- Passiflora Incarnata Artificial Pollination: Boosting Passion Fruit Production!
- The Importance of Artificial Pollination
- Process of Artificial Pollination
- Advantages of Artificial Pollination
- Conclusion
- Increasing Passion Fruit Yield: Artificial Pollination is the Key!
- The Importance of Pollination
- The Process of Artificial Pollination
- The Benefits of Artificial Pollination
- Conclusion
- Why Natural Pollination is Inefficient for Passion Fruit Plants?
- The Advantages of Artificial Pollination in Passion Fruit Cultivation
- Increased Yield
- Improved Fruit Quality
- Reduced Dependency on Bees
- Extended Harvest Season
- Increased Control and Precision
- Reduced Cross-Pollination Risks
- Higher Efficiency
- Steps to Perform Artificial Pollination for Passiflora Incarnata
- Best Time and Methods for Artificial Pollination of Passion Fruit Flowers
- 1. Timing
- 2. Flower Selection
- 3. Pollination Methods
- 4. Protective Measures
- 5. Repeat Pollination
- Tips for Successful Artificial Pollination: Maximizing Passion Fruit Production
- 1. Understand the Pollination Process
- 2. Identify the Right Time for Pollination
- 3. Select the Right Tools
- 4. Practice Proper Pollen Collection and Transfer
- 5. Monitor and Repeat
- 6. Consider Cross-Pollination
- 7. Provide Suitable Growing Conditions
- 8. Regular Pruning and Training
- 9. Protect from Pests and Diseases
- 10. Harvest at the Right Time
- Achieving Consistent Yields: Importance of Regular Artificial Pollination
- 1. Maximizing Fruit Set
- 2. Overcoming Pollinator Limitations
- 3. Ensuring Fruit Quality
- 4. Managing Flowering Patterns
- 5. Increasing Crop Yield Potential
- The Future of Passion Fruit Production: Artificial Pollination Innovations
- Benefits of Artificial Pollination
- Innovative Artificial Pollination Techniques
- The Future Outlook
- Q&A:
- What is Passiflora Incarnata?
- How do you identify Passiflora Incarnata?
- Why is artificial pollination important for Passion Fruit production?
- How do you perform artificial pollination on Passiflora Incarnata?
- What are the benefits of Passion Fruit production?
- Video: How to pollinate passion fruit flowers
If you have ever tasted a juicy and sweet passion fruit, you know how delicious it can be. But have you ever wondered how these exotic fruits are produced? The secret lies in a process called artificial pollination, which is crucial for the production of passion fruit. In this article, we will delve into the details of Passiflora Incarnata artificial pollination, and explore why it is the key to passion fruit production!
The Passiflora Incarnata, commonly known as the passion flower, is a vine that produces the beautiful and unique passion fruit. However, unlike many other plants, the Passiflora Incarnata cannot rely on natural pollination methods, such as wind or insects, to reproduce. Without proper pollination, the flowers of this plant would wither and die, and the fruits would never grow.
This is where artificial pollination comes into play. By manually transferring the pollen from the male part of the flower to the female part, growers can ensure successful fertilization and fruit production. This process requires careful attention to detail, as any mishap during pollination can result in a decrease in fruit yield.
Artificial pollination of Passiflora Incarnata is typically performed by trained workers who use small brushes or cotton swabs to collect pollen from the anthers of the male flowers. They then carefully transfer the pollen to the stigma of the female flowers, ensuring that each flower receives an adequate amount of pollen. This meticulous process is repeated multiple times to ensure maximum pollination efficiency.
Thanks to the art of artificial pollination, passion fruit production has been greatly enhanced. Growers are now able to control the timing and frequency of pollination, resulting in a more predictable and abundant harvest. Additionally, artificial pollination allows for cross-pollination, which can lead to the development of new and improved passion fruit varieties with desirable traits.
