- What is an Acidic Bed?
- Benefits of an Acidic Bed
- How to Create an Acidic Bed
- Conclusion
- Benefits of an Acidic Bed
- Step 1: Choosing the Right Location
- 1. Sunlight
- 2. Soil pH
- 3. Drainage
- 4. Space
- 5. Accessibility
- Step 2: Preparing the Soil
- 1. Test the soil pH
- 2. Adjust the pH level
- 3. Consider soil amendments
- 4. Incorporate nutrients
- 5. Water the soil thoroughly
- 6. Test the soil regularly
- Step 3: Selecting Blueberries and Hydrangeas
- Blueberries
- Hydrangeas
- Step 4: Planting and Transplanting
- 1. Choosing the right location:
- 2. Digging the planting hole:
- 3. Preparing the root ball:
- 4. Planting or transplanting the blueberry or hydrangea:
- 5. Mulching and staking:
- Step 5: Watering and Mulching
- 1. Watering
- 2. Mulching
- Step 6: Fertilizing
- 1. Choose the right fertilizer
- 2. Apply the fertilizer at the right time
- 3. Spread the fertilizer evenly
- 4. Water thoroughly after fertilizing
- 5. Monitor the plants
- Step 7: Pruning and Maintenance
- 1. Pruning Blueberries:
- 2. Pruning Hydrangeas:
- 3. Maintenance:
- Questions and Answers:
- Why do blueberries and hydrangeas require an acidic bed?
- What is the best way to test the pH level of the soil?
- How can I lower the pH level of the soil to make it more acidic?
- Can I use vinegar to create an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas?
- How often should I test the pH level of the soil?
- Videos: How to grow blueberries at home?
If you love gardening and want to create the perfect environment for blueberries and hydrangeas, then you’ll need to create an acidic bed. Blueberries and hydrangeas thrive in acidic soil, so it’s important to provide the right conditions for these plants to grow and flourish. In this ultimate guide, we’ll take you through the steps to create an acidic bed that will be the perfect home for your blueberries and hydrangeas.
The first step in creating an acidic bed is to test the pH level of your soil. Blueberries and hydrangeas prefer a pH level between 4.5 and 5.5, so it’s important to make sure your soil is within this range. You can purchase a soil testing kit from your local garden center or use a pH meter to test the acidity of your soil. Once you know the pH level of your soil, you can take the necessary steps to adjust it to the ideal range for blueberries and hydrangeas.
One way to lower the pH level of your soil is to add organic matter, such as compost or peat moss. These materials are naturally acidic and will help to lower the pH level of your soil over time. Spread a layer of compost or peat moss over your soil and mix it in thoroughly. Make sure to water the soil well after adding organic matter to help it settle and break down.
Another option to acidify your soil is to use sulfur or aluminum sulfate. These products are specifically designed to lower the pH level of soil and are readily available at garden centers. Follow the instructions on the packaging to determine the correct amount to use for your specific soil type and size of your bed. Apply the sulfur or aluminum sulfate to the soil and water well to help it penetrate and mix in.
Once you have adjusted the pH level of your soil, it’s time to plant your blueberries and hydrangeas. Dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of your plant and gently place it in the hole. Backfill the hole with soil, making sure to firm it gently around the plant. Water the newly planted blueberries and hydrangeas well to help them settle in and establish their roots.
In conclusion, creating an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas is a crucial step in ensuring the success of these plants. By testing the pH level of your soil and taking the necessary steps to adjust it to the ideal range, you can provide the perfect conditions for your blueberries and hydrangeas to thrive. Whether you choose to use organic matter or sulfur and aluminum sulfate, your efforts will be rewarded with healthy and vibrant plants that will delight you with their beautiful flowers and delicious fruits.
What is an Acidic Bed?
