- Benefits of Growing Clivia Plants
- 1. Beautiful and Vibrant Blooms
- 2. Low Maintenance
- 3. Air Purification
- 4. Long Blooming Period
- 5. Low Allergenicity
- 6. Versatile Use
- 7. Propagation
- How to Grow Clivia Plants
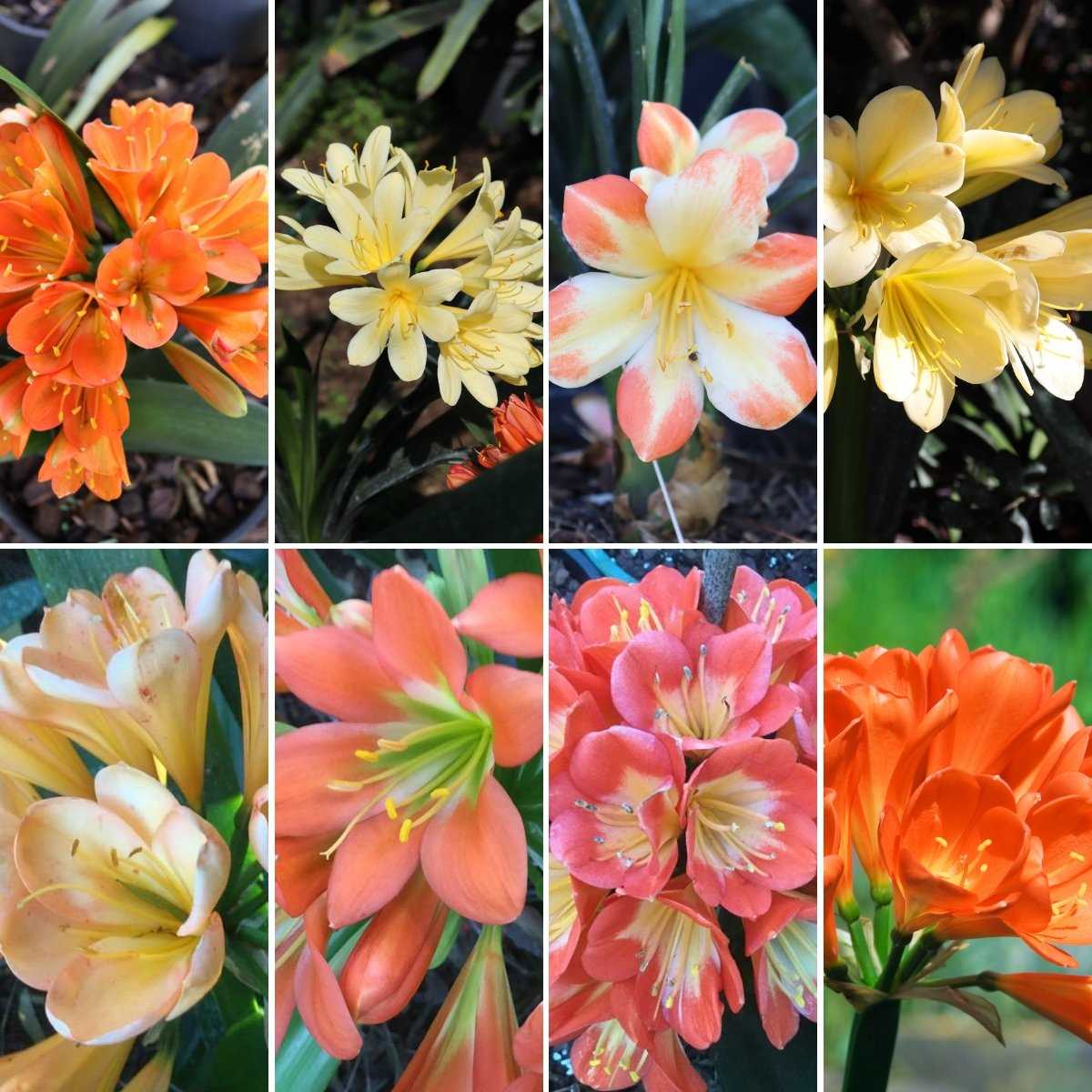
- Different Types of Clivia Plants
- 1. Clivia miniata
- 2. Clivia nobilis
- 3. Clivia gardenii
- 4. Clivia caulescens
- 5. Clivia mirabilis
- 6. Clivia robusta
- 7. Clivia cyrtanthiflora
- Popular Varieties of Clivia Plants
- Expert Tips for Growing Clivia Plants
- 1. Light
- 2. Temperature
- 3. Watering
- 4. Soil
- 5. Fertilizer
- 6. Humidity
- 7. Repotting
- 8. Propagation
- 9. Pest control
- 10. Blooming
- Common Issues in Clivia Plant Care
- 1. Overwatering
- 2. Underwatering
- 3. Insufficient Light
- 4. Pests
- 5. Lack of Fertilization
- 6. Improper Temperature
- 7. Lack of Dormancy
- Clivia Plant Propagation Methods
- 1. Division
- 2. Seed Propagation
- 3. Offshoot Planting
- Q&A:
- What is Clivia?
