- When to Plant a Rose with an Open Root System in the Spring
- Early Spring Planting
- Soil Conditions
- Preparing the Rose
- Planting Depth
- Watering and Mulching
- Choosing the Right Location for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System
- Preparing the Soil for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System
- 1. Choose the Right Location
- 2. Clear the Area
- 3. Test and Improve the Soil
- 4. Provide Drainage
- 5. Prepare the Planting Hole
- 6. Water the Soil
- 7. Backfill and Firm the Soil
- 8. Mulch the Area
- 9. Water Thoroughly
- How to Dig the Hole for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System
- Planting the Rose with an Open Root System
- 1. Prepare the Soil
- 2. Dig the Hole
- 3. Soak the Roots
- 4. Place the Rose in the Hole
- 5. Backfill with Soil
- 6. Water and Mulch
- 7. Provide Support
- 8. Regular Maintenance
- Watering and Mulching a Rose with an Open Root System
- Pruning and Fertilizing a Rose with an Open Root System
- 1. Pruning:
- 2. Fertilizing:
- 3. Additional Tips:
- Caring for a Rose with an Open Root System in the Spring
- Watering
- Fertilizing
- Mulching
- Pruning
- Pest and Disease Control
- Support
- Regular Monitoring
- Questions and Answers:
- When is the best time to plant roses with an open root system?
- Videos: 6 Methods for Rose Propagation
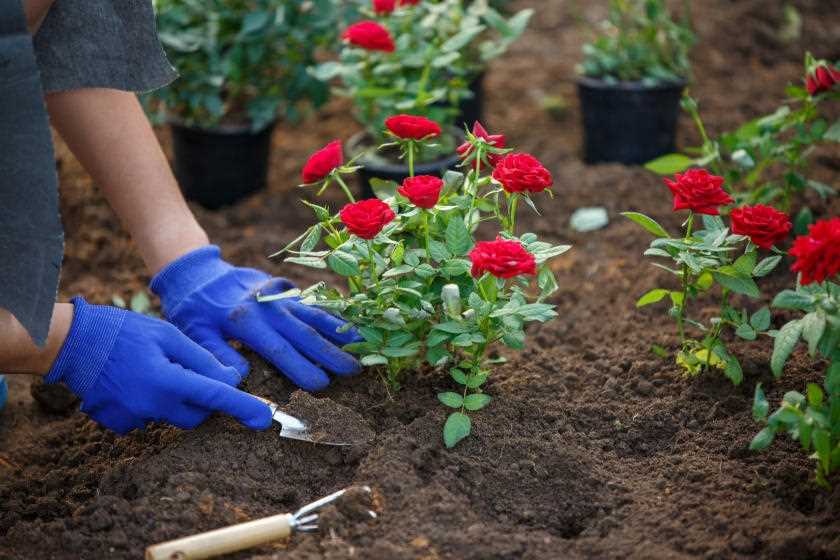

