- Lupus Cultivation and Planting
- Choosing the Right Location
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Lupus
- Watering and Care
- Pruning and Maintenance
- Conclusion
- Essential Steps for Successful Lupus Cultivation
- 1. Site Selection
- 2. Soil Preparation
- 3. Planting
- 4. Watering
- 5. Fertilization
- 6. Mulching
- 7. Pruning
- 8. Pest and Disease Control
- 9. Staking
- 10. Winter Care
- Tips for Planting Lupus in Your Garden
- Choose the right location
- Prepare the soil
- Start seeds indoors
- Transplant young seedlings
- Water regularly
- Fertilize adequately
- Support tall varieties
- Deadhead spent flowers
- Protect from pests
- Winter care
- Monitor for diseases
- Enjoy the beauty of lupus
- Lupus Species and Varieties
- Species
- Varieties
- Common Lupus Species Found in Gardens
- Lupus Albus
- Lupus Vulgaris
- Lupus Multiflorus
- Lupus Perennis
- Unique Varieties of Lupus for a Distinct Garden
- 1. Arctic Lupus
- 2. Rainbow Lupus
- 3. Chocolate Lupus
- 4. Red Rum Lupus
- 5. Pina Colada Lupus
- 6. Dwarf Lupus
- 7. Bandana Lupus
- Characteristics and Care of Lupus
- Characteristics
- Care
- Conclusion
- Understanding the Characteristics of Lupus Plants
- Variety of Colors
- Perennial Nature
- Thrives in Full Sun
- Well-Draining Soil
- Tolerant of Drought
- Pruning Requirements
- Attracts Pollinators
- Deer-Resistant
- Additional Considerations
- Tips for Proper Care of Lupus Plants
- 1. Sunlight:
- 2. Watering:
- 3. Soil:
- 4. Fertilization:
- 5. Pruning:
- 6. Pest and Disease Control:
- 7. Mulching:
- 8. Winter Protection:
- Lupus and its Medicinal Properties
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Antioxidant Activity
- Digestive Health
- Diuretic Effects
- Wound Healing
- Cautions and Considerations
- Questions and Answers:
- What is lupus?
- How can I plant and cultivate lupus?
- What are the different species of lupus?
- What are the best varieties of lupus to grow?
- Can lupus be cured?
- What are the common symptoms of lupus?
- What are some tips for growing lupus successfully?
- Videos: Guide to Growing Lupines

Lupus, also known as lupine or lupinus, is a versatile flowering plant that belongs to the legume family. With its vibrant colors and striking appearance, lupus has become a popular choice for gardeners and landscaping enthusiasts. In this ultimate guide, we will explore everything you need to know about planting and cultivating lupus, as well as the different species and varieties available.
Planting and Cultivation:
Before planting lupus, it is important to choose the right location. Lupus thrives in well-drained soil and full sun, so make sure to select a spot that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. It is also essential to prepare the soil by removing any weeds or grass and adding organic matter to improve drainage.
When it comes to planting, lupus seeds can be directly sown into the ground in early spring or fall. The seeds should be planted at a depth of about 1 inch and spaced about 12-18 inches apart. Once planted, make sure to water the seeds thoroughly and provide regular watering until the plants are established.
Species and Varieties:
Lupinus comes in a wide range of species and varieties, each with its unique characteristics. One of the most common species is Lupinus polyphyllus, which is known for its tall spires of flowers in various shades of blue, purple, and pink. Another popular species is Lupinus perennis, also known as the wild lupus, which produces clusters of vibrant blue flowers.
In addition to the common species, there are also numerous hybrid varieties available. These hybrids have been bred to enhance certain traits, such as larger flower spikes or more compact growth habits. Some popular hybrid varieties include ‘Russell Hybrids’, ‘Gallery Series’, and ‘Chandelier’.
Conclusion:
Whether you are an experienced gardener or just starting out, growing lupus can be a rewarding experience. With its stunning flowers and easy cultivation, lupus is sure to add a touch of beauty to any garden or landscape. By following the planting and cultivation tips outlined in this guide and choosing the right species and varieties, you can enjoy the beauty of lupus year after year.