- How do I grow Clivia?
- Can I grow Clivia indoors?
- What types of Clivia are there?
- How long does it take for Clivia to flower?
- Video: Clivia : Care and Growing Tips
Clivia is a popular flowering plant that is known for its vibrant and colorful blooms. Native to South Africa, this plant belongs to the Amaryllidaceae family and is commonly grown in gardens and as houseplants around the world. Its striking flowers and easy cultivation make it a favorite among gardeners and plant enthusiasts.
There are several types and varieties of Clivia, each with its unique characteristics and requirements. The most common type is Clivia miniata, which is known for its bright orange or red blooms. This variety is relatively easy to grow and is often used as an indoor plant.
In addition to Clivia miniata, there are other species and hybrids available, such as Clivia nobilis and Clivia caulescens. These varieties can have different flower colors and sizes, ranging from yellow to peach and even white. Some Clivia varieties also produce fragrant blooms, adding another layer of charm to this already beautiful plant.
Growing Clivia requires a few specific conditions to thrive. It prefers indirect sunlight and well-draining soil, and it is important to water the plant regularly without overwatering. Clivia is also a slow-growing plant, so patience is key when cultivating it. With proper care and attention, Clivia can reward gardeners with stunning blooms that brighten up any space.
Whether you are a seasoned plant enthusiast or just starting your gardening journey, this expert guide on growing Clivia will provide valuable information to help you successfully cultivate and enjoy this unique and beautiful plant.
Benefits of Growing Clivia Plants
Growing Clivia plants in your garden or indoor space brings a wide range of benefits. These beautiful flowering plants offer both aesthetic and practical advantages, making them a popular choice for plant lovers.
