- Environmental Impact of Conventional Farming
- 1. Soil Degradation
- 2. Water Pollution
- 3. Loss of Biodiversity
- 4. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- 5. Wildlife Harm
- Benefits of Organic Farming
- Cost Considerations of Conventional Farming
- 1. Initial Investment
- 2. Equipment and Technology
- 3. Productivity and Yield
- 4. Labor Costs
- 5. Certification and Compliance
- 6. Market Demand and Price
- Health Effects of Organic Farming
- Better Nutritional Content
- No Chemical Residues
- Reduced Risk of Antibiotic Resistance
- No Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
- Beneficial for Environmental Health
- Potential Health Benefits for Farmers
- Pesticide Use in Conventional Farming
- Soil Health in Organic Farming
- GMOs in Conventional Farming
- Questions and Answers:
- What is conventional farming?
- What is organic farming?
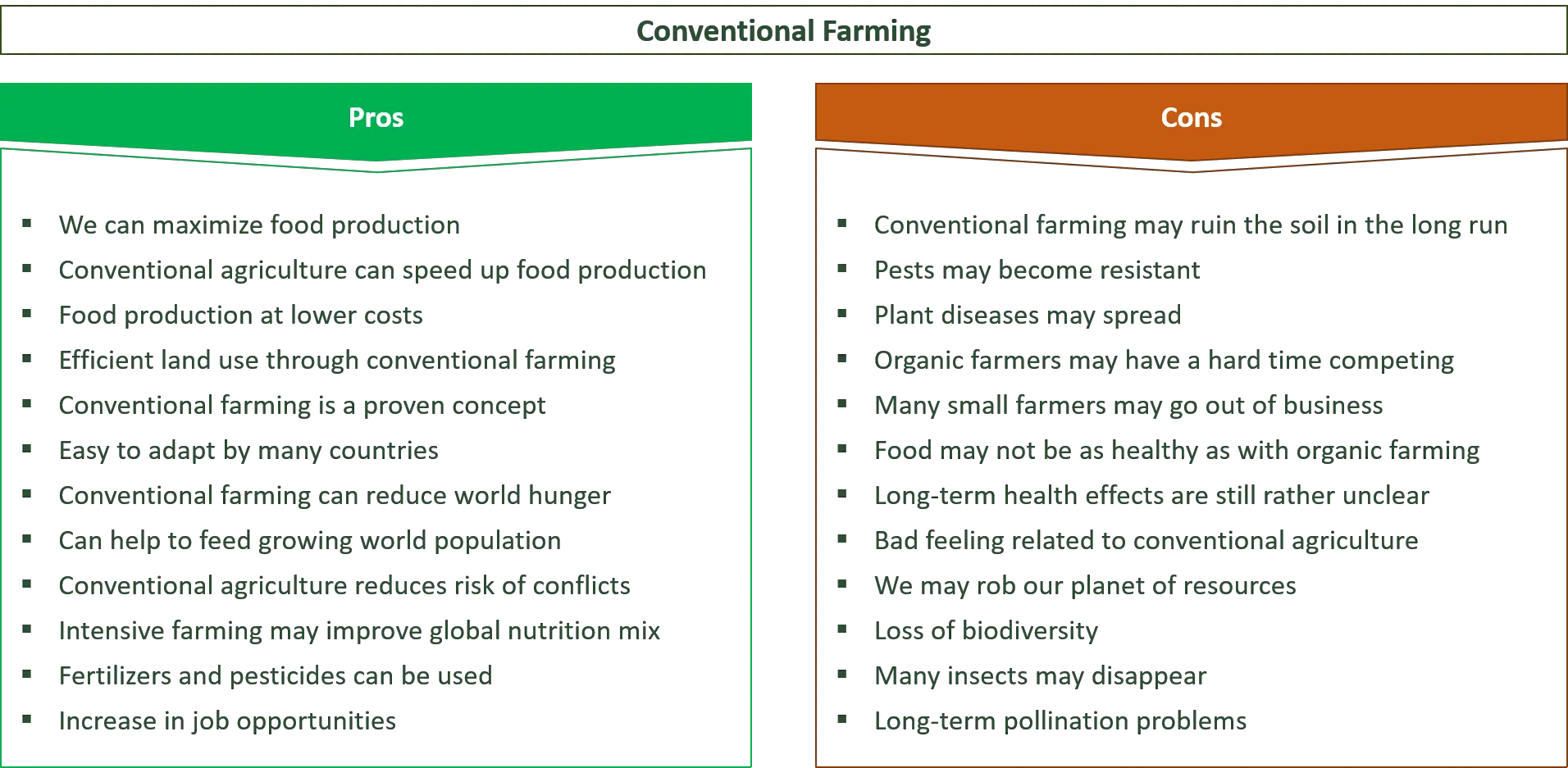
- What are the pros of conventional farming?
