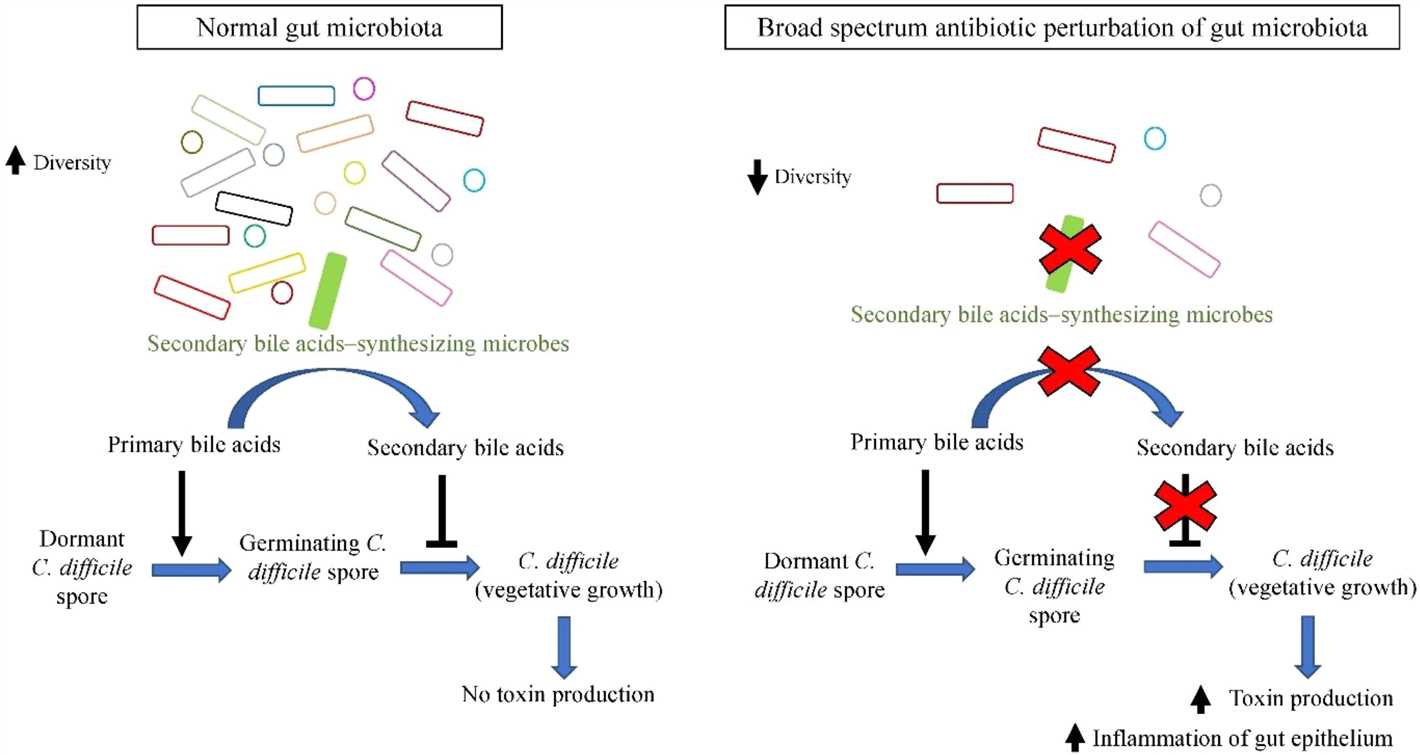
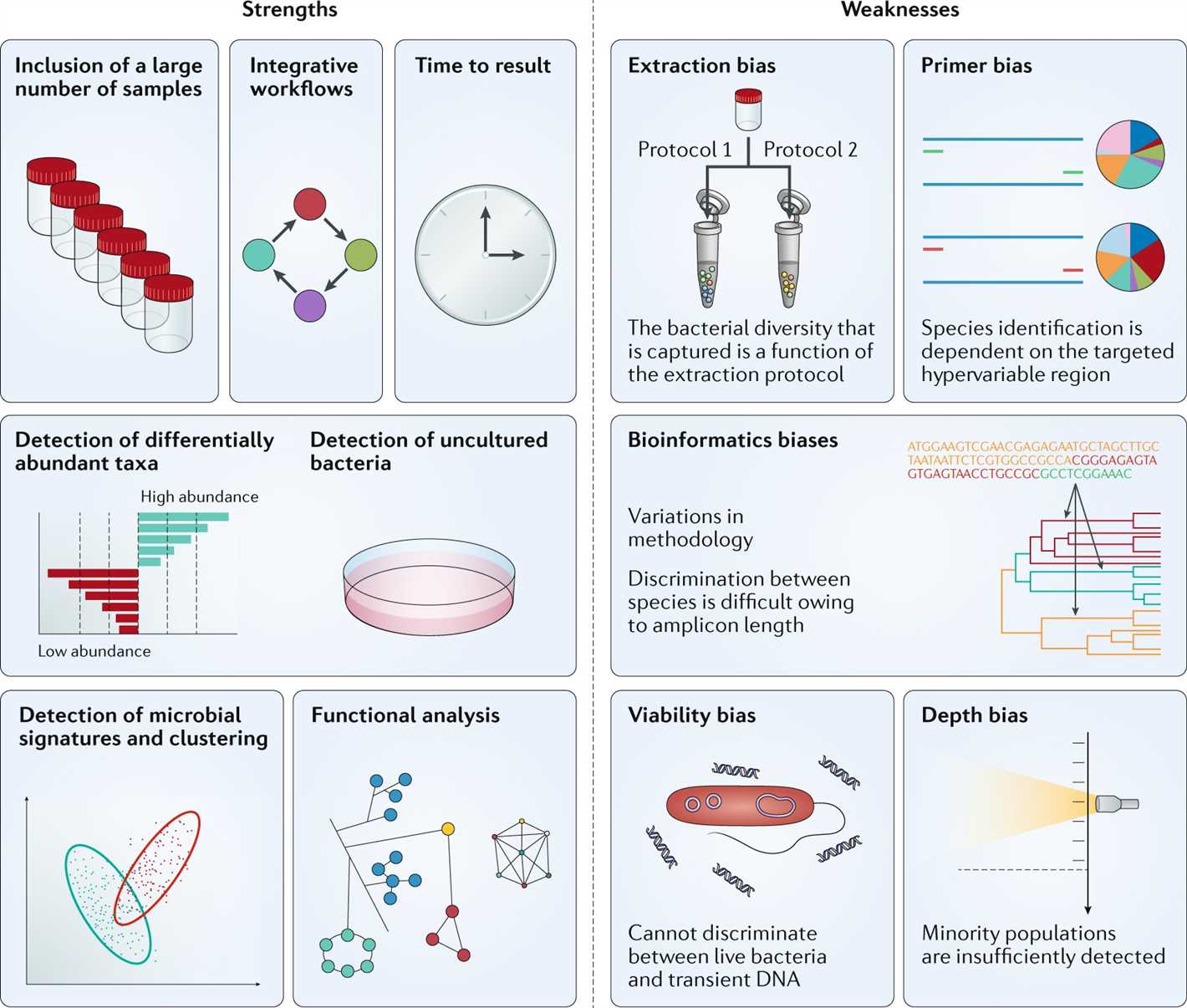
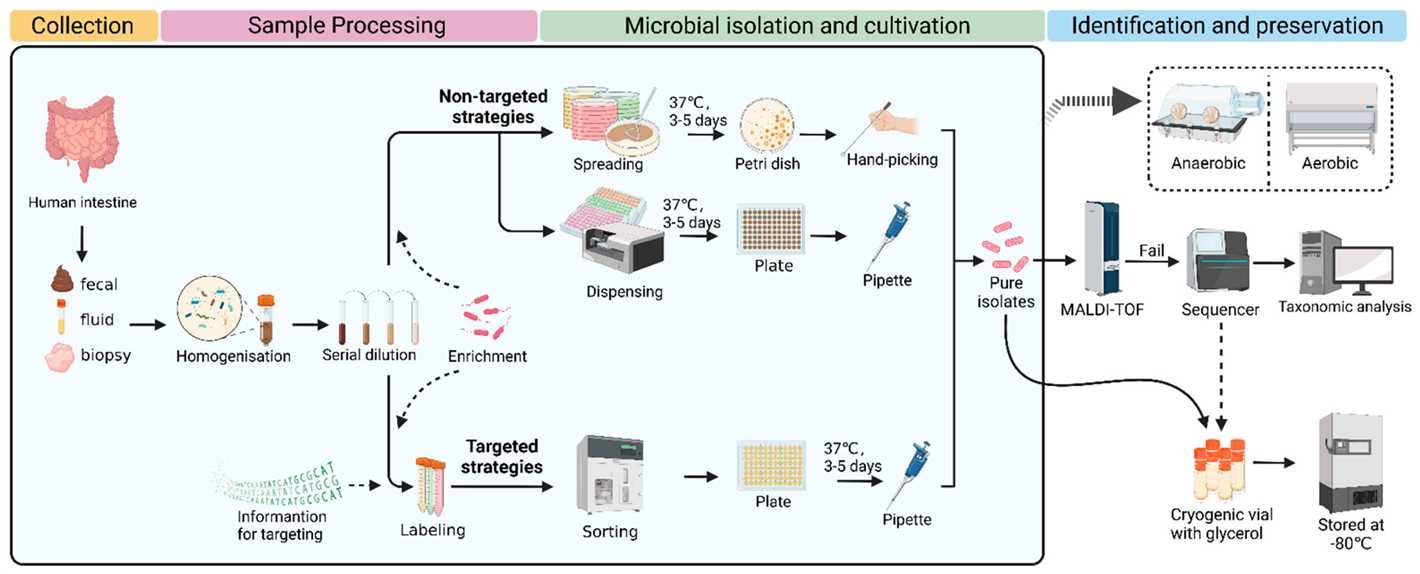
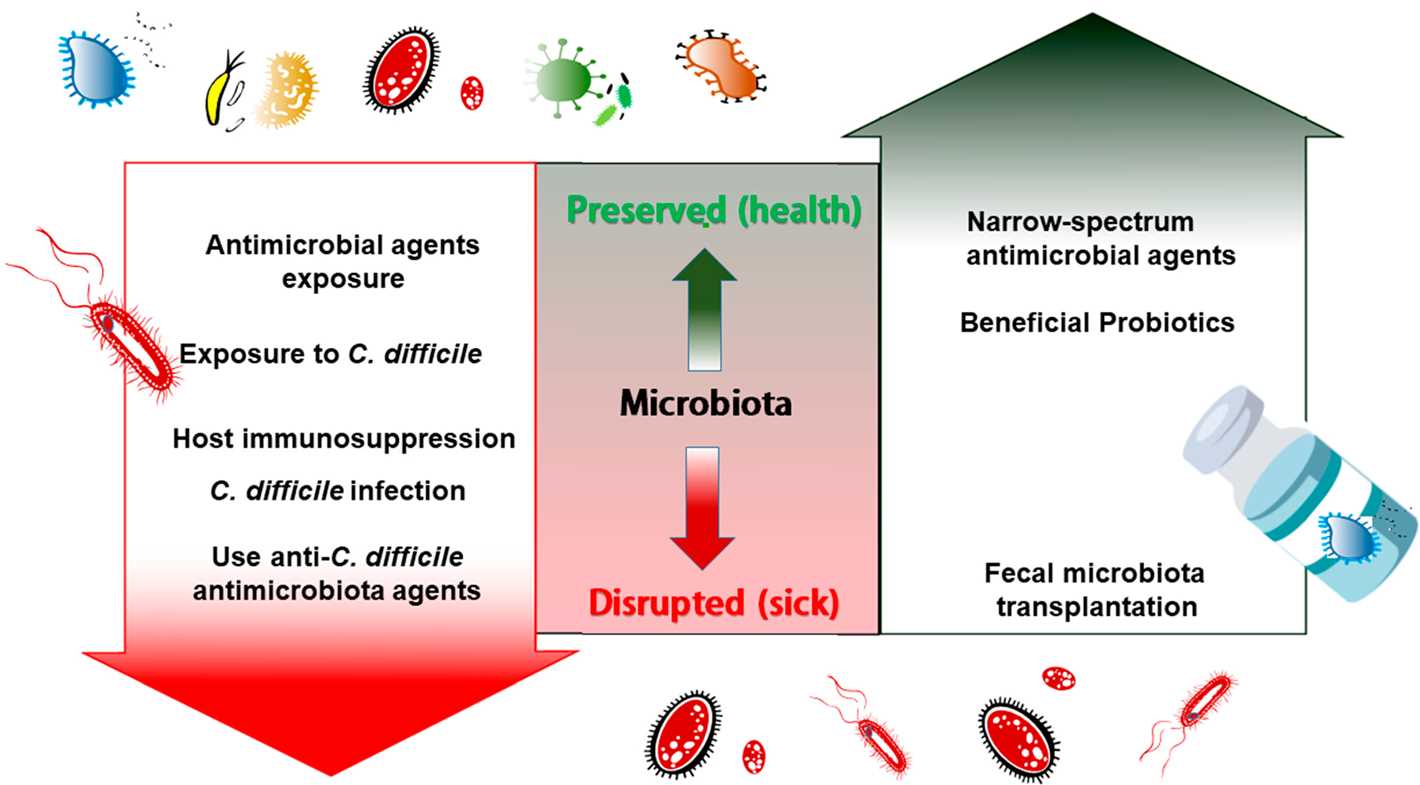
- Understanding the Role of Microbiota in the Body
- The Gut-Brain Axis
- Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
- Conclusion
- The Impact of Lifestyle on Microbiota
- Diet:
- Physical activity:
- Stress:
- Sleep:
- Hygiene habits:
- Medication use:
- Smoking and alcohol consumption:
- Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
- 1. Eat a diverse diet
- 2. Consume probiotics
- 3. Avoid excessive use of antibiotics
- 4. Manage stress
- 5. Stay hydrated
- 6. Avoid excessive use of disinfectants
- 7. Consider prebiotic supplements
- The Connection Between Microbiota and Digestive Health
- The Role of Microbiota in Digestion
- Impacts of Imbalanced Microbiota
- Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
- Boosting Immunity through Microbiota Care
- How can we boost immunity through microbiota care?
- The Influence of Microbiota on Mental Health
- Microbiota and Skin Health: Tips for a Healthy Microbiome
- 1. Cleanse without disrupting
- 2. Avoid overwashing
- 3. Use probiotic skincare products
- 4. Moisturize regularly
- 5. Avoid excessive use of antibacterial products
- 6. Maintain a healthy diet
- 7. Limit stress
- Summary and Practical Tips for Microbiota Optimization
- Key Points:
- Conclusion:
- Questions and Answers:
- What is microbiota?
- How does microbiota affect our health?
- Can the composition of microbiota be changed?
- What are some ways to cultivate a healthy microbiota?
- Can microbiota imbalance lead to health problems?
- Are there any supplements or products that can improve microbiota?
- What are some signs of an unhealthy microbiota?
- Videos: OPTIMIZE YOUR GUT to Fight Disease: New Science of Eating Well | Dr. Tim Spector X Rich Roll Podcast
The human body is inhabited by trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiota. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining our health and well-being. Research has shown that a healthy and diverse microbiota is essential for optimal functioning of the immune system, digestion, metabolism, and even mental health.
Cultivating and caring for our microbiota is therefore of utmost importance. One way to promote a healthy microbiota is through the consumption of probiotics. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. They can be found in certain foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, or can be taken as supplements.
In addition to probiotics, a diet rich in fiber and plant-based foods can also support a healthy microbiota. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing fuel for beneficial bacteria in the gut. By consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, we can nourish our microbiota and promote its diversity.
It’s important to note that the cultivation and care of our microbiota extend beyond just diet. Factors such as stress, antibiotics, and exposure to certain chemicals can also have an impact on the composition and diversity of our microbiota. Therefore, adopting a holistic approach to health, which includes managing stress, minimizing the use of antibiotics when not necessary, and reducing exposure to harmful chemicals, is essential for maintaining a healthy microbiota.
