- Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide
- Introduction
- Light Requirements
- Watering
- Temperature and Humidity
- Soil and Fertilizer
- Propagation
- Pests and Diseases
- Conclusion
- Choosing the Right Caladium: Factors to Consider
- 1. Light Requirements
- 2. Temperature Tolerance
- 3. Soil Type and Drainage
- 4. Size and Shape
- 5. Leaf Color and Pattern
- 6. Growth Habit
- 7. Disease Resistance
- 8. Availability and Source
- Understanding Caladium’s Light and Temperature Needs
- Light Requirements
- Temperature Requirements
- Tips for Light and Temperature Care
- Providing Optimal Soil and Watering Conditions for Caladium
- Soil Requirements
- Watering Needs
- Frequency of Watering
- Watering Techniques
- Additional Tips:
- Fertilizing Caladium: Dos and Don’ts
- Why is fertilizing important?
- When to fertilize?
- Types of fertilizer
- How much to apply?
- Application method
- Frequency of fertilization
- Don’ts of fertilizing caladium
- Conclusion
- Managing Pests and Diseases: Common Issues and Solutions
- Pests
- Diseases
- Pruning and Propagating Caladium: Step-by-Step Guide
- Pruning Caladium Plants
- Propagating Caladium Plants
- Overwintering Caladium: Tips for Cold Climate Regions
- 1. Dig up the tubers
- 2. Clean and dry the tubers
- 3. Store in a cool and dry place
- 4. Use suitable containers
- 5. Check for any signs of decay
- 6. Provide occasional moisture
- 7. Replant in the spring
- Frequently Asked Questions about Caladium Care
- 1. How often should I water my caladium?
- 2. What is the best temperature for caladiums?
- 3. How much light does a caladium need?
- 4. How often should I fertilize my caladium?
- 5. How do I propagate my caladium?
- 6. Should I prune my caladium?
- 7. Can caladiums be grown indoors?
- 8. Why are the leaves of my caladium turning yellow?
- 9. Are caladiums toxic to pets?
- 10. Can I keep my caladium outdoors in winter?
- Q&A:
- What is the best way to care for a Caladium plant?
- Is it possible to grow Caladium plants indoors?
- How often should I water my Caladium plant?
- Do Caladium plants require any special fertilization?
- How can I propagate Caladium plants?
- Video: CALADIUM CARE TIPS & TRICKS
Caladiums are stunning tropical plants known for their vibrant and patterned leaves. With their variety of colors and shapes, caladiums add a pop of color and tropical flair to any garden or indoor space. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about caring for caladiums and how to successfully reproduce them.
Caladium Care:
When it comes to caring for caladiums, there are a few key factors to keep in mind. First and foremost, caladiums thrive in warm and humid environments, so it is important to provide them with the right conditions. They prefer indirect sunlight or partial shade, as direct sunlight can scorch their delicate leaves. Regular watering is crucial for caladiums, as they require moist soil. However, be careful not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot. It is recommended to water caladiums whenever the top inch of soil becomes dry.
Tip: To enhance humidity levels, you can place a tray filled with water near your caladium plant or use a humidifier in the room.
Additionally, caladiums benefit from regular fertilization during their growing season. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer and follow the instructions on the label. Remember to reduce the frequency of fertilization during the winter months when caladiums go into dormancy. Pruning is also an important aspect of caladium care. Remove any yellow or damaged leaves to promote new growth and maintain the plant’s overall health.
Caladium Reproduction:
Reproducing caladiums can be done through two methods: division and tuber propagation. Dividing caladiums involves separating the tubers and planting them individually. This should be done during the plant’s dormant period in early spring. Gently remove the tubers from the mother plant and separate them with a clean, sharp knife. Plant each tuber in a well-draining potting mix and water thoroughly.
Tuber propagation is another popular method for reproducing caladiums. Start by selecting a healthy, large tuber to use as the parent plant. Using a clean, sharp knife, cut the tuber into several sections, making sure each section has at least one “eye” or bud. Plant these sections in a potting mix and water thoroughly. With proper care and regular watering, these sections will develop into new caladium plants.