Passiflora Incarnata artificial pollination is a labor-intensive but essential practice for passion fruit production. It enables growers to overcome the limitations of natural pollination and ensure the successful growth of passion fruits.Without this process, the world would be deprived of the delicious and refreshing taste of passion fruit!
Passiflora Incarnata Artificial Pollination: Boosting Passion Fruit Production!
The Passiflora Incarnata, also known as the Maypop, is a species of passion flower native to North America. It is a vigorous climbing vine that exhibits beautiful flowers and produces delicious passion fruit. However, for commercial production of passion fruit, artificial pollination is often necessary to ensure consistent yields and improve fruit quality.
The Importance of Artificial Pollination
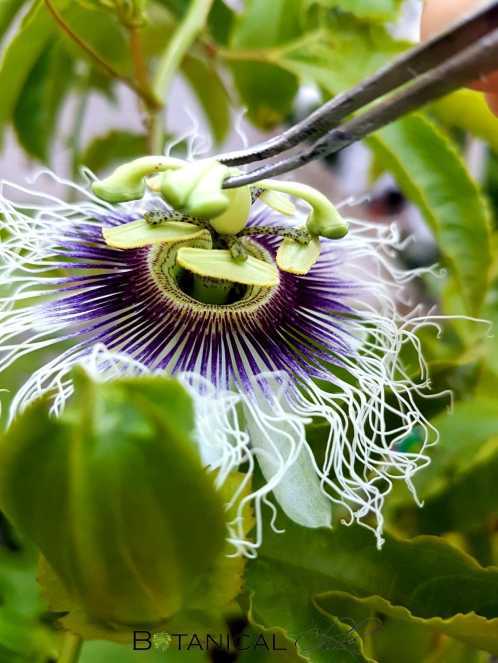

In the wild, passion flowers rely on insects like bees and butterflies for pollination. However, in commercial passion fruit production, artificial pollination is preferred to achieve higher fruit yields and improve consistency. Artificial pollination allows growers to control and enhance the pollination process, leading to better fruit set and a more efficient use of resources.
Process of Artificial Pollination
Artificial pollination involves transferring pollen from the male parts (anthers) of the passion flower to the female parts (stigmas) of the same or different flowers. This can be done manually using a small brush or by gently tapping the flowers to release the pollen. The pollen is then carefully transferred to the stigma of another flower, ensuring proper fertilization.
Steps for artificial pollination:
- Select mature flowers: Choose flowers that are fully opened and have well-developed anthers and stigmas.
- Preparation: Gently remove the petals surrounding the male parts (anthers) to expose the pollen.
- Pollen transfer: Use a small brush or your finger to collect the pollen from the anthers. Transfer the collected pollen to the stigma of another flower, applying it gently and evenly.
Advantages of Artificial Pollination
Artificial pollination offers several advantages for passion fruit production:
- Increased fruit yield: By manually transferring pollen, growers can ensure that each flower receives enough pollen for proper fertilization, leading to higher fruit set and increased yields.
- Better fruit quality: Artificial pollination allows growers to control the pollination process, resulting in more uniform and high-quality fruit.
- Time-saving: With artificial pollination, growers can accelerate the pollination process, reducing the time required for fruits to develop.
