- Clivia (Clivia): Care, Photos, Species – The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction
- Care Tips
- Photos
- Species
- Clivia Care Tips
- Clivia Species and Varieties
- 1. Clivia miniata
- 2. Clivia nobilis
- 3. Clivia caulescens
- 4. Clivia gardenii
- 5. Clivia x cyrtanthiflora
- How to Propagate Clivia
- 1. Division
- 2. Leaf Cuttings
- 3. Seed Propagation
- Clivia Pests and Diseases
- Common Pests
- Common Diseases
- Preventing Pests and Diseases
- Clivia Potting and Soil Requirements
- Potting:
- Soil:
- Watering:
- Fertilizer:
- Clivia Flowering and Blooming Season
- Factors that affect Clivia blooming season:
- Clivia Photo Gallery
- Q&A:
- What is Clivia?
- How do I care for Clivia plants?
- Are there different species of Clivia?
- Can Clivia plants be grown indoors?
- How often should I water Clivia plants?
- How long does it take for Clivia plants to bloom?
- Video: Planting seeds (Clivia seeds)
Welcome to the ultimate guide to Clivia plants! Clivia, also known as Clivia miniata, is a beautiful flowering plant that has become popular among plant enthusiasts. Native to South Africa, Clivia plants are prized for their vibrant clusters of trumpet-shaped flowers in shades of red, orange, and yellow. In addition to their stunning blooms, Clivia plants also have elegant dark green foliage that adds to their overall appeal.
Caring for Clivia plants is relatively easy, making them a popular choice for both experienced gardeners and beginners. These plants prefer bright, indirect light and should be kept out of direct sunlight, as it can scorch their leaves. Clivia plants also prefer well-draining potting soil and should be watered regularly, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. However, they are also somewhat drought-tolerant, so it’s important not to overwater them.
Clivia plants are known for their long-lasting flowers, with blooms lasting for several weeks. Once the flowers have faded, it’s important to remove them to encourage new growth. Additionally, it’s recommended to fertilize Clivia plants once a month during the spring and summer months with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer. This will help to promote healthy foliage and future blooms.
There are several species and varieties of Clivia plants available, each with its own unique characteristics and color variations. Some popular species include Clivia miniata var. citrina, which has pale yellow flowers, and Clivia miniata var. aurea, which has golden yellow flowers. No matter which species you choose, Clivia plants are sure to add a touch of elegance and beauty to any indoor or outdoor space.
In this ultimate guide, we will explore in detail the care requirements of Clivia plants, along with tips for propagation, common pests and diseases, and how to successfully grow these stunning plants. We will also showcase stunning photos of various Clivia species to inspire you in your gardening journey.
Clivia (Clivia): Care, Photos, Species – The Ultimate Guide
Introduction
Clivia, also known as Clivia miniata, is a popular flowering plant native to southern Africa. It is loved for its vibrant flowers and its ability to thrive in low light conditions. In this ultimate guide, we will explore everything you need to know about caring for Clivia, including care tips, photos, and different species.
Care Tips
- Light: Clivia does best in bright, indirect light. Avoid placing it in direct sunlight as it can burn the leaves.
- Temperature: Clivia prefers temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C). It can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures, but avoid extreme heat or cold.
- Watering: Water your Clivia regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist. Avoid overwatering or letting the plant sit in standing water.
- Fertilization: Feed your Clivia with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer once a month during the growing season. Reduce or stop fertilization during the winter months.
- Repotting: Clivia plants prefer to be slightly root-bound, so only repot when necessary. Use a well-draining potting mix and repot during the spring.
Photos
Here are some photos of Clivia plants showcasing their stunning blooms:
 |  |
 |  |
Species
There are several different species of Clivia, each with their own unique characteristics. Here are some popular Clivia species:
- Clivia miniata: This is the most commonly cultivated species, known for its bright orange or red flowers.