By following these care and propagation guidelines, you will be able to enjoy the beauty of caladiums in your garden or indoor space. With their vibrant colors and unique patterns, caladiums are sure to make a statement and become a favorite among plant enthusiasts.
Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide
![Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide | [Name of the website] 1 Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide](https://1ogorod.ru/en/wp-content/uploads/wpallimport/files/caladium-care-and-reproduction-fug1uhz3.jpg)
Introduction
Caladiums are popular tropical plants known for their colorful and vibrant foliage. They are native to South America and are commonly grown as ornamental plants in gardens and as houseplants. This guide will provide you with all the information you need to care for and propagate caladiums.
Light Requirements
Caladiums prefer bright, indirect light. They thrive in areas with filtered sunlight, such as near a north or east-facing window. Direct sunlight can scorch their leaves, so it’s important to provide them with shade during the hottest part of the day.
Watering
Caladiums require consistent moisture, but it’s important not to overwater them. The soil should be kept evenly moist, but not waterlogged. Check the top inch of soil and water when it feels dry to the touch. Avoid letting the plant sit in standing water, as this can lead to root rot.
Temperature and Humidity
Caladiums thrive in warm temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C). They are tropical plants and do not tolerate cold temperatures. Maintain a humidity level of 50-70% to ensure proper growth. You can increase humidity by misting the foliage or placing the plant on a tray filled with water and pebbles.
Soil and Fertilizer
Caladiums prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. A mix of potting soil and perlite or sand works well. Fertilize caladiums every 4-6 weeks during the growing season with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as this can result in leaf burn.
Propagation
Caladiums can be propagated through tubers or by division. To propagate using tubers, carefully remove them from the parent plant and plant them in a separate pot with well-draining soil. To propagate by division, separate the overcrowded tubers during the dormant season and plant them individually.
Pests and Diseases
![Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide | [Name of the website] 2 Pests and Diseases](https://1ogorod.ru/en/wp-content/uploads/wpallimport/files/caladium-care-and-reproduction-tx1ljhf5.jpg)
Caladiums are relatively pest-resistant, but they can occasionally be affected by aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs. Regularly inspect the leaves for signs of pests and treat them with insecticidal soap or neem oil if necessary. Overwatering can lead to fungal diseases, so it’s important to ensure proper drainage.
Conclusion
With proper care and attention, caladiums can thrive as beautiful and colorful additions to your indoor or outdoor space. By providing them with the right lighting, watering, and temperature conditions, as well as protecting them from pests and diseases, you can enjoy the stunning foliage of caladiums for years to come.
Choosing the Right Caladium: Factors to Consider
When it comes to choosing the right caladium for your garden or indoor space, there are several factors to consider. The following are some important considerations to help you make an informed decision:
1. Light Requirements
Caladiums thrive in bright, indirect light. They prefer dappled or partial shade, making them perfect for outdoor spaces that receive filtered sunlight. If you plan to grow caladiums indoors, choose a location near a window with indirect sunlight.
2. Temperature Tolerance
![Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide | [Name of the website] 3 2. Temperature Tolerance](https://1ogorod.ru/en/wp-content/uploads/wpallimport/files/caladium-care-and-reproduction-ad478p6j.jpg)
Caladiums are tropical plants that love warmth and humidity. They cannot tolerate temperatures below 60°F (15°C). Before purchasing a caladium, make sure the climate in your area is suitable for its growth.
3. Soil Type and Drainage
Caladiums require well-draining soil. They prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Ensure that the soil has good drainage to prevent waterlogging, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot.
4. Size and Shape
Caladiums come in a variety of sizes and shapes. Some varieties have large leaves, while others have smaller ones. Consider the available space in your garden or indoor area and choose a caladium that fits well.
5. Leaf Color and Pattern
One of the most appealing features of caladiums is their vibrant leaf colors and patterns. From solid colors like green, red, or pink to combinations of colors and intricate patterns, there is a wide variety to choose from. Select a caladium with leaf colors and patterns that complement your overall garden or indoor decor.
