- The Importance of Fertilising Seedlings
- Benefits of Proper Fertilisation
- 1. Improved Nutrient Availability
- 2. Enhanced Root Development
- 3. Increased Resistance to Diseases and Pests
- 4. Enhanced Flowering and Fruit Production
- 5. Overall Plant Vigor
- Understanding Nutrient Needs
- Macronutrients
- Micronutrients
- pH Balance
- Feeding Schedule
- Choosing the Right Fertiliser
- Nutrient Content
- Form of Fertiliser
- Organic vs. Synthetic
- Safety and Environmental Impact
- Types of Fertilisers
- Organic Fertilisers
- Inorganic Fertilisers
- Water-Soluble Fertilisers
- Granular Fertilisers
- Slow-Release Fertilisers
- Specialty Fertilisers
- Conclusion
- Considerations for Seedling Fertilisation
- 1. The Right Timing
- 2. Choosing the Right Fertilizer
- 3. Slow-Release or Liquid Fertilizer
- 4. Proper Application
- 5. Watering Techniques
- 6. Monitoring and Adjusting
- Applying Fertiliser to Seedlings
- 1. Choose the Right Fertiliser
- 2. Start with a Diluted Solution
- 3. Apply Fertiliser Gently
- 4. Apply at the Right Time
- 5. Follow a Schedule
- 6. Monitor Growth and Adjust
- Timing and Frequency
- 1. Initial Fertilisation
- 2. Seedling Stage
- 3. Vegetative Growth Stage
- 4. Flowering and Fruit Set Stage
- 5. Maintenance Fertilisation
- Application Techniques
- 1. Top Dressing
- 2. Liquid Fertilizer Application
- 3. Foliar Feeding
- 4. Controlled-Release Fertilizers
- 5. Starter Fertilizers
- Monitoring and Adjusting Fertilisation
- Visual Inspection
- Soil Testing
- Fertiliser Schedule
- Watering and Fertilisation
- Maintaining Records
- Questions and Answers:
- How often should I fertilize seedlings?
- What type of fertilizer is best for seedlings?
- Can I use compost as a fertilizer for seedlings?
- Should I use organic or synthetic fertilizers for seedlings?
- What are the signs of over-fertilization in seedlings?
- Can I use liquid fertilizers for seedlings?
- When should I stop fertilizing seedlings?
- Videos: Seed Starting, Fertilizer For Seedlings, Up potting, Transplanting Plants COMPLETE GUIDE!
When it comes to growing healthy seedlings, proper fertilization techniques are essential. Fertilizing your seedlings can provide them with the nutrients they need to develop strong roots, healthy foliage, and vibrant flowers or fruits. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, mastering the art of fertilization will greatly improve your gardening success.
Before diving into the specifics of fertilization techniques, it’s important to understand the different types of fertilizer available. There are organic fertilizers, which are derived from natural sources, and synthetic fertilizers, which are chemically produced. Organic fertilizers, such as compost or manure, are rich in nutrients and improve soil structure. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, provide precise nutrient ratios and are quickly absorbed by plants.
Once you have chosen your fertilizer, it’s important to follow a few key steps when fertilizing your seedlings. First, you need to determine the correct timing for fertilization. In general, it’s best to wait until your seedlings have developed their first set of true leaves before applying fertilizer. This ensures that they have established a strong root system and can efficiently absorb the nutrients.
The next step is to apply the fertilizer correctly. It’s important to read the instructions on the fertilizer package and follow them closely. Generally, you will dilute the fertilizer in water and apply it evenly to the soil surrounding the seedlings. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as this can damage the delicate seedlings. A good rule of thumb is to apply the fertilizer at half the recommended strength, and gradually increase the strength as the seedlings mature.
Proper fertilization techniques can make a world of difference in the growth and health of your seedlings. By understanding the different types of fertilizer and following the correct timing and application methods, you can ensure that your seedlings receive the nutrients they need for optimal growth. So, roll up your sleeves and get ready to fertilize your way to gardening success!
