- Disease of Grapes: Treatments and Pest Protection
- Treatments for Grape Diseases
- Pest Protection for Grapes
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Conclusion
- Grapevine Diseases and Their Impact
- 1. Powdery Mildew
- 2. Downy Mildew
- 3. Black Rot
- 4. Grapevine Leafroll Disease
- 5. Phomopsis Cane and Leaf Spot
- Conclusion
- Preventive Measures for Grape Diseases
- 1. Plant Disease-resistant Varieties
- 2. Maintain Proper Vineyard Sanitation
- 3. Pruning and Training
- 4. Monitoring and Early Detection
- 5. Implement Pest Management Strategies
- 6. Proper Irrigation and Drainage
- 7. Fertilizer Management
- 8. Use of Protective Sprays
- Chemical Treatments for Grape Diseases
- 1. Fungicides
- 2. Insecticides
- 3. Herbicides
- Common Pests Affecting Grapevines
- 1. Grape Phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae)
- 2. Grape Berry Moth (Paralobesia viteana)
- 3. Grape Leafhopper (Erythroneura spp.)
- 4. Grape Mealybug (Pseudococcus maritimus)
- 5. Vineyard Snails (Helix spp.)
- Natural Pest Control Methods
- 1. Companion Planting
- 2. Biological Controls
- 3. Trap Crops
- 4. Physical Barriers
- 5. Organic Sprays
- 6. Proper Vineyard Management
- 7. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Integrated Pest Management for Grapes
- 1. Pest Identification
- 2. Cultural Practices
- 3. Biological Control
- 4. Mechanical Controls
- 5. Chemical Controls
- 6. Monitoring and Record-Keeping
- Conclusion
- Tips for Disease-free Grape Cultivation
- Importance of Regular Grapevine Maintenance
- Prevention of Diseases
- Pest Control
- Improved Fruit Production
- Optimal Vine Growth
- Longer Vine Lifespan
- Overall Vineyard Appearance
- Question-answer:
- What are the most common diseases that affect grapes?
- How can I identify powdery mildew on grapevines?
- What are the treatment options for powdery mildew on grapes?
- How can I control black rot in my grape vineyard?
- What is the best way to prevent downy mildew on grapevines?
- What is grey mold and how can I manage it in my grape vineyard?
- Are there any natural or organic treatments for grape diseases?
- Video: 25 Amazing Heavy Agriculture Machines Working At Another Level ▶28
Grapes are a popular fruit with a rich history dating back thousands of years. However, like any other crop, grapes are susceptible to a variety of diseases that can greatly impact their growth and quality. In order to ensure a successful harvest, it is important for grape growers to be familiar with the common diseases that affect grapes and the treatments and pest protection methods that can be used to control them.
One of the most common diseases that affect grapes is powdery mildew. This fungal disease appears as a white, powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and berries of the grapevine. If left untreated, powdery mildew can significantly reduce the yield and quality of the grapes. To control powdery mildew, grape growers can use a variety of fungicides and sulfur-based compounds that are effective against the fungus. Additionally, practicing good vineyard management techniques, such as pruning and maintaining proper air circulation, can help prevent the spread of powdery mildew.
Another disease that can affect grapes is downy mildew. Unlike powdery mildew, which thrives in dry conditions, downy mildew prefers damp and humid environments. This fungal disease appears as yellow spots on the upper surface of the leaves, which are accompanied by a downy, white growth on the underside of the leaves. To control downy mildew, grape growers can apply fungicides that are effective against the fungus. It is also important to remove and destroy any infected plant material to prevent the disease from spreading. In addition to fungal diseases, grapes can also be vulnerable to various pests, such as grape phylloxera and grapevine leafhoppers, which can damage the leaves and fruit of the grapevine.