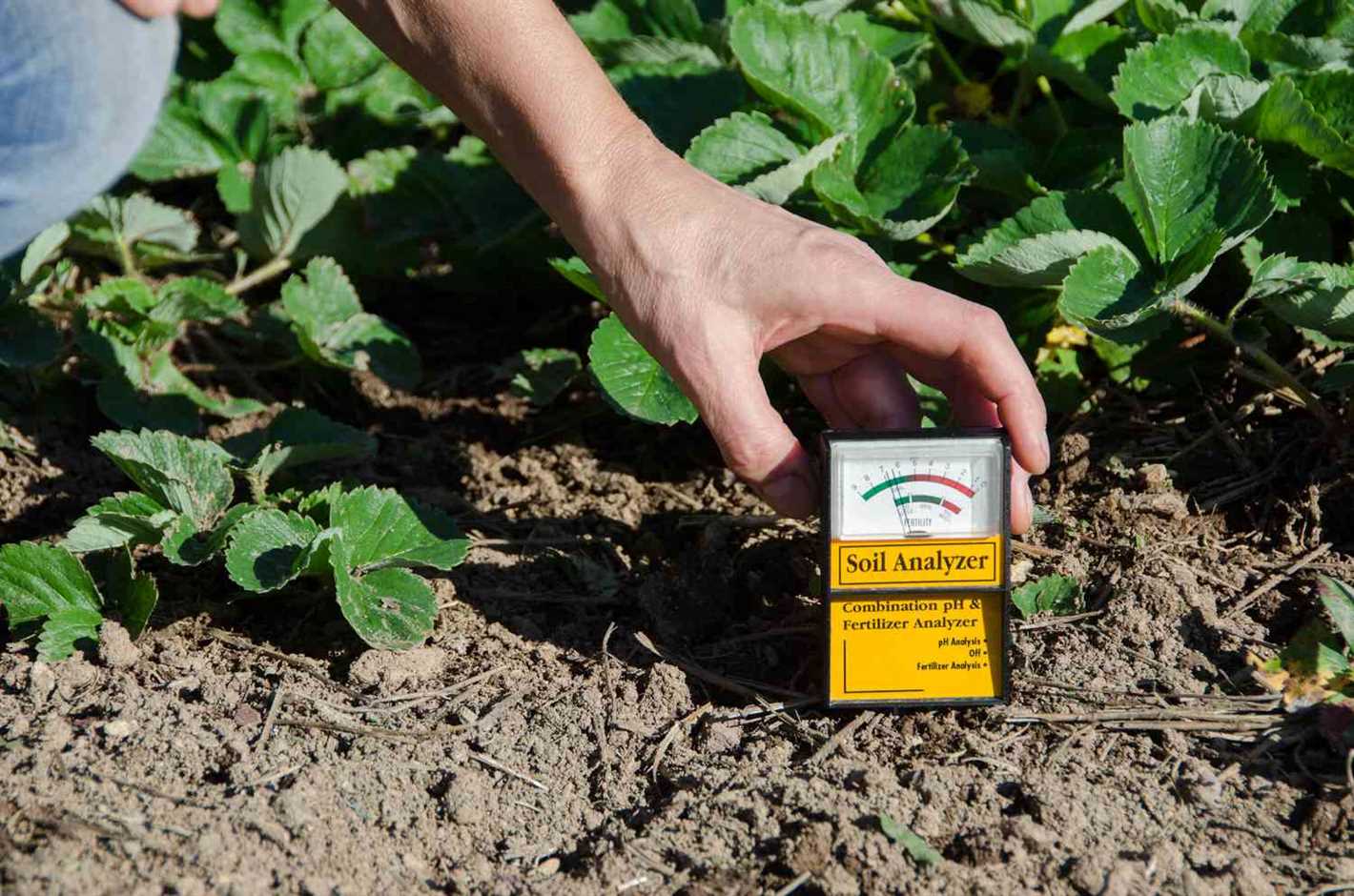

An acidic bed refers to the soil or growing medium that has a low pH level, typically below 7. It is specifically designed to meet the requirements of acid-loving plants such as blueberries and hydrangeas. These plants thrive in an acidic environment and require certain nutrients that are more readily available in acidic soils.
Benefits of an Acidic Bed
Creating an acidic bed for your blueberries and hydrangeas can offer several benefits:
- Optimal Nutrient Availability: Acidic soil conditions promote the availability of important nutrients like iron, manganese, and phosphorus. These nutrients are essential for the growth and development of acid-loving plants.
- Improved Soil Structure: Acidic soils tend to have better structure, allowing for improved drainage and preventing waterlogging. This is crucial for preventing root rot and other diseases that can affect the health of blueberries and hydrangeas.
- Enhanced Flower Color: For hydrangeas, the acidity of the soil can influence the color of their flowers. More acidic conditions result in blue flowers, while less acidic or alkaline conditions produce pink or purple flowers.
