- Importance of Camellia Care
- 1. Maintaining Soil Moisture
- 2. Providing Sufficient Sunlight
- 3. Pruning and Shaping
- 4. Fertilizing at the Right Time
- 5. Protecting from Pests and Diseases
- 6. Winter Protection
- Understanding Camellia Plants
- Growth Habit and Size
- Flower Characteristics
- Light and Temperature Requirements
- Soil and Watering Needs
- Pruning and Maintenance
- Choosing the Right Location
- In summary, here are some key points to remember when choosing the right location for your camellia plants:
- Proper Watering Techniques
- The Role of Fertilizer
- Pruning and Shaping Camellias
- Why Prune Camellias
- When to Prune Camellias
- Tools for Pruning
- Pruning Techniques
- Shaping Camellias
- Conclusion
- Protecting Camellias from Pests and Diseases
- 1. Common Pests
- 2. Camellia Diseases
- 3. Preventive Measures
- 4. Camellia Varieties
- Propagating Camellias
- 1. Propagation by Seeds
- 2. Propagation by Cuttings
- 3. Propagation by Grafting
- Capturing the Beauty of Camellias: Photos and Species
- Introduction
- Photos of Camellias
- Popular Camellia Species
- Caring for Camellias
- Conclusion
- Q&A:
- When is the best time to plant camellias?
- How often should I water camellia plants?
- How do I prune my camellia plants?
- What kind of soil do camellia plants prefer?
- What are some common pests and diseases that affect camellia plants?
- Video: Growing Camellias – the most breathtaking varieties
Camellias are beautiful evergreen plants that are native to Eastern and Southern Asia. Known for their stunning flowers and glossy, dark green leaves, camellias make a great addition to any garden or landscape. However, like any plant, camellias require proper care in order to thrive and produce an abundance of blooms. In this article, we will explore the key factors in camellia care, including watering, fertilizing, pruning, and protecting against pests and diseases.
One of the most important aspects of camellia care is watering. Camellias are relatively drought-tolerant once established, but they still require regular watering, especially during dry periods. It is best to water camellias deeply and infrequently rather than giving them frequent light watering. This encourages the roots to grow deep into the soil, making the plant more resilient to dry conditions. However, it is also important not to overwater camellias, as this can lead to root rot and other problems. A good rule of thumb is to water camellias when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch.
In addition to watering, camellias also require regular fertilizing to ensure healthy growth and abundant blooms. It is best to fertilize camellias in the spring, just before they begin their active growth period. A slow-release, balanced fertilizer is ideal for camellias, as it provides a steady supply of nutrients over a longer period of time. Be sure to follow the package instructions for the correct amount of fertilizer to use, as over-fertilization can lead to weak growth and fewer blooms.
Pruning is another important aspect of camellia care. Regular pruning helps to maintain the shape and size of the plant, as well as encourage new growth and blooming. It is best to prune camellias immediately after they finish blooming in the spring. Remove any dead or damaged branches, as well as any inward-growing or crossing branches. This will help to improve air circulation and reduce the risk of disease. Be sure to use clean, sharp pruning shears to make clean cuts and avoid tearing the plant’s bark.
Finally, it is important to protect camellias against pests and diseases. Camellias are relatively pest-resistant, but they can occasionally be attacked by aphids, scales, or spider mites. Regular inspections and early intervention are key to preventing these pests from causing significant damage to your camellias. If you notice any signs of infestation, such as discolored leaves or sticky residue, treat the plant with an appropriate insecticide or pesticide. Additionally, camellias can be susceptible to fungal diseases, such as leaf spot and petal blight. Regularly inspect the plant for any signs of disease and promptly remove and dispose of any infected leaves or flowers.
By following these key care tips, you can ensure that your camellias thrive and reward you with their stunning blooms. Whether you choose a classic Japanese camellia, a ruffled peony camellia, or a delicate sasanqua camellia, these plants are sure to add beauty and elegance to your garden.