Taking care of our microbiota is not only important for our physical health but also for our mental well-being. Research has shown that imbalances in the microbiota are associated with a variety of health conditions, including obesity, autoimmune diseases, and even mental disorders such as depression and anxiety. By nurturing our microbiota, we can optimize our overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Role of Microbiota in the Body
The human body is home to a vast community of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiota. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi, and they reside on the skin, in the mouth, in the gut, and in various other parts of the body. While some of these microorganisms can cause disease, many of them play important roles in maintaining our health and well-being.
One of the key functions of the microbiota is to aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. The bacteria in our gut, for example, help break down complex carbohydrates, produce certain vitamins, and promote the absorption of minerals. Additionally, the microbiota helps regulate our immune system, by interacting with immune cells in the gut and preventing harmful pathogens from colonizing the intestines.
Furthermore, recent research has shown that the microbiota has an influence on many aspects of our health, including metabolism, mental health, inflammation, and even our risk of developing chronic diseases. Imbalances in the microbiota, known as dysbiosis, have been linked to conditions like obesity, diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome, and autoimmune disorders.
The Gut-Brain Axis
One fascinating area of research is the connection between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis. The microbiota in the gut can communicate with the brain through various mechanisms, including the production of neurotransmitters, immune molecules, and signaling molecules. This bidirectional communication has been found to play a role in the regulation of mood, behavior, and even cognitive function.
Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
To maintain a healthy microbiota, it is important to adopt habits that promote its growth and diversity. This includes consuming a varied and balanced diet rich in fiber, which serves as a prebiotic and supports the growth of beneficial bacteria. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management are also important, as they can all have an impact on the composition of the microbiota.
Additionally, the use of antibiotics should be judicious, as they can disrupt the balance of the microbiota and lead to dysbiosis. When antibiotics are necessary, it may be important to take steps to support the recovery of the microbiota, such as consuming probiotic-rich foods or taking probiotic supplements.
Conclusion
The microbiota plays a crucial role in the body, influencing our digestion, immune system, and overall health. By understanding and caring for our microbiota, we can promote optimal health and well-being. Maintaining a diverse and balanced microbiota through proper diet and lifestyle choices is key to supporting its beneficial functions and ensuring long-term health.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Microbiota
Lifestyle choices and habits can have a significant impact on the diversity and composition of the microbiota, which in turn can affect overall health and well-being. Here are some lifestyle factors that can influence the microbiota:
Diet:
The food we eat plays a crucial role in shaping the microbiota. A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats can lead to an imbalance in the microbiota and an overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
Physical activity:
Regular exercise has been shown to positively influence the composition of the microbiota. Exercise can increase the diversity of the gut microbiota, which is associated with better health outcomes. It also helps reduce inflammation and promotes a healthy gut barrier function.
Stress:
Chronic stress can negatively impact the microbiota. Stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, leading to changes in gut motility and increased permeability of the gut barrier. This can allow harmful bacteria to penetrate the gut lining and cause inflammation.
Sleep:
Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep duration can disrupt the microbiota. Studies have shown that sleep disturbances can alter the composition of the gut microbiota, leading to an imbalance and potential negative health effects.
Hygiene habits:
Excessive use of antibacterial soaps and sanitizers can disrupt the natural balance of the skin and gut microbiota. While it is important to maintain proper hygiene, overuse of these products can potentially reduce the diversity of beneficial bacteria.
Medication use:
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can have a profound effect on the microbiota. Antibiotics, while necessary to treat bacterial infections, can also eliminate beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to an imbalance. Other medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can also impact the microbiota.