- Clivia nobilis: This species has larger, yellow flowers and is native to the Eastern Cape region of South Africa.
- Clivia gardenii: Gardenii has smaller, pale orange flowers and is native to the coastal forests of South Africa.
- Clivia caulescens: This species has white or pale cream-colored flowers and is known for its long, strappy leaves.
Now that you have a better understanding of Clivia care, photos, and species, you can confidently care for your own Clivia plant and enjoy its beautiful blooms.
Clivia Care Tips
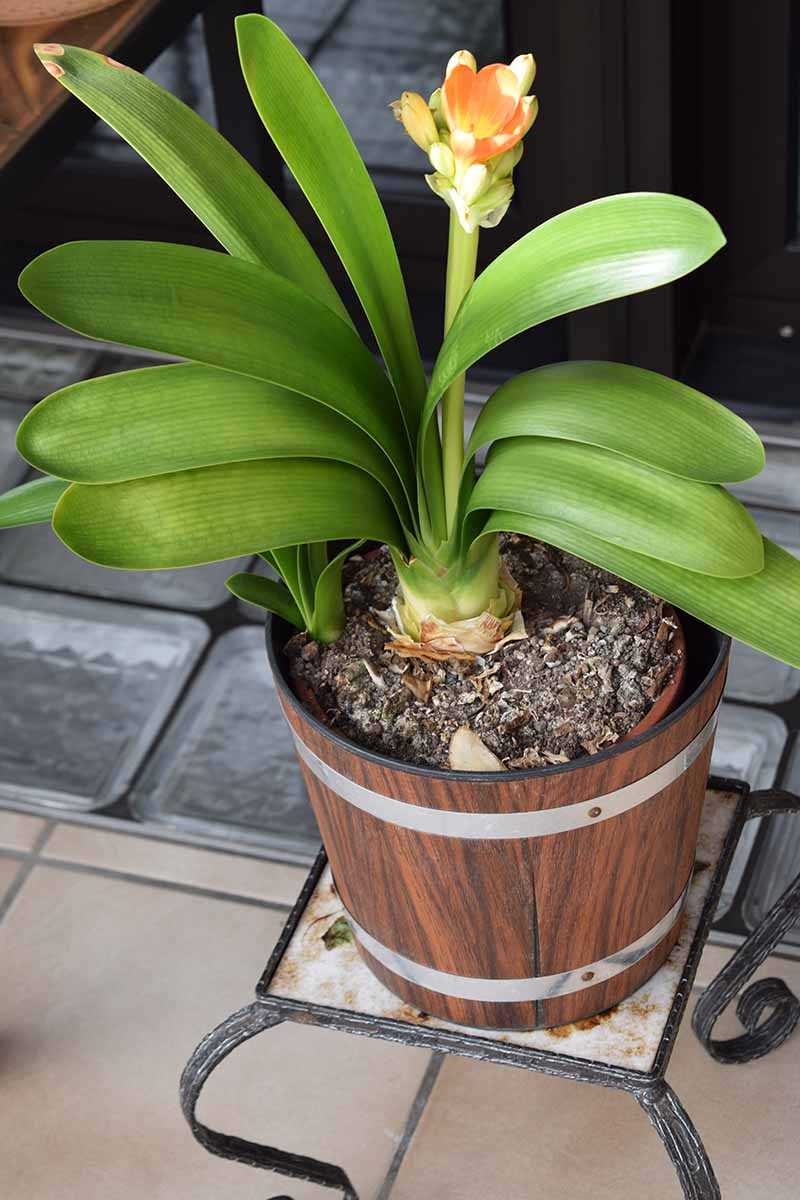

- Light: Clivias prefer bright, indirect light. Place them near a window where they can receive filtered sunlight. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
- Temperature: Clivias thrive in temperatures between 60-85°F (15-29°C). Keep them away from drafts and extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Watering: Water your Clivia when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Be careful not to overwater, as it can lead to root rot. Allow the excess water to drain out of the pot.