Grape phylloxera is a small insect that feeds on the roots of grapevines, causing them to swell and eventually die. To protect against grape phylloxera, grape growers can use resistant rootstocks or graft their vines onto phylloxera-resistant rootstocks. Additionally, keeping the vineyard area clean and free of weeds can help prevent the spread of grape phylloxera.
Grapevine leafhoppers are small, winged insects that feed on the leaves of grapevines, causing them to turn yellow and eventually die. To control grapevine leafhoppers, grape growers can use insecticides that are effective against the leafhoppers. It is also important to monitor the vineyard regularly and remove any infected plants to prevent the spread of the insects.
Disease of Grapes: Treatments and Pest Protection
Treatments for Grape Diseases
- Fungicides: Using fungicides is one of the primary methods to treat grape diseases. Fungicides such as copper-based products are effective in controlling fungal infections.
- Pruning: Pruning infected grape vines helps in removing diseased plant parts and promoting better air circulation, which reduces the risk of fungal infections.
- Cultural Practices: Implementing good cultural practices such as maintaining proper spacing between plants, adequate irrigation, and timely fertilization can help prevent the occurrence of diseases in grapevines.
- Resistant Varieties: Planting grape varieties that are resistant to common diseases can significantly reduce the need for treatments.
Pest Protection for Grapes
- Netting: Covering grape vines with netting can provide protection against birds and other pests.
- Monitoring: Regularly inspecting grape vines for signs of pest infestations, such as chewed leaves or clusters, can help identify and address pest issues early on.
- Insecticides: Insecticides can be used to control pests like aphids, spider mites, and leafhoppers that can damage grapevines. However, it is important to choose insecticides that are safe for grapes and follow the recommended application guidelines.
- Traps: Placing traps near grape vines can help catch and control pests like fruit flies, stink bugs, and beetles.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an approach that combines multiple pest control methods to minimize the use of chemicals and promote sustainable grape production. This approach involves monitoring pests, identifying the pest population threshold, and using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods as required. IPM aims to prevent excessive pesticide use while effectively managing pests and minimizing their impact on grapevines.
Conclusion
Protecting grapevines from diseases and pests is crucial for a healthy and productive vineyard. By implementing the treatments mentioned above and adopting Integrated Pest Management practices, grape growers can minimize the risks of diseases and pests, ensuring the successful cultivation of high-quality grapes.
Grapevine Diseases and Their Impact
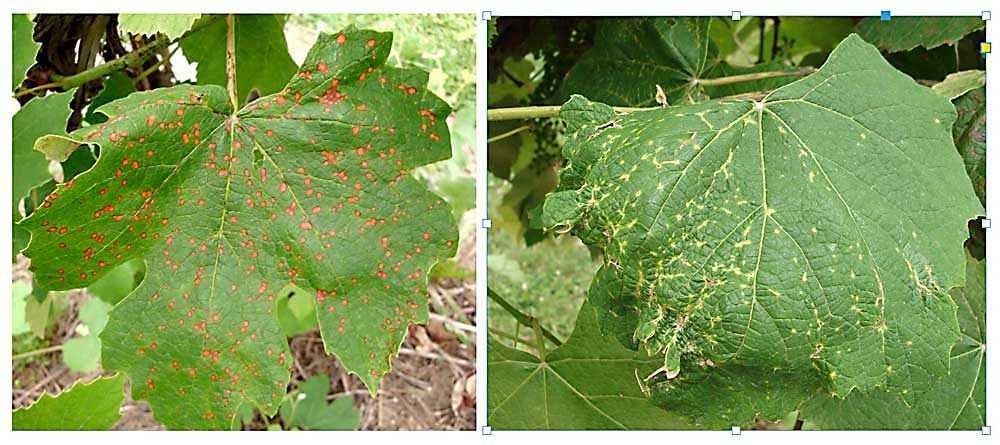
Grapes are susceptible to various diseases that can have a significant impact on their growth, productivity, and overall health. It is important for grape growers to be aware of these diseases and take necessary measures to prevent and control them.
1. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is one of the most common diseases affecting grapevines. It is caused by a fungus that forms a powdery white coating on the leaves, stems, and fruit of the grapevine. This coating can reduce the vine’s ability to photosynthesize and negatively impact the quality and yield of the grapes. To control powdery mildew, growers can use fungicides and practice proper vineyard management techniques, such as pruning and removing infected plant parts.
2. Downy Mildew
Downy mildew is another fungal disease that affects grapevines. It can cause yellow or brown spots on the leaves and a downy white growth on the underside of the leaves. Downy mildew can lead to defoliation and reduced grape quality and yield. To manage downy mildew, grape growers can use fungicides and practice cultural controls, such as proper pruning and canopy management to improve air circulation and reduce humidity.
3. Black Rot

Black rot is a fungal disease that primarily affects the fruit of grapevines. It causes black, circular lesions on the grapes and can lead to fruit decay and shriveling. Infected grapes often drop prematurely from the vine. To control black rot, grape growers can use fungicides and implement cultural practices such as removing and destroying infected plant parts and improving air circulation in the vineyard.
4. Grapevine Leafroll Disease
Grapevine leafroll disease is a viral disease that affects the leaves of grapevines. Infected vines show symptoms of reddening and rolling of the leaves, which can reduce the vine’s ability to produce sugars and affect the ripening process. There is no known cure for leafroll disease, so prevention is crucial. Grape growers should use virus-free planting material, practice strict sanitation measures, and remove infected vines to control the spread of the disease.
5. Phomopsis Cane and Leaf Spot

Phomopsis cane and leaf spot is a fungal disease that affects the canes and leaves of grapevines. It causes sunken spots on the canes and brown lesions on the leaves. Severe infections can lead to dieback and reduced vine vigor. To manage Phomopsis cane and leaf spot, grape growers can use fungicides and implement cultural practices such as pruning and removing infected plant parts.
Conclusion
Grapevine diseases can have a significant impact on vine health, grape quality, and yield. Grape growers should be vigilant in monitoring and managing these diseases to ensure the long-term success of their vineyards. By practicing good vineyard management techniques and using appropriate disease control measures, growers can minimize the impact of these diseases and maintain healthy grapevines.
Preventive Measures for Grape Diseases
1. Plant Disease-resistant Varieties
Grapevine diseases can be prevented by planting disease-resistant grape varieties. These varieties have been selectively bred to have increased resistance to common grape diseases. It is important to choose varieties that are resistant to the specific diseases prevalent in your region.
2. Maintain Proper Vineyard Sanitation
Keeping the vineyard clean and free from debris is essential in preventing the spread of diseases. Regularly remove fallen leaves, pruned vines, and other plant materials that may harbor pathogens. Properly dispose of infected plant material to prevent the spread of diseases.
3. Pruning and Training
Proper pruning and training techniques help improve air circulation and sunlight penetration within the vineyard. This reduces the chances of disease development and creates an environment less favorable for pathogens. It is important to follow the recommended pruning and training practices for grapevines.
4. Monitoring and Early Detection
Regularly inspect the grapevines for signs of disease. Early detection allows for early intervention, preventing the spread of diseases. Train vineyard workers to recognize the symptoms of common grape diseases and implement a monitoring system to regularly assess the health of the vines.
5. Implement Pest Management Strategies
Pests can often carry and spread diseases in vineyards. Implement pest management strategies to control pests and minimize their impact on the vines. This may include the use of insecticides, cultural practices, and biological controls.
6. Proper Irrigation and Drainage
Water management is crucial in preventing the development of certain grape diseases. Proper irrigation practices should be implemented to avoid overwatering, which can promote fungal growth. Additionally, ensuring adequate drainage helps prevent waterlogged conditions that favor disease development.
7. Fertilizer Management
Proper fertilization is important for maintaining the health and vigor of grapevines. However, excessive fertilization can lead to increased susceptibility to certain diseases. It is important to follow recommended fertilization practices and avoid excessive application of nitrogen, which can make the vines more susceptible to diseases.