Spring is the perfect time to plant roses with an open root system. Many gardeners prefer this method of planting as it allows the roots to establish themselves more quickly and effectively. If you’re thinking about planting a rose with open roots this spring, there are a few expert tips you should keep in mind.
First, make sure you choose a healthy rose with a strong open root system. Look for plants with well-developed roots and avoid ones with any signs of disease or damage. It’s also important to select a variety that is suitable for your climate and growing conditions.
Before planting your rose, prepare the soil by adding organic matter and ensuring good drainage. Roses prefer well-drained soil that is rich in nutrients. You can also use a planting mix specifically designed for roses to give them the best start.
When planting, dig a hole wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots without crowding them. Make sure the bud union (the swollen area where the rose was grafted onto the rootstock) is level with or slightly above the soil surface. This helps protect the graft and prevents it from being buried too deeply.
After planting, water the rose thoroughly to settle the soil and eliminate any air pockets around the roots. It’s also a good idea to apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Expert Tip: Regular watering and proper maintenance are key to ensuring the success of your newly planted rose. Be sure to check the moisture levels regularly and water as needed, especially during hot and dry periods. Pruning and fertilizing at the appropriate times will also help promote healthy growth and abundant blooms.
By following these expert tips, you can successfully plant a rose with an open root system in the spring and enjoy beautiful blooms all season long. Happy gardening!
When to Plant a Rose with an Open Root System in the Spring
Planting a rose with an open root system in the spring can be a daunting task, but with the right timing, it can lead to a beautiful and flourishing rose garden. It is important to choose the right time to plant your rose to ensure its success.
Early Spring Planting
- Planting a rose with an open root system is best done in early spring, ideally after the last frost has passed.
- This timing allows the rose to establish its roots before the hot summer months, giving it the best chance for survival and growth.
Soil Conditions
- Before planting your rose, ensure that the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter.
- You can amend the soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve its fertility and drainage.
Preparing the Rose
- Before planting, soak the rose’s roots in water for a few hours to ensure they are well-hydrated.
- Trim any damaged or broken roots to promote healthy growth.
- Prune back any long canes to encourage a more compact and bushy growth habit.
Planting Depth
- Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the rose’s root system.
- Make sure the bud union, the swollen area where the rose is grafted onto the rootstock, is level with or slightly above the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil and gently firm it around the roots.
Watering and Mulching
- After planting, water the rose thoroughly to help settle the soil and eliminate any air pockets.
- Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the rose to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your rose with an open root system has the best chance of establishing and thriving in your garden. Remember to provide the rose with regular care, including watering, fertilizing, and pruning, to promote healthy growth and abundant blooms.
Choosing the Right Location for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System
When planting a rose with an open root system in the spring, choosing the right location is crucial for the plant’s success and growth. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting the ideal spot for planting your rose:
- Sunlight: Roses thrive in full sunlight, so choose a location that receives at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight each day. Avoid areas that are heavily shaded or blocked by trees or buildings.
- Soil: Roses prefer well-drained soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 6.5. Conduct a soil test to determine the soil’s nutrient content and adjust it if necessary. Avoid areas with heavy clay soil or poor drainage.
- Air Circulation: Good air circulation around the rose plant helps prevent the development of diseases. Avoid planting roses in areas with high humidity or that are enclosed by walls, fences, or other structures.
- Proximity to Other Plants: Roses should be spaced at least two to three feet apart from other plants to allow for adequate air circulation and prevent competition for nutrients and water.
- Protection from Harsh Weather: Consider the location’s exposure to strong winds, heavy rains, and frost. Plant your rose in a spot that offers some protection from these elements, such as near a wall or fence.
By considering these factors and choosing the right location for planting your rose with an open root system, you can provide the optimal growing conditions for your plant and ensure its long-term health and beauty.
Preparing the Soil for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System
Before planting a rose with an open root system in the spring, it is important to prepare the soil to ensure optimal growth and health of the plant. Here are some key steps to follow:
1. Choose the Right Location
Select a location that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily and has well-draining soil. Roses thrive in full sun and do not tolerate excessive shade. Avoid planting roses in low-lying areas where water tends to accumulate.
2. Clear the Area
Remove any weeds, grass, or debris from the planting area. This will help prevent competition for nutrients and moisture. Use a garden fork or tiller to loosen the soil and remove any large rocks or roots.
3. Test and Improve the Soil
Test the soil pH with a soil testing kit to determine if it is within the ideal range for roses, which is slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0-7.0). If the pH is too low or too high, amend the soil accordingly. Add lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
In addition to pH, it is important to improve the soil’s fertility and structure. Add organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or peat moss to improve drainage, moisture retention, and nutrient content. Incorporate the organic matter into the top 12-18 inches of soil using a garden fork or tiller.
4. Provide Drainage

Ensure that the planting area has good drainage to prevent waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot. If the soil is heavy and clayey, create raised beds or mounds to improve drainage. Alternatively, add sand or perlite to the soil to increase its porosity.
5. Prepare the Planting Hole
Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the rose’s root system. The hole should be at least two times wider and deeper than the roots. Gently loosen the roots and remove any broken or damaged ones. Trim any excessively long roots to facilitate planting.
6. Water the Soil
Moisten the soil in the planting hole before placing the rose in it. Watering the soil will help prevent the roots from drying out and will provide an initial source of moisture for the plant.
7. Backfill and Firm the Soil
Backfill the hole with the amended soil, making sure to fill in all the spaces around the roots. Gently firm the soil around the base of the rose with your hands or a gardening tool. Avoid compacting the soil too much, as this can restrict air circulation and root growth.
8. Mulch the Area
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of the rose. Mulching helps conserve moisture, suppresses weeds, and regulates soil temperature. Leave a small gap between the mulch and the stem to prevent rotting.
9. Water Thoroughly
After planting, water the rose thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots and remove any air pockets. Provide enough water to moisten the entire root zone. Watering deeply and infrequently is more beneficial than frequent shallow watering, as it encourages deep root growth.
By taking the time to prepare the soil properly before planting a rose with an open root system in the spring, you will create a favorable environment for the plant to establish and thrive for years to come.
How to Dig the Hole for Planting a Rose with an Open Root System