Lupus Cultivation and Planting
The Lupus plant is a beautiful flowering perennial that is native to Mediterranean regions. It is known for its vibrant colors and long-lasting blooms, making it a popular choice for gardeners. Cultivating and planting Lupus requires some specific techniques to ensure its optimal growth and health.
Choosing the Right Location
Before planting Lupus, it is important to select the right location for optimal growth. Lupus plants prefer full sun or partial shade, so choose a spot in your garden that receives at least 6 hours of sunlight per day. Ensure that the soil is well-draining as Lupus plants do not thrive in wet or waterlogged conditions.
Preparing the Soil
The next step in cultivating Lupus is to prepare the soil. Start by removing any weeds or debris from the planting area. Loosen the soil using a garden fork or tiller, ensuring good aeration and drainage. Lupus plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil, so you may need to amend the soil with organic matter or compost to achieve the desired pH level.
Planting Lupus
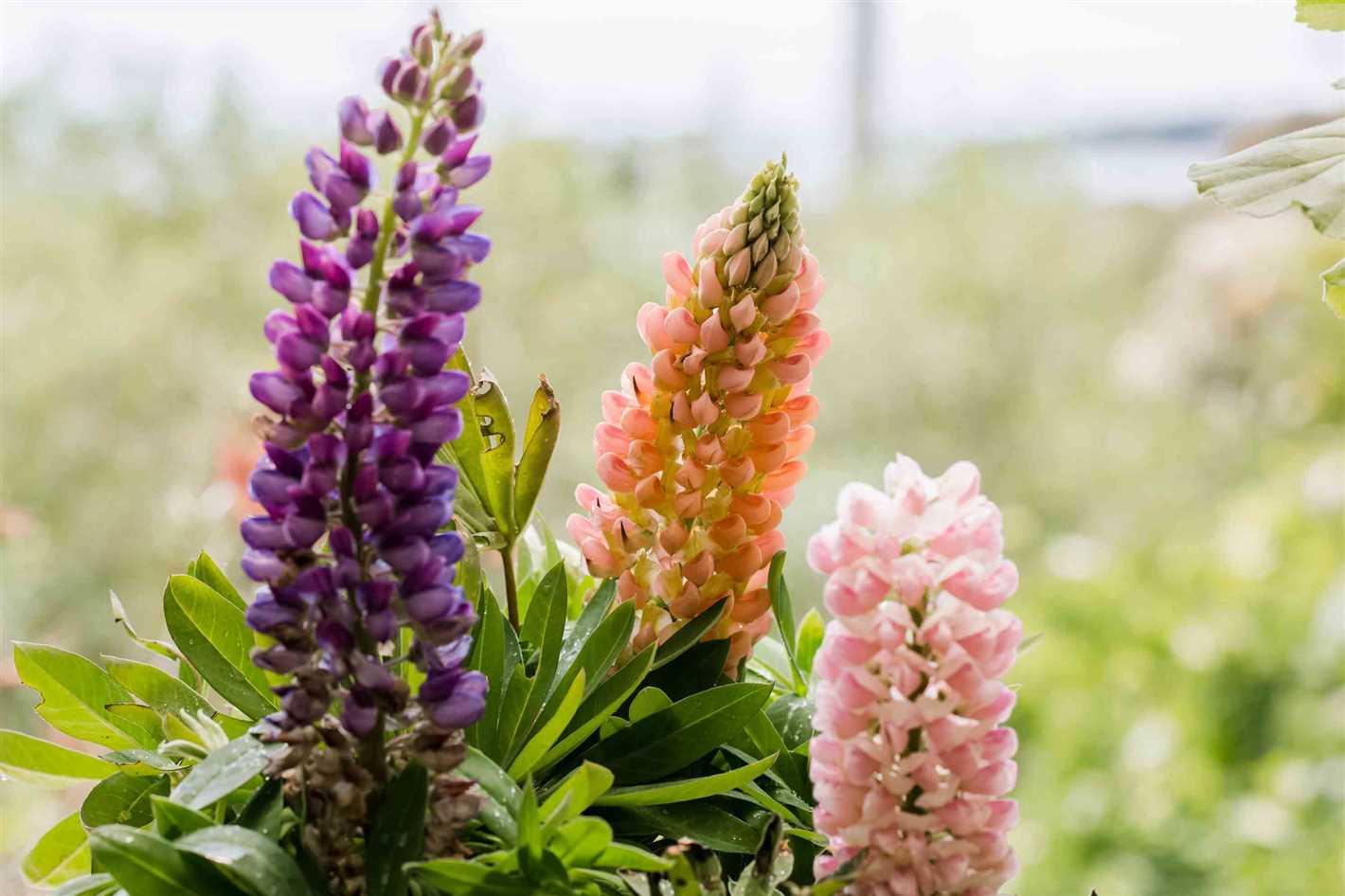


Once the soil is prepared, it’s time to plant your Lupus. Dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the plant. Place the Lupus plant in the hole, ensuring that it is planted at the same depth as it was in its original container. Gently backfill the hole with soil, firming it around the base of the plant to ensure good root-to-soil contact.