How to Create an Acidic Bed
Creating an acidic bed involves several steps:
- Testing Soil pH: Start by testing the pH level of your existing soil. You can use a pH testing kit or send a soil sample to a laboratory for analysis. This will help you determine the current acidity and whether adjustments are necessary.
- Adding Organic Matter: Organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or pine needles can help increase the acidity of the soil. Incorporate these materials into the soil to improve its structure and increase nutrient availability.
- Applying Acidifiers: If the soil is still not acidic enough, you can use specific acidifiers like sulfur or aluminum sulfate. Follow the instructions on the product packaging for proper application and dosage.
- Maintaining pH Levels: Regularly monitor the pH levels of your acidic bed to ensure they stay within the optimal range for your blueberries and hydrangeas. Adjustments may be necessary over time to maintain the desired acidity.
Conclusion
An acidic bed is essential for growing blueberries and hydrangeas, as it provides the ideal environment for these acid-loving plants to thrive. By following the steps mentioned above, you can create and maintain an acidic bed that will promote healthy growth and abundant blooms.
Benefits of an Acidic Bed
Creating an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas has several benefits. The acidity of the soil helps to create the optimal growing conditions for these plants, allowing them to thrive and produce bountiful blooms or fruits. Here are some of the key benefits of an acidic bed:
Enhanced nutrient availability: Acidic soil allows for better nutrient availability. Blueberries and hydrangeas have specific nutrient requirements, and an acidic bed can help ensure that these plants can easily access the necessary nutrients to grow and develop properly.
Better flower and fruit production: The acidity of the soil affects the color of flowers in hydrangeas and the flavor and size of blueberries. With the right acidity levels, blueberries can develop their signature sweet taste, and hydrangeas can produce vibrant and colorful blooms.
Improved soil structure: Acidic soil tends to have a looser, crumblier structure, which allows for better root development and water drainage. This promotes healthier root systems and reduces the risk of root rot or waterlogging.
Insect and disease resistance: Many pests and diseases thrive in alkaline soil environments. By creating an acidic bed, you can help create a less hospitable environment for these harmful organisms, reducing the risk of infestations and disease outbreaks in your blueberries and hydrangeas.
Overall, creating an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas is essential for ensuring healthy growth and maximizing the yield or visual appeal of these plants. By providing the right conditions, you can enjoy the benefits of vibrant blooms, delicious fruits, and pest-free plants.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Location
Choosing the right location for your blueberries and hydrangeas is essential to ensure their optimal growth and health. Here are some important factors to consider when selecting a location:
1. Sunlight
Blueberries and hydrangeas thrive in full sun to partial shade. Make sure to choose a location that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. Avoid areas with excessive shade, as this can result in poor growth and fruiting.
2. Soil pH
Both blueberries and hydrangeas prefer acidic soil with a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5. It’s crucial to test the soil pH in the selected location before planting. You can use a pH testing kit or take a soil sample to a local agricultural extension office for testing.
3. Drainage
Blueberries and hydrangeas require well-drained soil to thrive. Avoid low-lying areas or locations with heavy clay soil that tends to retain water. If necessary, consider amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost, to improve drainage.
4. Space
Ensure that you have enough space for your blueberries and hydrangeas to grow and spread out. Blueberry bushes can reach heights of 4-8 feet and have a spread of 2-6 feet, depending on the variety. Hydrangeas can also grow quite large, so make sure there is enough room for them to reach their full size.
5. Accessibility
Consider the accessibility of the chosen location for maintenance tasks, such as watering, fertilizing, and pruning. Make sure the area is easily accessible with a watering source nearby to ensure proper care for your plants.
Take the time to carefully choose the right location for your blueberries and hydrangeas, considering these factors. This will help set a solid foundation for their growth and increase their chances of thriving in an acidic bed.
Step 2: Preparing the Soil

Preparing the soil is an essential step in creating an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas. By ensuring that the soil has the right pH level, you can provide the optimal conditions for these plants to thrive. Follow these steps to prepare the soil:
1. Test the soil pH
The first step is to test the pH level of your soil. Blueberries and hydrangeas prefer acidic soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 5.5. You can purchase a soil testing kit from a garden center or send a sample of your soil to a laboratory for testing.
2. Adjust the pH level
If your soil pH is not within the preferred range, you will need to adjust it. To make the soil more acidic, you can add organic matter such as peat moss or pine needles. These materials gradually release acids into the soil, lowering the pH level over time. Mix the organic matter into the top 6-8 inches of soil using a garden fork or tiller.