Digging the right hole is crucial for the successful planting of a rose with an open root system. Follow these steps to ensure your rose gets off to a healthy start:
- Choose the right location: Select a spot in your garden that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily and has well-draining soil. Roses thrive in full sun and need good air circulation to prevent diseases.
- Measure the root system: Measure the length and width of the root system of your rose plant. The hole you dig should be wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots comfortably, without crowding or bending them.
- Prepare the soil: Digging a hole with well-prepared soil is essential for the rose’s growth. Remove any weeds or grass from the planting area and enrich the soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve fertility and drainage.
- Mark the hole: Use a spray can or stakes to mark the outline of the hole you need to dig. This will help you dig accurately and ensure the proper placement of the rose plant.
- Dig the hole: Start digging the hole, making it wider and slightly deeper than the measurements of the rose’s root system. Use a shovel or a garden fork to loosen the soil and create a well-aerated bed for the roots.
- Break up the bottom: Loosen the soil at the bottom of the hole to provide better drainage for the plant. Breaking up any compacted soil will help the roots establish themselves more easily.
- Prepare the hole: Mix organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, with the soil you removed from the hole. This will help improve soil fertility and create a favorable environment for root growth.
- Backfill the hole: Place a small mound of the prepared soil mixture in the center of the hole. Gently spread the roots of the rose plant over the mound, ensuring they are not twisted or bent.
- Fill the hole: Gradually fill the hole with the remaining soil mixture, packing it gently around the roots. Avoid compacting the soil too tightly, as it can hinder root growth and water drainage.
- Water thoroughly: After planting, water the rose thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots and eliminate any air pockets. Provide enough water to moisten the entire root ball and surrounding soil.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the hole for planting a rose with an open root system is properly prepared, giving your rose the best chance to thrive and flourish.
Planting the Rose with an Open Root System
Planting a rose with an open root system can be a delicate process that requires careful attention to detail. Follow these expert tips to ensure a successful planting:
1. Prepare the Soil
The first step in planting a rose with an open root system is to prepare the soil. Choose a location with well-draining soil that receives at least six hours of sunlight a day. Remove any weeds or grass from the area, and loosen the soil with a garden fork or tiller.
2. Dig the Hole
Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the rose’s roots. The hole should be at least twice as wide as the roots and deep enough so that the bud union – the swollen area where the rose was grafted onto a rootstock – is level with the soil surface.
3. Soak the Roots
Before planting the rose, thoroughly soak the roots in a bucket of water for about 30 minutes. This will help to hydrate the roots and prepare them for planting.
4. Place the Rose in the Hole
Gently place the rose into the hole, spreading out the roots as you do so. Make sure that the bud union is level with the soil surface. If the hole is too deep, add or remove soil as necessary.
5. Backfill with Soil
Fill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the roots as you go. Avoid packing the soil too tightly, as this can prevent air and water from reaching the roots.
6. Water and Mulch
After planting, water the rose thoroughly to help settle the soil and eliminate any air pockets. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant to help conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
7. Provide Support
If necessary, install a trellis or stake to provide support for the rose as it grows. This will help to prevent the plant from leaning or being damaged by strong winds.
8. Regular Maintenance
Once the rose is planted, it will require regular maintenance to ensure healthy growth. This includes regular watering, fertilizing, pruning, and protecting the plant from pests and diseases.
By following these expert tips, you can successfully plant a rose with an open root system in the spring and enjoy beautiful blooms for years to come.
Watering and Mulching a Rose with an Open Root System
Watering is an essential aspect of caring for a rose with an open root system, especially during the spring when the plant is establishing its roots. Here are some expert tips on watering a rose with an open root system:
- Consistent watering: It is important to provide a consistent supply of water to the rose plant to ensure proper growth and development. During the spring, water the rose thoroughly at least once a week, making sure the water reaches the roots.
- Proper drainage: Ensure that the soil around the rose plant has good drainage to prevent waterlogged conditions, which can lead to root rot. If the soil is heavy and does not drain well, consider adding organic matter or creating raised beds to improve drainage.
- Deep watering: Water the rose deeply, allowing the water to penetrate down to the depth of the roots. This encourages the roots to grow deeper into the soil, resulting in a stronger and healthier plant.
- Morning watering: It is best to water the rose in the early morning. This allows the foliage to dry off during the day, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Mulching is another important practice when planting a rose with an open root system. Here are some tips on mulching:
- Mulch types: Use organic mulch such as wood chips, straw, or compost around the rose plant. Avoid using plastic mulch as it can trap moisture and prevent air circulation.
- Mulch depth: Apply a layer of mulch 2-4 inches deep around the base of the rose plant. This helps to conserve moisture, regulate soil temperature, and prevent weed growth.
- Keep mulch away from the stem: Make sure to keep the mulch a few inches away from the stem of the rose plant to prevent rot and fungal diseases.
- Renew mulch regularly: Over time, organic mulch decomposes and loses its effectiveness. Renew the mulch layer every year to maintain its benefits.
By following these watering and mulching practices, you can ensure the proper growth and health of your rose with an open root system.
Pruning and Fertilizing a Rose with an Open Root System