Watering and Care
After planting, it’s important to provide proper care to ensure the healthy growth of your Lupus plant. Water the plant thoroughly after planting and continue to provide regular watering throughout the growing season, especially during dry spells. However, be careful not to overwater as Lupus plants are susceptible to root rot.
Additionally, it is recommended to apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture and suppress weed growth. Fertilize the Lupus plant once a month during the growing season with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to provide essential nutrients.
Pruning and Maintenance
To maintain the appearance and health of your Lupus plant, regular pruning is necessary. Prune the plant after the blooming period to remove any dead or damaged stems and encourage new growth. This will also help the plant maintain a compact shape and produce more flowers in the next blooming season.
Regularly inspect your Lupus plant for any signs of pests or diseases. Common issues that may affect Lupus plants include aphids, snails, and powdery mildew. If any of these problems are observed, take appropriate measures to control and treat them promptly.
Conclusion
Cultivating and planting Lupus can be a rewarding experience for any garden enthusiast. By choosing the right location, preparing the soil, providing proper care, and performing regular maintenance, you can enjoy the beauty of Lupus plants in your garden year after year.
Essential Steps for Successful Lupus Cultivation
1. Site Selection


Choose a well-drained location with full or partial sunlight for your lupus plants. Lupus requires at least six hours of sunlight per day to thrive.
2. Soil Preparation
Prepare the soil by removing any weeds or grass. Lupus plants prefer a neutral to slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil to improve drainage and fertility.
3. Planting
Plant lupus seeds or seedlings in early spring once the soil has warmed up and there is no longer a risk of frost. Space the plants about 12 to 18 inches apart to allow for adequate air circulation. Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball, place the plant in the hole, and backfill with soil, firming it gently around the roots.
4. Watering
Water lupus plants thoroughly after planting and keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Water the plants deeply at least once a week, or more often during periods of hot and dry weather.
5. Fertilization
Feed lupus plants with a balanced slow-release fertilizer in early spring and again in midsummer. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the correct application rate. Avoid over-fertilization, as it can lead to excessive foliage growth with fewer flowers.
6. Mulching
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of lupus plants to help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use materials like straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves, and apply the mulch to a depth of 2 to 3 inches.
7. Pruning
Regularly remove spent flowers and prune back leggy or overgrown stems to encourage bushier growth and more blooms. Cut the stems back to just above a set of leaves or a side shoot. Perform more severe pruning in early spring to rejuvenate older plants.
8. Pest and Disease Control
Monitor lupus plants for common pests such as aphids, spider mites, and slugs. Use organic insecticides or other suitable control methods if an infestation occurs. Keep the plants well-ventilated to prevent diseases such as powdery mildew, and promptly remove any infected foliage.
9. Staking
If your lupus plants have tall stems that are prone to bending or breaking, provide support by staking them. Use bamboo stakes or other suitable materials and gently tie the stems to the stakes with soft ties to prevent damage.
10. Winter Care
In regions with cold winters, protect lupus plants by mulching the base with straw or leaves to insulate the roots. Container-grown lupus should be moved indoors or to a protected area. Check for and remove any dead or damaged foliage during the winter months.