Conclusion
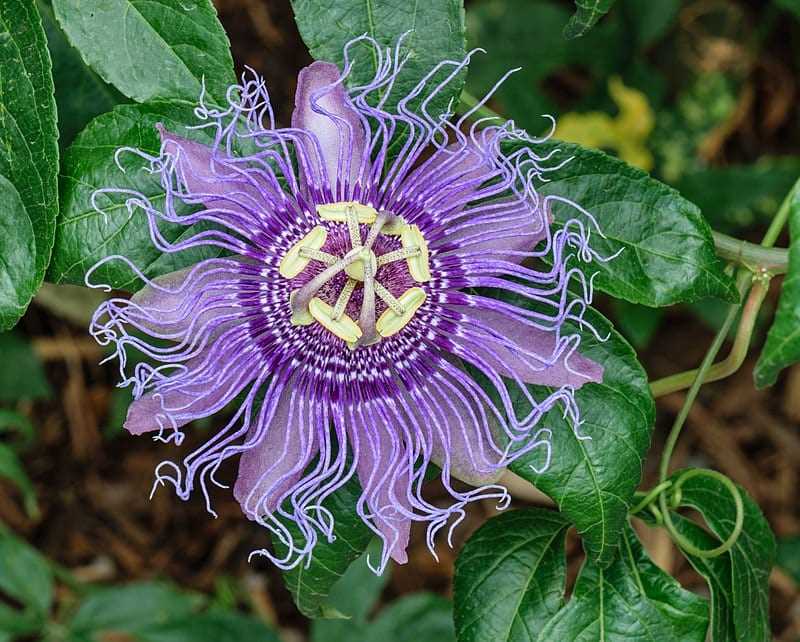

Artificial pollination is a key technique in boosting passion fruit production. By taking control of the pollination process, growers can enhance fruit set, improve fruit quality, and increase overall yields. Understanding the process and implementing artificial pollination can greatly benefit passion fruit growers, ensuring a successful and profitable harvest.
Increasing Passion Fruit Yield: Artificial Pollination is the Key!
Passion fruit, scientifically known as Passiflora incarnata, is a tropical and subtropical vine that produces delicious and exotic fruits. However, one of the main challenges for passion fruit growers is low fruit yield and variable quality.
The Importance of Pollination
Pollination plays a critical role in the production of passion fruit. The flowers of passion fruit are both male and female, but they need to be pollinated for fruit to develop. In the wild, passion fruit plants rely on insects and wind for pollination. However, this natural pollination process can be inconsistent and unreliable.
Artificial Pollination: A Solution for Passion Fruit Growers
To overcome the limitations of natural pollination, many passion fruit growers have turned to artificial pollination techniques. By manually transferring pollen from the male parts of the flower to the female parts, growers can ensure more efficient and reliable pollination.
The Process of Artificial Pollination
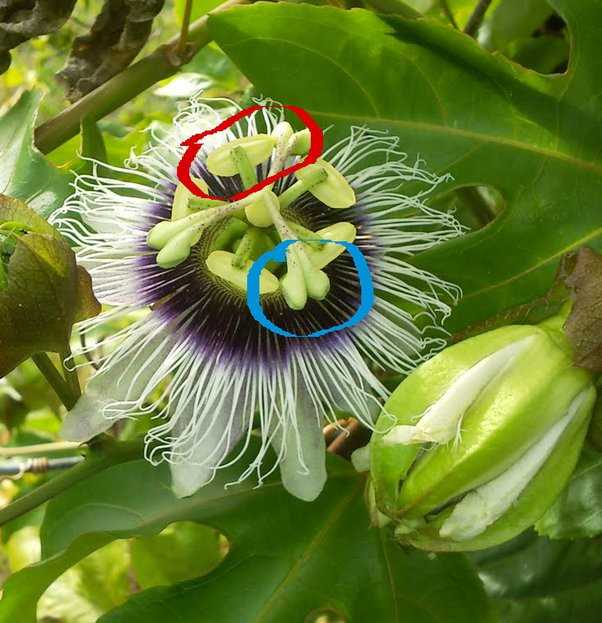

Artificial pollination involves the following steps:
- Identify the Flowers: Passion fruit flowers have distinct features. Look for flowers with both male and female parts intact.
- Gather Pollen: Carefully collect the pollen using a fine brush or cotton swab. Ensure that the pollen is fresh and abundant.
- Transfer Pollen: Gently transfer the collected pollen from the male parts (anthers) to the female part (stigma) of other flowers. Repeat this process for multiple flowers.
- Observe and Monitor: Keep track of the flowers that have been artificially pollinated and monitor their progress. Regularly check for the development of fruits.