The Importance of Fertilising Seedlings
Fertilising seedlings is a crucial step in their growth and development. By providing the right nutrients at the right time, you can ensure that your seedlings have the best chance of thriving. Here are some reasons why fertilising seedlings is important:
- Enhances Nutrient Availability: Seedlings rely on nutrients to fuel their growth and development. Fertilisers provide essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for the seedlings to develop strong roots, healthy leaves, and robust stems.
- Promotes Healthy Growth: A well-fed seedling is more likely to grow into a healthy plant. Fertilisers not only provide the nutrients that seedlings need, but they also help improve soil fertility. This creates an ideal environment for seedlings to grow, leading to stronger and more vigorous plants.
- Prevents Nutrient Deficiencies: Seedlings are more susceptible to nutrient deficiencies than mature plants. Fertilising seedlings can help address nutrient deficiencies before they become a problem. For example, a lack of nitrogen can cause stunted growth and yellowing leaves, while a deficiency in phosphorus can result in poor root development.
- Boosts Disease Resistance: Proper nutrition can strengthen seedlings’ immune systems, making them less vulnerable to diseases and pests. Fertilisers can help improve seedling health and increase their resistance to common plant diseases, such as damping-off, which can be caused by soilborne pathogens.
- Improves Overall Yields: Fertilising seedlings sets the stage for higher yields in the future. Well-fed seedlings have a greater chance of reaching their full potential and producing a bountiful harvest. By investing time and effort in fertilising your seedlings, you are laying the foundation for a successful gardening season.
In conclusion, fertilising seedlings is essential for their growth and development. It provides the necessary nutrients, promotes healthy growth, prevents nutrient deficiencies, boosts disease resistance, and improves overall yields. By understanding the importance of fertilisation and using the proper techniques, you can ensure the success of your seedlings and enjoy a productive garden.
Benefits of Proper Fertilisation
Fertilising seedlings properly is essential for their healthy development and growth. Here are some benefits of proper fertilisation:
1. Improved Nutrient Availability
Proper fertilisation ensures that the seedlings have access to the necessary nutrients for optimum growth. By providing the right fertilisers in the right amounts, you can help replenish the soil’s nutrient content and create an ideal growing environment for the seedlings.
2. Enhanced Root Development
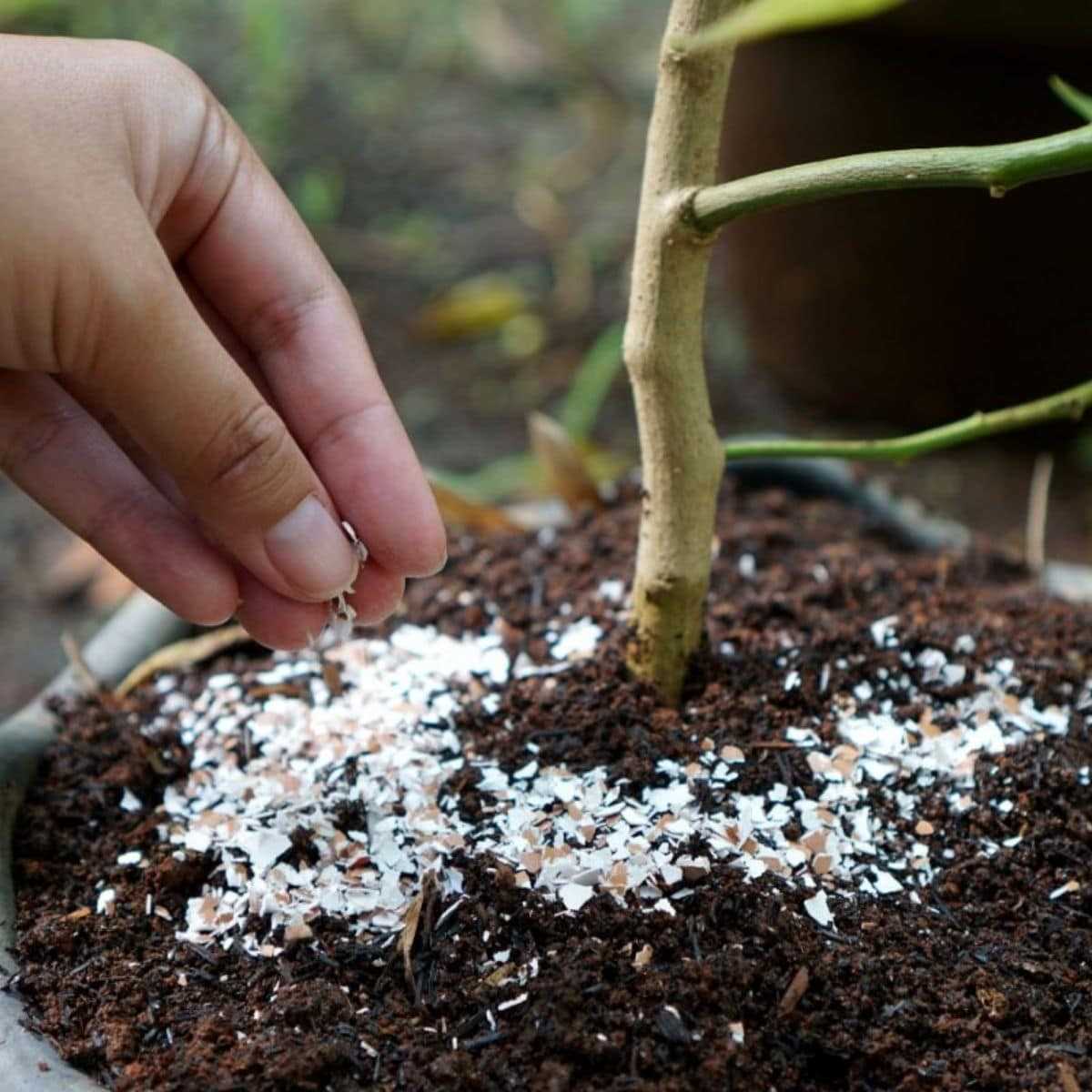