- Humidity: Clivias prefer moderate humidity levels. If the air in your home is too dry, you can place the plant on a tray filled with water and pebbles to increase humidity around it.
- Fertilizer: Feed your Clivia with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer every two weeks during the growing season (spring and summer). Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package.
- Pruning: Prune any yellow or damaged leaves to maintain the plant’s appearance. Remove spent flowers to encourage new bloom growth.
- Repotting: Clivias like to be slightly root-bound, so repotting is only necessary every 2-3 years. Use a well-draining potting mix to avoid waterlogged roots.
- Pests and Diseases: Clivias are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, they may occasionally get infested with mealybugs or scale insects. Treat infestations with insecticidal soap or a horticultural oil.
Following these care tips will help you keep your Clivia healthy and thriving. Enjoy the beautiful blooms and lush foliage of this stunning plant!
Clivia Species and Varieties
Clivia is a genus of flowering plants native to South Africa. There are several species and varieties of Clivia that are cultivated for their beautiful flowers and lush foliage. Here are some of the popular species and varieties:
1. Clivia miniata
Clivia miniata, also known as the Natal lily or bush lily, is the most common and widely cultivated species of Clivia. It has large clusters of trumpet-shaped flowers ranging in color from orange to red. The leaves are long and strap-shaped.
2. Clivia nobilis
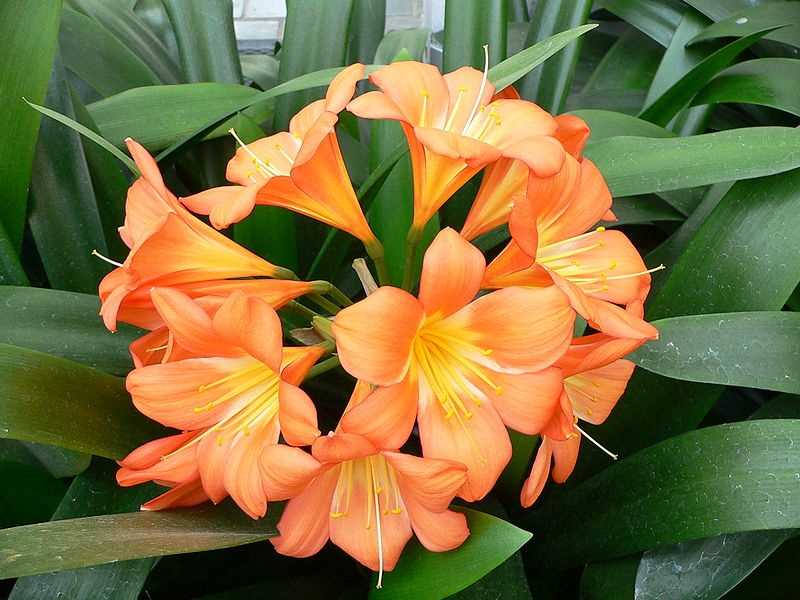

Clivia nobilis is a smaller species compared to the Clivia miniata. It has narrow, dark green leaves and produces small clusters of orange or red flowers. This species is known for its fragrant flowers.
3. Clivia caulescens
Clivia caulescens is a species with a more compact growth habit. It has broader leaves than Clivia miniata and produces sprays of orange flowers. This species is usually more tolerant of colder temperatures.
4. Clivia gardenii
Clivia gardenii is a species with smaller and narrower leaves compared to other Clivia species. It produces clusters of yellow or green-tinged flowers. This species is known for its delicate beauty.
