- Nutritional Value of Lingonberries
- 1. Antioxidants
- 2. Vitamin C
- 3. Fiber
- 4. Vitamin K
- 5. Manganese
- Health Benefits of Lingonberries
- Cultivating Lingonberries: Techniques and Tips
- 1. Choosing the right location
- 2. Planting
- 3. Mulching
- 4. Watering
- 5. Fertilizing
- 6. Pruning
- 7. Pest and disease control
- 8. Harvesting
- Lingonberry Species: Varieties and Characteristics
- 1. Vaccinium vitis-idaea
- 2. Vaccinium uliginosum
- 3. Vaccinium oxycoccos
- The Role of Lingonberries in Traditional Cuisine
- Jams and Preserves
- Sauces and Syrups
- Beverages
- Baked Goods
- Sides and Accompaniments
- Lingonberries in Modern Culinary Applications
- Sauces and Condiments
- Baked Goods
- Beverages
- Salads and Dressings
- Cheese Pairings
- Preserves and Jellies
- Question-answer:
- What are the health benefits of lingonberries?
- How can I cultivate lingonberries in my garden?
- What are the different species of lingonberries?
- How do lingonberries compare to cranberries?
- Can lingonberries help prevent urinary tract infections?
- Are lingonberries safe for everyone to consume?
- Video: Lingonberries Health Benefits
Lingonberries are a delicious and nutritious fruit that is native to the cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Often referred to as “redberries,” these small, bright red berries are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a popular choice for health-conscious individuals. In addition to their nutritional value, lingonberries also offer a range of health benefits, such as improving digestion, boosting the immune system, and reducing inflammation.
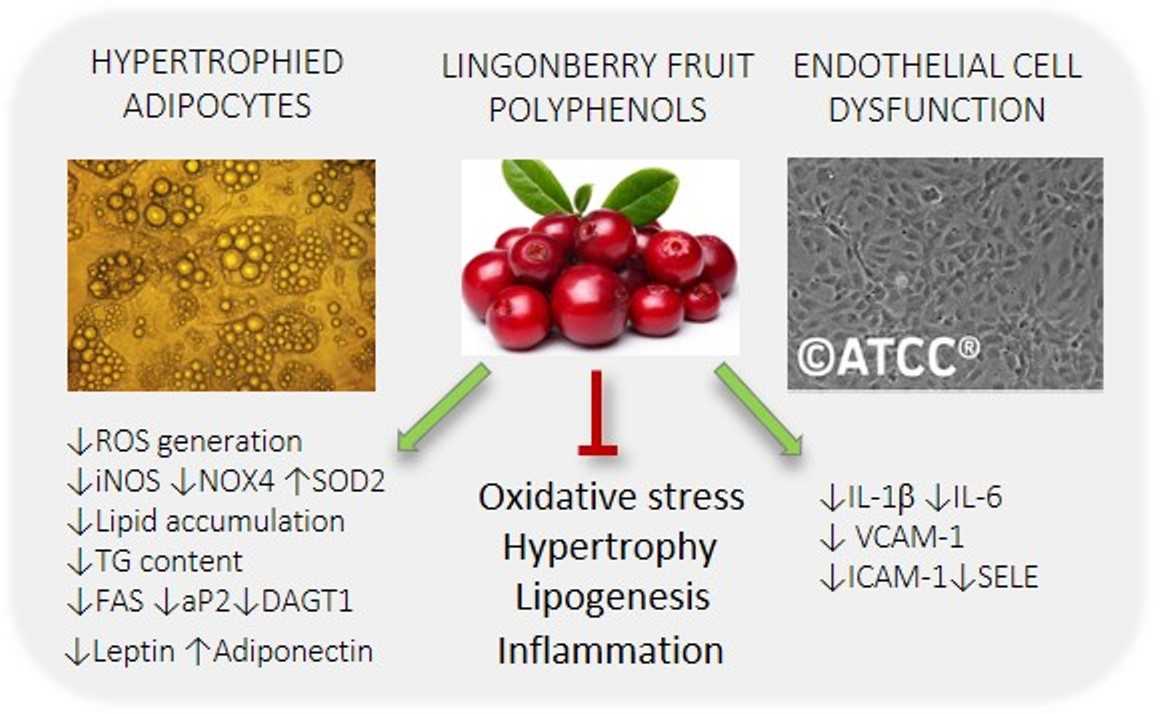
One of the reasons why lingonberries are considered a superfood is their high antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body against damage from harmful free radicals, which can contribute to chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. Lingonberries are rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, and various phytochemicals, including anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins, which have been shown to have powerful antioxidant properties.