By following these essential steps, you can ensure successful cultivation of lupus plants and enjoy their vibrant flowers throughout the growing season.
Tips for Planting Lupus in Your Garden
Choose the right location
Select a location in your garden that receives full sun or partial shade. Lupus plants thrive in areas with at least 6 hours of sunlight per day. Ensure that the soil is well-drained and fertile.
Prepare the soil
Before planting lupus, prepare the soil by removing any weeds and debris. Loosen the soil and amend it with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve its fertility and drainage.
Start seeds indoors
If you are starting lupus from seeds, begin the germination process indoors about 8-10 weeks before the last expected frost date. Sow the seeds in seed trays or pots filled with seed-starting mix, and keep them in a warm and well-lit area until they sprout.
Transplant young seedlings


Once the danger of frost has passed, transplant the young lupus seedlings into your garden. Dig holes that are slightly larger than the root balls of the seedlings and space them about 12-24 inches apart, depending on the specific lupus variety.
Water regularly
Lupus plants require regular watering to establish their root systems and ensure healthy growth. Water the plants deeply at least once a week, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
Fertilize adequately
Provide your lupus plants with regular doses of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and abundant flowering. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as it can damage the plants.
Support tall varieties
If you are growing tall varieties of lupus, use stakes or trellises to provide support for the plants. This will prevent them from flopping over and breaking under their own weight, especially when in full bloom.
Deadhead spent flowers
To encourage continuous blooming, regularly deadhead the spent flowers from your lupus plants. This will prevent the plants from redirecting their energy towards seed production and instead promote the growth of new flowers.
Protect from pests
Keep an eye out for common pests, such as aphids and slugs, that can damage lupus plants. Use organic pest control methods or insecticidal soap to protect your plants from infestations. Remove any weeds or plants that may harbor pests.
Winter care
In colder climates, lupus plants may require protection during the winter months. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plants to insulate the soil and protect the root system from freezing temperatures.
Monitor for diseases
Regularly inspect your lupus plants for signs of diseases, such as powdery mildew or leaf spot. Remove and dispose of any infected leaves or plants to prevent the spread of the disease. Additionally, avoid planting lupus in areas where the same family of plants has previously suffered from diseases.
Enjoy the beauty of lupus
Once your lupus plants are established and thriving, sit back and enjoy their colorful blooms. Lupus are known for their vibrant flowers and long blooming season, bringing beauty and charm to your garden.
Lupus Species and Varieties
Lupus, also known as lupine, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. There are over 200 species of lupus, which are native to North America, Europe, and Asia. These plants are known for their vibrant and colorful flowers, making them a popular choice for gardens and landscapes.
Species
- Lupus polyphyllus: This is the most common species of lupus, with tall spikes of flowers in shades of purple, blue, pink, and white. It is native to western North America.
- Lupus perennis: Also known as sundial lupus, this species has low-growing foliage and flowers that open and close with the sun. It is native to eastern North America.
- Lupus arboreus: Commonly referred to as tree lupus, this species is a small shrub with yellow flowers. It is native to the Canary Islands and Madeira.
- Lupus luteus: This species has bright yellow flowers and is native to southern Europe and North Africa. It is commonly found in dry, rocky habitats.
Varieties
In addition to the various species of lupus, there are also many cultivated varieties available. These varieties have been bred for specific traits, such as flower color, size, and growth habit. Some popular varieties include:
- Lupus ‘Gallery Blue’: This variety has compact growth and produces spikes of vibrant blue flowers.
- Lupus ‘Chandelier’: Known for its tall, branching stems and golden yellow flowers, this variety adds a dramatic touch to any garden.
- Lupus ‘Red Rum’: With its deep red flowers, this variety is a standout in any landscape.
- Lupus ‘The Governor’: This variety features large, pale pink flowers and is prized for its fragrance.
When selecting lupus species or varieties for your garden, consider the climate and soil conditions of your region, as well as the desired aesthetic. With their beautiful flowers and striking foliage, lupus are sure to enhance the beauty of any landscape.