- What are the cons of conventional farming?
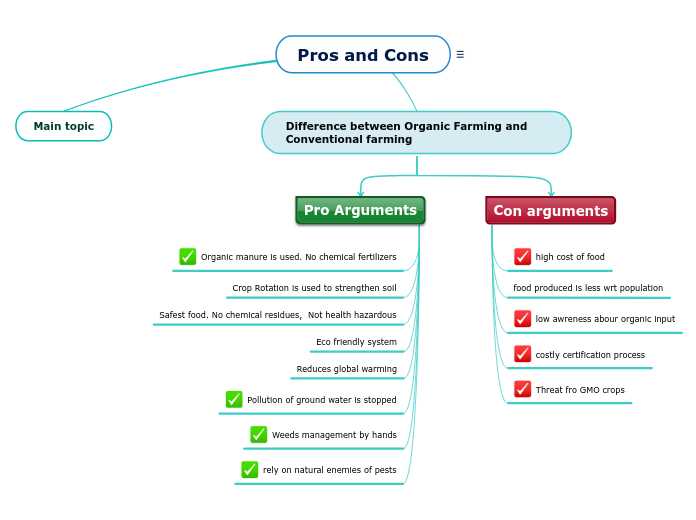
- What are the pros of organic farming?
- What are the cons of organic farming?
- Videos: Are GMOs Good or Bad? Genetic Engineering & Our Food
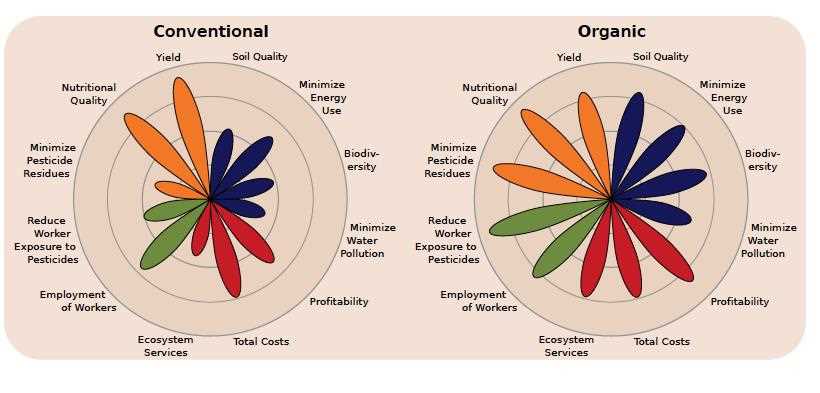
When it comes to agriculture, there are two main approaches: conventional farming and organic farming. Both methods have their pros and cons, and understanding the differences between them is crucial for making informed decisions about the food we consume.
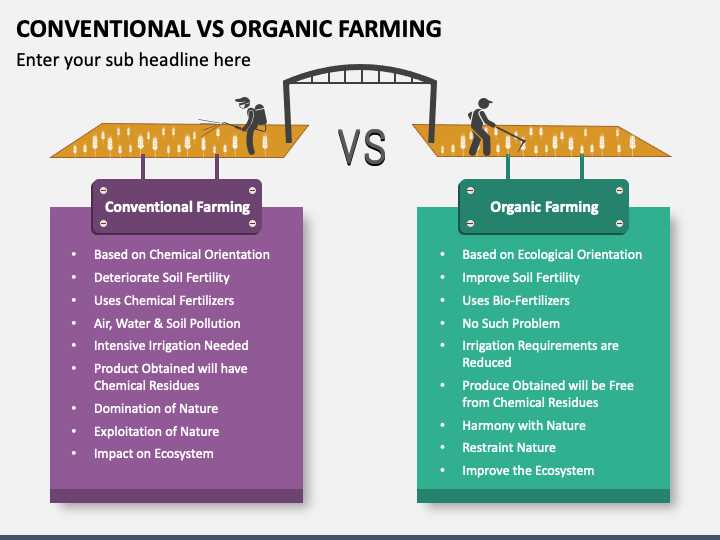
Conventional farming, also known as industrial or traditional farming, is the most common approach to agriculture worldwide. It relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to enhance crop yields and minimize losses to pests and diseases. Conventional farming practices often involve monocultures, where a single crop is grown on a large scale, and the use of heavy machinery to increase efficiency.