Proper fertilisation promotes the development of strong and healthy roots. Adequate nutrient supply encourages root growth, enabling the seedlings to establish a robust root system. This strong foundation allows the seedlings to better absorb water and nutrients from the soil, leading to improved overall plant health.
3. Increased Resistance to Diseases and Pests
When seedlings are properly fertilised, they are better equipped to withstand diseases and pests. Nutrient deficiencies weaken the plants, making them more susceptible to infections and infestations. By providing the necessary nutrients, you can boost the seedlings’ immune systems, increasing their resistance to diseases and pests.
4. Enhanced Flowering and Fruit Production
Proper fertilisation plays a crucial role in the flowering and fruit production of seedlings. By supplying the right balance of nutrients, you can promote healthy flower formation and stimulate fruit development. This leads to improved yields and higher-quality harvests.
5. Overall Plant Vigor
When seedlings receive proper fertilisation, they exhibit increased vigor and vitality. Adequate nutrient supply helps the plants grow faster, appear healthier, and exhibit better overall performance. Properly fertilised seedlings are more likely to thrive and reach their full potential.
By understanding the benefits of proper fertilisation, you can ensure that your seedlings receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development. Implementing proper fertilisation techniques will set the stage for healthy and productive plants in the long run.
Understanding Nutrient Needs
In order for seedlings to grow and develop properly, they require a balanced supply of nutrients. These nutrients are essential for various processes within the plant, such as energy production, tissue development, and overall growth. Understanding the specific nutrient needs of seedlings is crucial for successful fertilization.
Macronutrients
Seedlings require macronutrients in relatively large quantities to support their growth. The primary macronutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are often represented as the NPK ratio on fertilizer labels.
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is necessary for the production of proteins and chlorophyll. It plays a vital role in leaf and stem development. A lack of nitrogen can result in stunted growth and yellowing of leaves.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer and root development. It is especially important during the early stages of growth when seedlings are establishing their root systems.
- Potassium (K): Potassium helps regulate water uptake and maintain overall plant health. It plays a role in disease resistance and nutrient utilization.