Importance of Camellia Care
Proper care is essential for the health and beauty of camellia plants. Camellias are popular ornamental plants that are valued for their vibrant flowers and glossy evergreen foliage. To ensure their optimal growth and long lifespan, it is important to provide them with the right care.
1. Maintaining Soil Moisture

Camellias prefer well-draining soil that retains moisture but does not become waterlogged. It is important to keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the growing season. Regular watering and mulching can help retain moisture and prevent the soil from drying out.
2. Providing Sufficient Sunlight
While camellias can tolerate partial shade, they thrive in areas with bright, indirect sunlight. It is important to choose a location that receives at least 4-6 hours of sunlight per day. Insufficient sunlight can lead to poor blooming and weak growth.
3. Pruning and Shaping
Regular pruning is important for the health and appearance of camellias. Pruning helps maintain a desired shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and promote new growth. It is best to prune camellias after they finish blooming, typically in late winter or early spring.
4. Fertilizing at the Right Time
Camellias benefit from regular fertilization to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in late winter or early spring before the new growth begins. Avoid over-fertilization, as it can lead to excessive foliage growth and reduced flower production.
5. Protecting from Pests and Diseases

Camellias can be susceptible to various pests and diseases, including aphids, scale insects, and fungal infections. Regular inspection and prompt treatment are important to prevent damage. Horticultural oils or insecticidal soaps can be used to control pests, and fungicides may be necessary to combat fungal diseases.
6. Winter Protection
Depending on the specific variety and climate, winter protection may be required for camellias. Mulching around the base of the plant can help insulate the roots and protect them from extreme cold. If frost is a concern, covering the plant with a frost cloth or burlap can provide additional protection.
Remember, proper camellia care is crucial for their overall health and longevity. By following these care guidelines, you can enjoy the beauty of camellias in your garden for years to come.
Understanding Camellia Plants
Camellia plants are beautiful, evergreen shrubs that are known for their stunning flowers and glossy, dark green leaves. They belong to the family Theaceae and are native to East Asia. There are over 200 species of camellias, with various colors, sizes, and shapes.
These plants are highly valued in gardening and landscaping due to their attractive foliage and gorgeous blooms. Camellias typically bloom in late winter or early spring, brightening up gardens and landscapes during the colder months.
Growth Habit and Size
Camellias have a dense and compact growth habit, with a rounded or upright shape. They can range in size from compact varieties that grow only a few feet tall to large, tree-like specimens that can reach 20 feet or more in height.
When selecting a camellia plant for your garden or landscape, consider the available space and the plant’s ultimate size. Smaller varieties can be grown in containers or used as hedges, while larger specimens make beautiful focal points or shade trees.
Flower Characteristics
The most prominent feature of camellia plants is their beautiful flowers. The flowers can be single, semi-double, or double, with layers of petals forming a full and symmetrical bloom. Depending on the species, camellia flowers can be white, pink, red, or even variegated.
It’s worth noting that not all camellia plants produce flowers of the same size or shape. Some varieties have large blooms, while others have smaller, more delicate flowers. The blooms are often fragrant and can last for several weeks, adding beauty and fragrance to your garden.
Light and Temperature Requirements
Camellias thrive in partially shaded areas, where they receive filtered sunlight or indirect light. They prefer morning sun and afternoon shade, as direct sunlight can scorch their leaves and flowers. In hotter climates, camellias may require additional shade during the hottest part of the day.
These plants are also adapted to cool to mild temperatures, and they don’t fare well in extreme heat or cold. They prefer average temperatures between 50°F and 70°F (10°C to 21°C). If you live in an area with extremely cold winters, consider growing camellias in containers that can be brought indoors during the coldest months.
Soil and Watering Needs
Camellias thrive in well-draining, slightly acidic soil. They prefer a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If your soil is alkaline, you may need to amend it with organic matter, such as compost or pine needles, to lower the pH.