1. Beautiful and Vibrant Blooms
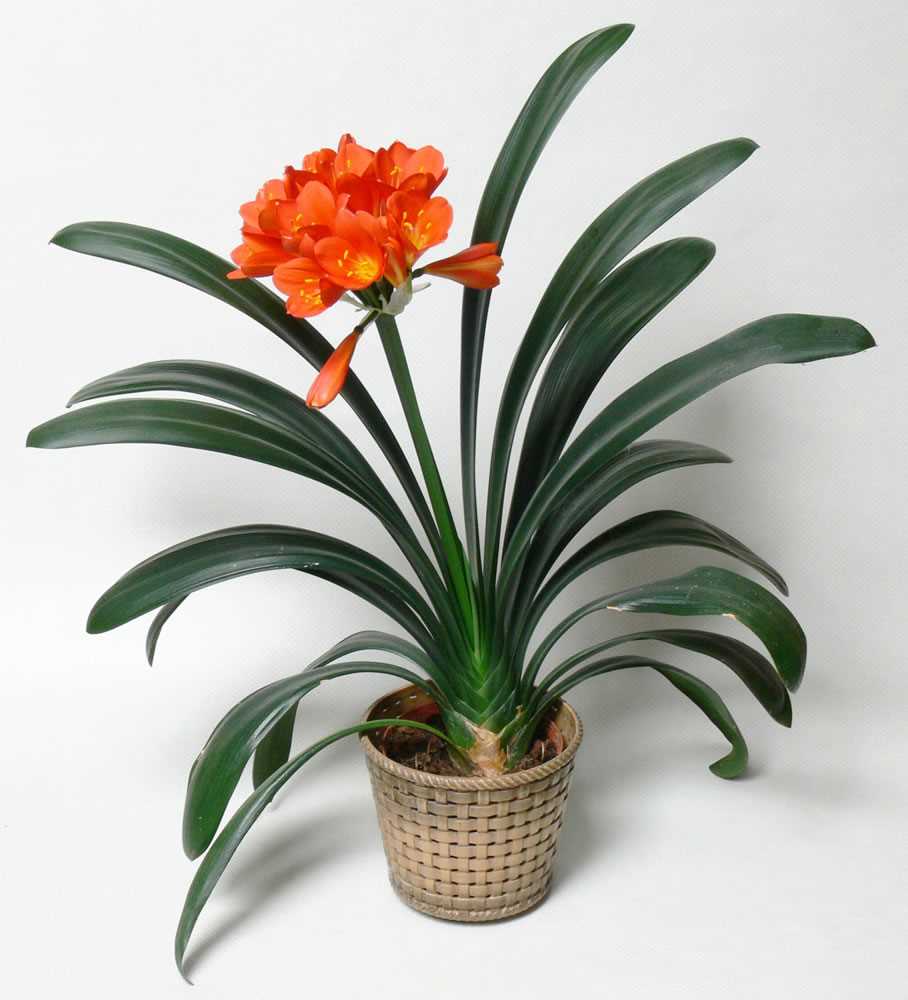
Clivia plants produce stunning blooms in shades of orange, yellow, red, and even white. These vibrant flowers add a pop of color to any space and create a visually appealing focal point in your garden or home.
2. Low Maintenance
Clivia plants are known for being relatively easy to care for. They do well in a variety of environments and can tolerate lower light conditions. With proper watering and occasional fertilization, Clivia plants can thrive with minimal effort.
3. Air Purification
Like many other houseplants, Clivia plants help improve the air quality in your home. They naturally remove toxins from the air and release oxygen, creating a healthier indoor environment. This can have a positive impact on your overall well-being.
4. Long Blooming Period
Clivia plants have a long blooming period, typically lasting several weeks to months. This extended flowering time allows you to enjoy their beautiful blooms for an extended period, adding natural beauty to your space.
5. Low Allergenicity
For individuals with allergies or sensitivities, Clivia plants are a great choice. They have low allergenicity, meaning they are less likely to trigger allergic reactions. This makes them a suitable option for allergy sufferers who still want to enjoy the benefits of indoor plants.
6. Versatile Use
Clivia plants can be grown both indoors and outdoors, making them highly versatile. They can be used as potted plants, garden plants, or even as cut flowers for floral arrangements. Their versatility allows you to incorporate them in various settings and designs.
7. Propagation
Clivia plants are relatively easy to propagate, making them an excellent choice for plant enthusiasts who enjoy propagation. They can be propagated through division or by collecting and planting their seeds. This allows you to expand your Clivia collection or share the plants with friends and family.
In conclusion, growing Clivia plants offers numerous benefits, including beautiful blooms, low maintenance care, air purification, a long blooming period, low allergenicity, versatile use, and the opportunity for propagation. Consider adding these stunning plants to your indoor or outdoor space to enjoy all the advantages they bring.
How to Grow Clivia Plants
- Choose a suitable location for your Clivia plant. It prefers an area with bright, indirect sunlight.
- Prepare the soil by mixing in organic matter such as compost or peat moss to improve drainage and fertility.
- Plant the Clivia bulb or division in the prepared soil. Make sure to bury it shallowly, with the top of the bulb or division just above the soil surface.