5. Clivia x cyrtanthiflora
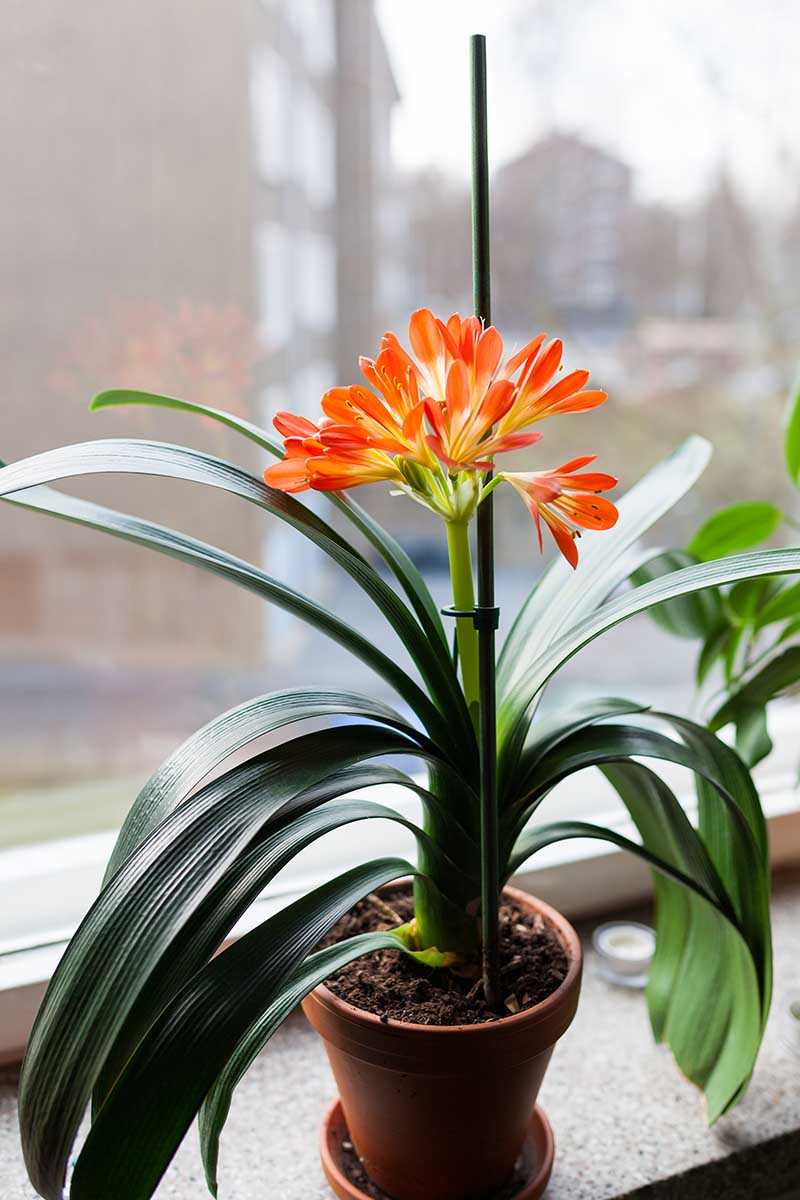

Clivia x cyrtanthiflora is a hybrid between Clivia miniata and Clivia nobilis. It inherits the large clusters of flowers from Clivia miniata and the fragrance from Clivia nobilis. The flowers can range in color from pale yellow to deep red.
In addition to these species, there are numerous cultivars and hybrids available in various sizes, colors, and flower forms. These include striped, variegated, and double-flowered varieties, to name a few.
When selecting Clivia plants, it’s important to consider their specific care requirements and the conditions in your garden or home. Each species and variety may have different preferences for light, temperature, and watering. Choose the ones that are best suited to your environment to ensure successful growth and beautiful blooms.
How to Propagate Clivia
Propagating Clivia can be done through a few different methods. Here are three common ways to propagate Clivia:
1. Division
Division is the most common and easiest way to propagate Clivia. This method is usually done in the spring when the plant is actively growing.
To propagate Clivia by division:
- Carefully remove the plant from its pot.
- Separate the bulbs or offsets that have formed at the base of the plant.
- Gently remove any excess soil and separate the bulbs or offsets.
- Plant each bulb or offset in its own pot, using a well-draining potting mix.