Common Lupus Species Found in Gardens
Lupus Albus
The Lupus Albus, also known as the White Lupus, is a beautiful lupus species with white flowers. It is a popular choice for gardeners who want a classic and elegant look in their gardens. The Lupus Albus typically grows to a height of 1 to 2 feet and blooms in late spring or early summer.
Lupus Vulgaris
The Lupus Vulgaris, or the Common Lupus, is one of the most widely cultivated lupus species. It has vibrant purple flowers that add a splash of color to any garden. The Lupus Vulgaris is a hardy plant that can tolerate a variety of soil conditions and is easy to grow. It grows to a height of 1 to 3 feet and blooms in mid to late summer.
Lupus Multiflorus
The Lupus Multiflorus, also known as the Many-flowered Lupus, is a stunning lupus species that produces an abundance of flowers. It is known for its vibrant colors, including shades of pink, purple, and white. The Lupus Multiflorus can grow up to 3 feet tall and blooms from late spring to early fall.
Lupus Perennis
The Lupus Perennis, or the Perennial Lupus, is a long-lived lupus species that can add beauty to a garden year after year. It has blue or purple flowers that bloom from late spring to early summer. The Lupus Perennis prefers well-drained soil and can tolerate full sun or partial shade. It grows to a height of 2 to 4 feet.
In addition to these common lupus species, there are many other varieties and hybrids available for gardeners to choose from. Whether you prefer classic white flowers or vibrant hues, there is sure to be a lupus species that will thrive in your garden.
Unique Varieties of Lupus for a Distinct Garden
If you’re looking to add a touch of uniqueness to your garden, consider planting some of the following varieties of Lupus. These distinct lupine species will not only add vibrant colors but also attract pollinators to your garden.
1. Arctic Lupus
The Arctic Lupus, also known as Lupinus arcticus, is a beautiful and rare lupine variety that is native to the Arctic regions. It features stunning white flowers that contrast against its silver-gray foliage, making it a standout in any garden.
2. Rainbow Lupus
As the name suggests, the Rainbow Lupus variety is known for its colorful blossoms. With flowers ranging from pink and purple to yellow and white, this lupine species will bring a vibrant and cheerful atmosphere to your garden.
3. Chocolate Lupus
If you’re a fan of unique flower colors, the Chocolate Lupus variety is a must-have. With its rich, dark brown flowers, this lupine species adds a touch of elegance and sophistication to any garden.
4. Red Rum Lupus
The Red Rum Lupus is a striking variety with deep red flowers that stand out among other lupine species. Its bold color and tall spikes make it a focal point in the garden, attracting attention from both humans and pollinators.
5. Pina Colada Lupus
For a tropical touch in your garden, consider the Pina Colada Lupus variety. This unique lupine species features creamy white flowers with hints of yellow, resembling the refreshing drink it is named after.
6. Dwarf Lupus
If you have limited space in your garden, the Dwarf Lupus variety is a great option. With its compact size and colorful flowers, this lupine species can thrive in small gardens or even containers, adding a pop of color to any space.
7. Bandana Lupus
The Bandana Lupus variety offers a mix of vibrant colors in its flower spikes, ranging from purple and pink to white and red. With its multi-colored blooms, this lupine species adds a lively and dynamic element to any garden.
| Variety | Color | Height | Growth Habit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arctic Lupus | White | Tall | Upright |
| Rainbow Lupus | Pink, Purple, Yellow, White | Tall | Upright |
| Chocolate Lupus | Dark Brown | Tall | Upright |
| Red Rum Lupus | Deep Red | Tall | Upright |
| Pina Colada Lupus | Creamy White with Yellow | Tall | Upright |
| Dwarf Lupus | Various Colors | Short | Compact |
| Bandana Lupus | Purple, Pink, White, Red | Tall | Upright |
Whatever variety you choose, planting these unique lupine species will surely make your garden stand out and create a distinct and beautiful landscape.
Characteristics and Care of Lupus
Characteristics
- Lupus is a perennial flowering plant that belongs to the family Fabaceae.
- It is characterized by its vibrant and showy flowers, which come in a range of colors including purple, blue, pink, white, and yellow.
- The flowers of lupus are often trumpet-shaped and have a distinctively pleasant fragrance.
