organic matter that decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide, which is then absorbed by the soil. This helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Better Crop Quality: Organic fertilisers promote healthier plant growth, resulting in improved crop quality. They enhance the flavor, aroma, and nutritional value of fruits, vegetables, and grains, making them more desirable in the market.
Cost-Effective: While organic fertilisers may initially have a higher cost than synthetic fertilisers, they provide long-term benefits to the soil and overall crop production. With improved soil fertility, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced crop quality, organic fertilisers offer a cost-effective solution for sustainable agriculture.
In conclusion, organic fertilisers offer numerous benefits for sustainable agriculture. They promote soil health, protect the environment, and improve crop yield and quality. By choosing organic fertilisers, farmers can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient farming system that ensures a secure food supply for future generations.
Enhanced Soil Fertility
Organic fertilisers play a crucial role in enhancing soil fertility, which is essential for the productivity and sustainability of agriculture. They provide essential nutrients to the soil, promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms, and improve the physical structure of the soil. Here are some ways in which organic fertilisers contribute to enhancing soil fertility:
1. Nutrient-rich Composition
Organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources such as plant and animal wastes, compost, and manure. These materials are rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and trace elements. When organic fertilisers are applied to the soil, they release these nutrients slowly and steadily, providing a continuous supply of essential elements for plant growth.
2. Beneficial Microorganisms
Organic fertilisers also contain a variety of beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms. These microorganisms play a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients in the soil. They help break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms that plants can absorb, making the nutrients more available for plant uptake.
3. Soil Structure Improvement
Another benefit of organic fertilisers is their ability to improve the physical structure of the soil. They help to increase the soil’s water-holding capacity, allowing plants to access moisture more efficiently. Organic matter from organic fertilisers also helps to bind soil particles together, improving soil structure and reducing erosion. This leads to better aeration of the soil, which promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms and root development.
4. Long-term Nutrient Supply
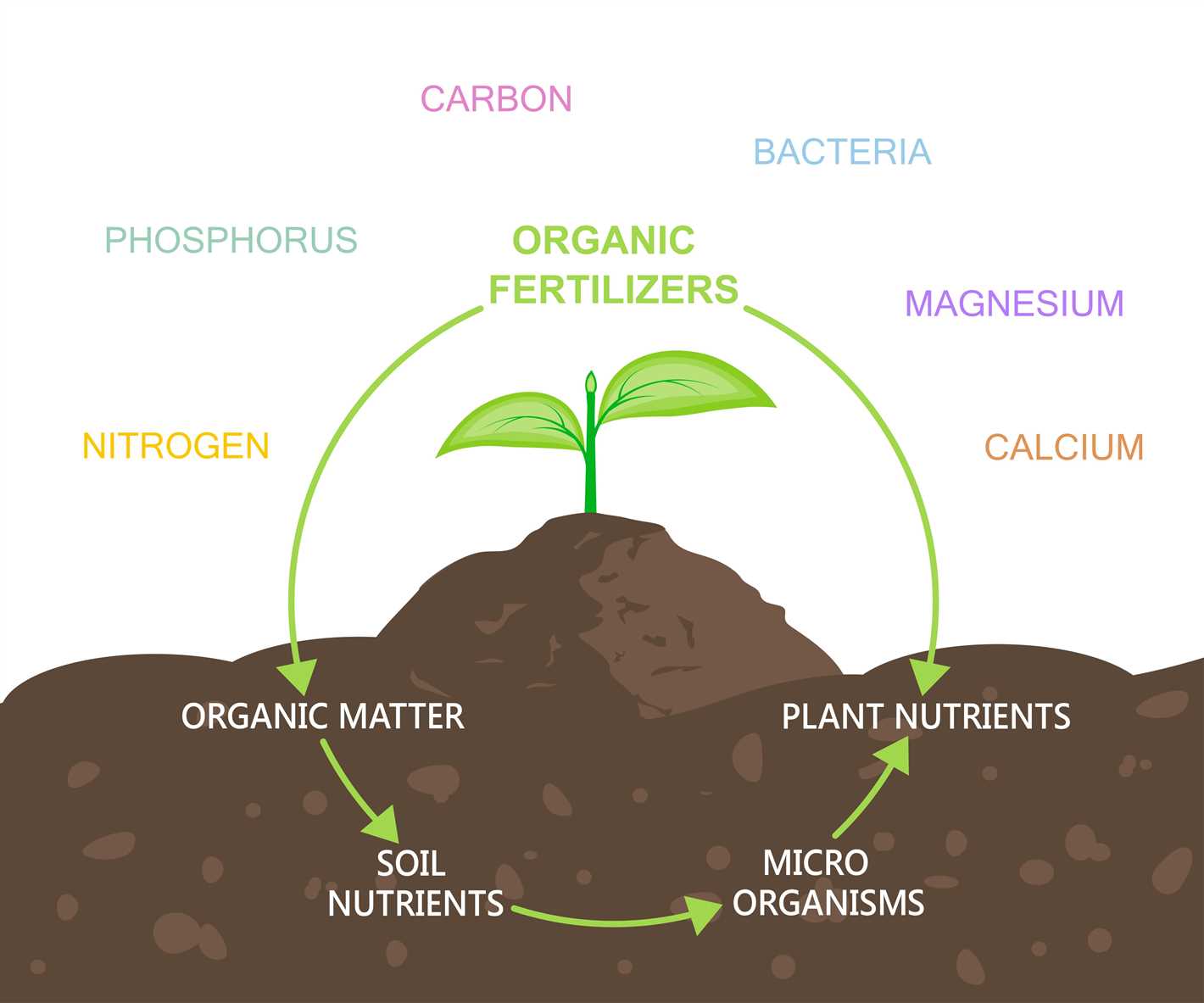
Unlike synthetic fertilisers, organic fertilisers provide a long-term nutrient supply to the soil. The nutrients in organic fertilisers are slowly released over time, ensuring that plants have a continuous supply of nutrients throughout their growth cycle. This reduces the risk of nutrient leaching and runoff, which can contribute to water pollution and the loss of valuable nutrients.
5. Environmental Benefits
The use of organic fertilisers also has several environmental benefits. Organic fertilisers are generally derived from renewable resources and do not contribute to the depletion of non-renewable resources like fossil fuels. They also reduce the need for synthetic fertilisers, which are often produced using energy-intensive processes and can have negative impacts on the environment. Additionally, organic fertilisers help to improve soil health and fertility, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides.