Another notable health benefit of lingonberries is their potential to improve digestive health. These berries are a good source of dietary fiber, which can aid in digestion and promote regular bowel movements. Additionally, lingonberries contain natural compounds, such as tannins, that can help kill harmful bacteria in the gut and maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria.
When it comes to cultivation, lingonberries are relatively easy to grow and maintain. They are hardy plants that thrive in acidic soils and cool climates, making them suitable for regions with short growing seasons. Lingonberries can be propagated from seeds, cuttings, or by dividing established plants. They require well-drained soil and prefer a sunny or partially shaded location. Regular watering and mulching can help retain moisture and control weeds. With proper care, lingonberries can produce a bountiful crop of delicious berries.
There are several species of lingonberries, but the two most common ones are Vaccinium vitis-idaea and Vaccinium oxycoccos. Vaccinium vitis-idaea, also known as the mountain cranberry or lingonberry, is primarily found in North America, Europe, and Asia. It is a low-growing evergreen shrub that produces bright red berries that are slightly tart in taste. On the other hand, Vaccinium oxycoccos, commonly known as the bog cranberry or small cranberry, is native to the wetlands of North America, Europe, and Asia. It has a creeping habit and produces small, light-red berries that are slightly acidic.
Nutritional Value of Lingonberries
Lingonberries are small red berries that grow in acidic soil in the cooler regions of the Northern Hemisphere. They are known for their tart flavor and are commonly used in jams, preserves, and desserts. In addition to their delicious taste, lingonberries also offer a range of health benefits and contain several essential vitamins and minerals.
1. Antioxidants
Lingonberries are rich in antioxidants, including flavonoids and anthocyanins, which help protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation. These compounds have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Vitamin C
Lingonberries are an excellent source of vitamin C, which is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. Vitamin C also acts as an antioxidant and helps in the production of collagen, a protein necessary for the health of skin, bones, and connective tissues.
3. Fiber
Lingonberries are a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes feelings of fullness. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
4. Vitamin K
Lingonberries contain vitamin K, which plays a vital role in blood clotting and bone health. Adequate intake of vitamin K may also help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
5. Manganese
Lingonberries are a good source of manganese, a mineral that plays a role in bone health, metabolism, and the production of collagen. Manganese also acts as an antioxidant and helps protect against cellular damage.
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 43 |
| Carbohydrates | 9.6g |
| Fiber | 4.6g |
| Sugar | 4.2g |
| Fat | 0.1g |
| Protein | 0.5g |
| Vitamin C | 24mg |
| Vitamin K | 40.3µg |
| Manganese | 0.26mg |
It’s important to note that the nutritional content may vary slightly depending on the variety and ripeness of the lingonberries.
Incorporating lingonberries into your diet can provide a range of nutritional benefits and may contribute to overall health and well-being.