Micronutrients
In addition to macronutrients, seedlings also require micronutrients in smaller quantities. These include elements such as iron, manganese, zinc, and copper. While micronutrients are needed in smaller amounts, they are still essential for proper plant growth and development.
pH Balance
Another crucial factor in meeting seedlings’ nutrient needs is maintaining the proper pH balance of the soil or growing medium. The pH level affects nutrient availability to seedlings. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0-7.0. Testing the pH of the soil or growing medium and making necessary adjustments can help ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
Feeding Schedule
It is important to establish a feeding schedule for fertilizing seedlings. Generally, seedlings require a weak fertilizer solution every 1-2 weeks, gradually increasing the concentration as they grow. However, it is essential to monitor the seedlings for any signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses and adjust the feeding schedule accordingly.
| Nutrient | Function | Deficiency Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Protein and chlorophyll production, leaf and stem development | Stunted growth, yellowing leaves |
| Phosphorus | Energy transfer, root development | Poor root growth, purple or red leaves |
| Potassium | Water regulation, disease resistance, nutrient utilization | Leaf scorch, yellowing edges |
Understanding the nutrient needs of seedlings and providing the proper fertilization can greatly increase the chances of successful growth and development. Regular monitoring, adjusting nutrient levels as needed, and maintaining a balanced feeding schedule will help ensure healthy and thriving seedlings.
Choosing the Right Fertiliser
When it comes to fertilising your seedlings, choosing the right fertiliser is crucial for their healthy growth and development. Here are some factors to consider when selecting the perfect fertiliser for your seedlings:
Nutrient Content
One of the most important considerations when choosing a fertiliser is its nutrient content. Different plants have different nutrient requirements at various stages of growth. Generally, fertilisers contain three main nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These are often represented by three numbers on the packaging, such as 10-10-10, which indicates the percentage of each nutrient in the fertiliser. Pay attention to these numbers and choose a fertiliser that matches your seedlings’ specific nutrient needs.
Form of Fertiliser
Fertilisers come in different forms, including granules, powders, and liquids. The form you choose depends on your preference and the application method you prefer. Granular fertilisers are typically applied directly to the soil and are ideal for outdoor seedlings or those grown in pots. Powdered fertilisers can be mixed with water and applied as a liquid solution, making them suitable for both soil and foliar applications. Liquid fertilisers are already in a soluble form and can be easily sprayed onto the leaves of seedlings for quick absorption.
Organic vs. Synthetic
Another factor to consider is whether to use organic or synthetic fertilisers. Organic fertilisers are derived from natural sources, such as compost, animal manure, or bone meal. They are slow-release and provide a gradual supply of nutrients to the seedlings. Synthetic fertilisers, on the other hand, are chemically formulated and provide an instant nutrient boost. They are typically faster-acting but may carry the risk of over-fertilisation if not applied correctly. Consider the specific needs of your seedlings and the pros and cons of each type before making a decision.
Safety and Environmental Impact
It’s essential to consider the safety and environmental impact of the fertiliser you choose. Read the product labels and instructions carefully to ensure that the fertiliser is safe for use around children, pets, and beneficial insects. Additionally, consider the potential environmental impact of the fertiliser. Look for fertilisers that are low in heavy metals, have minimal leaching potential, and are produced using sustainable practices.
By considering these factors and choosing the right fertiliser for your seedlings, you can provide them with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth without harming the environment or compromising safety. Remember to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for best results.
Types of Fertilisers
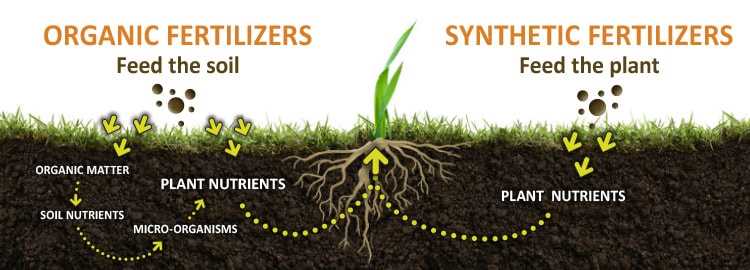
When it comes to fertilising seedlings, there are various types of fertilisers available on the market. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important to choose the right type based on your specific needs and the requirements of your seedlings.