6. Growth Habit
Caladiums have different growth habits, such as erect, spreading, or bushy. Consider the growth habit of the caladium you intend to purchase, as this will determine its suitability for pots, hanging baskets, or as a ground cover.
7. Disease Resistance
Some caladium varieties exhibit better disease resistance than others. Look for caladiums that are known for their resistance to common pests and diseases, such as leaf spot or fungal infections.
8. Availability and Source
Lastly, consider the availability of caladium varieties in your area and the reliability of the source. Check with local nurseries or reputable online plant sellers to find a wide selection of healthy caladiums to choose from.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right caladium variety that fits your specific needs and preferences. Whether you want to add a pop of color to your garden or create an eye-catching indoor display, caladiums are an excellent choice.
Understanding Caladium’s Light and Temperature Needs
Caladiums are tropical plants that thrive in warm and humid conditions. To keep your caladium healthy and vibrant, it’s important to provide the right amount of light and maintain the appropriate temperature.
Light Requirements
Caladiums prefer bright, indirect light. They can tolerate some direct sunlight, but too much can scorch their leaves. It’s best to place your caladium in a location that receives bright, filtered light for most of the day. Avoid placing them in full shade, as this can cause the plant’s colors to fade.
If you’re growing caladiums indoors, place them near a window that receives bright, indirect light. You can also use sheer curtains or blinds to filter the light if necessary. If natural light is limited, you can supplement it with fluorescent or grow lights to ensure your caladium receives enough light.
Temperature Requirements
Caladiums thrive in temperatures between 65°F (18°C) and 85°F (29°C). They are sensitive to cold drafts and temperatures below 60°F (15°C). It’s important to keep your caladium away from windows and doors that may let in cold drafts, especially during the winter months.
During the summer, if the temperature rises above 85°F (29°C), it’s important to provide your caladium with some shade or move it to a cooler location. High temperatures can cause the plant’s leaves to wilt and discolor.
In addition to the ambient temperature, caladiums also prefer a humid environment. If your home has dry air, you can increase the humidity by placing a tray filled with water near the plant or using a humidifier in the room. Misting the leaves with water occasionally can also help increase humidity.
Tips for Light and Temperature Care
- Place your caladium in a location that receives bright, indirect light.
- Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
- Keep your caladium away from cold drafts, as they are sensitive to low temperatures.
- Maintain a temperature between 65°F (18°C) and 85°F (29°C) for optimal growth.
- Increase humidity if necessary by using a humidifier or placing a tray with water near the plant.
- Monitor the temperature and light conditions regularly to ensure your caladium is thriving.
By understanding and meeting the light and temperature needs of your caladium, you can enjoy its beautiful foliage and ensure its long-term health.
Providing Optimal Soil and Watering Conditions for Caladium
Soil Requirements
![Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide | [Name of the website] 4 Soil Requirements](https://1ogorod.ru/en/wp-content/uploads/wpallimport/files/caladium-care-and-reproduction-m03bsalj.jpg)
Caladium plants thrive in well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. A mixture of peat moss, perlite, and loam soil is an ideal choice. The peat moss helps retain moisture while the perlite ensures good drainage. The loam soil provides essential nutrients for the plant’s growth.
Before planting your caladium bulbs or tubers, prepare the soil by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris. Mix in the organic material to improve the soil’s fertility and structure.
Watering Needs
Caladiums require consistent and adequate moisture to thrive. However, they are sensitive to overwatering and can develop root rot if the soil remains waterlogged. It is essential to strike a balance in watering to provide moisture without causing excessive dampness.
An effective way to determine watering needs is to use the “finger test”. Insert your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. If it feels dry at that level, it’s time to water. If the soil feels moist, wait a little longer before watering.
Frequency of Watering
The frequency of watering depends on various factors, such as the temperature, humidity, and soil type. In general, caladiums require watering once or twice a week. However, during periods of high heat and dryness, you may need to water more frequently to prevent the soil from drying out.
It’s important to water deeply, ensuring that the water reaches the roots. Shallow watering can lead to shallow root growth and weak plants.
Watering Techniques
When watering your caladiums, aim to thoroughly wet the soil. Use a watering can or a garden hose with a gentle flow to prevent the soil from becoming compacted or disrupted.