Smoking and alcohol consumption:
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the composition of the microbiota. Smoking has been shown to decrease the diversity of gut bacteria, while excessive alcohol consumption can alter the gut microbiota and disrupt gut barrier function.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Microbiota |
|---|---|
| Diet | Can promote or disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria |
| Physical activity | Increase diversity and promote a healthy gut barrier function |
| Stress | Can lead to an imbalance and increased inflammation |
| Sleep | Disturbances can alter the composition of the microbiota |
| Hygiene habits | Excessive use of antibacterial products can reduce diversity |
| Medication use | Antibiotics and certain medications can disrupt the balance |
| Smoking and alcohol consumption | Both can alter the composition of the microbiota |
Overall, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular physical activity, proper sleep, and stress management can contribute to a diverse and thriving microbiota, which is essential for optimal health and well-being.
Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
A healthy microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and minimizing the presence of harmful pathogens, a balanced microbiota helps support digestion, immunity, and various other physiological processes.
1. Eat a diverse diet
A diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides a wide range of nutrients that support the growth of a diverse microbiota. These foods are also rich in fiber, which acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
2. Consume probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria or yeasts that are beneficial to the microbiota. They can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. Consuming probiotics regularly can help introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut and promote a healthy microbiota.
3. Avoid excessive use of antibiotics
Antibiotics are often necessary to treat bacterial infections, but they can also disrupt the natural balance of the microbiota. To maintain a healthy microbiota, it is important to only use antibiotics when absolutely necessary and to follow the prescribed dosage and duration.
4. Manage stress
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on the microbiota. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, and spending time with loved ones, can help maintain a balanced microbiota.
5. Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water is essential for overall health, including a healthy microbiota. Water helps to hydrate the body, support digestion, and flush out toxins. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
6. Avoid excessive use of disinfectants
While disinfectants are important for maintaining cleanliness and preventing the spread of harmful pathogens, excessive use can also kill off beneficial bacteria. Use disinfectants sparingly and focus on maintaining good hygiene practices instead.
7. Consider prebiotic supplements
In addition to consuming prebiotic-rich foods, prebiotic supplements can also be beneficial for cultivating a healthy microbiota. These supplements contain specific types of fibers that selectively feed beneficial bacteria in the gut.
By following these tips and incorporating them into your lifestyle, you can help cultivate a healthy microbiota and support your overall health and well-being.
The Connection Between Microbiota and Digestive Health
Our digestive system is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining our digestive health and overall well-being. Research has shown that a balanced and diverse microbiota is important for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients, as well as for the prevention of gastrointestinal disorders.
The Role of Microbiota in Digestion
Microbiota help with the breakdown and fermentation of complex carbohydrates, such as dietary fiber, that our bodies cannot digest on their own. This process produces short-chain fatty acids, which serve as an important energy source for the cells lining the intestine. Additionally, microbiota produce enzymes that help break down proteins and fats, aiding in their digestion.
One of the most well-known functions of the gut microbiota is the production of vitamins, particularly B vitamins and vitamin K. These vitamins are essential for various biological processes, including energy production and blood clotting, respectively. Without a healthy microbiota, our bodies may have difficulty obtaining an adequate supply of these vitamins.
Impacts of Imbalanced Microbiota
An imbalance in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various digestive disorders. For example, an overgrowth of certain bacteria, such as Clostridium difficile, can cause diarrhea and severe inflammation of the intestines. Similarly, an imbalance in the microbiota has been associated with the development of inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
In addition to digestive disorders, imbalanced microbiota can also have systemic effects. Research has shown a link between dysbiosis and conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and even mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. It is believed that the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication network between the gut and the brain, plays a role in these associations.
Cultivating a Healthy Microbiota
To promote a healthy microbiota and improve digestive health, it is important to focus on cultivating a diverse and balanced microbial community. This can be achieved through a variety of lifestyle factors:
- Eating a diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, such as yogurt and sauerkraut, which provide beneficial bacteria.
- Taking probiotic supplements, which can help populate the gut with beneficial bacteria.
- Avoiding excessive use of antibiotics, as they can disrupt the balance of the microbiota.
- Managing stress, as it can negatively impact the diversity and composition of the microbiota.
By prioritizing the care of our microbiota, we can support our digestive health and overall well-being. Maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiota is key to optimal digestion and the prevention of various gastrointestinal and systemic disorders.