- Water the plant regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overwatering as this can cause root rot.
- Feed the plant with a balanced fertilizer during the growing season, following the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates.
- Provide support for the Clivia plant by staking it if necessary, especially as the flowers develop.
- Keep the plant in a temperature range of 65-75°F (18-24°C) during the day and around 60°F (15°C) at night.
- Protect the plant from extreme temperatures, frost, and direct sunlight, as these can damage or kill the plant.
- Monitor the plant for pests such as aphids or mealybugs, and treat with appropriate insecticides if necessary.
- Prune the plant as needed to remove dead or damaged leaves, but avoid excessive pruning as this can inhibit flower formation.
By following these basic guidelines, you can successfully grow Clivia plants and enjoy their beautiful flowers year after year.
Different Types of Clivia Plants
Clivia plants are popular houseplants known for their vibrant flowers and sturdy leaves. There are several types and varieties of Clivia plants, each with unique characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Clivia miniata
Clivia miniata is the most widely known and cultivated species of Clivia. It features large clusters of trumpet-shaped flowers in vibrant shades of orange or red. The leaves are dark green and arch gracefully.
2. Clivia nobilis
Clivia nobilis is a smaller species with more slender leaves compared to Clivia miniata. It produces clusters of small, tubular flowers in shades of yellow or orange. This species is native to South Africa.
3. Clivia gardenii
Clivia gardenii has narrower leaves and smaller flowers compared to Clivia miniata. The flowers are usually yellow or pale orange. This species is more tolerant of lower light conditions.
4. Clivia caulescens

Clivia caulescens is a larger species with broader leaves and clusters of small, tubular flowers. The flowers range in color from pale yellow to vibrant orange. This species is native to the Eastern Cape province in South Africa.
5. Clivia mirabilis
Clivia mirabilis is a rarer species with narrow, upright leaves and trumpet-shaped flowers. The flowers can be various shades of red, yellow, or orange. This species is known for its unique and striking flower shape.
6. Clivia robusta
Clivia robusta is a special clivia species that can tolerate full sun exposure. It has broader, more upright leaves compared to other species. The flowers are usually orange, but there can also be variations in color.
7. Clivia cyrtanthiflora
Clivia cyrtanthiflora is a rare species that features long, tubular flowers in shades of red and yellow. The leaves are narrow and elongated. This species is native to the forests of Mpumalanga and Swaziland.
These are just a few examples of the different types of Clivia plants available. Each species has its own unique beauty and characteristics, making them a delightful addition to any indoor plant collection.
Popular Varieties of Clivia Plants
Clivia plants come in a variety of colors and sizes. Here are some popular varieties that have gained popularity among gardeners:
- Clivia Miniata: This is the most commonly found variety of Clivia. It has bright orange or red flowers that are trumpet-shaped. The leaves of Clivia Miniata are dark green and strap-like.
- Clivia Nobilis: This variety is known for its fragrant flowers, which can be white, yellow, or pale orange. The leaves of Clivia Nobilis are lighter green and narrower compared to other varieties.
- Clivia Gardenii: Gardenii is a smaller variety of Clivia with narrower leaves and smaller flowers. The flowers of Clivia Gardenii are usually yellow and have a sweet fragrance.
- Clivia Mirabilis: Mirabilis is a rare variety of Clivia that is native to South Africa. It has tubular-shaped yellow flowers and wide, dark green leaves.
In addition to these popular varieties, there are also hybrid varieties of Clivia plants available in various colors and patterns. These hybrids are created by crossing different Clivia species to produce new and unique characteristics.
Clivia plants are known for their ability to thrive in shady areas and their stunning floral displays. Whether you choose a traditional variety or a hybrid, Clivia plants are sure to add beauty and elegance to your garden or indoor space.
Expert Tips for Growing Clivia Plants
1. Light
Clivia plants thrive in bright, indirect light. Place them near a north or east-facing window to provide them with enough light to grow. Avoid placing them in direct sunlight as it can scorch the leaves.