Organic Fertilisers
Organic fertilisers are made from natural materials such as compost, manure, bone meal, and fish emulsion. These fertilisers are preferred by many gardeners because they are gentle on the environment and provide slow-release nutrients to the seedlings. Organic fertilisers also improve soil structure and promote beneficial microbial activity.
Inorganic Fertilisers
Inorganic fertilisers, also known as synthetic or chemical fertilisers, are made from chemical compounds and are readily available in many different forms. These fertilisers provide fast-release nutrients to the seedlings, but they can be harmful to the environment if not used properly. Inorganic fertilisers are often used for quick nutrient boosts or to correct specific nutrient deficiencies.
Water-Soluble Fertilisers
Water-soluble fertilisers come in the form of powders or liquids and are easily dissolved in water. They are usually applied to seedlings by watering them directly with the fertiliser solution. Water-soluble fertilisers provide a quick nutrient uptake for the seedlings and are convenient to use. However, they require frequent applications to maintain optimal nutrient levels.
Granular Fertilisers
Granular fertilisers are solid pellets or beads that are scattered around the base of the seedlings. They slowly release nutrients into the soil over time, providing a long-lasting source of nutrients for the seedlings. Granular fertilisers are easy to apply and require less frequent applications compared to water-soluble fertilisers. However, they may take longer to show results.
Slow-Release Fertilisers

Slow-release fertilisers are designed to release nutrients gradually over an extended period of time. These fertilisers come in different forms such as granules, spikes, or coated pellets. Slow-release fertilisers are convenient to use as they require fewer applications and provide a continuous supply of nutrients to the seedlings. However, they can be more expensive compared to other types of fertilisers.
Specialty Fertilisers
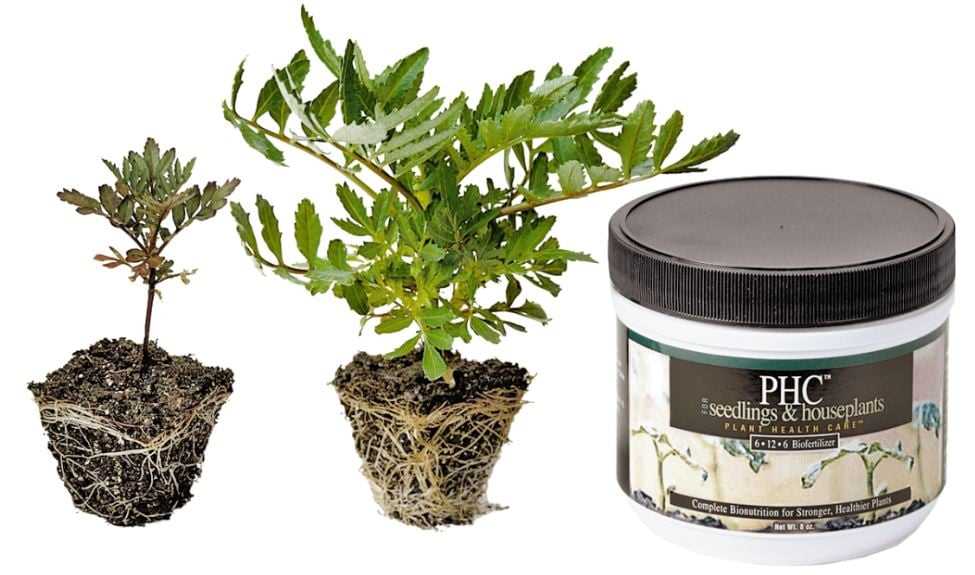

There are also specialty fertilisers available for specific types of seedlings or for certain stages of growth. These fertilisers are formulated to provide the right balance of nutrients and micronutrients that are essential for the specific needs of the seedlings. Specialty fertilisers can be beneficial for achieving optimal growth and development of seedlings.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of fertiliser is crucial for the success of your seedlings. Consider the specific needs of your seedlings, the advantages and disadvantages of each type of fertiliser, and your gardening practices before making a decision. Experimentation and regular observation of your seedlings’ growth will help you determine the most effective fertilisation technique for your specific situation.