Organic farming focuses on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. It avoids the use of synthetic chemicals, GMOs, and promotes biodiversity and soil fertility. Organic farmers rely on natural fertilizers, such as compost and manure, as well as biological pest control methods. Crop rotation is commonly practiced, which helps prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
In recent years, organic farming has gained popularity due to increasing consumer demand for pesticide-free and environmentally friendly products. However, conventional farming has its proponents, who argue that it is more efficient in terms of crop yields and can better meet the growing global food demand.
With both approaches having their advantages and disadvantages, it is important to weigh the pros and cons of each when it comes to choosing the best method for farming.
Environmental Impact of Conventional Farming
Conventional farming practices have a significant impact on the environment. Let’s explore some of the key environmental concerns associated with conventional farming.
1. Soil Degradation
Conventional farming methods often rely on the extensive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can lead to soil degradation. These chemicals can kill beneficial microorganisms in the soil, decrease soil fertility, and contribute to erosion. Over time, this can result in reduced soil quality and productivity.
2. Water Pollution
Another environmental impact of conventional farming is water pollution. The excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can contaminate nearby water sources. When it rains, these chemicals can be washed off the fields and enter rivers, lakes, and groundwater. This pollution can harm aquatic ecosystems, kill fish, and make water unsafe for drinking or recreational activities.
3. Loss of Biodiversity
Conventional farming practices, such as monocropping, can lead to a loss of biodiversity. Monocropping involves planting large areas of land with a single crop, which reduces the variety of plants and habitats available for wildlife. This can disrupt natural ecosystems and decrease populations of beneficial insects, birds, and other animals.
4. Greenhouse Gas Emissions

Conventional farming contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through the use of synthetic fertilizers and machinery. The production, transport, and application of these fertilizers require energy, often derived from fossil fuels, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Furthermore, conventional farming practices may lead to deforestation, another significant source of greenhouse gas emissions.
5. Wildlife Harm
The use of pesticides in conventional farming can harm wildlife, including beneficial insects, birds, and mammals. Pesticides designed to kill pests can also have unintended consequences for non-target species. For example, bees and other pollinators can be negatively affected by pesticide exposure, which can have far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and food production.
It is essential to consider these environmental impacts when evaluating the sustainability and long-term viability of conventional farming practices. Finding ways to mitigate these impacts and transitioning to more sustainable agricultural systems is crucial for the health of our planet.
Benefits of Organic Farming
Environmental Sustainability: One of the key benefits of organic farming is its focus on environmental sustainability. Organic farmers use natural methods to promote soil health, prevent water pollution, and conserve biodiversity. By avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic farming contributes to the preservation of ecosystems and the reduction of the agricultural industry’s impact on climate change.
Healthier Food: Organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural soil amendments, crop rotation, and biological pest control methods, resulting in healthier food. Organic fruits, vegetables, and animal products are often higher in nutrients, free from residues of synthetic chemicals, and produced without the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Improved Soil Quality: Organic farming techniques, such as composting and the use of cover crops, contribute to the improvement of soil quality. These practices enhance soil fertility, structure, and water-holding capacity, promoting long-term soil health and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
Biodiversity Preservation: By avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides and relying on natural pest control methods, organic farming systems support biodiversity conservation. Organic farms provide suitable habitats for various beneficial insects, birds, and wildlife, fostering a more balanced and resilient ecosystem.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Organic farming methods minimize the use of synthetic chemicals, which can have negative effects on water quality, wildlife, and non-target organisms. By reducing pesticide and fertilizer use, organic farming significantly decreases the environmental impact associated with conventional agricultural practices.
Support for Rural Communities: Organic farming can offer economic opportunities for small-scale and local farmers. By promoting sustainable agricultural practices, organic farming helps to create jobs and stimulate rural economies, while also promoting food security and reducing dependency on external inputs.
Overall, organic farming offers numerous benefits for the environment, human health, and rural communities. By adopting organic farming practices, we can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system for future generations.
Cost Considerations of Conventional Farming
Conventional farming is often seen as a more cost-effective option compared to organic farming. Here are some key cost considerations to take into account when it comes to conventional farming:
1. Initial Investment
Conventional farming generally requires a lower initial investment compared to organic farming. This is because conventional farmers rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which tend to be cheaper and more readily available than their organic counterparts.
2. Equipment and Technology
Conventional farming often relies on heavy machinery and advanced technologies to increase efficiency and productivity. While these equipment and technologies can be expensive to purchase and maintain, they can also significantly reduce labor costs in the long run.