When it comes to watering, camellias require regular moisture but don’t tolerate soggy conditions. Water your camellia plants deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather and soil conditions. Mulching the soil surface around the plants can help conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
Pruning and Maintenance
Camellias generally require minimal pruning, but it can help maintain their shape and promote healthy growth. Prune camellias after they finish blooming, as they set buds for the next season shortly afterward. Remove any dead or damaged branches, as well as any crossing or overcrowded branches.
Regular fertilization is essential to ensure healthy growth and abundant blooms. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants in early spring and early fall. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer label for proper application rates.
With proper care and attention, camellias can thrive and become focal points in your garden or landscape. Their stunning blooms and lush foliage will provide beauty and joy for years to come.
Choosing the Right Location
When it comes to choosing the right location for your camellia plants, there are a few key factors to consider. Camellias thrive in partial shade, so it’s important to find a spot in your garden that provides some protection from direct sunlight. Too much sun can scorch the leaves and flowers of your camellias, so a location with filtered or dappled sunlight is ideal.
Additionally, camellias prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Avoid planting your camellias in areas with heavy clay soil or areas that tend to stay wet for long periods of time. These conditions can lead to root rot and other problems for your camellias. If your soil is not ideal, you can improve it by adding compost or other organic matter.
Another important consideration when choosing a location for your camellias is wind exposure. Strong winds can damage the delicate blooms and leaves of your camellias, so try to find a spot that is protected from gusty winds. If your garden is particularly windy, you may need to create a windbreak or provide some other form of protection for your camellias.
Finally, consider the proximity of other plants and trees when choosing a location for your camellias. Camellias have shallow root systems, and they can be sensitive to competition from other plants. Avoid planting your camellias near large trees or shrubs that may compete for water and nutrients.
In summary, here are some key points to remember when choosing the right location for your camellia plants:
- Choose a spot with partial shade and dappled sunlight.
- Avoid areas with heavy clay soil or poor drainage.
- Protect your camellias from strong winds.
- Avoid planting near large trees or shrubs that may compete for resources.
Proper Watering Techniques
Proper watering is essential for the health and beauty of your camellia plants. Here are some techniques to keep in mind:
- Consistency: Camellias prefer consistent moisture levels, so make sure to water them regularly. Aim for a deep watering about once a week to ensure the roots are thoroughly saturated.
- Avoid Overwatering: While camellias do enjoy moisture, overwatering can be detrimental to their health. Be mindful of not drenching the soil or allowing water to accumulate around the base of the plant.
- Water at the Base: When watering your camellias, direct the water at the base of the plant rather than spraying it overhead. This helps prevent leaf damage and disease.
- Water in the Morning: It is best to water your camellias in the morning, as this allows the foliage to dry by evening, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
- Provide Adequate Drainage: Camellias prefer well-draining soil, so ensure that the planting area has proper drainage. Consider raised beds or adding organic matter to improve drainage if needed.
- Monitor Moisture Levels: Regularly check the moisture levels of the soil around your camellias to ensure they are neither too dry nor too wet. Adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
- Mulch: Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or compost, around the base of your camellias can help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
| Signs | Description |
|---|---|
| Lush Green Foliage | Properly watered camellias exhibit healthy, vibrant green leaves. |
| Buds and Blooms | Regular watering encourages camellias to produce beautiful buds and blossoms. |
| Healthy Root System | By maintaining consistent moisture levels, camellias develop a strong and healthy root system. |
Remember, each camellia plant may have unique watering needs depending on factors such as its species, the climate, and the soil conditions. It’s important to observe your plants and adjust your watering practices accordingly.
The Role of Fertilizer
Fertilizer plays a crucial role in the care and maintenance of camellia plants. It provides essential nutrients that are necessary for the plants’ growth and overall health.
Camellias have specific nutritional requirements, and applying the right fertilizer at the right time is essential for their well-being. They require a balanced fertilizer with a higher percentage of nitrogen (N) for healthy foliage growth, phosphorus (P) for flower development, and potassium (K) for overall plant vigor and root development.