- Water the newly potted bulbs or offsets and place them in a location with bright, indirect light.
2. Leaf Cuttings
Clivia can also be propagated by leaf cuttings, although this method can be a bit more challenging.
To propagate Clivia by leaf cuttings:
- Select a healthy and mature leaf from the plant.
- Cut the leaf into sections, making sure each section has a small portion of the white base.
- Place the leaf sections in a tray with damp sand or a well-draining potting mix.
- Keep the tray in a warm and humid location, ideally with bottom heat.
- After a few weeks, roots should start to develop.
- Once the new plants have developed several leaves and a good root system, they can be potted into individual containers.
- Keep the newly potted plants in a warm and humid environment until they establish.
3. Seed Propagation
Propagation of Clivia via seeds is the most time-consuming method, as it can take several years for the plants to mature.
To propagate Clivia from seeds:
- Collect ripe seeds from the plant. The seeds are usually bright red or orange when they are mature.
- Clean the seeds and remove any pulp or flesh attached to them.
- Plant the seeds in a well-draining potting mix, covering them lightly with soil.
- Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged.
- Place the seed container in a warm and well-lit area, but out of direct sunlight.
- Germination may take several weeks to months.
- Once the seedlings have grown several leaves, they can be transplanted into individual pots.
Remember, no matter which propagation method you choose, patience is key. It can take some time for the new plants to establish and grow into mature Clivia plants.
Clivia Pests and Diseases
Clivias are generally hardy plants, but they can still be affected by pests and diseases. It is important to identify and treat these issues promptly to maintain the health and beauty of your Clivia plants.
Common Pests
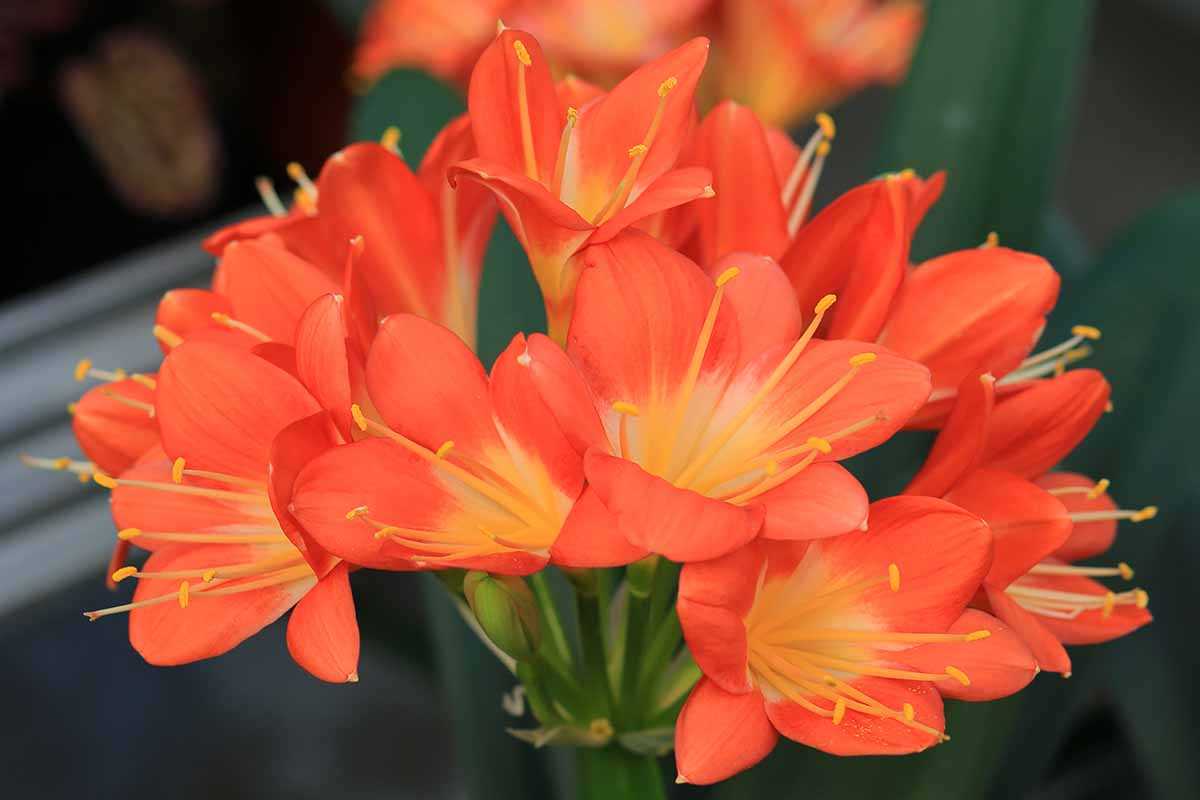

- Mealybugs: These small, white insects can infest the leaves and flowers of Clivias. They suck the sap from the plant, causing stunted growth and yellowing leaves. To control mealybugs, use a cotton swab soaked in rubbing alcohol to remove the insects or apply an organic insecticidal soap.