3. Consider soil amendments
In some cases, the pH level of your soil may be difficult to adjust using organic matter alone. In such cases, you can consider using soil amendments specifically designed to lower pH levels. These amendments often contain sulfur, which helps to acidify the soil. Follow the instructions on the package for the recommended application rate and method.
4. Incorporate nutrients
Blueberries and hydrangeas benefit from specific nutrients to support their growth and development. Before planting, it is a good idea to incorporate a balanced fertilizer into the soil. Look for a fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application.
5. Water the soil thoroughly
After adjusting the pH level and incorporating nutrients, water the soil thoroughly to ensure that everything is well-mixed and evenly distributed. This will also help to settle the soil and create a good growing environment for your blueberries and hydrangeas.
6. Test the soil regularly
Once you have prepared the soil, it is important to monitor its pH level regularly. The pH level can change over time, so it’s a good idea to test the soil at least once a year to ensure that it remains within the optimal range for your plants.
By following these steps and preparing the soil properly, you can create an acidic bed that is perfect for growing blueberries and hydrangeas. Take the time to prepare the soil before planting to give your plants the best chance of success.
Step 3: Selecting Blueberries and Hydrangeas
If you’ve successfully created an acidic bed for your blueberries and hydrangeas, now it’s time to choose the right varieties of these plants for your garden. Different varieties have different preferences in terms of soil pH levels, so it’s important to select the ones that thrive in acidic conditions.
Blueberries
When choosing blueberries, look for varieties that are known to prefer acidic soil. Some popular blueberry varieties for acidic beds include:
- Bluecrop: This variety is known for its high yields and large, flavorful berries. It thrives in acidic soil and is a popular choice among blueberry enthusiasts.
- Patriot: Patriot blueberries are known for their cold-hardiness and resistance to diseases. They produce medium-sized berries and are a good choice for acidic beds.
- Legacy: Legacy blueberries are prized for their sweet, juicy berries and their ability to tolerate a wide range of soil conditions, including acidic ones.
Hydrangeas
When selecting hydrangeas for your acidic bed, keep in mind that the color of their blooms can be influenced by the pH level of the soil. Acidic soil tends to produce blue or purple blooms. Here are a few hydrangea varieties that thrive in acidic conditions:
- Nikko Blue: This is one of the most popular hydrangea varieties and is known for its big, beautiful blue blossoms. It prefers acidic soil and can add a stunning pop of color to your garden.
- Endless Summer: The Endless Summer variety is prized for its ability to bloom continuously from early summer to fall. It produces pink or blue flowers that can be influenced by soil pH.
- Forever Pink: As the name suggests, this hydrangea variety produces beautiful pink blooms. However, the color can turn blue in acidic soil, making it a great choice for an acidic bed.
Remember to research specific varieties and their soil preferences before making your final selection. This will ensure that your blueberries and hydrangeas thrive in your acidic bed and provide you with beautiful blooms and tasty berries.
Step 4: Planting and Transplanting
Once you have prepared the acidic soil and chosen the appropriate blueberry or hydrangea varieties, it’s time to plant or transplant them. Follow these steps to ensure a successful planting process:
1. Choosing the right location:
- Select a site that receives full or partial sun, as blueberries and hydrangeas require at least 6 hours of sunlight per day.
- Avoid planting them in low-lying areas that are prone to waterlogged soil, as this can lead to root rot.
- Ensure there is enough space for the plants to grow to their full size.
- Consider the proximity to other plants, keeping in mind the soil requirements and potential interference with their growth.
2. Digging the planting hole:
- Dig a hole that is twice as wide and deep as the root ball.
- Loosen the soil at the bottom of the hole.
- If planting multiple blueberries or hydrangeas, space the holes according to the recommended planting distance for the specific variety.
3. Preparing the root ball:
- Gently remove the plant from its container, being careful not to damage the roots.
- Inspect the roots for any signs of disease or damage, and trim off any dead or unhealthy roots.
- Loosen the root ball slightly with your hands or a garden fork to encourage proper root growth.
4. Planting or transplanting the blueberry or hydrangea:
- Place the plant in the center of the prepared hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with the soil you dug out, gently firming it around the plant as you go.
- Water the plant thoroughly to settle the soil and eliminate air pockets.
5. Mulching and staking:
- Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant, leaving a gap around the stem to prevent moisture-related problems.