It is important to apply the fertilizer evenly around the base of the camellia plants, avoiding direct contact with the stem to prevent any potential harm. Over-fertilization can lead to salt accumulation in the soil, which can damage the roots and negatively impact the plant’s health.
There are several types of fertilizers suitable for camellias, including slow-release granular fertilizers and liquid fertilizers. Slow-release fertilizers provide a continuous supply of nutrients over an extended period and are usually applied once or twice a year. Liquid fertilizers are quickly absorbed by the plants and can be applied more frequently during the growing season.
It is crucial to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for proper application rates and timing. Applying too much fertilizer or applying it at the wrong time can result in foliage burn or an imbalance of nutrients, which can harm the plants.
In addition to the regular application of fertilizer, it is also beneficial to regularly monitor the pH level of the soil. Camellias prefer slightly acidic soil, with a pH of around 6.0 to 6.5. If the soil becomes too alkaline, the plants may struggle to take up essential nutrients, even if they are present in the soil. It may be necessary to periodically amend the soil with acidifying agents, such as sulfur or ammonium sulfate, to maintain the optimal pH level.
Proper fertilization is an integral part of camellia care and can significantly contribute to their growth and overall health. By providing the necessary nutrients, camellias can thrive and produce beautiful flowers season after season.
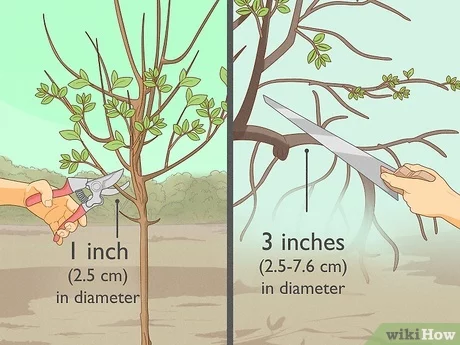
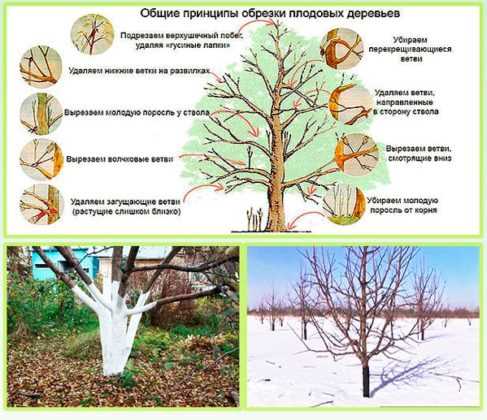
Pruning and Shaping Camellias
Why Prune Camellias
Pruning is an essential part of camellia care that helps to maintain the health and shape of the plant. Regular pruning promotes new growth, improves air circulation and sunlight penetration, and reduces the risk of disease and pest infestation.
When to Prune Camellias

Camellias should be pruned immediately after the blooming period, which typically occurs in late winter or early spring. This allows the plant to recover and produce new growth before the next blooming season.
Tools for Pruning
Before pruning camellias, make sure to have the right tools handy:
- Sharp bypass pruning shears
- Loppers for thicker branches
- Pruning saw for larger branches
- Gardening gloves for protection
Pruning Techniques
Follow these pruning techniques to shape and maintain your camellias:
- Begin by removing any dead, damaged, or diseased branches using sharp pruning shears. Cut back to healthy wood.
- Next, thin out dense or overcrowded areas by selectively removing branches that are crossing or rubbing against each other.
- If you want to control the size and shape of your camellia, prune back the longest branches to a desired length.
- When pruning, make clean cuts just above a bud or a lateral branch to promote healthy regrowth.
- Finally, remove any suckers or basal shoots that are emerging from the base of the plant.