In conclusion, organic fertilisers enhance soil fertility by providing essential nutrients, promoting beneficial microorganisms, improving soil structure, and ensuring a long-term nutrient supply. Their use in sustainable agriculture practices can contribute to increased productivity, reduced environmental impact, and the long-term sustainability of our food production systems.
Reduced Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a major concern in agriculture as it can result in the loss of fertile topsoil. Organic fertilizers play a crucial role in reducing soil erosion and maintaining the health and productivity of agricultural land.
One of the primary reasons organic fertilizers help reduce soil erosion is their ability to improve soil structure. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, are rich in organic matter. When organic matter is added to the soil, it improves soil structure by binding soil particles together, creating a stable and crumbly soil texture. This soil structure is more resistant to erosion compared to compacted or sandy soils.
In addition, organic fertilizers enhance the water-holding capacity of soil. The organic matter in these fertilizers acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining water, which helps to prevent soil erosion caused by water runoff. By increasing the soil’s water-holding capacity, organic fertilizers also contribute to better plant growth and reduce the need for excessive irrigation, further minimizing the risk of erosion.
Moreover, organic fertilizers promote the growth of deep-rooted plants. These plants develop stronger root systems that stabilize the soil and bind it together, making it less prone to erosion. Deep-rooted plants also improve water infiltration, allowing rainwater to penetrate deeper into the soil instead of running off the surface.
Another way organic fertilizers help reduce soil erosion is by improving soil organic matter content. Adding organic fertilizers to the soil increases the organic matter content, which further enhances soil structure and stability. Organic matter also contributes to the formation of soil aggregates, which prevent soil particles from being easily washed away.
In summary, organic fertilizers contribute to reduced soil erosion by improving soil structure, enhancing water-holding capacity, promoting deep-rooted plant growth, and increasing soil organic matter content. These benefits not only protect the soil from erosion but also positively impact the overall sustainability and productivity of agricultural systems.
Improved Nutrient Retention
One of the key benefits of using organic fertilisers in sustainable agriculture is the improved nutrient retention. Organic fertilisers contain a variety of essential nutrients that are slowly released into the soil, providing a steady and continuous supply of nutrients to the plants.
Conventional fertilisers, on the other hand, often contain high concentrations of nutrients that are quickly released into the soil. This can lead to nutrient leaching, where the nutrients are washed away by rain or irrigation water before the plants have a chance to absorb them. Not only does this result in wastage of fertilisers, but it can also contribute to water pollution.
Organic fertilisers, however, have a lower risk of nutrient leaching due to their slow release nature. The nutrients are released gradually over time, allowing plants to take up the nutrients as needed. This improves nutrient use efficiency and reduces the risk of nutrient runoff into water sources.