The Benefits of Artificial Pollination
By adopting artificial pollination techniques, passion fruit growers can expect the following benefits:
- Increased Yield: Artificial pollination ensures that a higher percentage of flowers are successfully fertilized, leading to increased fruit production.
- Uniform Quality: With artificial pollination, growers have more control over which flowers are pollinated, resulting in fruits of more consistent size, shape, and flavor.
- Reduced Dependence on Insects: Artificial pollination reduces the reliance on external factors like insects for pollination, allowing growers to have greater control over the pollination process.
Conclusion
Artificial pollination is a key technique for increasing passion fruit yield. By taking control of the pollination process, growers can ensure higher fruit production, consistent fruit quality, and reduced dependence on natural pollinators. Implementing artificial pollination techniques can greatly benefit passion fruit production and help meet the growing demand for this popular tropical fruit.
Why Natural Pollination is Inefficient for Passion Fruit Plants?
Passion fruit plants, also known as Passiflora incarnata, rely on pollination to produce fruits. While the natural pollination process occurs through the help of insects like bees, butterflies, and beetles, it is often inefficient for passion fruit plants due to various reasons:
- Lack of pollinators: Passion fruit plants may not attract a sufficient number of pollinators to ensure effective pollination. This can be due to factors such as competition for floral resources, changes in habitat, or a decline in pollinator populations.
- Low pollinator visitation rate: Even if there are enough pollinators in the area, passion fruit plants may not receive enough visits for optimal pollination. This can be influenced by the availability of alternative nectar sources or the attractiveness of the passion fruit flowers compared to other flowers in the vicinity.
- Flower structure: The unique flower structure of passion fruit plants can hinder natural pollination. The flowers have a complex, multi-part structure, including an elongated corolla tube, which can make it difficult for small insects to reach the reproductive parts and transfer pollen effectively.
- Self-incompatibility: Some passion fruit plant varieties exhibit self-incompatibility, meaning they are unable to pollinate themselves. This requires cross-pollination with other compatible varieties, which may not always occur naturally in the same area.
- Unpredictable weather conditions: Natural pollination can also be affected by unpredictable weather conditions, such as rain or strong winds, which may reduce pollinator activity or damage delicate passion fruit flowers.
Due to these factors, relying solely on natural pollination for passion fruit plants can result in low fruit set and incomplete fertilization, leading to reduced fruit quality and quantity. Artificial pollination techniques, such as hand pollination or the use of pollinator attractants, can help overcome these limitations and significantly improve passion fruit production.
The Advantages of Artificial Pollination in Passion Fruit Cultivation
Increased Yield
Artificial pollination in passion fruit cultivation can significantly increase the yield of fruit. By carefully selecting and transferring pollen from one flower to another, growers can ensure that each flower is properly fertilized, leading to a higher number of fruits being produced per plant.
Improved Fruit Quality
Artificial pollination allows growers to control the breeding process and ensure the production of high-quality fruit. By selecting specific varieties for cross-pollination, growers can create hybrids with desirable traits such as improved flavor, size, and disease resistance.
Reduced Dependency on Bees
Passion fruit plants rely on bees for pollination in their natural habitat. However, the availability of bees can be unpredictable, leading to inconsistent fruit set. Artificial pollination provides a reliable method for ensuring pollination, reducing the dependency on bees and minimizing the risk of low fruit yields.
Extended Harvest Season
Through artificial pollination, growers can manipulate the timing of the fruiting cycle, allowing for an extended harvest season. By introducing controlled pollination at specific times, growers can stagger the maturity of the fruit, ensuring a continuous supply of ripe passion fruits throughout the season.