Shaping Camellias

If you want to shape your camellias into a specific form, such as a hedge or a tree, consider using the following techniques:
- Hedge: Regularly prune the sides and top of the plant to create a dense and uniform hedge. Use a string line or guide for straight cuts.
- Tree: Train a young camellia into a single-trunk tree by selecting a strong central leader and removing any competing branches. Prune lower branches as the tree grows to create a clear trunk.
- Espalier: Espalier your camellia against a wall or fence by pruning and tying the branches horizontally to create a flat, decorative pattern.
Conclusion
Pruning is an important aspect of camellia care that helps to keep the plants healthy and well-shaped. By following the proper pruning techniques and shaping methods, you can enhance the beauty and longevity of your camellias.
Protecting Camellias from Pests and Diseases
Camellias are beautiful and popular plants, but unfortunately, they can be susceptible to various pests and diseases. It’s important to protect your camellias from these potential threats to ensure their health and longevity.
1. Common Pests

Camellias can be attacked by a range of pests, including aphids, scale insects, thrips, and spider mites. These pests can cause damage to the leaves, buds, and flowers of your camellias. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of infestation, such as distorted growth, sticky residues, or small insects on the foliage.
To control these pests, you can use insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils. These organic solutions can be applied directly to the affected areas to suffocate and kill the insects. Alternatively, you can introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings to your garden, as they feed on common camellia pests.
2. Camellia Diseases
Camellias can also be affected by several diseases, including root rot, leaf spot, and canker. Root rot is caused by over-watering or poorly drained soil, leading to the decay of the plant’s roots. Leaf spot is characterized by dark spots on the leaves, while canker appears as sunken, discolored areas on the stems.
To prevent these diseases, ensure proper drainage for your camellias by planting them in well-drained soil. Avoid over-watering and maintain good air circulation around the plants. If you notice signs of disease, promptly remove and destroy infected plant parts to prevent further spread.
3. Preventive Measures
In addition to controlling pests and diseases, there are several preventive measures you can take to keep your camellias healthy. Regularly prune your plants to remove dead or diseased branches, and to improve air circulation. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture and suppress weed growth.
Proper watering is essential for camellias. Water deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings. Avoid wetting the foliage, as this can promote the growth of fungal diseases.
4. Camellia Varieties
Some camellia varieties are more resistant to pests and diseases than others. When choosing camellia plants for your garden, consider selecting cultivars that are known for their disease resistance. Research different varieties and consult with local experts or nurseries to find the best options for your region.
By following these tips and maintaining a vigilant approach to plant care, you can protect your camellias from pests and diseases and enjoy their beautiful blooms for many years to come.
Propagating Camellias
Camellias can be propagated by several methods, including seeds, cuttings, and grafting. Each method has its own advantages and may be more suitable for particular situations.
1. Propagation by Seeds
- Collect ripe seeds from a healthy camellia plant.
- Remove the outer shell of the seeds and soak them in water for 24 hours.
- Fill a seed tray or pots with a well-draining soil mix.
- Sow the seeds on the surface of the soil and lightly cover them with a thin layer of soil.
- Keep the soil moist and place the tray or pots in a warm, shaded area.
- Germination can take several weeks to months, so be patient.
- Once the seedlings have developed several true leaves, they can be transplanted into individual pots.
2. Propagation by Cuttings
Propagating camellias from cuttings is a common method that allows you to clone the desired characteristics of a mature camellia plant.
- Select a healthy, non-flowering branch from a mature camellia plant.
- Make a clean cut just below a leaf node, using a sharp knife or pruners.
- Remove the leaves from the lower two-thirds of the cutting.
- Dip the bottom of the cutting in rooting hormone powder.
- Insert the cutting into a container filled with a well-draining rooting medium.
- Keep the cutting moist and place a plastic bag over the container to create a humid environment.
- Place the container in a bright, indirect light location.
- Rooting can take several weeks to months, so be patient.
- Once the cutting has developed roots, it can be transplanted into a larger pot or directly into the garden.