- Consider staking or providing support for the plant if it is top-heavy or prone to wind damage.
Follow these steps when planting or transplanting blueberries and hydrangeas, and you’ll be on your way to enjoying healthy and vibrant plants in your acidic bed.
Step 5: Watering and Mulching
Proper watering and mulching are essential for maintaining an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas. Follow these guidelines to ensure your plants thrive:
1. Watering
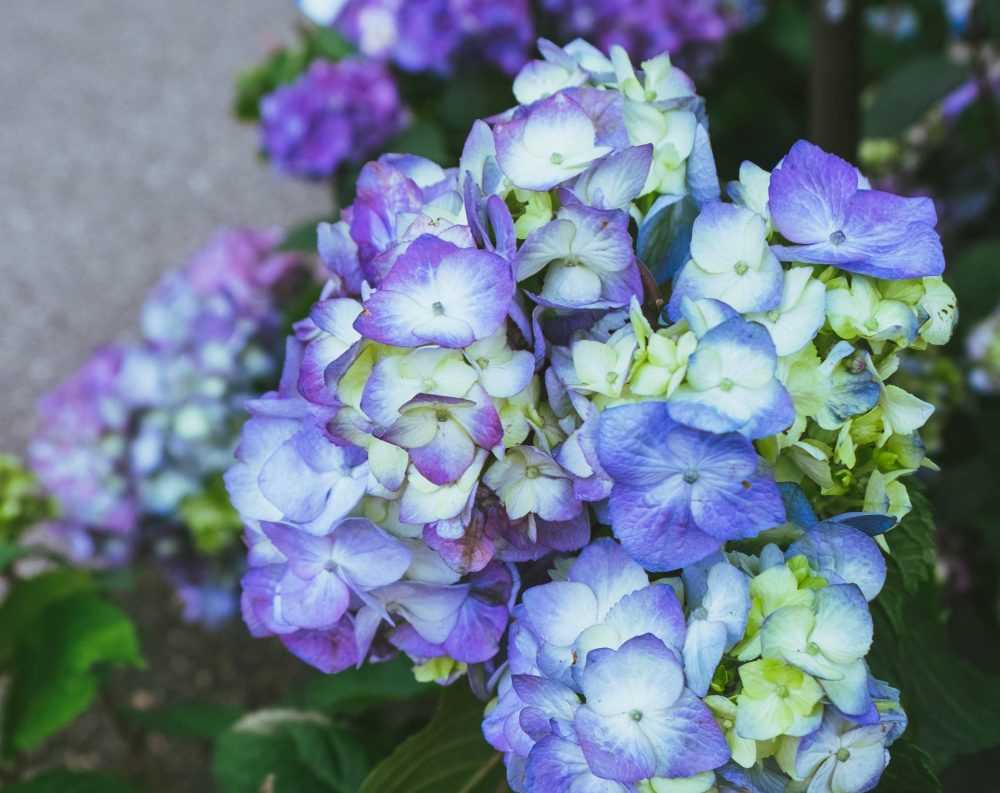

Blueberries and hydrangeas require regular watering to maintain soil moisture and acidity. Here’s how to properly water your plants:
- Water deeply once a week, especially during dry periods.
- Provide about 1 to 2 inches of water per week, evenly distributed around the plants.
- Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
- Use rainwater or distilled water to prevent alkaline substances from affecting soil pH.
2. Mulching
Mulching helps conserve soil moisture, maintain a cool root zone, and suppress weed growth. Here’s how to mulch your plants effectively:
- Apply a 2 to 4-inch layer of organic mulch around the base of the plants.
- Use materials such as pine needles, pine bark, or wood chips, as they can help acidify the soil over time.
- Avoid using materials like limestone or marble chips, which can raise soil pH.
- Keep the mulch 2 to 4 inches away from the base of the plants to prevent stem rot.
By following these watering and mulching practices, you can maintain a healthy and acidic bed for your blueberries and hydrangeas.
Step 6: Fertilizing
Once you have prepared your acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas, it is important to fertilize the soil to provide the necessary nutrients for optimal plant growth and health. Fertilizing can help boost the acidity of the soil and provide essential macronutrients and micronutrients that your plants need.