8. Use of Protective Sprays
When necessary, the use of protective sprays can help prevent the occurrence and spread of grape diseases. Fungicides and bactericides may be used according to the specific disease prevention guidelines provided by local agricultural extension services or experts.
By implementing these preventive measures, grape growers can minimize the occurrence and severity of diseases in their vineyards and ensure the health and productivity of their grapevines.
Chemical Treatments for Grape Diseases
Chemical treatments are commonly used in grape farming to control and prevent diseases. These treatments consist of applying various chemical compounds to the vines and surrounding areas to target specific pathogens or pests. While chemical treatments can be effective in managing grape diseases, they should be used judiciously and in accordance with local regulations and guidelines.
1. Fungicides
Sulfur-based fungicides: These fungicides are commonly used to control powdery mildew and downy mildew, which are two of the most common fungal diseases affecting grapevines. Sulfur-based fungicides work by preventing the growth and spread of fungal spores.
Copper-based fungicides: Copper-based fungicides are effective against a wide range of fungal pathogens, including powdery mildew, downy mildew, and botrytis bunch rot. These fungicides have a protective effect on the vines, preventing the establishment of fungal infections.
Triazole fungicides: Triazole fungicides are systemic fungicides that are absorbed by the plant and provide long-lasting protection against a variety of fungal diseases. They are especially effective against black rot, anthracnose, and phomopsis cane and leaf spot.
2. Insecticides
Pyrethroid insecticides: Pyrethroid insecticides are commonly used to control a range of grape pests, including leafhoppers, grape berry moths, and grape phylloxera. They work by disrupting the nervous system of insects, leading to paralysis and death.
Neonicotinoid insecticides: Neonicotinoid insecticides are highly effective against sucking insects, such as aphids, whiteflies, and leafhoppers. These insecticides act as nerve toxins, affecting the feeding and reproductive behavior of pests.
Organophosphate insecticides: Organophosphate insecticides are broad-spectrum insecticides that are effective against a wide range of grape pests. However, they can also have negative impacts on beneficial insects and non-target organisms, so their use should be carefully regulated.
3. Herbicides
Glyphosate-based herbicides: Glyphosate-based herbicides are widely used to control weeds in grape vineyards. They work by inhibiting an enzyme that is essential for plant growth, effectively killing unwanted vegetation.
Pre-emergent herbicides: Pre-emergent herbicides are applied prior to weed germination and growth. They create a barrier in the soil that prevents weed seeds from sprouting, reducing the need for post-emergent herbicides.
It is important to note that chemical treatments should be used as part of an integrated pest management (IPM) approach, which includes cultural and biological control methods. This helps to minimize the reliance on chemical treatments and reduce the environmental impact of grape farming.
Common Pests Affecting Grapevines
Grapevines are susceptible to a variety of pests that can damage the foliage, fruit, and overall health of the vine. It is important for grape growers to be aware of these common pests and take appropriate measures to prevent and control their populations.
1. Grape Phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae)
Grape phylloxera is a tiny aphid-like insect that feeds on the roots of grapevines. It is one of the most destructive pests affecting grapevines worldwide. Infected vines will show symptoms such as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and eventual death. The best way to prevent phylloxera infestation is to plant grafted vines on phylloxera-resistant rootstocks.
2. Grape Berry Moth (Paralobesia viteana)
The grape berry moth is a common pest that affects grapevines in many wine-growing regions. The larvae of this moth feed on grape berries, causing damage by tunneling and feeding on the fruit. Infested berries may develop rot and become susceptible to other diseases. Proper pest management practices, including the use of pheromone traps and insecticides, can help control grape berry moth populations.