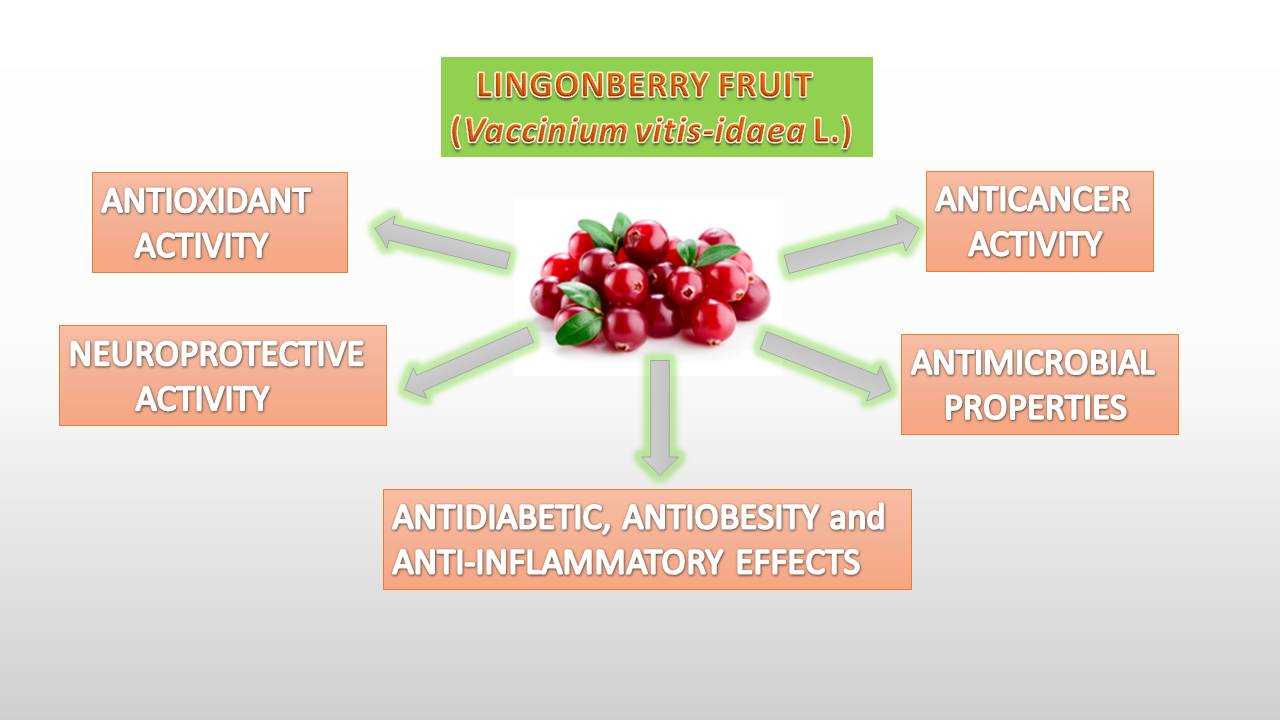
Health Benefits of Lingonberries
- Lingonberries are rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body against harmful free radicals.
- They contain high levels of vitamin C, which boosts the immune system and helps fight off colds and infections.
- Lingonberries have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
- These berries are a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and can help prevent constipation.
- Studies have suggested that lingonberries may have antimicrobial properties and could help fight against certain types of bacteria.
- Due to their high antioxidant content, lingonberries may have neuroprotective effects and help reduce the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Eating lingonberries may help protect against cardiovascular disease by reducing blood pressure and improving heart health.
- These berries have a low glycemic index, meaning they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels, making them a good option for those with diabetes or trying to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Research has suggested that lingonberries may have anti-cancer properties, but more studies are needed to fully understand their potential in cancer prevention and treatment.
Cultivating Lingonberries: Techniques and Tips
Growing lingonberries can be a rewarding endeavor, as they are not only delicious but also packed with health benefits. If you’re interested in cultivating lingonberries in your garden or backyard, here are some techniques and tips to help you get started.
1. Choosing the right location
Lingonberries prefer full sun but can also tolerate partial shade. When selecting a spot, make sure it has well-drained soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 6.5. Lingonberries have shallow roots, so avoid areas with compacted soil or heavy clay.