1. Choose the right fertilizer
When it comes to fertilizing acidic-loving plants like blueberries and hydrangeas, it is important to choose a fertilizer that is specifically formulated for acid-loving plants. Look for a fertilizer with a higher amount of sulfur and iron, as well as other essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
2. Apply the fertilizer at the right time
The best time to apply fertilizer to your acidic bed is in early spring, just before the growing season begins. This will give the plants ample time to absorb the nutrients and promote healthy growth. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging for the recommended application rate and frequency.
3. Spread the fertilizer evenly
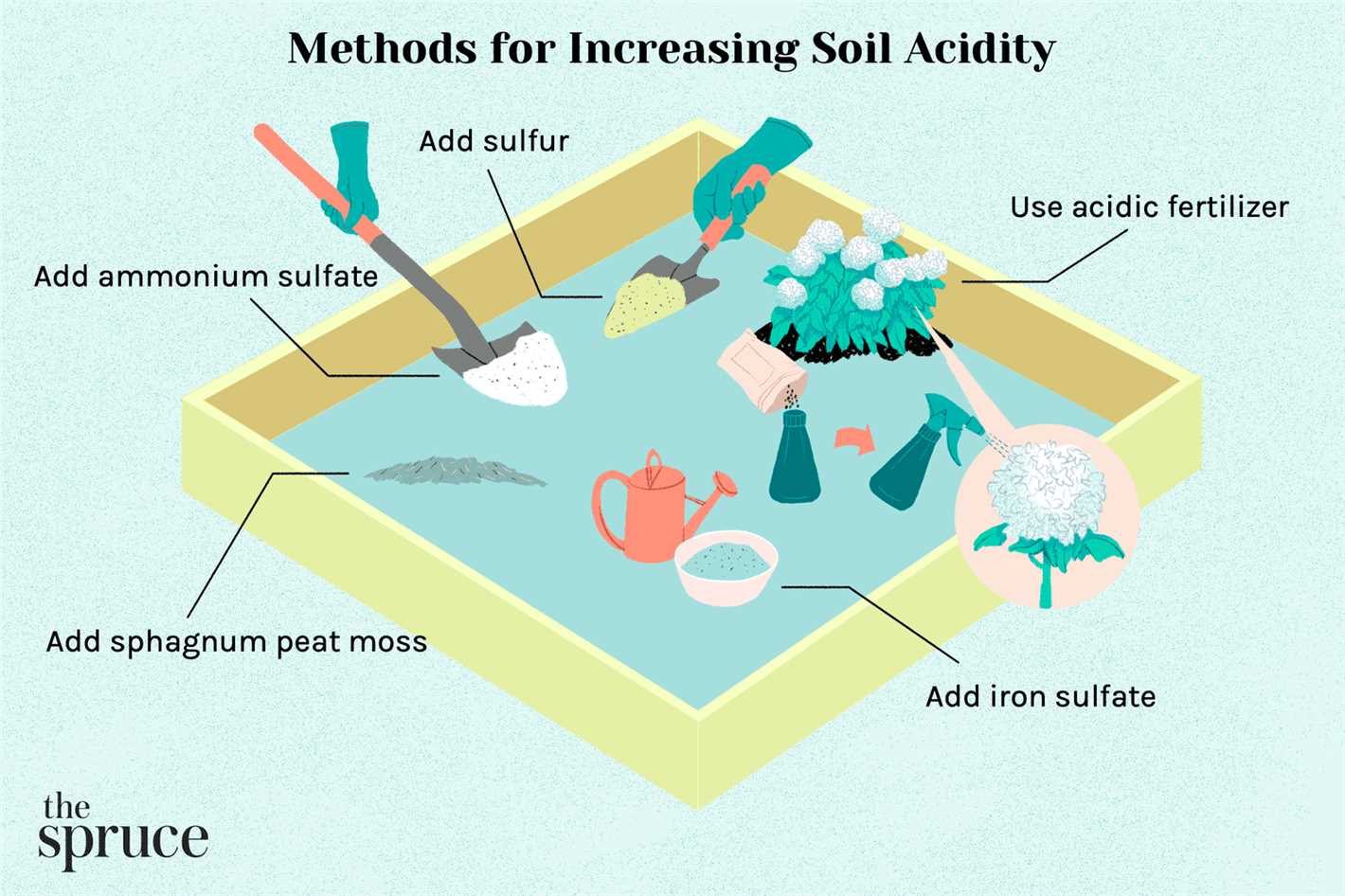
When applying the fertilizer, make sure to spread it evenly across the entire bed. You can either broadcast the fertilizer by hand or use a spreader to ensure an even distribution. Avoid applying the fertilizer too close to the plant stems to prevent root burn.