- Scale Insects: Scale insects appear as small brown bumps on the leaves and stems of Clivias. They feed on the sap of the plant, causing leaves to turn yellow and drop. Manual removal of the insects or using a horticultural oil spray can help control scale infestations.
- Aphids: Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that can cluster on new growth and flower buds of Clivias. They suck sap from the plant, causing distortion and yellowing of leaves. Natural predators such as ladybugs can help control aphid populations or use an insecticidal soap.
Common Diseases
- Leaf Spot: Leaf spot is a fungal disease that causes dark spots on the leaves of Clivias. To prevent leaf spot, ensure good air circulation around the plant and avoid overhead watering. Remove and destroy infected leaves. Fungicidal sprays may be necessary in severe cases.
- Root Rot: Root rot is caused by overwatering or poorly draining soil, leading to fungal infections. To prevent root rot, allow the soil to dry out between waterings and use well-draining soil. Trim and remove infected roots and repot the plant if necessary.
- Viral Infections: Viral infections can cause mottled or distorted growth in Clivias. There is no cure for viral infections, so infected plants should be removed and destroyed to prevent the spread of the virus to healthy plants.
Preventing Pests and Diseases

Here are some preventive measures you can take to keep your Clivias healthy:
- Inspect new plants before bringing them indoors to ensure they are pest-free.
- Keep the foliage dry by watering at the base of the plant.
- Ensure good air circulation around the plant.
- Remove dead leaves and spent flowers promptly.
- Provide regular fertilizer to promote overall plant health.
By being proactive in monitoring and caring for your Clivias, you can prevent and manage pests and diseases effectively, ensuring your plants thrive and flourish.
Clivia Potting and Soil Requirements

Choosing the right pot and soil for your Clivia plant is essential for its health and growth. Here are some tips on potting and soil requirements for Clivia:
Potting:
When choosing a pot for your Clivia, make sure it has drainage holes at the bottom. This will prevent water from pooling and causing root rot. A pot that is slightly larger than the current pot is ideal, allowing enough space for growth.
Clivia plants prefer to be slightly root-bound, so there’s no need to immediately repot a young plant into a larger pot. Repotting can be done every 2-3 years as the plant grows and fills the pot.
When repotting, use fresh potting mix and remove any dead or damaged roots. Gently tease the roots apart if they are tangled, being careful not to damage them.
Soil:
Clivia plants prefer a well-draining soil mix that is rich in organic matter. A recommended soil mix for Clivia is one part peat moss, one part perlite or sand, and one part well-rotted compost.
Make sure the soil mix is slightly acidic with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Using a pH testing kit can help you determine the acidity of your soil mix.
Watering:
Clivia plants prefer to be slightly dry between waterings. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases. Water your Clivia plant thoroughly, allowing the water to flow through the drainage holes, and then let the soil dry out slightly before watering again.