3. Propagation by Grafting
Grafting is a more advanced method of propagating camellias that involves combining the desirable traits of a cultivated camellia variety with the strong root system of a wild camellia species.
- Choose a scion, which is a healthy branch or bud from the desired camellia variety.
- Prepare a rootstock, which is a wild camellia species with a strong root system.
- Make a slanted cut on both the scion and the rootstock.
- Place the scion onto the rootstock, aligning the cambium layers.
- Secure the graft with grafting tape or a grafting clip.
- Keep the grafted plant in a warm, humid environment until the graft union has healed.
- Once the graft has successfully bonded, the plant can be transplanted into a larger pot or directly into the garden.
| Propagation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Seeds | Easy method, can produce new varieties | Long germination period, not guaranteed to inherit desired traits |
| Cuttings | Clones desired traits, faster results than seeds | Requires more skill and knowledge |
| Grafting | Combines desirable traits with strong rootstock | Requires advanced knowledge and skill, longer process |
Capturing the Beauty of Camellias: Photos and Species
Introduction
Camellias are exquisite flowering plants prized for their stunning blooms and glossy foliage. With a wide variety of species and cultivars available, these plants can bring beauty and color to any garden or indoor space. In this article, we will explore some captivating photos of camellias and highlight a few popular species.
Photos of Camellias
Below are some stunning photos showcasing the beauty of camellias:
- A close-up shot of a vibrant red camellia blossom, its petals delicately layered and beautifully textured.
- An elegant white camellia with perfectly symmetrical petals, exuding an air of grace and purity.
- A pink camellia in full bloom, its petals opening up like a delicate rose.
- A variegated camellia with unique patterns and colors, adding a touch of whimsy and charm to any garden.
Popular Camellia Species

Camellia plants belong to the family Theaceae and are native to East Asia. Here are a few popular species:
- Camellia japonica: This species is known for its large, showy flowers and glossy dark green leaves. It comes in a variety of colors, including red, pink, and white.
- Camellia sasanqua: These camellias bloom in the fall, earlier than other species. They have smaller flowers and more compact growth habits, making them perfect for smaller gardens or containers.
- Camellia reticulata: With its larger-than-life blooms, this species is often seen as the queen of camellias. Its flowers can reach up to 8 inches in diameter and come in a wide range of colors and patterns.
Caring for Camellias
To ensure the continued beauty of your camellia plants, it’s important to provide proper care and maintenance. Here are a few tips:
- Plant camellias in well-draining soil and choose a location that receives morning sun and afternoon shade.
- Water camellias regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring to promote healthy growth and flowering.
- Prune camellias after they have finished flowering to maintain their shape and remove any dead or diseased branches.
- Protect camellias from extreme temperatures and strong winds, as they can damage the delicate flowers and foliage.
Conclusion
Camellias are truly enchanting plants that can bring a touch of elegance and beauty to any garden or indoor space. With their stunning blooms and glossy foliage, these plants are a joy to behold. By following proper care and maintenance practices, you can enjoy the captivating beauty of camellias for years to come.
Q&A:
When is the best time to plant camellias?
The best time to plant camellias is in the fall or early spring, when the weather is cool and the plants are dormant.
How often should I water camellia plants?
Camellia plants should be watered regularly, especially during periods of hot weather. They prefer moist soil, so it’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
How do I prune my camellia plants?
Camellia plants should be pruned after they have finished blooming. The best time to prune is in late spring or early summer. You should remove any dead or diseased branches, and thin out the plant to improve air circulation.
What kind of soil do camellia plants prefer?
Camellia plants prefer well-draining, acidic soil. You can improve the soil by adding organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to increase acidity.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect camellia plants?
Some common pests that affect camellia plants include aphids, scale insects, and tea mites. Diseases that can affect camellias include camellia flower blight and camellia leaf gall. It’s important to regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or disease and take appropriate measures to control them.
Video:
Growing Camellias – the most breathtaking varieties