In addition, organic fertilisers also improve the soil’s ability to retain nutrients. They enhance the soil structure and increase its water-holding capacity, reducing the loss of nutrients through runoff. The organic matter in organic fertilisers provides a food source for beneficial microbes in the soil, which in turn help to break down nutrients into plant-available forms.
By using organic fertilisers, farmers can ensure that the nutrients are retained in the soil for longer periods, reducing the need for frequent applications of fertilisers. This not only saves costs for farmers but also reduces the environmental impact of agriculture by minimizing nutrient runoff and water pollution.
Healthier Plant Growth
Organic fertilisers contribute to healthier plant growth in several ways:
- Nutrient-rich soil: Organic fertilisers, such as compost and manure, add essential nutrients to the soil. These nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like magnesium, calcium, and iron. As a result, plants grown in organic soil have access to a wide range of nutrients, promoting their overall health and growth.
- Better root development: The gradual release of nutrients from organic fertilisers allows plants to develop a strong and extensive root system. This enables them to absorb water and nutrients more effectively, leading to improved nutrient uptake and overall plant growth.
- Enhanced soil structure: Organic fertilisers improve soil structure by increasing its ability to retain water and nutrients. This improved soil structure creates a favorable environment for beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and microbes, which help break down organic matter and release nutrients into the soil. These organisms also improve aeration and drainage, further contributing to healthier plant growth.
- Reduced risk of nutrient leaching: Organic fertilisers release nutrients slowly over time, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching. This means that nutrients are less likely to be washed away by rain or irrigation, ensuring that plants have a continuous supply of nutrients for sustained growth.
- Minimized chemical exposure: Using organic fertilisers reduces the reliance on synthetic chemicals in agriculture. This leads to fewer chemical residues in the soil, water, and crops. By minimizing chemical exposure, organic farming promotes healthier plant growth and reduces the potential risks associated with chemical fertilisers.
In conclusion, the use of organic fertilisers promotes healthier plant growth by providing essential nutrients, improving soil structure, and minimizing chemical exposure. This results in stronger and more resilient plants, which in turn contribute to sustainable agriculture.
Non-Toxic and Safe
One of the major benefits of using organic fertilisers for sustainable agriculture is that they are non-toxic and safe for both the environment and human health. Unlike synthetic fertilisers that often contain harmful chemicals and toxins, organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources and do not have any adverse effects.
Organic fertilisers are made from organic matter such as compost, manure, and plant residues. These materials are rich in essential nutrients and micronutrients that are vital for plant growth and development. By using organic fertilisers, farmers can provide plants with the necessary nutrients without introducing harmful chemicals into the soil.
Non-toxic and safe fertilisers also contribute to the overall health of the soil. Synthetic fertilisers can harm beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and microbes, which play a crucial role in maintaining soil fertility and structure. Organic fertilisers, on the other hand, promote soil biodiversity and create a favorable environment for beneficial organisms to thrive.
Furthermore, the use of non-toxic fertilisers helps prevent the contamination of groundwater and surface water. Synthetic fertilisers can leach into water bodies, causing pollution and posing a threat to aquatic life. Organic fertilisers, being natural and biodegradable, do not have such negative impacts on water resources.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, organic fertilisers are also safe for human health. Conventional fertilisers often contain chemical residues that can be harmful when ingested or inhaled. Organic fertilisers, being free from synthetic chemicals, eliminate this health risk.
Overall, the non-toxic and safe nature of organic fertilisers makes them an ideal choice for sustainable agriculture. They not only provide essential nutrients to plants but also promote soil health, prevent water pollution, and ensure the safety of both the environment and human health.
Environmentally Friendly
One of the biggest benefits of using organic fertilisers in sustainable agriculture is their environmental friendliness. Unlike conventional chemical fertilisers, organic fertilisers are made from natural ingredients that do not harm the environment.
Reduced Chemical Use
Organic fertilisers are made from organic matter such as compost, animal manure, and plant residues. These materials are rich in nutrients and provide plants with the necessary elements for growth. Because they are made from natural ingredients, organic fertilisers do not contain harmful chemicals that can be toxic to plants, animals, and the environment.
Non-toxic
Chemical fertilisers often contain synthetic substances that can leave residues in the soil and water. These residues can be harmful to beneficial organisms such as earthworms, bees, and other insects that play important roles in ecosystem health. Organic fertilisers, on the other hand, do not leave toxic residues and are safe for use around humans, animals, and wildlife.
Improving Soil Quality
Using organic fertilisers can help improve soil quality and fertility. Organic matter in the fertilisers improves the structure of the soil, making it more resistant to erosion and better able to retain water. This is especially important in sustainable agriculture, as it helps reduce the need for irrigation and minimises soil degradation.