2. Temperature
Clivia plants prefer temperatures between 60°F and 80°F (15°C and 27°C). They can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures in the winter, but avoid exposing them to temperatures below 50°F (10°C) for an extended period.
3. Watering
Water your Clivia plants thoroughly when the top inch (2.5 cm) of soil feels dry to the touch. Allow the excess water to drain out from the bottom of the pot and never let the plant sit in standing water, as it can lead to root rot.
4. Soil
Use a well-draining potting mix for your Clivia plants. A mix of peat moss, perlite, and sand works well. This type of soil will allow the roots to breathe and prevent waterlogged conditions.
5. Fertilizer
Feed your Clivia plants with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer once a month during the growing season (spring and summer). Dilute the fertilizer to half the recommended strength to avoid overfeeding. Do not fertilize during the winter months.
6. Humidity

Clivia plants prefer moderate humidity levels. If the air is too dry, consider using a humidifier or placing a tray with water near the plant to increase the humidity. Mist the leaves occasionally to provide some moisture.
7. Repotting
Clivia plants generally do not require frequent repotting. Repot them only when the roots become crowded and fill the pot. Spring is the best time for repotting, using a slightly larger pot to accommodate the growth.
8. Propagation
Clivia plants can be propagated through division. Divide the plant every 3 to 5 years in the spring. Gently separate the offsets from the main plant and replant them in their own pots using a well-draining potting mix.
9. Pest control
Monitor your Clivia plants for common pests such as mealybugs and spider mites. If necessary, treat the infestation with an appropriate insecticide or use natural remedies like neem oil or insecticidal soap.
10. Blooming
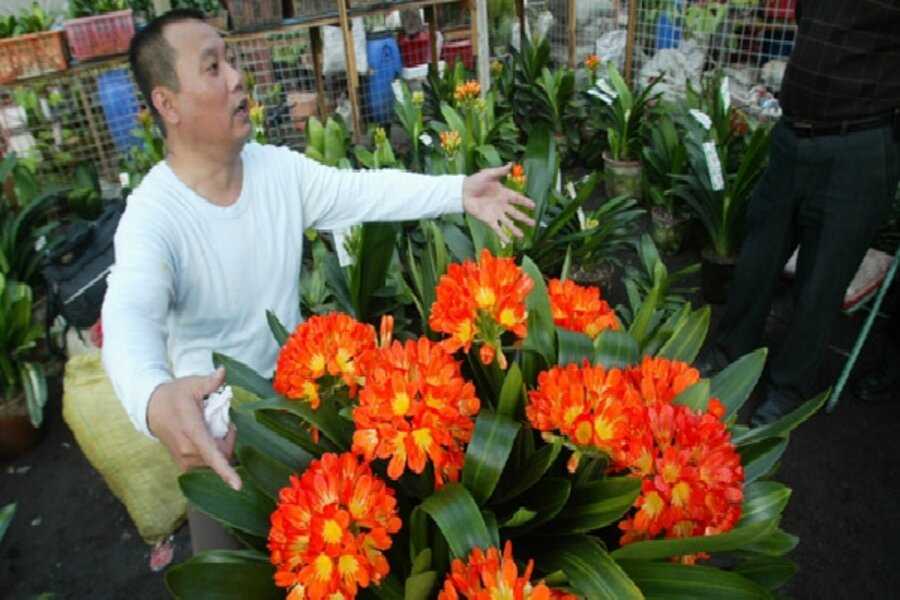

Clivia plants typically bloom in the late winter or early spring. To encourage blooming, the plant needs a period of cooler temperatures (around 50°F or 10°C) for about 6 weeks in the fall. Limit watering and avoid fertilizing during this time to initiate flower development.
Common Issues in Clivia Plant Care
Despite their hardy nature, Clivia plants can still encounter some common issues that may affect their growth and overall health. It’s important to identify and address these issues promptly to ensure the well-being of your Clivia plant.