Increased Control and Precision
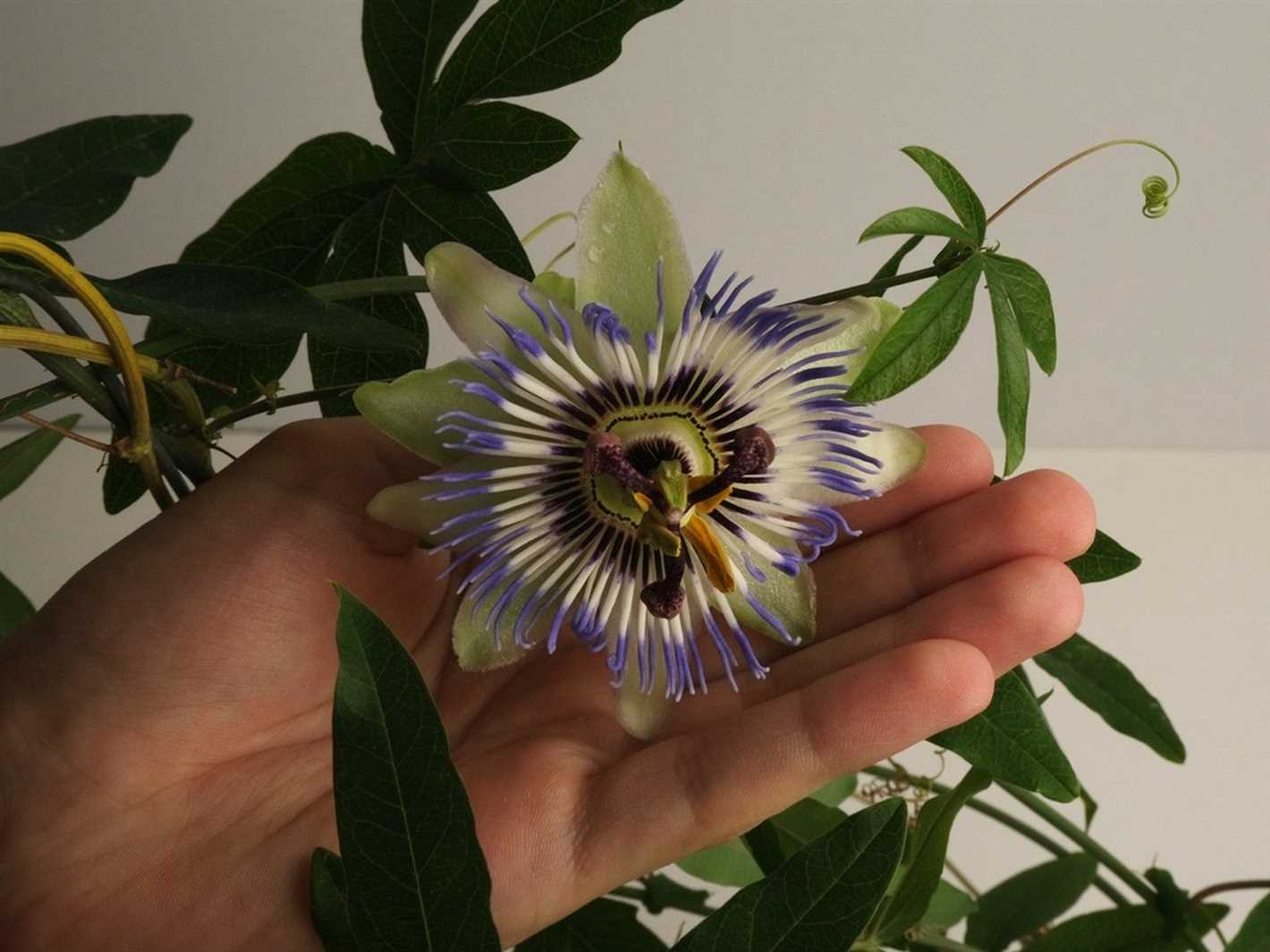

Artificial pollination gives growers increased control and precision in the breeding process. By hand-pollinating specific flowers, growers can select desired parent plants, control the timing of pollination, and ensure that every flower receives the desired pollen. This level of control allows for the production of passion fruits with consistent quality and characteristics.