2. Planting
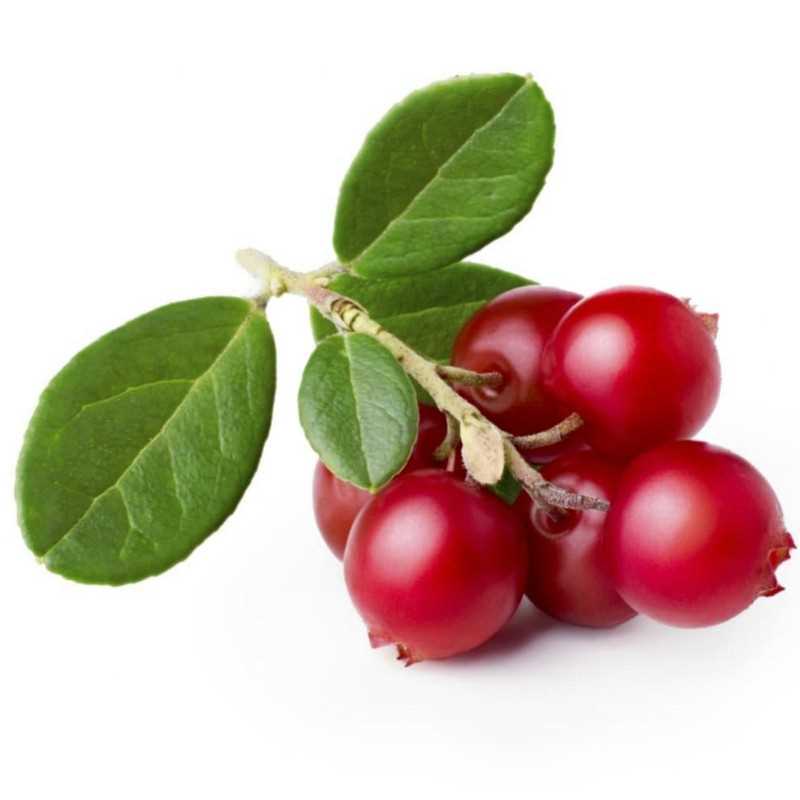

It is best to plant lingonberries in the early spring or fall. Space the plants about 12-18 inches apart in rows that are 2-3 feet apart. Dig a hole slightly larger than the plant’s root ball and gently place it in the hole, ensuring that the crown is level with the soil surface. Fill the hole with soil, compacting it gently around the plant.
3. Mulching
Lingonberries benefit from a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips. Apply a 2-3 inch layer around the plants to suppress weeds, conserve moisture, and regulate soil temperature.
4. Watering
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. During dry periods, provide supplemental watering to ensure that the plants receive about 1 inch of water per week. Avoid overhead watering as it can promote diseases.
5. Fertilizing
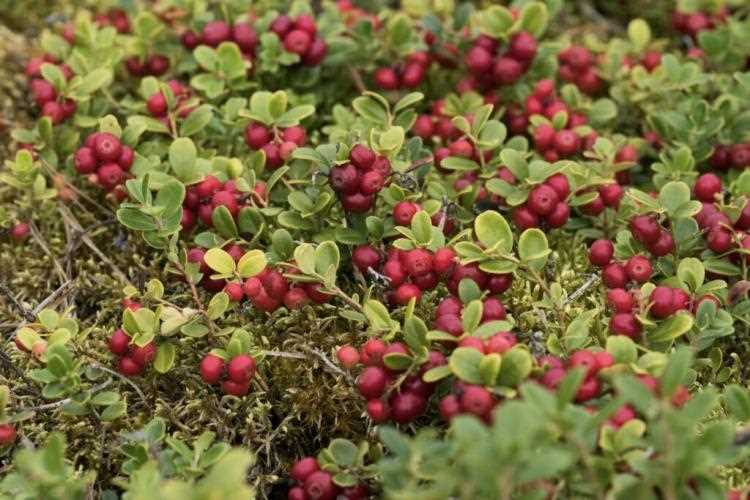

Before planting, incorporate compost or well-rotted manure into the soil to provide organic matter and nutrients. A balanced fertilizer can also be applied in early spring to promote healthy growth. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dosage and application.