Avoid watering the foliage directly, as wet leaves can encourage the development of fungal diseases. Instead, water at the base of the plant, allowing the water to soak into the soil.
Additional Tips:
- Avoid letting the soil dry out completely between watering, as this can stress the plant.
- Consider using a layer of mulch around the plants to help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
- Regularly monitor the moisture level of the soil to adjust watering accordingly.
- During winter, reduce watering as the caladiums enter a dormant period.
By providing the optimal soil and watering conditions for your caladium plants, you can ensure their healthy growth and vibrant foliage.
Fertilizing Caladium: Dos and Don’ts
Why is fertilizing important?
Fertilizing caladium plants is essential for their health and growth. These tropical plants require a steady supply of nutrients to thrive and produce vibrant foliage. Proper fertilization can help enhance their color, size, and overall appearance.
When to fertilize?
It is best to fertilize caladium plants during their active growing season, which is typically from spring to early fall. During this period, the plants are actively producing new leaves and require extra nutrients to support their growth. Avoid fertilizing during the dormant winter months as the plant’s metabolic activity slows down.
Types of fertilizer
When choosing a fertilizer for your caladium plants, opt for a balanced, slow-release fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). A 14-14-14 or 10-10-10 fertilizer is suitable for caladiums. These numbers represent the ratio of the three essential nutrients, respectively. Slow-release fertilizers provide a steady supply of nutrients over time and are less likely to cause nutrient burn.
How much to apply?
Follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging for the recommended dosage, as it can vary depending on the brand and formulation. In general, apply 1 tablespoon of fertilizer per square foot of soil, or follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. Over-fertilizing can lead to nutrient burn, so it’s crucial not to exceed the recommended dosage.
Application method
Spread the fertilizer evenly around the base of the caladium plant, avoiding direct contact with the foliage. Gently scratch the surface of the soil to incorporate the fertilizer and water thoroughly to ensure nutrients reach the roots. Applying fertilizer when the soil is moist can help prevent fertilizer burn.
Frequency of fertilization
Generally, fertilize caladium plants every 4-6 weeks during the active growing season. However, always check the specific instructions on the fertilizer packaging, as different brands may have different recommendations. Avoid over-fertilizing, as it can lead to nutrient build-up in the soil, causing harm to the plant.
Don’ts of fertilizing caladium
- Don’t fertilize caladium plants during their dormant period in winter.
- Don’t over-fertilize, as it can cause nutrient burn.
- Don’t apply fertilizer directly onto the foliage.
- Don’t exceed the recommended dosage mentioned on the fertilizer packaging.
Conclusion
Fertilizing caladium plants is important for their health and vitality. Choosing a balanced, slow-release fertilizer and applying it at the right time and in the proper amount will promote robust foliage growth and vibrant coloration. Remember to follow the dos and don’ts of fertilization to ensure the best care for your caladium plants.
Managing Pests and Diseases: Common Issues and Solutions
Pests
- Aphids: One common pest that affects Caladiums is aphids. These small insects feed on the sap of the plants and can cause damage to the leaves. To get rid of aphids, you can wash the leaves with a mild soap solution or use an insecticidal soap. Regularly inspecting the plants and removing any infested leaves can also help prevent the spread of aphids.
- Spider Mites: Spider mites are another common pest that can attack Caladiums. These tiny pests can cause discoloration and webbing on the leaves. To control spider mites, you can use a miticide or wash the leaves with a strong stream of water. Increasing humidity levels around the plants can also help prevent spider mite infestations.
- Mealybugs: Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects that often appear as white, cotton-like masses on the leaves and stems. To eliminate mealybugs, you can use a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol to remove them manually. In severe cases, an insecticide may be necessary. Proper plant maintenance and regular inspection can help prevent mealybug infestations.
Diseases
- Leaf Spot: Leaf spot is a common fungal disease that affects Caladiums. It causes brown or black spots on the leaves and can lead to leaf damage or defoliation. To control leaf spot, remove the infected leaves and ensure good air circulation around the plants. Avoid overhead watering, as it can create a favorable environment for the fungus to thrive.