Reduced Cross-Pollination Risks
In natural pollination processes, there is a risk of unwanted cross-pollination between different varieties of passion fruit plants. This can lead to undesirable traits or compromised fruit quality. Artificial pollination allows growers to carefully control which plants are cross-pollinated, reducing the risk of unwanted genetic combinations and maintaining the purity of desired varieties.
Higher Efficiency
Artificial pollination can be a more efficient method compared to relying solely on bees for pollination. With manual pollination, growers can target specific flowers and ensure thorough pollination, avoiding missed or inadequate pollination by insects. This increased efficiency can result in higher fruit set and overall productivity.
| Advantages |
|---|
| Increased Yield |
| Improved Fruit Quality |
| Reduced Dependency on Bees |
| Extended Harvest Season |
| Increased Control and Precision |
| Reduced Cross-Pollination Risks |
| Higher Efficiency |
Steps to Perform Artificial Pollination for Passiflora Incarnata
Artificial pollination is an important technique used in Passiflora incarnata cultivation to ensure reliable fruit production. It involves transferring pollen from the male reproductive organs (anthers) to the female reproductive organs (stigmas) of the flower, enabling fertilization and fruit development. Here are the steps to perform artificial pollination for Passiflora incarnata:
- Selecting the flowers: Choose flowers that are fully open and in prime condition. Look for flowers with fully-developed stigmas and anthers that contain mature pollen.
- Preparing the tools: Prepare a small brush or cotton swab for transferring pollen. Ensure that the tool is clean and dry to avoid contamination.
- Identifying the reproductive parts: Locate the male reproductive organs (anthers) and the female reproductive organ (stigma) within the flower. The anthers are usually surrounded by petals and a corona, while the stigma is located in the center.
- Extracting pollen: Gently brush or dab the anthers with the brush or cotton swab to collect the pollen. Make sure to tap multiple anthers to gather a sufficient amount of pollen.
- Transferring pollen: Carefully transfer the collected pollen to the stigma by gently brushing or dabbing it onto the receptive surface. Ensure that the pollen is evenly distributed on the stigma for better chances of successful fertilization.
- Labeling and tracking: After pollination, mark the flowers with a label or tag to indicate that pollination has been performed. This helps to keep track of the flowers that have been pollinated and enables monitoring of fruit development.
Remember, proper timing is crucial for successful artificial pollination. It is recommended to perform pollination during the morning when the flowers are fully open and the pollen is most viable. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the flowers used for pollination are from healthy and disease-free plants to maximize fruit production.
Best Time and Methods for Artificial Pollination of Passion Fruit Flowers
Artificial pollination is a crucial technique in passion fruit production to ensure a higher yield and fruit quality. By manually transferring pollen from the male to the female flower, growers can overcome limitations in natural pollination and increase fruit set rates. Here are some key factors to consider when performing artificial pollination of passion fruit flowers:
1. Timing
Timing is essential in artificial pollination for passion fruit. The best time to conduct pollination is during the morning hours when the flowers are fully open and active. This is usually around 6:00 am to 10:00 am when the temperature is cooler and the air is less turbulent.
2. Flower Selection
Choose healthy and fully developed flowers for artificial pollination. Look for flowers that have fully matured and display a vibrant color. Avoid flowers that are wilting or showing signs of disease or pest damage.
3. Pollination Methods
There are several methods you can use for artificial pollination of passion fruit flowers:
- Brushing: Use a soft paintbrush or feather to transfer pollen from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of the flower. Gently brush the anther, collecting the pollen, and then brush it onto the stigma.
- Direct Transfer: Carefully remove the petals of a male flower to expose the anther. Hold the male flower above a female flower and gently tap it to transfer the pollen directly onto the stigma.
- Pollen Collection: Collect pollen from a male flower by removing the anthers and storing them in a clean container. Later, carefully apply the collected pollen onto the stigma of a female flower using a brush or your fingers.