Reduced Water Pollution
Chemical fertilisers can leach into groundwater and nearby water bodies, causing water pollution. Organic fertilisers, being natural and biodegradable, do not pose the same risk. They release nutrients slowly and are absorbed by plants more efficiently, reducing the risk of nutrient runoff and water pollution.
Promoting Biodiversity

By using organic fertilisers, sustainable agriculture practices can help promote biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Organic methods support the growth of beneficial insects, birds, and other organisms that contribute to the balance of ecosystems. This helps create a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system that is less dependent on chemical inputs.
Long-Term Soil Health
Organic fertilisers play a crucial role in maintaining long-term soil health by providing essential nutrients and improving soil structure. Unlike synthetic fertilisers, which only provide nutrients, organic fertilisers also contribute to improving soil fertility and sustainability over time.
1. Nutrient Retention
Organic fertilisers supply a wide range of nutrients to the soil, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. These nutrients are released slowly and gradually, allowing plants to access them over an extended period. This slow-release mechanism helps prevent nutrient leaching and runoff, reducing environmental pollution and ensuring that the nutrients are available to plants when needed.
2. Enhancing Soil Structure
Organic fertilisers contribute to improving soil structure by increasing its organic matter content. This organic matter helps bind soil particles together, creating well-structured soil that retains water and prevents erosion. Improved soil structure also promotes better root development, nutrient uptake, and microbial activity, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
3. Microbial Activity
Organic fertilisers provide a food source for beneficial soil microbes, such as bacteria and fungi. These microbes play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients in forms that plants can readily absorb. Furthermore, they help in maintaining a balanced soil ecosystem, suppressing harmful pathogens, and improving overall soil fertility.
4. Long-Term Sustainability
Using organic fertilisers promotes long-term soil sustainability by reducing dependence on synthetic and chemical inputs. Organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources like compost, animal manure, and plant residues, making them renewable and sustainable. Their use helps improve soil quality and fertility without depleting natural resources or causing harm to the environment.
In conclusion, incorporating organic fertilisers into agricultural practices is essential for long-term soil health. By providing essential nutrients, enhancing soil structure, promoting microbial activity, and ensuring sustainability, organic fertilisers contribute to creating healthier and more productive soils that can support sustainable agriculture practices.
Sustainable and Cost-Effective
One of the key benefits of using organic fertilisers in sustainable agriculture is their ability to promote long-term sustainability while being cost-effective.
Environmental Sustainability
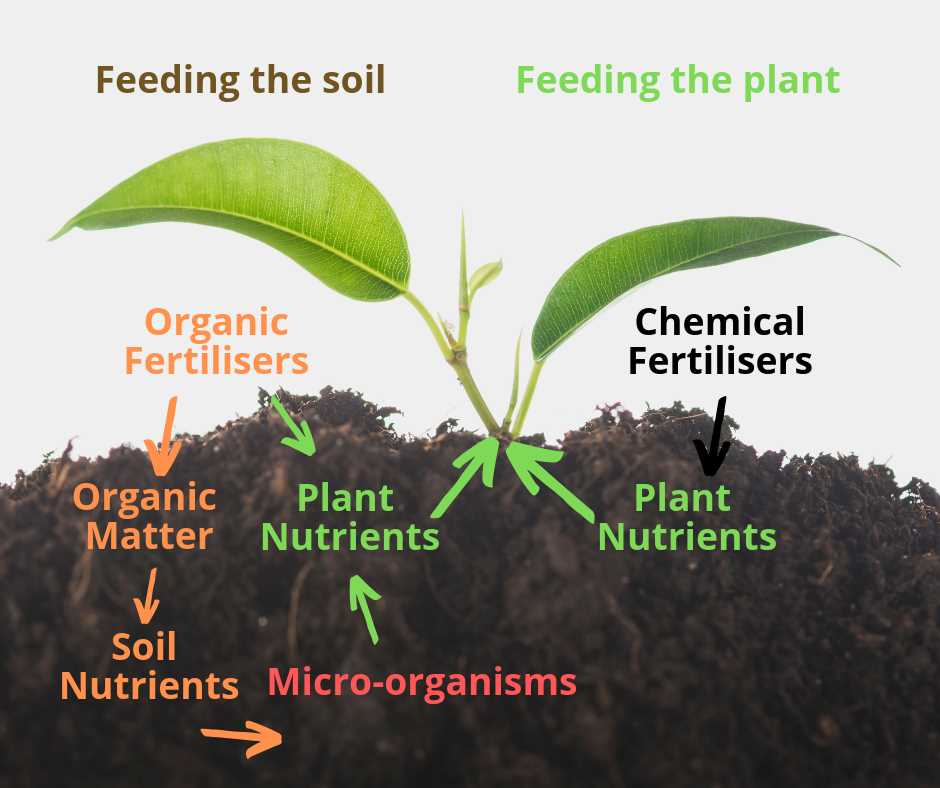
Organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources such as compost, animal manure, and plant residues. Unlike synthetic fertilisers, organic fertilisers do not contain harmful chemicals or pollutants that can seep into the soil and water sources, contributing to environmental degradation.