3. Productivity and Yield
Conventional farming methods, such as the use of genetically modified crops and high-yielding varieties, are known to result in higher crop productivity and higher yields compared to organic farming. This higher productivity can help offset the lower initial investment and equipment costs.
4. Labor Costs
Conventional farming typically requires less manual labor compared to organic farming. This is because conventional farmers rely on synthetic chemicals to control pests and weeds, reducing the need for extensive hand labor. As a result, labor costs may be lower in conventional farming operations.
5. Certification and Compliance
Unlike organic farming, conventional farming does not require certification and compliance with specific organic standards. This means that conventional farmers do not have to bear the additional costs associated with obtaining organic certifications and meeting organic regulations.
6. Market Demand and Price
Conventional farming often benefits from higher market demand and price for conventionally grown products. This is mainly due to the wider availability and familiarity of conventionally grown produce among consumers. Higher market demand and price can lead to increased profitability for conventional farmers.
| Cost Consideration | Conventional Farming | Organic Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower | Higher |
| Equipment and Technology | Expensive but can reduce labor costs | Dependent on manual labor |
| Productivity and Yield | Higher | Lower |
| Labor Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Certification and Compliance | Not required | Required |
| Market Demand and Price | Higher | Varies |
While conventional farming may have lower initial costs and higher productivity, it is important to consider the potential impacts on the environment and human health. Additionally, market trends and consumer preferences for organic products should also be taken into account when making farming decisions.
Health Effects of Organic Farming
Better Nutritional Content
Organically grown fruits and vegetables have been found to contain higher levels of certain nutrients compared to conventionally grown produce. The absence of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides allows organic plants to develop stronger natural defense mechanisms, leading to increased levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
No Chemical Residues
One of the main advantages of organic farming is the absence of chemical residues on products. Conventionally grown crops are often sprayed with synthetic pesticides and herbicides, which can leave behind harmful residues. Organic farming, on the other hand, relies on natural methods to control pests and diseases, resulting in produce that is free from chemical contaminants.
Reduced Risk of Antibiotic Resistance
In conventional farming, antibiotics are often used to prevent and treat diseases in livestock. However, the excessive use of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a risk to human health. Organic farming prohibits the routine use of antibiotics, reducing the likelihood of antibiotic resistance.
No Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)

Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) have become a common feature in conventional agriculture. These genetically engineered crops have raised concerns about their potential long-term health effects. Organic farming strictly prohibits the use of GMOs, offering consumers a choice to avoid these controversial crops.
Beneficial for Environmental Health
Organic farming practices aim to minimize the impact on the environment by promoting biodiversity, conserving water resources, and reducing soil erosion. By using natural fertilizers and biological pest control methods, organic farming helps maintain a healthy ecosystem, which in turn supports human health.
Potential Health Benefits for Farmers
The use of toxic pesticides and chemicals in conventional farming can pose significant health risks to farmers and farm workers. By transitioning to organic farming, farmers can reduce their exposure to these hazardous substances and potentially improve their own health and well-being.
Pesticide Use in Conventional Farming
High levels of pesticide use: Conventional farming relies heavily on the use of synthetic pesticides to control pests, weeds, and diseases. These pesticides are often applied in large quantities, and their use has been increasing over the years.
Potential health risks: Pesticides used in conventional farming have been linked to various health risks, including cancers, neurological disorders, and reproductive problems. Exposure to these chemicals can occur through direct contact with the pesticides or by consuming food and water contaminated with residues.
Environmental impact: The use of pesticides in conventional farming can have detrimental effects on the environment. Pesticides can contaminate soil, water, and air, leading to a loss of biodiversity and harm to non-target organisms such as beneficial insects, birds, and aquatic life.
Potential for pesticide resistance: Over time, pests can develop resistance to pesticides, making them less effective in controlling pest populations. This can result in the need for increased pesticide applications or the use of higher toxicity pesticides, leading to further environmental and health concerns.
Soil Health in Organic Farming
One of the key principles of organic farming is the focus on soil health. Organic farmers prioritize the long-term health and sustainability of the soil, recognizing its vital role in plant growth, nutrient availability, and overall ecosystem health.
Benefits of Organic Farming for Soil Health:
- Increase in Soil Organic Matter: Organic farming practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting contribute to the increase in soil organic matter. This, in turn, enhances soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: Organic farmers encourage biodiversity by avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms such as earthworms, bacteria, and fungi, which play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and soil structure maintenance.