1. Overwatering
Overwatering is one of the most common mistakes when it comes to Clivia plant care. These plants prefer to be kept slightly on the dry side, so excessive watering can lead to root rot and other problems. Allow the top inch of soil to dry out before watering again, and ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogged conditions.
2. Underwatering
On the other hand, underwatering can also be detrimental to Clivia plants. While they don’t require constant moisture, they still need regular watering to thrive. Monitor the moisture level of the soil, and water when the top inch feels dry. Avoid letting the plant sit in dry soil for extended periods.
3. Insufficient Light
Clivia plants require bright, indirect light to grow and flower. Insufficient light can result in weak growth and reduced flowering. Place your Clivia plant near a north or east-facing window where it can receive bright, filtered light. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
4. Pests
Like any plant, Clivia plants can also fall victim to pest infestations. Common pests that may affect Clivias include aphids, mealybugs, and scale insects. Regularly inspect your plant for any signs of pests, such as sticky residue or unusual discoloration. Treat any infestations promptly with an appropriate insecticide.
5. Lack of Fertilization
Clivia plants benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season to support healthy growth and flowering. Use a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for houseplants, and apply according to the package instructions. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to salt buildup and nutrient toxicity.
6. Improper Temperature
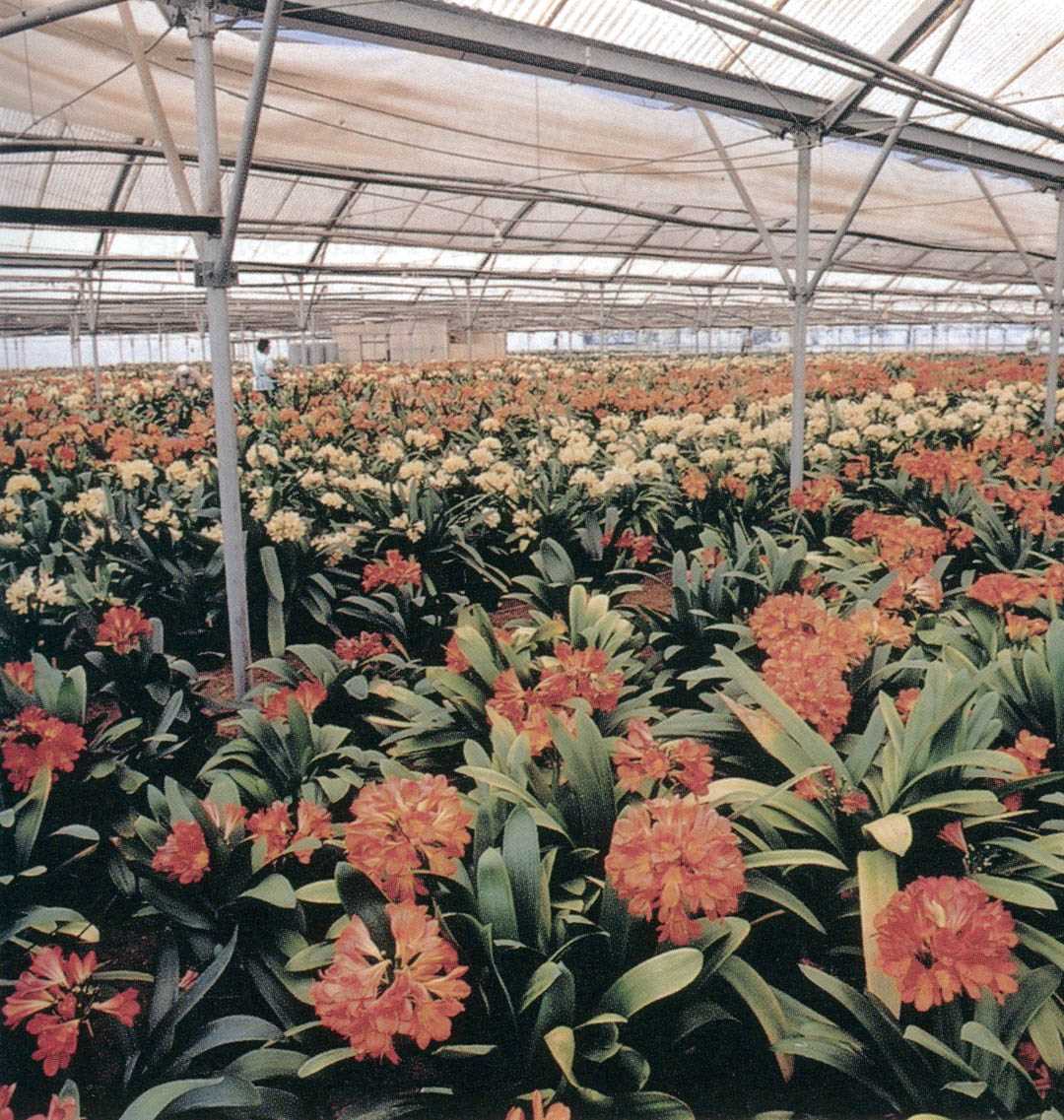

Clivia plants prefer moderate temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). Extreme heat or cold can stress the plant and inhibit its growth. Avoid placing your Clivia plant near drafts or heaters, as rapid temperature fluctuations can also negatively impact its health.
7. Lack of Dormancy
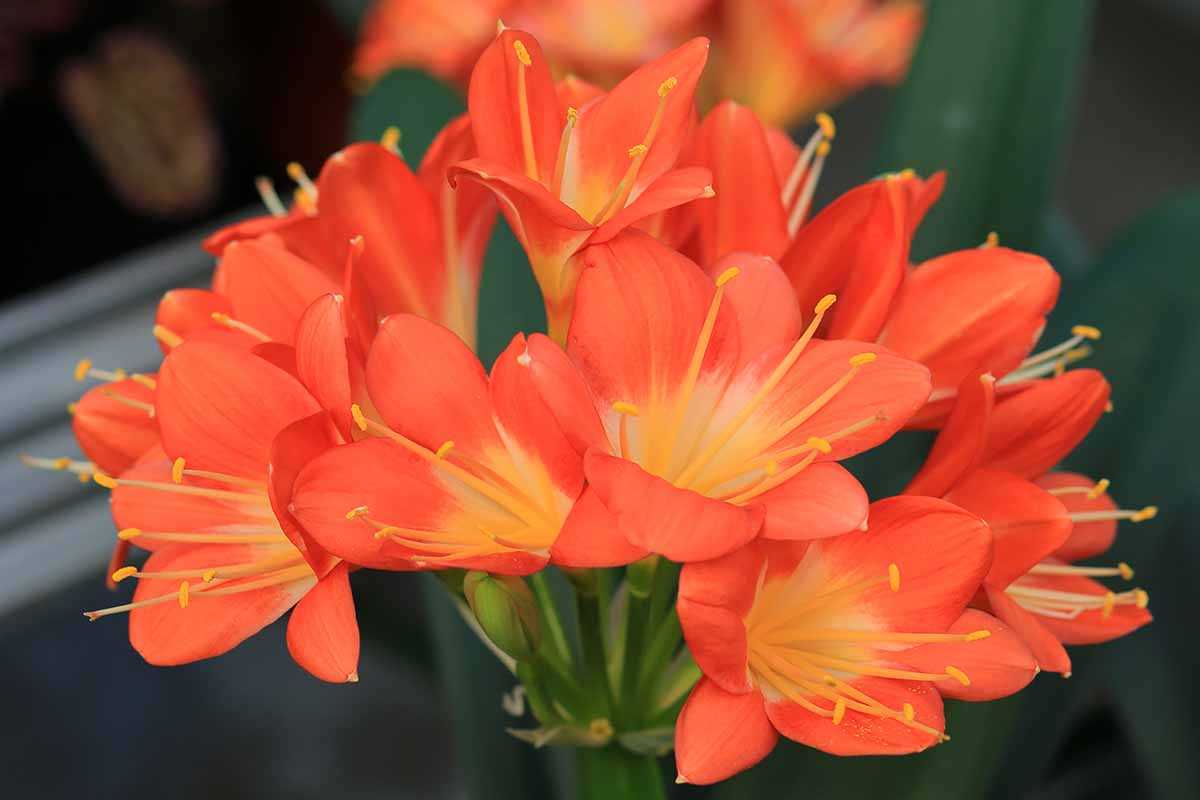

Clivia plants require a period of dormancy to flower successfully. During the winter months, reduce watering and move the plant to a cooler location (around 50-55°F or 10-13°C). This dormant period is essential for the plant to store energy and prepare for flowering. Avoid disturbing the plant during this time.