6. Pruning

Pruning lingonberry plants is essential to maintain their health and productivity. In late winter or early spring, remove any dead or damaged branches. Also, thin out overcrowded growth to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration. Prune old canes after fruiting to encourage new growth.
7. Pest and disease control
Lingonberries are generally resistant to pests and diseases, but occasional issues may arise. Inspect the plants regularly for signs of aphids, spider mites, or fungal infections. If necessary, treat the affected plants with organic pest control methods or consult a horticulturist for advice.
8. Harvesting
Lingonberries usually ripen in the late summer or early fall. Harvest the berries when they are fully colored and slightly soft to the touch. Use your fingers or a small rake to gently remove the berries from the plants. The berries can be stored in the refrigerator for up to two weeks or preserved in various forms, such as jams or sauces.
By following these techniques and tips, you can successfully cultivate lingonberries and enjoy their delicious flavor and health benefits throughout the year.
Lingonberry Species: Varieties and Characteristics
Lingonberries, also known as cowberries or foxberries, belong to the Vaccinium genus and are native to the cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. There are several species of lingonberries, each with its own unique characteristics and growing conditions.
1. Vaccinium vitis-idaea
Vaccinium vitis-idaea is the most common species of lingonberry. It is a low-growing, evergreen shrub that can reach a height of 6-12 inches. The leaves of this species are dark green, glossy, and leathery, while the flowers are small, pink, and bell-shaped. The berries are bright red and have a tart taste.
2. Vaccinium uliginosum
Vaccinium uliginosum, also known as bog blueberry, is another species of lingonberry. It is a taller shrub, growing up to 1-3 feet in height. The leaves of this species are oval and slightly serrated, and the flowers are white or pink. The berries of Vaccinium uliginosum are dark blue and have a milder, sweeter flavor compared to Vaccinium vitis-idaea.
3. Vaccinium oxycoccos
Vaccinium oxycoccos, commonly known as small cranberry, is a closely related species to lingonberries. It is a low-growing perennial with creeping stems. The leaves are small and elliptical, and the flowers are pink or red. The berries of Vaccinium oxycoccos are red and have a tangy taste similar to lingonberries.
These are just a few examples of the different species of lingonberries. Each species has its own unique flavor profile and growing requirements, but they all share the common health benefits associated with lingonberries, such as being rich in antioxidants and vitamin C.
The Role of Lingonberries in Traditional Cuisine
Lingonberries are a staple in traditional cuisine in many Nordic countries, particularly Sweden, Norway, and Finland. These small red berries are known for their tart and slightly sweet flavor, making them a popular ingredient in a variety of dishes. Here are some of the ways lingonberries are used in traditional cuisine:
Jams and Preserves
Lingonberry jam is a classic condiment in Scandinavian cuisine. The berries are cooked down with sugar to create a thick and tangy jam that is often served with meatballs, grilled meats, or as a spread on bread. Lingonberry preserves are also commonly used as fillings in pastries and desserts.
Sauces and Syrups
The tartness of lingonberries makes them an ideal ingredient for sauces and syrups. Lingonberry sauce is traditionally served with game meats, such as reindeer or venison, to add a vibrant burst of flavor. Lingonberry syrup is often used as a topping for pancakes, waffles, and ice cream.
Beverages

Lingonberries are a popular ingredient in traditional Nordic beverages, particularly in the form of juice or as a flavoring for alcoholic drinks. Lingonberry juice can be enjoyed on its own or mixed with other fruit juices. Lingonberries are also used to flavor liqueurs and infused spirits.
Baked Goods
The tangy flavor of lingonberries is often incorporated into baked goods, such as breads, cakes, and muffins. Lingonberry bread is a common treat in Scandinavian countries, and lingonberry-filled pastries are a favorite among locals.
Sides and Accompaniments
Lingonberries are frequently served as a side dish or accompaniment to savory dishes. Their tartness complements rich and fatty foods, such as roasted meats, sausages, and liver pâtés. Lingonberries are often served alongside traditional Swedish dishes, such as meatballs or pickled herring.