3. Grape Leafhopper (Erythroneura spp.)
Grape leafhoppers are small insects that feed on the leaves of grapevines, causing damage by sucking sap from the leaves. Infested leaves may turn yellow, curl, and drop prematurely. Leafhoppers can also transmit viral diseases to grapevines. Regular monitoring and the use of insecticides or biological control methods can help prevent and manage grape leafhopper infestations.
4. Grape Mealybug (Pseudococcus maritimus)
The grape mealybug is a common pest that feeds on the sap of grapevines. Mealybugs are covered with a white, waxy substance, making them easy to identify. Infested vines may show symptoms such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and decreased fruit quality. Control measures for grape mealybugs include the use of insecticides, natural enemies, and cultural practices such as pruning and weed control.
5. Vineyard Snails (Helix spp.)
Snails can be a nuisance in vineyards, especially in cooler and wetter regions. They feed on grape foliage, buds, and fruit, causing damage and reducing vine productivity. Manual removal of snails, planting cover crops, and the use of snail barriers or baits are common control measures for vineyard snails.
These are just a few examples of the common pests that can affect grapevines. Proper pest management practices, including regular monitoring, the use of preventive measures, and targeted control methods, can help grape growers protect their vines and ensure healthy grape production.
Natural Pest Control Methods
1. Companion Planting
Companion planting involves planting certain types of plants together to create a mutually beneficial environment. Some plants have insect-repelling properties that can help keep pests away from grapevines. For example, planting marigolds or mint around grapevines can deter pests like aphids and nematodes.
2. Biological Controls
Using biological controls involves introducing natural predators or parasites that feed on grapevine pests. This method is often used for controlling insect pests like mites, thrips, and leafhoppers. Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites are commonly used as biological controls in grape vineyards.
3. Trap Crops
Trap crops are sacrificial plants that are planted near grapevines to attract and trap pests away from the main crop. These plants are usually more attractive to pests than grapevines, and by planting them strategically, you can divert pests away from your grapes. For example, planting sunflowers or millet near grapevines can help control bird damage.
4. Physical Barriers
Physical barriers can be used to protect grapevines from pests. For example, using netting or mesh to cover grapevines can prevent birds and insects from reaching the grapes. This method is particularly effective for preventing bird damage and reducing the risk of insect infestation.
5. Organic Sprays
Organic sprays made from natural ingredients can help control pests on grapevines. These sprays are often made from substances such as neem oil, garlic, hot pepper, or soap. They can be applied directly to the plants to repel or kill pests without harming the environment.
6. Proper Vineyard Management
Implementing proper vineyard management practices can help prevent pest infestations. This includes regular pruning to maintain vine health and airflow, removing diseased or damaged plants, and practicing good hygiene by keeping the vineyard clean and free from debris. By maintaining a healthy vineyard environment, you can reduce the risk of pest problems.
7. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is a holistic approach to pest control that combines multiple techniques to manage pests effectively. This approach involves monitoring pests, identifying thresholds for treatment, using cultural practices, implementing biological controls, and only resorting to chemical pesticides when necessary. By using a combination of methods, grape growers can reduce the need for chemical intervention and promote a more sustainable vineyard ecosystem.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Companion Planting | Planting insect-repelling plants near grapevines |
| Biological Controls | Introducing natural predators to feed on pests |
| Trap Crops | Using sacrificial plants to attract pests away from grapevines |
| Physical Barriers | Using netting or mesh to protect grapevines from pests |
| Organic Sprays | Using natural sprays to repel or kill pests |
| Proper Vineyard Management | Maintaining a healthy vineyard environment |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Using a combination of methods to manage pests |
Integrated Pest Management for Grapes
Grapes are susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases that can cause significant damage to the plants and reduce yields. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest management that combines multiple strategies to control pests while minimizing the use of harmful pesticides.
1. Pest Identification
The first step in implementing an IPM program for grapes is to accurately identify the pests and diseases that are present in the vineyard. Different pests may require different control measures, so it is important to correctly identify the pest before taking any action.