By addressing these common issues promptly and providing proper care, you can ensure the long-term health and beauty of your Clivia plant. With patience and attention, you’ll be rewarded with stunning blooms and lush foliage.
Clivia Plant Propagation Methods
Clivia plants can be propagated using several different methods. Here are three common methods of propagating Clivia plants:
1. Division
Division is the most common method of propagating Clivia plants. It involves separating and replanting the offshoots or divisions that grow from the main plant. To propagate Clivia using division, follow these steps:
- Select a mature Clivia plant with several healthy offshoots.
- Carefully dig up the plant, trying not to damage the roots.
- Gently separate the offshoots from the main plant, ensuring that each division has its own roots.
- Plant each division in a separate pot, making sure to cover the roots with soil.
- Water the newly planted divisions thoroughly and place them in a bright, shaded area.
- Continue to water the divisions regularly and provide them with the proper care to encourage growth.
2. Seed Propagation
Propagation from seeds is another method of growing Clivia plants. Here’s how to propagate Clivia using seeds:
- Collect ripe Clivia seeds from the flowerheads.
- Remove the outer coating of the seed, being careful not to damage the inner embryo.
- Fill a seed tray or pot with a well-draining potting mix.
- Place the seeds on the surface of the potting mix, spacing them apart.
- Lightly cover the seeds with a thin layer of potting mix.
- Water the seeds gently, ensuring that the potting mix remains moist but not waterlogged.
- Keep the seed tray or pot in a warm, well-lit area, away from direct sunlight.
- Monitor the seeds closely, and as soon as they germinate, provide them with proper care, including regular watering and fertilizing.
3. Offshoot Planting
Offshoot planting is another easy way to propagate Clivia plants. Here’s how to do it:
- Identify healthy offshoots or suckers growing from the main plant.
- With a sharp, clean knife, cut off the offshoots from the main plant, ensuring that each offshoot has its own roots.
- Plant the offshoots directly into pots or in well-prepared garden soil.
- Water the newly planted offshoots thoroughly and place them in a shaded area.
- Continue to water the offshoots regularly and provide them with the necessary care to promote growth.
By following these propagation methods, you can easily multiply your Clivia plants and enjoy their beautiful flowers year after year.
Q&A:
What is Clivia?
Clivia is a genus of flowering plants native to southern Africa. It belongs to the family Amaryllidaceae and is known for its beautiful, trumpet-shaped flowers.
How do I grow Clivia?
Growing Clivia is relatively easy. They prefer bright but indirect sunlight, and should be grown in well-draining soil. Water them regularly, but allow the soil to dry out between waterings. Clivia also benefit from regular fertilizing during the growing season.
Can I grow Clivia indoors?
Yes, Clivia can be grown indoors as long as they receive enough bright, indirect sunlight. They can be placed near a window or under artificial grow lights. Indoor Clivia may require more frequent watering due to the drier indoor air.
What types of Clivia are there?
There are several different types of Clivia, including Clivia miniata, Clivia gardenii, and Clivia nobilis. Each type has its own unique characteristics and flower colors.
How long does it take for Clivia to flower?
Clivia plants usually take around 3-4 years to reach maturity and start blooming. Once they reach maturity, they typically flower once a year in late winter or early spring.
Video:
Clivia : Care and Growing Tips