- The plant has palmate leaves with a distinctive silver or grayish-green color.
- Lupus can grow up to 2-4 feet in height, depending on the variety.
Care
- Lupus prefers full sun exposure, although it can tolerate partial shade.
- It requires well-draining soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.5.
- Regular watering is essential to keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged, especially during dry periods.
- Deadheading spent flowers will encourage the plant to produce more blooms and extend the flowering season.
- It is advisable to mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture and suppress weed growth.
- Lupus is generally pest and disease resistant, but it can be susceptible to aphids and powdery mildew in humid conditions.
- Applying organic fertilizers, such as compost or well-rotted manure, in the spring can help promote healthy growth.
- Pruning should be done in early spring to remove any dead or damaged growth and to shape the plant.
- Dividing lupus every 3-4 years can help rejuvenate the plant and promote better growth.
Conclusion
Lupus is a stunning flowering plant that can add vibrant colors to any garden. With proper care and maintenance, it can thrive and provide beautiful blooms throughout the growing season. Remember to provide adequate sunlight, well-draining soil, regular watering, and necessary pruning to ensure the health and longevity of your lupus plant.
Understanding the Characteristics of Lupus Plants
Lupus plants are known for their vibrant colors and unique foliage. Understanding the characteristics of lupus plants is essential for successful cultivation and care.
Variety of Colors
Lupus plants come in a wide variety of colors, including shades of purple, blue, pink, and white. These colorful flowers add a touch of beauty and elegance to any garden or landscape.
Perennial Nature
Lupus plants are perennials, meaning they come back year after year. This makes them an excellent choice for long-lasting garden displays. However, they may require some maintenance to ensure their continued growth and blooming.
Thrives in Full Sun
Lupus plants thrive in full sun and require at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. Planting them in a sunny spot will help them grow strong and produce abundant blooms.
Well-Draining Soil
Lupus plants prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. The soil should be slightly acidic with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. Adding compost or organic matter to the soil can improve drainage and provide essential nutrients for healthy plant growth.
Tolerant of Drought
Lupus plants are known for their drought tolerance once established. However, they still require regular watering during periods of dry weather. It is important to water the plants deeply and allow the soil to dry out between waterings to prevent root rot.
Pruning Requirements
Pruning lupus plants is not necessary for their growth. However, removing any dead or faded flowers can encourage new blooms and keep the plant looking tidy. Additionally, cutting back the plant in late winter or early spring can help promote vigorous growth and prevent overcrowding.
Attracts Pollinators
Lupus plants are known to attract various pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, with their colorful and fragrant flowers. Adding lupus plants to your garden can help create a welcoming environment for these important pollinators.
Deer-Resistant
Lupus plants are often considered deer-resistant, making them a suitable choice for gardens in areas with deer populations. However, it is important to note that no plant is completely deer-proof, and hungry deer may still nibble on lupus plants if food sources are scarce.
Additional Considerations
To ensure the health and vitality of lupus plants, it is essential to provide them with adequate water, proper soil conditions, and regular fertilization. Regularly monitoring for pests and diseases can also help prevent any potential issues from escalating.
Tips for Proper Care of Lupus Plants
Lupus plants require proper care to ensure their health and continuous growth. Here are some tips to help you care for your lupus plants:
1. Sunlight:

Lupus plants thrive in full sunlight exposure. It is essential to place them in a location where they can receive at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day. This will help the plant produce vibrant flowers and maintain healthy foliage.
2. Watering:
Proper watering is crucial to the health of lupus plants. It is best to water them deeply, allowing the water to penetrate the root system. However, be cautious not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot. Water the plants when the top inch of soil feels dry, and ensure that the soil has proper drainage to prevent waterlogged conditions.
3. Soil:
Lupus plants prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Ensure that the soil has good drainage to prevent water stagnation. You can amend the soil with compost or peat moss to improve its texture and fertility. Regularly monitor the pH level of the soil and maintain it within the recommended range.
4. Fertilization:
Lupus plants benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to provide essential nutrients. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and frequency. Avoid over-fertilization, as it can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of flower production.