By using organic fertilisers, farmers can reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilisers, which require the extraction and processing of non-renewable resources. This reduction in dependence on synthetics helps preserve natural resources and supports a more sustainable agricultural system.
Soil Health
Organic fertilisers improve soil health in the long run. They enhance soil structure and promote the development of beneficial microorganisms that help break down organic matter and make nutrients more available to plants.
Unlike synthetic fertilisers, which can lead to soil degradation and nutrient imbalances, organic fertilisers nourish the soil without causing harmful effects. This improves soil fertility, water retention, and overall soil health, allowing for more productive and sustainable agriculture.
Economic Benefits
Using organic fertilisers can also be cost-effective for farmers. While the initial cost of organic fertilisers might be higher compared to synthetic alternatives, the long-term benefits outweigh the upfront investment.
Organic fertilisers contribute to improved soil health, reducing the need for costly inputs like pesticides and additional fertilisers. Healthy soils retain more moisture, reducing water requirements and irrigation costs. Additionally, organic fertilisers help prevent nutrient runoff, minimizing the need for expensive remediation efforts.
Conclusion

In conclusion, using organic fertilisers in sustainable agriculture provides multiple benefits. They promote environmental sustainability by reducing chemical pollution and conserving natural resources. Additionally, organic fertilisers contribute to soil health and fertility, supporting long-term productivity. Moreover, the cost-effectiveness of organic fertilisers makes them a sustainable choice for farmers in the long run.
Q&A:
What are organic fertilisers?
Organic fertilisers are natural materials that are used to enrich the soil and provide essential nutrients to plants. These fertilisers are derived from organic sources, such as animal manure, compost, and plant residues.
Why are organic fertilisers beneficial for sustainable agriculture?
Organic fertilisers are beneficial for sustainable agriculture because they help improve soil fertility, promote nutrient cycling, and reduce the reliance on synthetic chemical fertilisers. They also enhance soil structure, increase water-holding capacity, and support the growth of beneficial soil organisms.
What are the advantages of using organic fertilisers over synthetic fertilisers?
Using organic fertilisers has several advantages over synthetic fertilisers. Organic fertilisers release nutrients slowly and steadily, providing long-term nourishment for plants. They also improve soil health and structure, reduce the risk of nutrient leaching, and enhance the soil’s ability to hold water. Additionally, organic fertilisers are made from renewable resources and are generally safer for the environment and human health.
Can organic fertilisers improve crop yields?
Yes, organic fertilisers can improve crop yields. By enriching the soil with essential nutrients and promoting soil health, organic fertilisers provide a favorable environment for plant growth. However, it’s important to note that organic farming is a holistic approach that involves various sustainable practices, and solely relying on organic fertilisers may not guarantee high crop yields. Proper crop management and other sustainable techniques are also essential.
Are there any disadvantages of using organic fertilisers?
While organic fertilisers have numerous benefits, they also have some disadvantages. Organic fertilisers tend to have lower nutrient concentrations compared to synthetic fertilisers, which means larger quantities may be required. They can also be more expensive and harder to find in some areas. Additionally, organic fertilisers need time to break down and release nutrients, so their effects may not be immediate.
Can organic fertilisers reduce the environmental impact of agriculture?
Yes, organic fertilisers can reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. Unlike synthetic fertilisers, organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources and do not contain harmful chemicals that can pollute waterways or damage ecosystems. Organic fertilisers also help improve soil quality and reduce the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides. Overall, organic farming practices, including the use of organic fertilisers, contribute to more sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural systems.
What other sustainable practices should be combined with the use of organic fertilisers?
While organic fertilisers are an important component of sustainable agriculture, they should be combined with other sustainable practices for optimal results. These practices may include crop rotation, cover cropping, integrated pest management, conservation tillage, and water conservation measures. Taking a holistic approach to farming and incorporating various sustainable techniques can help maximize the benefits of organic fertilisers and promote long-term agricultural sustainability.
Video:
Understanding Our Soil: The Nitrogen Cycle, Fixers, and Fertilizer