Considerations for Seedling Fertilisation
When it comes to fertilising seedlings, there are several important considerations that every gardener should keep in mind. Proper fertilisation techniques can greatly enhance the growth and development of seedlings, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
1. The Right Timing
Timing is crucial when it comes to fertilising seedlings. It is important to wait until the seedlings have developed a few sets of true leaves before applying fertilizer. Applying fertilizer too early can burn the delicate roots of young seedlings, leading to stunted growth or even death.
2. Choosing the Right Fertilizer
Choosing the right fertilizer is essential for the healthy development of seedlings. Look for a fertilizer that is specifically formulated for seedlings or young plants. These fertilizers typically have a higher concentration of phosphorus, which aids in root development and overall plant growth.
3. Slow-Release or Liquid Fertilizer
There are two main types of fertilizers to choose from: slow-release and liquid. Slow-release fertilizers are granular and release nutrients slowly over time, providing a continuous source of nutrition for the seedlings. Liquid fertilizers, on the other hand, are mixed with water and applied directly to the seedlings. They provide a quick boost of nutrients but may need to be reapplied more frequently.
4. Proper Application
Proper application of fertilizer is essential to ensure that seedlings receive the necessary nutrients without causing harm. It is important to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and apply the recommended amount. Over-fertilisation can lead to nutrient burn and damage to the seedlings.
5. Watering Techniques
Watering techniques can also impact the efficiency of seedling fertilisation. It is important to water the seedlings thoroughly before applying fertilizer to prevent root burn. After fertilising, water the seedlings again to ensure that the nutrients are properly absorbed.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting
Regular monitoring of the seedlings is crucial to ensure that they are receiving the right amount of nutrients. If the seedlings show signs of nutrient deficiency or excess, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, adjustments to the fertiliser application may be necessary.
By considering these important factors, gardeners can ensure that their seedlings receive the right amount of nutrients at the right time, leading to healthy and robust plants.
Applying Fertiliser to Seedlings

Properly applying fertiliser to seedlings is crucial in their early stages of growth. This helps provide them with the necessary nutrients to establish strong roots and promote healthy development. Here are some essential tips for applying fertiliser to seedlings:
1. Choose the Right Fertiliser
There are different types of fertilisers available, such as organic and synthetic options. It is important to select a fertiliser that is suitable for seedlings. Look for a balanced formula with a ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) that is ideal for promoting healthy root growth.
2. Start with a Diluted Solution
Seedlings are delicate and can be easily damaged by excessive fertiliser. Start by diluting the fertiliser according to the instructions on the packaging. This will ensure that the seedlings receive the necessary nutrients without overwhelming them.
3. Apply Fertiliser Gently

When applying fertiliser to seedlings, it is important to do so gently to avoid disturbing the fragile roots. Use a watering can or spray bottle to apply the diluted fertiliser solution directly to the soil around the seedlings. Avoid pouring the fertiliser directly onto the leaves or stems.
4. Apply at the Right Time
Timing is crucial when applying fertiliser to seedlings. It is typically best to apply fertiliser once the seedlings have developed their first true leaves. This is usually a few weeks after germination. Applying fertiliser too early can damage the young seedlings.
5. Follow a Schedule
Establish a fertilising schedule to provide regular nutrition to the seedlings. This will promote consistent growth and development. Consult the instructions on the fertiliser packaging or seek advice from a gardening expert to determine the appropriate frequency and amount of fertiliser to apply.
6. Monitor Growth and Adjust
Keep a close eye on the seedlings and monitor their growth. If they appear to be growing well and exhibiting healthy development, continue with the fertilising schedule. However, if the seedlings show signs of nutrient deficiencies or excessive growth, adjust the fertiliser application accordingly.
By following these tips, you will be able to apply fertiliser effectively to your seedlings, providing them with the essential nutrients they need for healthy and robust growth.