5. Pruning:
Regular pruning helps maintain the shape and size of lupus plants. Remove any dead or damaged branches to promote healthy growth. Additionally, pinch back the tips of the stems to encourage bushier growth and more abundant flowering. Pruning should be done in early spring before new growth begins.
6. Pest and Disease Control:
Monitor lupus plants for common pests such as aphids, spider mites, and snails. Use organic pest control methods or insecticidal soaps to eliminate pests. Additionally, watch out for signs of diseases such as powdery mildew or leaf spots. Remove infected leaves and treat the plants with appropriate fungicides if necessary.
7. Mulching:
Mulching helps conserve moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of lupus plants, taking care not to mound it against the stems. This will also help improve soil fertility as the mulch breaks down over time.
8. Winter Protection:


In regions with cold winters, lupus plants may require winter protection. Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plants to insulate the roots and prevent freezing. You can also cover the plants with burlap or other protective material to shield them from harsh winds and frost.
Following these care tips will help ensure the health and vigor of your lupus plants, making them a beautiful addition to your garden or landscape.
Lupus and its Medicinal Properties
Lupus is a highly versatile plant that not only makes a beautiful addition to any garden but also possesses various medicinal properties. The plant has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat a wide range of ailments.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
One of the most prominent medicinal properties of lupus is its anti-inflammatory effects. The plant contains compounds known as flavonoids and saponins, which have been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. This makes lupus an effective remedy for conditions such as arthritis, joint pain, and muscle soreness.
Antioxidant Activity
Lupus is rich in antioxidants, including vitamin C, beta-carotene, and flavonoids. These antioxidants help protect the body against damage caused by harmful free radicals and oxidative stress. Regular consumption of lupus can strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of various chronic diseases, including heart disease and cancer.
Digestive Health
The leaves of the lupus plant have mild laxative properties, which can help promote healthy digestion. Lupus leaves are often used in traditional herbal remedies for indigestion, constipation, and other digestive disorders. The plant’s gentle laxative effect can help regulate bowel movements and relieve discomfort.
Diuretic Effects
Lupus has diuretic properties, meaning it promotes increased urine production and can help flush out toxins and excess fluids from the body. This can be beneficial for individuals who experience water retention or are at risk of developing kidney stones. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before using lupus as a diuretic.
Wound Healing
Lupus has been traditionally used to treat wounds and promote healing. The plant’s antimicrobial properties help protect against infection, while its anti-inflammatory effects reduce swelling and pain. Applying a poultice made from lupus leaves or using lupus-infused creams can help speed up the healing process of cuts, bruises, and minor skin irritations.
Cautions and Considerations
While lupus has many potential medicinal benefits, it is important to note that individual reactions may vary. Some people may be allergic to lupus or may experience side effects when consuming or applying lupus products. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before using lupus for medicinal purposes.
In conclusion, lupus is a versatile plant with various medicinal properties. From its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects to its digestive health and wound healing benefits, lupus offers a natural and holistic approach to promoting overall well-being.
Questions and Answers:
What is lupus?
Lupus is a type of autoimmune disease that affects various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and lungs.
How can I plant and cultivate lupus?
To plant and cultivate lupus, you need to choose a sunny spot in your garden, prepare the soil by loosening it and adding organic matter, sow the lupus seeds, water them regularly, and provide support as they grow.
What are the different species of lupus?
There are several species of lupus, including Lupinus perennis, Lupinus texensis, and Lupinus polyphyllus. Each species has its own unique characteristics and requirements.
What are the best varieties of lupus to grow?
Some popular varieties of lupus to consider growing are ‘Gallery Blue’, ‘Chandelier’, ‘Russell Hybrids’, and ‘The Governor’. These varieties have beautiful blooms and are easy to grow.
Can lupus be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for lupus. However, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for people with lupus.
What are the common symptoms of lupus?
The common symptoms of lupus include fatigue, joint pain and stiffness, skin rashes, fever, chest pain, and hair loss. However, the symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
What are some tips for growing lupus successfully?
To grow lupus successfully, make sure to provide them with well-drained soil, water them regularly but avoid overwatering, fertilize them every few months, and protect them from pests and diseases.