Tip: Regular scouting of the vineyard can help identify pests before they become a problem. Look for signs of pest damage, such as chewed leaves or discolored fruit.
2. Cultural Practices
Cultural practices play a key role in preventing pest infestations and disease outbreaks. These practices include proper pruning, adequate irrigation, and regular fertilization. By maintaining healthy vines, grape growers can reduce the susceptibility of the plants to pests and diseases.
Tip: Avoid over-fertilizing the vines, as excess nitrogen can make them more attractive to pests and diseases.
3. Biological Control
Biological control involves the use of natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to control pests. This can include releasing beneficial insects or using microbial products that target specific pests. Biological control can be an effective and sustainable way to manage pests in the vineyard.
Tip: Encourage natural predators by planting flowering plants in or near the vineyard to provide nectar and pollen sources.
4. Mechanical Controls
Mechanical controls involve physical methods to manage pests. This can include hand-picking and removing infected plant material, installing netting to protect grapes from birds, or using traps to monitor and capture pests.
Tip: Use pheromone traps to monitor pest populations and determine the best timing for pesticide applications.
5. Chemical Controls
Pesticides should be used as a last resort and only when other control methods have failed. When selecting pesticides, choose those that are least toxic to beneficial insects and follow label instructions carefully. Use pesticides sparingly and only when necessary to minimize the impact on the environment.
Tip: Rotate the use of pesticides with different modes of action to reduce the risk of pests developing resistance.
6. Monitoring and Record-Keeping
Regular monitoring of the vineyard is essential to detect pest and disease outbreaks early. Keep detailed records of pest populations, pesticide applications, and the effectiveness of control measures. These records can help determine the success of the IPM program and make informed decisions for future pest management.
Tip: Use online or mobile apps to record and track pest populations and treatments conveniently.
Conclusion
Integrated Pest Management combines various strategies to effectively manage pests and diseases in grape vineyards while minimizing the use of harmful pesticides. By implementing IPM practices, grape growers can maintain healthy vineyards and produce high-quality grapes.
Tips for Disease-free Grape Cultivation
- Choose resistant grape varieties: When starting your grape cultivation, select grape varieties that have high resistance to common diseases. This can greatly reduce the risk of disease outbreaks in your vineyard.
- Provide adequate spacing: Proper spacing between grape vines is essential for disease prevention. It allows for good air circulation, reducing the chances of fungal infections. Make sure to follow the recommended spacing guidelines for the specific grape variety you are growing.
- Prune properly: Pruning is a critical step in grape cultivation. It helps in maintaining proper vine structure and allows for better sunlight penetration, which can prevent diseases caused by excess moisture. Ensure that you prune your grape vines during the dormant season, removing any dead or diseased parts.
- Practice good sanitation: Regularly cleaning and maintaining your vineyard is crucial for disease prevention. Remove any fallen leaves, weeds, or other plant debris that can harbor pests and pathogens. This will help reduce the risk of infection spreading to healthy grape vines.
- Monitor for pests and diseases: Regularly inspect your grape vines for signs of pests or diseases. Keep an eye out for symptoms such as discoloration, spots, or wilting. Early detection can help prevent the spread of diseases and allow for timely treatments.
- Use organic fungicides: If you need to use fungicides to control diseases, opt for organic products. There are several organic fungicides available that are less harmful to the environment and have fewer negative impacts on beneficial insects and other organisms.
- Implement integrated pest management (IPM): IPM is an approach that combines various pest control methods to minimize the use of chemicals. By incorporating techniques such as biological control, crop rotation, and trap crops, you can reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and promote a healthier growing environment for your grape vines.
- Maintain proper irrigation: Overwatering grape vines can create a favorable environment for disease development. Ensure that you provide adequate, but not excessive, irrigation. Use drip irrigation systems or other targeted watering methods to minimize moisture on the leaves and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
- Stay informed and seek professional advice: Keep yourself updated with the latest research and recommendations on grape disease management. Attend workshops and seek guidance from agricultural extension services or local grape growers’ associations. Their expertise can help you make informed decisions and prevent or mitigate disease outbreaks in your vineyard.