- Root Rot: Root rot is a disease caused by overwatering or poor drainage. It leads to the decay of the plant’s roots and can cause wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth. To prevent root rot, ensure that the soil is well-draining and allow it to dry out slightly between waterings. Avoid leaving the plant in standing water.
- Botrytis Blight: Botrytis blight is a fungal disease that affects many plants, including Caladiums. It causes gray mold on the leaves and can spread quickly in cool, humid conditions. To control botrytis blight, remove the affected leaves and improve air circulation around the plants. Avoid excessive watering and overhead watering, as it creates favorable conditions for the fungus.
Regularly inspecting your Caladium plants and taking action at the first sign of pests or diseases can help keep them healthy and thriving. Proper plant care, including providing adequate light, watering, and fertilizing, can also help prevent stress and make the plants more resistant to problems.
Pruning and Propagating Caladium: Step-by-Step Guide
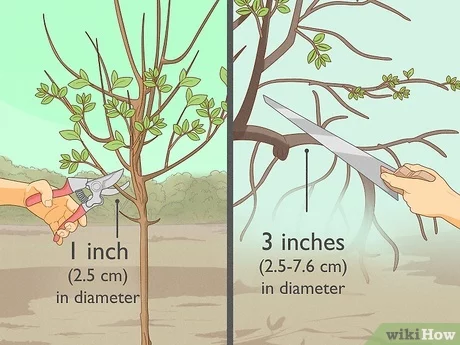
Pruning Caladium Plants
Pruning caladium plants is an important part of their care routine. Here are the steps to prune your caladium:
- Start by inspecting the plant for any withered or yellowing leaves. These can be removed to encourage new growth and maintain a neat appearance.
- Using clean and sharp pruning shears, cut the withered leaves at the base, as close to the main stem as possible. Be careful not to damage the healthy leaves or stems.
- If you notice any dead or diseased portions of the plant, remove them immediately to prevent the spread of disease.
- Once you have finished pruning, dispose of the removed plant material properly to avoid attracting pests or diseases.
Propagating Caladium Plants
If you want to propagate your caladium plants and create new ones, here is a step-by-step guide to follow:
- Wait until your caladium plant has matured and developed several healthy tubers. This usually takes around three to four months after planting.
- Carefully dig up the caladium plant, taking care not to damage the tubers.
- Gently separate the tubers from the main plant, making sure each tuber has its own set of roots.
- If there are any damaged or diseased tubers, discard them to prevent the spread of disease.
- Prepare a well-draining potting mix and plant each tuber separately, ensuring that they are covered with soil but not buried too deeply.
- Place the newly planted tubers in a warm and humid environment, as caladiums thrive in such conditions.
- Water the tubers regularly, keeping the soil moist but not soggy. Avoid overwatering, as this can cause rotting.
- After a few weeks, you should start to see new shoots emerging from the tubers.
Note: It’s important to remember that propagating caladium plants through tubers takes time and patience. The success rate may vary, but with proper care, you can increase your chances of success.
Overwintering Caladium: Tips for Cold Climate Regions
Caladiums are tropical plants that thrive in warm climates and do not tolerate cold temperatures. If you live in a cold climate region and want to keep your caladiums alive through the winter, overwintering them is essential. Here are some tips for overwintering caladiums in cold climate regions:
1. Dig up the tubers
Before the first frost, carefully dig up the caladium tubers from the ground using a garden fork or shovel. Be cautious not to damage the tubers during the process.
2. Clean and dry the tubers
Once the tubers are out of the ground, gently remove any excess soil and let them air dry for a few days. It’s crucial to remove any remaining soil to prevent rotting during the storage period.
3. Store in a cool and dry place
![Caladium Care and Reproduction: A Complete Guide | [Name of the website] 5 3. Store in a cool and dry place](https://1ogorod.ru/en/wp-content/uploads/wpallimport/files/caladium-care-and-reproduction-rhoyvzd2.jpg)
Find a cool and dry location to store the caladium tubers during the winter months. Ideally, the temperature should be around 50-60°F (10-16°C). A basement or garage can be suitable storage spots, as long as the conditions are appropriate.