Pruning and fertilizing are important aspects of caring for a rose with an open root system during the spring season. By properly pruning and fertilizing your rose plant, you can ensure its healthy growth and vibrant blooms. Here are some expert tips to help you with this process:
1. Pruning:
- Start by removing any dead or damaged branches. These can hinder the growth of the plant and make it more susceptible to diseases.
- Next, prune any crossing or rubbing branches. This will prevent them from causing damage to each other and improve air circulation.
- Trim back any leggy or overgrown branches to promote compact and bushy growth.
- Make the cuts at a 45-degree angle, about ¼ inch above an outward-facing bud.
2. Fertilizing:

- Before fertilizing, ensure that the soil around the rose plant is moist.
- Choose a balanced slow-release fertilizer specifically formulated for roses.
- Apply the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Generally, you can sprinkle it around the base of the plant and water it in.
- It’s advisable to fertilize roses in early spring, just as new growth begins.
- Reapply the fertilizer every 4 to 6 weeks throughout the growing season, following the package directions.
3. Additional Tips:

- After pruning and fertilizing, mulch around the base of the rose plant with a layer of organic material. This will help retain moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate the soil temperature.
- Regularly check the rose plant for any signs of pests or diseases. If detected, take appropriate action to prevent their spread and maintain the plant’s health.
- Water the rose plant deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods. Aim to keep the soil evenly moist, but not waterlogged.
- Regularly remove any spent flowers to encourage continuous blooming.
By following these pruning and fertilizing tips, you can ensure that your rose plant with an open root system thrives and produces beautiful blooms throughout the spring season.
Caring for a Rose with an Open Root System in the Spring
Once you have successfully planted a rose with an open root system in the spring, it is important to provide proper care to ensure its healthy growth and blooming. Here are some expert tips on caring for your newly planted rose:
Watering
Water is crucial for the initial establishment of the rose plant. It is recommended to water the rose deeply immediately after planting to help settle the soil around the roots. For the first few weeks, make sure to water the plant regularly, keeping the soil slightly moist but not overly saturated. Avoid overhead watering to prevent diseases.
Fertilizing
Proper fertilization is essential for the rose plant’s overall health and vigor. Apply a slow-release balanced fertilizer around the base of the plant, following the manufacturer’s instructions. It is usually recommended to fertilize in early spring, just as new growth begins, and again in early summer. Avoid fertilizing late in the season as it can disrupt the plant’s dormancy.
Mulching
Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the rose plant provides numerous benefits. Mulch helps to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Apply a 2-3 inch layer of mulch, such as wood chips or shredded bark, around the plant, avoiding direct contact with the stem.
Pruning
Pruning is an important practice in maintaining the health, shape, and blooming of the rose plant. In the spring, prune any damaged or dead canes, as well as any crossing branches that can create congestion. Remove any suckers that may emerge from the rootstock, as they can drain energy from the main plant. Consult a rose pruning guide for specific instructions on pruning techniques.
Pest and Disease Control

Vigilance is key to prevent and control pests and diseases that can affect rose plants. Regularly inspect the plant for any signs of infestation or disease, such as aphids, black spot, or powdery mildew. Use appropriate organic or chemical controls as needed, following the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Support
Depending on the variety, some roses may require support to prevent the canes from bending or breaking under the weight of the blooms. Install a sturdy support system, such as trellises or stakes, in the early spring before the plant begins to grow vigorously. Tie the canes to the support structure using soft ties or twine, ensuring they have enough room for air circulation.
Regular Monitoring
Regularly monitor the rose plant for any changes in growth or appearance. Look for signs of stress, such as wilting or yellowing leaves, and take appropriate action. Addressing any issues promptly can help maintain the health and vitality of the plant.
By following these expert tips and providing proper care, your rose with an open root system will thrive and reward you with beautiful blooms throughout the spring and summer seasons.
Questions and Answers:
When is the best time to plant roses with an open root system?
The best time to plant roses with an open root system is in the spring, when the soil has thawed and the risk of frost has passed.