Boosting Immunity through Microbiota Care
The human immune system plays a crucial role in defending the body against harmful pathogens. It is a complex network consisting of different cell types and organs, all working together to keep us healthy. However, maintaining a strong and balanced immune system requires more than just the body’s innate defenses. The gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms that resides in our digestive tract, also plays a significant role in shaping our immune system.
The gut microbiota is composed of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. These microbes interact with our bodies in various ways, including influencing the development and function of our immune cells.
Research has shown that the diversity and composition of the gut microbiota can have a profound impact on our immune system. A healthy and diverse microbiota is essential for optimal immune function. On the other hand, an imbalance or dysbiosis in the gut microbiota, characterized by a decrease in beneficial bacteria and an increase in harmful microbes, has been associated with chronic inflammation and an increased risk of autoimmune diseases.
How can we boost immunity through microbiota care?
1. Probiotics: Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, provide health benefits. They can help promote a balanced gut microbiota by increasing the population of beneficial bacteria. Probiotics can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, or can be taken as supplements.
2. Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in our gut. They help stimulate the growth and activity of these bacteria, promoting a healthy microbiota. Prebiotics can be found in foods such as onions, garlic, bananas, and whole grains.
3. Fiber-rich diet: Consuming a diet high in fiber can help support a healthy gut microbiota. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by our bodies but can be fermented by the gut bacteria. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and help support a healthy immune system.
4. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics: While antibiotics can be life-saving in certain situations, overuse or misuse of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota. It is important to use antibiotics only when necessary and as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
5. Stress management: Chronic stress has been shown to have a negative impact on the gut microbiota and immune system. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies can help support a healthy microbiota and immune system.
Conclusion: Taking care of our gut microbiota is crucial for maintaining a strong and balanced immune system. By incorporating probiotics, prebiotics, fiber-rich foods, and stress management techniques into our daily lives, we can promote a healthy microbiota and boost our immunity. It is essential to prioritize our microbiota care to optimize our overall health and well-being.
The Influence of Microbiota on Mental Health
Mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s, have become increasingly prevalent in the modern world. While many factors contribute to these conditions, emerging research suggests that the composition and diversity of our microbiota may play a significant role in mental health.
Gut-Brain Axis:
One of the key mechanisms through which the microbiota influences mental health is the gut-brain axis. This bidirectional communication system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the enteric nervous system (nervous system of the gut). The gut-brain axis allows for direct communication between the gut and the brain, influencing both physiological and psychological processes.
Microbial Diversity:
Studies have shown a correlation between reduced microbial diversity in the gut and mental health disorders. A diverse community of microbiota is essential for optimal gut function and overall well-being. Reduced microbial diversity, on the other hand, has been associated with inflammatory conditions and altered neurotransmitter production, both of which can contribute to mental health disorders.
Neurotransmitter Production:
The microbiota plays a crucial role in the production of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters are vital for mood regulation and cognitive function. Imbalances in neurotransmitter levels have been implicated in various mental health disorders. Research suggests that specific strains of gut bacteria can enhance the production of these neurotransmitters, potentially helping to improve mental well-being.
Inflammation:
Chronic low-grade inflammation has also been linked to mental health disorders. The microbiota can influence the immune system and modulate inflammatory responses. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, can lead to increased inflammation, which has been associated with the development of depression and anxiety.
Therapeutic Potential:
The growing understanding of the gut-brain axis and the influence of microbiota on mental health has opened up new possibilities for therapeutic interventions. Probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation are some of the approaches being explored to modulate the gut microbiota and improve mental well-being. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complex relationship between the microbiota and mental health.
Conclusion:
The microbiota has a profound influence on mental health through its interactions with the gut-brain axis, neurotransmitter production, inflammation, and overall gut health. Understanding and cultivating a diverse and balanced microbiota may offer significant opportunities for promoting mental well-being and preventing mental health disorders.