4. Use suitable containers
Place the dried tubers in breathable containers, such as mesh bags, paper bags, or wooden crates. Avoid using airtight containers or plastic bags, as they can trap moisture and cause rotting.
5. Check for any signs of decay
Regularly inspect the stored caladium tubers for any signs of decay or mold. If you notice any soft spots, discoloration, or unusual odors, remove the affected tubers immediately to prevent spreading.
6. Provide occasional moisture
While the tubers should not be kept wet, it is important to prevent them from drying out completely. Spray a light mist of water on the tubers every few weeks to maintain some moisture without saturating them.
7. Replant in the spring
As the winter season ends and the danger of frost is gone, you can replant the caladium tubers in your garden or containers. Choose a location with partial shade and well-draining soil for optimal growth.
By following these tips for overwintering caladiums in cold climate regions, you can ensure the survival of your plants and enjoy their vibrant foliage year after year.
Frequently Asked Questions about Caladium Care
1. How often should I water my caladium?
Caladiums prefer to be kept evenly moist but not waterlogged. Water the plant thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
2. What is the best temperature for caladiums?
Caladiums thrive in temperatures between 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C). They can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures, but it’s best to keep them away from drafts and cold air.
3. How much light does a caladium need?
Caladiums prefer bright, indirect light. Avoid exposing them to direct sunlight, as it can scorch their leaves. Place them near a window with filtered sunlight or in a spot where they receive bright but indirect light.
4. How often should I fertilize my caladium?
During the growing season (spring and summer), fertilize your caladium every two to four weeks with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer. Dilute the fertilizer to half strength and apply it to the soil according to the package instructions.
5. How do I propagate my caladium?
Caladiums can be propagated through division or by taking bulb offsets. To propagate through division, carefully separate the tubers and plant them in separate pots. To propagate through bulb offsets, remove the small bulbs that form around the main bulb and plant them in individual pots.
6. Should I prune my caladium?
Caladiums do not require pruning. However, you can remove any yellow or dead leaves to maintain the plant’s appearance. Use clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears to make clean cuts.
7. Can caladiums be grown indoors?
Yes, caladiums can be grown indoors as long as they receive adequate light and temperature conditions. Choose a bright spot near a window or provide artificial grow lights to ensure they get enough light.
8. Why are the leaves of my caladium turning yellow?
Yellow leaves can indicate overwatering, underwatering, or improper light conditions. Check the soil moisture and adjust your watering accordingly. Ensure the plant is not exposed to direct sunlight, which can cause leaf scorching.
9. Are caladiums toxic to pets?
Yes, caladiums are toxic to cats and dogs if ingested. Keep them out of reach of pets or choose pet-safe houseplants.
10. Can I keep my caladium outdoors in winter?
Caladiums are tropical plants and cannot tolerate cold temperatures or frost. It’s best to bring them indoors before the first frost or keep them in a warm, protected area if you live in a mild climate.
Q&A:
What is the best way to care for a Caladium plant?
The best way to care for a Caladium plant is to place it in a location with bright, indirect light and to keep the soil consistently moist. Caladiums also prefer warm temperatures and high humidity.
Is it possible to grow Caladium plants indoors?
Yes, it is possible to grow Caladium plants indoors. They can be grown in pots or containers and placed in a location with bright, indirect light. Indoor Caladiums should be kept in a warm and humid environment.
How often should I water my Caladium plant?
Caladium plants require consistently moist soil, so they should be watered whenever the top inch of soil feels dry. It’s important to avoid overwatering or letting the soil dry out completely.
Do Caladium plants require any special fertilization?
While Caladium plants do not require frequent fertilization, they can benefit from a monthly application of a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer during the growing season. This will help promote healthy foliage growth.
How can I propagate Caladium plants?
Caladium plants can be propagated through division or by planting tubers. To divide Caladium plants, carefully separate the tubers during the dormant season and plant them in separate containers. Tubers can be planted in pots or directly in the ground, and new plants will grow from them.
Video:
CALADIUM CARE TIPS & TRICKS