In conclusion, lingonberries play a significant role in traditional Nordic cuisine. Their tart and slightly sweet flavor adds depth and versatility to a range of dishes, from jams and sauces to baked goods and beverages. The use of lingonberries in traditional cuisine highlights their cultural importance and the unique flavors they bring to the table.
Lingonberries in Modern Culinary Applications
Lingonberries have been used in traditional cuisine for centuries, but in recent years, they have also gained popularity in modern culinary applications. Their unique flavor and nutritional benefits make them a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes. Here are some ways you can incorporate lingonberries into your cooking:
Sauces and Condiments
Lingonberries are often used to make sauces and condiments that complement savory dishes. Their tangy flavor adds a tartness that balances out rich flavors, making them a great pairing for meats and cheeses. Lingonberry jam, for example, can be served as a condiment for roast beef or used as a glaze for grilled chicken.
Baked Goods
Lingonberries can be incorporated into a wide range of baked goods, from breads and muffins to pies and tarts. Their natural tartness adds a refreshing twist to sweet treats. Lingonberry muffins, lingonberry-filled pastries, and lingonberry pies are just a few examples of how lingonberries can be used in baking.
Beverages
Lingonberries can be used to infuse flavor into beverages such as cocktails, smoothies, and teas. Their tartness provides a refreshing element to these drinks and can be balanced out with sweeteners or other fruits. Lingonberry-infused vodka, lingonberry smoothies, and lingonberry iced tea are all delicious options.
Salads and Dressings
Lingonberries can be a great addition to salads, providing a burst of flavor that complements the greens and other ingredients. They can be used fresh or as part of a dressing or vinaigrette. Lingonberries also add a vibrant color to salads, making them visually appealing.
Cheese Pairings

Lingonberries are often served alongside cheeses, especially ones with strong flavors. The tanginess of lingonberries helps cut through the richness of the cheese and adds a touch of sweetness. Lingonberries can be served with a cheese board or incorporated into cheese-based dishes like baked brie.
Preserves and Jellies
Lingonberries are commonly used to make preserves and jellies due to their natural pectin content. These can be enjoyed on toast, crackers, or as a topping for pancakes or waffles. Lingonberry preserves also make great gifts.
In conclusion, lingonberries offer a range of culinary possibilities due to their unique flavor and versatile nature. Whether used in sauces, baked goods, beverages, salads, cheese pairings, or preserves, lingonberries can elevate your dishes with their tartness and nutritional benefits.
Question-answer:
What are the health benefits of lingonberries?
Lingonberries are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that offer numerous health benefits. They help boost the immune system, improve digestion, promote cardiovascular health, and have anti-inflammatory properties.
How can I cultivate lingonberries in my garden?
Cultivating lingonberries requires acidic soil, preferably with a pH of 4.5 to 5.5. They thrive in well-drained soil and prefer partial shade. Plant them in early spring or early fall, and make sure to water them regularly. Provide a layer of mulch to help retain moisture and control weeds.
What are the different species of lingonberries?
There are several species of lingonberries, including Vaccinium vitis-idaea, Vaccinium microcarpum, and Vaccinium oxycoccos. The most common species is Vaccinium vitis-idaea, which is native to northern Europe and North America.
How do lingonberries compare to cranberries?
Lingonberries and cranberries are both tart berries that belong to the same Vaccinium genus. However, lingonberries are smaller and less tart than cranberries. They also have a milder flavor and are commonly used in Scandinavian cuisine.
Can lingonberries help prevent urinary tract infections?
Yes, lingonberries have been found to help prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to their high content of proanthocyanidins. These compounds prevent bacteria from sticking to the walls of the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infection.
Are lingonberries safe for everyone to consume?
Lingonberries are generally safe for consumption for most people. However, individuals with a history of kidney stones or those on blood-thinning medications should exercise caution due to the high oxalate content of lingonberries. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about consuming lingonberries.