Timing and Frequency
Proper timing and frequency in fertilising seedlings is essential for ensuring their healthy growth and development. Below are some guidelines to follow:
1. Initial Fertilisation
It is important to provide seedlings with the necessary nutrients from the start. Typically, a slow-release organic fertiliser is used during the initial planting, which provides a balanced mix of essential nutrients. This helps in promoting healthy root development and overall growth.
2. Seedling Stage
During the seedling stage, it is best to use a diluted liquid fertiliser to provide the necessary nutrients. This can be done once or twice a week, depending on the plant’s specific requirements. It is crucial to closely monitor the seedlings and adjust the frequency and strength of the fertiliser solution accordingly.
3. Vegetative Growth Stage
As the seedlings transition into the vegetative growth stage, they require more nutrients to support their increased growth rate. Fertilising every two weeks with a balanced liquid or granular fertiliser is recommended. This stage is crucial for the development of strong stems, leaves, and roots.
4. Flowering and Fruit Set Stage
During this stage, it is important to provide the seedlings with a higher ratio of phosphorus and potassium to promote flower formation and fruit development. A specific fertiliser formulated for blooming plants or fruiting vegetables should be used. Fertilising every two to three weeks with this specialised formula is recommended.
5. Maintenance Fertilisation
Once the seedlings have reached their desired size and are well-established, a maintenance fertilisation schedule can be followed. This typically involves fertilising every four to six weeks with a balanced fertiliser. It is important to monitor the plants for any signs of nutrient deficiency and adjust the fertiliser accordingly.
Besides following a proper fertilisation schedule, it is essential to water the seedlings adequately to ensure the nutrients are being absorbed properly. Over-fertilisation should also be avoided as it can lead to nutrient burns and other plant health issues. Regular observation and adjustment of the fertilisation routine will help in ensuring the seedlings receive the right amount of nutrients at the right time.
Application Techniques
1. Top Dressing
A common and effective method of fertilizing seedlings is top dressing. This involves spreading a thin layer of fertilizer evenly over the soil surface around the base of the seedlings.
Steps:
- Measure and dilute the fertilizer according to the instructions on the package.
- Using a small garden trowel or your hands, sprinkle the diluted fertilizer evenly around the base of each seedling, making sure not to touch the stem.
- Gently work the fertilizer into the top layer of soil, being careful not to disturb or damage the seedlings.
2. Liquid Fertilizer Application
Another method of fertilizing seedlings is through liquid application. This involves using a liquid fertilizer solution that is applied directly to the seedling roots.
Steps:
- Prepare the liquid fertilizer solution according to the instructions on the package.
- Using a watering can or spray bottle, carefully apply the liquid fertilizer to the soil around the base of each seedling.
- Water the seedlings after the fertilizer application to help the nutrients penetrate deeper into the soil.
3. Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is a method of fertilization where nutrients are applied directly to the leaves of the seedlings. This can be done using a foliar spray or a diluted fertilizer solution.
Steps:
- Prepare the foliar spray or diluted fertilizer solution according to the instructions on the package.
- Spray the leaves of the seedlings with the foliar spray or use a spray bottle to apply the diluted fertilizer solution.
- Make sure to cover both sides of the leaves to maximize nutrient absorption.
4. Controlled-Release Fertilizers
For a more convenient and long-lasting fertilizer application, you can use controlled-release fertilizers. These fertilizers are designed to slowly release nutrients over time, providing a steady supply of nutrients to the seedlings.
Steps:
- Choose a controlled-release fertilizer that is suitable for your seedlings and follow the instructions on the package for application rates.
- Apply the controlled-release fertilizer to the soil around the base of each seedling, making sure to distribute it evenly.
- Water the seedlings after the fertilizer application to activate the slow-release mechanism.
5. Starter Fertilizers
Starter fertilizers are specifically formulated to provide the essential nutrients that seedlings need during the early stages of growth. They can be applied during the planting process or shortly after germination.
Steps:
- Choose a starter fertilizer that is appropriate for your seedlings and follow the instructions on the package for application rates.