4. Water thoroughly after fertilizing
After applying the fertilizer, water the bed thoroughly to help the nutrients penetrate into the soil and reach the roots of the plants. This will also prevent the fertilizer from burning the roots. Watering deeply and regularly throughout the growing season will help maintain the acidity of the soil.
5. Monitor the plants
Monitor the plants closely after fertilizing to ensure they are responding well to the nutrients. Look for signs of healthy growth, such as vibrant foliage and increased fruit or flower production. If you notice any signs of nutrient deficiency or excess, adjust your fertilization practices accordingly.
Fertilizing your acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas is an important step in maintaining healthy and thriving plants. By choosing the right fertilizer, applying it at the right time, spreading it evenly, watering thoroughly, and monitoring the plants, you can ensure optimal growth and yield for your acid-loving plants.
Step 7: Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning and maintenance are important tasks that help ensure the health and productivity of your blueberry and hydrangea plants. Here are some guidelines to follow:
1. Pruning Blueberries:
- Prune blueberry plants during late winter or early spring before new growth begins.
- Remove any dead, damaged, or diseased branches using sterilized pruning shears.
- Thin out overcrowded branches to improve airflow and sunlight penetration.
- Trim back long, leggy branches to encourage bushier growth.
- Prune older blueberry plants more aggressively to stimulate new growth.
2. Pruning Hydrangeas:
- Prune hydrangeas based on their specific type, as pruning practices may vary.
- Remove dead flowers and stems after blooming to maintain a tidy appearance.
- Prune back overgrown or straggly branches to rejuvenate the plant.
- Some hydrangeas bloom on old wood, so be cautious when pruning in order not to remove next season’s flower buds.
- Consult specific guidelines for your particular hydrangea variety for optimal pruning instructions.
3. Maintenance:
Regular maintenance is crucial for the overall health and success of your plants. Here are some important maintenance practices to keep in mind:
- Water your blueberries and hydrangeas regularly, especially during dry periods.
- Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plants to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Fertilize your plants annually with a balanced acidic fertilizer to provide essential nutrients.
- Monitor for pests and diseases, and take appropriate action if any infestations occur.
- Monitor for signs of nutrient deficiencies and adjust fertilizer application as needed.
- Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of stress or abnormalities and take appropriate action.
By following these pruning and maintenance practices, you can help ensure strong, healthy, and productive blueberry and hydrangea plants.
Questions and Answers:
Why do blueberries and hydrangeas require an acidic bed?
Blueberries and hydrangeas prefer to grow in acidic soil because it provides the necessary nutrients for their optimal growth and development. The pH level of the soil affects the availability of nutrients, and an acidic pH helps these plants absorb nutrients like iron and manganese more efficiently. Therefore, creating an acidic bed is essential for blueberries and hydrangeas to thrive.
What is the best way to test the pH level of the soil?
The pH level of the soil can be tested using a soil pH testing kit or by sending a soil sample to a laboratory for analysis. The testing kit usually includes a pH probe that is inserted into the soil, and the reading on the meter indicates the pH level. Alternatively, you can collect a soil sample and send it to a laboratory, where they will conduct a detailed analysis to determine the pH level.
How can I lower the pH level of the soil to make it more acidic?
There are several methods to lower the pH level of the soil. One common method is to add organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to the soil. These organic materials are naturally acidic and can help to lower the pH. Alternatively, sulfur can also be used to acidify the soil. You can apply elemental sulfur directly to the soil or use a sulfur-containing fertilizer. It’s important to follow the recommended application rates and guidelines when using sulfur to avoid over-acidifying the soil.
Can I use vinegar to create an acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas?
Vinegar, particularly white vinegar, can be used as a temporary solution to lower the pH level of the soil. However, it is not recommended for long-term use as it can harm beneficial soil organisms and affect the overall soil health. It’s best to rely on organic matter or sulfur to create a sustainable and balanced acidic bed for blueberries and hydrangeas.
How often should I test the pH level of the soil?
It is generally recommended to test the pH level of the soil every 1-2 years. However, if you notice any changes in the growth or health of your blueberries or hydrangeas, it may be beneficial to test the pH level more frequently. Regular pH testing will allow you to make any necessary adjustments and ensure that the soil remains within the optimal range for these plants.