Microbiota and Skin Health: Tips for a Healthy Microbiome
The skin is the largest organ of the human body and plays a crucial role in protecting against external threats. The microbiota, the community of microorganisms living on the skin, also plays a significant role in skin health. Maintaining a healthy microbiome is essential for optimal skin health and well-being. Here are some tips to promote a healthy microbiota and improve skin health:
1. Cleanse without disrupting
When cleansing the skin, it’s important to choose products that are gentle and do not disrupt the natural balance of the microbiota. Harsh cleansers can strip away the protective oils and beneficial bacteria that help keep the skin healthy. Look for pH-balanced cleansers that are free from harsh chemicals.
2. Avoid overwashing
Overwashing the skin can disrupt the microbiota and lead to dryness and irritation. It’s essential to find a balance between keeping the skin clean and maintaining its natural protective barrier. Washing once or twice a day is usually sufficient for most people, unless they have specific skin conditions that require more frequent washing.
3. Use probiotic skincare products
Probiotic skincare products contain beneficial bacteria that can help restore and maintain a healthy microbiome on the skin. These products can help improve skin hydration, reduce inflammation, and promote overall skin health. Look for products that contain live cultures or fermented ingredients.
4. Moisturize regularly
Proper hydration is essential for a healthy microbiota and overall skin health. Regularly moisturizing the skin helps to maintain its natural moisture barrier and prevent dryness. Choose moisturizers that are non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog pores, and contain ingredients like ceramides or hyaluronic acid.
5. Avoid excessive use of antibacterial products
While antibacterial products can be useful in certain situations, excessive use can disrupt the skin’s microbiota and lead to imbalances. Avoid using antibacterial soaps or cleansers unless necessary, and opt for gentler alternatives whenever possible.
6. Maintain a healthy diet
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support a diverse microbiota. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir can also contribute to a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria on the skin. Drinking plenty of water is vital for maintaining hydration and overall skin health.
7. Limit stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact the skin’s microbiota and lead to skin issues like acne and eczema. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones, can help support a healthy microbiome and improve skin health.
- Cleanse without disrupting
- Avoid overwashing
- Use probiotic skincare products
- Moisturize regularly
- Avoid excessive use of antibacterial products
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Limit stress
Summary and Practical Tips for Microbiota Optimization
Introduction: Microbiota refers to the trillions of microorganisms that live in and on our bodies, playing a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. Optimizing our microbiota is essential for maintaining a healthy gut and a strong immune system.
Key Points:
- Diet: A balanced and varied diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Limiting processed food and added sugars is also crucial for maintaining a healthy microbiota.
- Probiotics: Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet can help replenish and diversify your microbiota. Additionally, taking probiotic supplements can be beneficial, especially after antibiotic use.
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Foods rich in prebiotics include onions, garlic, bananas, oats, and asparagus. Consider incorporating these into your diet.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact your microbiota. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in your gut.
- Avoid Antibiotics When Possible: Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut. If antibiotics are necessary, talk to your healthcare provider about strategies to minimize their impact on your microbiota.
Conclusion:
Optimizing your microbiota is a key factor in maintaining optimal health and well-being. By following a balanced diet, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics, managing stress, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, you can support the growth of beneficial bacteria and improve the overall health of your gut microbiota.
Questions and Answers:
What is microbiota?
Microbiota refers to the community of microorganisms that live in and on the human body.
How does microbiota affect our health?
Microbiota plays a crucial role in various aspects of our health, including digestion, immune system function, and even mental health.
Can the composition of microbiota be changed?
Yes, the composition of microbiota can be influenced by factors such as diet, medication, and stress.
What are some ways to cultivate a healthy microbiota?
Eating a diverse and balanced diet, limiting the use of antibiotics, and managing stress are some ways to promote a healthy microbiota.
Can microbiota imbalance lead to health problems?
Imbalance in microbiota, also known as dysbiosis, has been linked to various health problems, including gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health conditions.
Are there any supplements or products that can improve microbiota?
Probiotics and prebiotics are commonly used to support the growth and diversity of microbiota. However, it is important to choose high-quality products and consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
What are some signs of an unhealthy microbiota?
Signs of an unhealthy microbiota can include digestive issues such as bloating and diarrhea, frequent infections, and changes in mood or mental well-being.