- Apply the starter fertilizer to the soil or mix it into the planting hole before transplanting the seedlings.
- Water the seedlings after the fertilizer application to help the nutrients reach the root zone.
Remember to always read and follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging for specific application rates and guidelines. Proper fertilization techniques will help your seedlings grow and thrive.
Monitoring and Adjusting Fertilisation
Monitoring the fertilisation of seedlings is crucial to ensure optimal growth and prevent any damage caused by over or under fertilisation. By regularly checking the plants and adjusting the fertiliser application as needed, you can maintain healthy and thriving seedlings.
Visual Inspection

One of the simplest ways to monitor the fertilisation of seedlings is through visual inspection. Regularly assess the appearance of the plants, including their foliage color, size, and overall health. Discolored or stunted growth may indicate that the plants are not receiving enough nutrients or are experiencing nutrient deficiencies. On the other hand, excessively dark and lush growth could mean over-fertilisation.
Pro Tip: Take notes or use a garden journal to track any changes in the appearance of the seedlings over time. This will help you identify patterns and make informed decisions about adjusting the fertilisation.
Soil Testing
Performing regular soil tests is another effective method to monitor and adjust fertilisation. Soil testing can provide valuable information about the nutrient levels in the soil and help you determine the appropriate fertiliser amounts and types to use.
There are different methods for soil testing, including DIY kits and professional laboratory analysis. Consider sending samples to a reputable lab for accurate and detailed results. Based on those results, you can make necessary adjustments to the fertiliser application.
Fertiliser Schedule
Creating a fertiliser schedule is essential for effective and consistent fertilisation. Adjust the schedule based on the plant’s growth stage and any observed deficiencies or excesses. For example, seedlings in their early stages may require less fertiliser compared to more mature plants.
- Start with a lower concentration of fertiliser and gradually increase it as the seedlings grow.
- Consider using a slow-release fertiliser to provide a steady supply of nutrients over a longer period.
- Regularly review and adjust the fertiliser schedule based on the visual inspection and soil testing results.
Watering and Fertilisation
Proper watering is closely tied to fertilisation. Overwatering can lead to nutrient leaching, while underwatering can limit nutrient uptake. It is crucial to maintain a balance between watering and fertilisation.
Pro Tip: Before applying fertiliser, ensure that the soil is adequately moist. This will help the plants absorb the nutrients more effectively.
Maintaining Records
To monitor and adjust fertilisation effectively, maintaining records is highly recommended. Keep track of the fertilisers used, quantities applied, and date of application. Additionally, record any observations and adjustments made based on visual inspections or soil testing. This information will serve as a valuable reference for future fertilisation efforts.
Pro Tip: Use a spreadsheet or gardening app to easily organize and access your fertilisation records.
By regularly monitoring your seedlings and adjusting fertilisation techniques, you can promote healthy growth and ensure they receive the optimal nutrients they need to thrive.
Questions and Answers:
How often should I fertilize seedlings?
Seedlings should be fertilized about once every two weeks to provide them with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
What type of fertilizer is best for seedlings?
A balanced fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is ideal for seedlings. Look for a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14.
Can I use compost as a fertilizer for seedlings?
Compost can be used as a fertilizer for seedlings, but it should be well-aged and mixed with soil to avoid burning the delicate roots of the seedlings.
Should I use organic or synthetic fertilizers for seedlings?
Both organic and synthetic fertilizers can be used for seedlings. Organic fertilizers, such as compost or manure, provide slow-release nutrients, while synthetic fertilizers offer more immediate results.
What are the signs of over-fertilization in seedlings?
Signs of over-fertilization in seedlings include leaf burn, stunted growth, and wilting. It is important to follow the recommended dosage and not exceed it to avoid damaging the seedlings.
Can I use liquid fertilizers for seedlings?
Liquid fertilizers can be used for seedlings, but they should be diluted to half the recommended strength to prevent burning the seedlings’ roots.
When should I stop fertilizing seedlings?
You should stop fertilizing seedlings once they have developed their second set of true leaves. At this point, they can be transplanted into larger containers or into the ground.