- Reduced Soil Erosion: Organic farming practices like conservation tillage, contour plowing, and terracing help prevent soil erosion. By reducing soil erosion, organic farming helps to preserve and protect the topsoil, which is essential for nutrient retention and moisture absorption.
- Minimized Chemical Contamination: Organic farming avoids the use of synthetic chemicals, reducing chemical inputs into the soil. This helps to prevent chemical contamination of the soil, which can have negative impacts on soil health and the surrounding environment.
Challenges in Maintaining Soil Health:
While organic farming has many benefits for soil health, it also presents some challenges:
- Weed Control: Organic farmers rely on manual or mechanical methods for weed control, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming. If not managed properly, weeds can compete with crops for nutrients and water.
- Nutrient Management: Maintaining proper nutrient balance in organic farming can be challenging. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, and testing and monitoring the soil’s nutrient levels are necessary to ensure optimal plant nutrition.
- Pests and Diseases: Organic farmers face challenges in pest and disease management without the use of synthetic pesticides. Integrated pest management techniques, such as biological controls and crop rotation, are employed to minimize pest and disease pressure.
| Factors | Conventional Farming | Organic Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Organic Matter | May decrease due to use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides | Increases due to organic farming practices such as composting and cover cropping |
| Biodiversity | May be reduced due to synthetic pesticide use | Promotes biodiversity by avoiding synthetic chemicals |
| Soil Erosion | May increase due to intensive tillage | Reduces erosion through practices like conservation tillage and terracing |
| Chemical Contamination | Potential for chemical contamination from synthetic inputs | Avoids chemical contamination by using organic inputs |
In conclusion, organic farming prioritizes soil health through practices that enhance soil organic matter, promote biodiversity, reduce soil erosion, and minimize chemical contamination. While it presents challenges in weed control, nutrient management, and pest/disease management, the long-term benefits for soil health make organic farming a sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach.
GMOs in Conventional Farming
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, are organisms whose genetic materials have been manipulated using genetic engineering techniques. In conventional farming, GMOs are commonly used to improve crop yield, enhance pest and disease resistance, and increase tolerance to herbicides.
Advantages of GMOs in Conventional Farming:
- Increased Crop Yield: GMOs have been developed to produce higher yields compared to their non-GMO counterparts. This helps to meet the growing global demand for food.
- Pest and Disease Resistance: Genetic modification allows plants to resist pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fungicides. This can result in higher crop quality and lower production costs.
- Herbicide Tolerance: Many GMO crops are engineered to withstand certain herbicides, allowing farmers to control weeds more effectively.
- Drought and Salinity Tolerance: Genetic modification can also enhance a crop’s ability to tolerate drought and high salinity levels in the soil, making it possible to grow crops in regions with challenging environmental conditions.
Disadvantages of GMOs in Conventional Farming:
- Potential Environmental Risks: GMOs may have unintended impacts on non-target organisms, potentially causing ecological imbalances in the environment.
- Health Concerns: Some studies suggest that consuming GMOs may have negative health effects, although scientific consensus on this issue is still debated.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The cultivation of GMO crops on a large scale can lead to the loss of traditional crop varieties and the genetic diversity they represent.
- Contamination of Non-GMO Crops: GMO crops have the potential to crossbreed with non-GMO crops, leading to the unintentional presence of GMOs in organic or non-GMO crops.
It is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of GMOs in conventional farming, taking into account the potential impact on the environment, human health, and biodiversity. Regulation and proper labeling of GMO products can help consumers make informed choices about the food they consume.
Questions and Answers:
What is conventional farming?
Conventional farming refers to the traditional method of farming that uses synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to manage pests and promote crop growth.
What is organic farming?
Organic farming is a method of farming that relies on natural fertilizers, biodiversity, and crop rotation to promote soil health and control pests, without the use of synthetic chemicals.
What are the pros of conventional farming?
Some advantages of conventional farming include higher yields, lower costs, and greater efficiency due to the use of synthetic chemicals and mechanized equipment.
What are the cons of conventional farming?
Conventional farming has several drawbacks, such as environmental pollution from chemical runoff, soil degradation, and the potential health risks associated with the use of synthetic pesticides.
What are the pros of organic farming?
Organic farming offers numerous benefits, including improved soil fertility, reduced chemical exposure for farmers and consumers, and the promotion of biodiversity.
What are the cons of organic farming?
Organic farming can have some disadvantages, such as higher costs and lower yields compared to conventional farming. Additionally, it may require more labor-intensive practices and greater land area to achieve the same level of production.