Importance of Regular Grapevine Maintenance
Grapevines are susceptible to a variety of diseases and pests that can significantly impact their health and productivity. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the well-being of the grapevines and the quality of the grapes they produce. Here are some reasons why regular grapevine maintenance is important:
Prevention of Diseases
Regular maintenance practices, such as pruning, can help prevent the occurrence and spread of diseases in grapevines. Pruning removes dead or diseased wood, improving air circulation and reducing the chances of fungal infections. It also helps open up the canopy, allowing sunlight to reach the leaves and reduce humidity, preventing conditions that favor the development of diseases.
Pest Control
Regular maintenance also includes monitoring and controlling pests that can cause damage to grapevines. Pests like aphids, mites, and grapevine moths can weaken the vines and reduce the yield. Regular inspection allows for early detection of pest infestations, enabling prompt treatment to prevent further damage.
Improved Fruit Production

By ensuring that grapevines are healthy and free from diseases and pests, regular maintenance promotes optimal fruit production. Healthy vines are more likely to produce higher-quality grapes that are free from defects. Regular pruning also helps regulate vine vigor, directing energy towards fruit production and improving the quality of the harvest.
Optimal Vine Growth
Regular maintenance practices, such as training and trellising, help promote optimal vine growth and maintain a desired vine structure. Proper training ensures that the vines receive adequate sunlight and airflow, reducing the risk of disease and ensuring even ripening. Trellising supports the vines and prevents them from trailing on the ground, reducing the chances of disease and facilitating vine management.
Longer Vine Lifespan
Regular maintenance helps prolong the lifespan of grapevines. By keeping them healthy and well-maintained, they are less likely to succumb to diseases and pests that can weaken and kill the vines. Regular pruning and management practices can also help rejuvenate older vines, extending their productive life.
Overall Vineyard Appearance
Regular maintenance not only ensures the health and productivity of grapevines but also contributes to the overall appearance of the vineyard. Well-maintained vines create a visually appealing landscape, enhancing the aesthetic value of the vineyard. This can be beneficial for vineyard owners who use their vineyards for tourism or wine tasting activities.
In conclusion, regular maintenance of grapevines is essential for disease prevention, pest control, optimal fruit production, vine growth, and overall vineyard health. It not only ensures the well-being of the vines but also contributes to the longevity and appearance of the vineyard.
Question-answer:
What are the most common diseases that affect grapes?
The most common diseases that affect grapes include powdery mildew, downy mildew, black rot, and grey mold.
How can I identify powdery mildew on grapevines?
Powdery mildew on grapevines appears as a white powdery substance on the leaves, shoots, and berries. It can also cause foliage distortion and reduce grape yield.
What are the treatment options for powdery mildew on grapes?
Treatment options for powdery mildew on grapes include the use of fungicides, cultural practices such as pruning and thinning, and the use of resistant grape varieties.
How can I control black rot in my grape vineyard?
To control black rot in a grape vineyard, it is important to remove and destroy infected plant parts, practice proper pruning and thinning, and use fungicides as recommended.
What is the best way to prevent downy mildew on grapevines?
The best way to prevent downy mildew on grapevines is to ensure good air circulation in the vineyard, avoid excessive irrigation, and use fungicides with preventative action.
What is grey mold and how can I manage it in my grape vineyard?
Grey mold is a fungal disease that affects grapes, causing rots and decay. To manage grey mold, it is important to remove and destroy infected plant parts, practice good canopy management, and use fungicides if necessary.
Are there any natural or organic treatments for grape diseases?
Yes, there are natural and organic treatments available for grape diseases. These include the use of biological controls, such as beneficial insects and microorganisms, as well as the use of organic fungicides and cultural practices.