Fertilizer:

Fertilize your Clivia plant once a month during the growing season (usually spring and summer) with a balanced liquid fertilizer. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the correct dosage.
During the dormant season (usually autumn and winter), reduce fertilization to once every two months or stop fertilizing altogether.
Following these potting and soil requirements will help ensure that your Clivia plant thrives and produces beautiful blooms.
Clivia Flowering and Blooming Season
Clivia is a beautiful flowering plant that is known for its vibrant and colorful flowers. The plant typically blooms once a year, usually in the spring or early summer. However, the blooming season may vary depending on the specific species and growing conditions.
During the flowering season, the clivia plant produces large clusters of trumpet-shaped flowers. These flowers can range in color from orange and yellow to red and even white. The flowers are also fragrant, adding to their appeal.
In order to promote blooming, it is important to provide the clivia plant with the right care and conditions. This includes providing the plant with proper sunlight, water, and fertilizer. The plant also requires a period of dormancy in order to stimulate blooming.
Factors that affect Clivia blooming season:

- Light: Clivia plants require bright, indirect light in order to bloom. Too much direct sunlight can scorch the leaves and inhibit flowering. Providing the plant with 12 to 14 hours of bright light each day is ideal.
- Temperature: Clivia plants prefer temperatures between 60°F (15°C) and 70°F (21°C) during their blooming season. Extreme temperature fluctuations can negatively affect flower production.
- Watering: It is important to water the clivia plant consistently during the blooming season. Water the plant when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch, but avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
- Fertilizer: Applying a balanced fertilizer during the blooming season can help promote flower production. Use a fertilizer with a higher phosphorus content to support blooming.
- Dormancy: Clivia plants require a period of dormancy in order to stimulate blooming. This typically occurs in the fall or winter, when the plant should be kept in a cool location with reduced watering and light.
By providing the clivia plant with the right care and conditions, you can ensure a healthy blooming season and enjoy the beautiful flowers it produces.
Clivia is a truly stunning plant that can brighten up any space with its vibrant flowers. Whether you have a green thumb or are a beginner gardener, the clivia plant is a great choice for adding color and beauty to your home or garden.
Clivia Photo Gallery
Take a look at these beautiful photos of Clivia plants:
Clivia miniata
Also known as the Bush Lily, this species is native to South Africa. It is characterized by its bold orange flowers and glossy dark green leaves.

Clivia nobilis
Native to the eastern regions of South Africa, this species has delicate clusters of red tubular flowers and long, strap-like leaves.

Clivia caulescens
This species is known for its unique pendant-shaped red flowers and narrow, arching leaves. It is endemic to the Eastern Cape province of South Africa.

Clivia plants are not only beautiful but also relatively easy to care for. These photos showcase the stunning diversity within the Clivia genus and will surely inspire any plant lover.
Q&A:
What is Clivia?
Clivia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to southern Africa and is popular for its beautiful flowers and lush foliage.
How do I care for Clivia plants?
Clivia plants require bright but indirect light, regular watering, and well-draining soil. They prefer temperatures between 60 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit and can be fertilized monthly during the growing season with a balanced fertilizer.
Are there different species of Clivia?
Yes, there are several different species of Clivia, including Clivia miniata, Clivia gardenii, and Clivia nobilis. Each species has its own unique characteristics and growing requirements.
Can Clivia plants be grown indoors?
Yes, Clivia plants can be grown indoors as long as they receive enough light. They prefer a well-lit location near a window, but be cautious of direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
How often should I water Clivia plants?
Clivia plants should be watered regularly, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so it’s important not to let the plant sit in standing water.
How long does it take for Clivia plants to bloom?
Clivia plants typically take three to five years to reach maturity and produce their first blooms. However, this can vary depending on the growing conditions and care provided.
Video:
Planting seeds (Clivia seeds)