4. Protective Measures
To ensure successful artificial pollination, it’s important to protect the stigma from contamination during the process. Avoid touching the stigma with your hands or any contaminated tools to prevent the introduction of foreign pollen, which could lead to cross-pollination or decrease fruit quality.
5. Repeat Pollination
Passion fruit flowers are receptive to pollination for only a short period. Therefore, it’s recommended to repeat the artificial pollination method every day or every other day to increase the chances of successful fertilization and fruit set. This is especially important when growing passion fruit in a controlled environment or during a limited flowering period.
By following these best practices for timing, flower selection, pollination methods, and protective measures, growers can maximize the success rate of artificial pollination in passion fruit production and ensure a higher yield of quality fruits.
Tips for Successful Artificial Pollination: Maximizing Passion Fruit Production
1. Understand the Pollination Process
Before attempting artificial pollination, it is important to have a good understanding of the natural pollination process of passion fruit. Passion flowers have both male and female reproductive parts, but they are typically self-incompatible, meaning they cannot pollinate themselves. Instead, they rely on pollinators like bees and butterflies to transfer pollen from the male stamens to the female pistil. Artificial pollination aims to mimic this process by manually transferring pollen.
2. Identify the Right Time for Pollination
Passion fruit plants are most receptive to artificial pollination during their peak flowering seasons. This is usually between early spring and early summer, depending on the region. Look for flowers that are fully open with vibrant colors and visible stamens. The pollen is most potent during this stage, increasing the chances of successful pollination.
3. Select the Right Tools
When it comes to artificial pollination, having the right tools is essential. A fine brush or q-tip can be used to collect pollen from the stamens of one flower and transfer it to the stigma of another flower. Make sure to choose a brush or q-tip that is small enough to fit inside the passion fruit flower without causing damage.
4. Practice Proper Pollen Collection and Transfer
When collecting pollen, gently brush the stamens of a mature flower with the brush or q-tip, ensuring that the pollen grains adhere to the bristles or cotton. To transfer the pollen to a different flower, carefully brush the stigma with the collected pollen. Be gentle to avoid damaging the flower or dislodging the pollen grains.
5. Monitor and Repeat
After artificial pollination, it is important to monitor the fruits closely to ensure successful fertilization. Look for signs of fruit development, such as swelling and slight color changes. If pollination has been successful, the fruit will start to grow within a few weeks. If no fruit is observed after a reasonable period, consider repeating the artificial pollination process to increase the chances of fertilization.
6. Consider Cross-Pollination
While artificial pollination can be effective in maximizing passion fruit production, consider cross-pollination between different passion fruit varieties for even better results. Cross-pollination can enhance fruit quality, yield, and overall plant vigor. Research and identify compatible passion fruit varieties for optimal cross-pollination.
7. Provide Suitable Growing Conditions
To maximize passion fruit production, provide the plants with adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients. Passion fruit plants thrive in well-draining soil and require regular watering, especially during periods of drought. Consider supplementing with organic fertilizers to promote healthy growth and fruit development.
8. Regular Pruning and Training
Pruning and training passion fruit vines are essential for proper growth and maintenance. Regularly remove dead or diseased branches, and train the vines along a trellis or support structure to ensure proper air circulation and sunlight exposure. This helps to prevent disease and promotes better fruit production.
9. Protect from Pests and Diseases
Passion fruit plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases, such as aphids, fruit flies, and fungal infections. Regularly inspect the plants for signs of infestation or disease, and take prompt action to control or treat them. Introducing biological control agents or using organic insecticides can help prevent damage and maintain a healthy passion fruit crop.
10. Harvest at the Right Time
Passion fruits should be harvested when they have fully ripened and developed their characteristic wrinkled skin and deep color. Gently twist the fruit from the vine to avoid damaging the plant. Harvesting at the right time ensures the fruits are at their peak flavor and sweetness, maximizing consumer satisfaction.
With these tips, you can increase the success of artificial pollination and maximize passion fruit production. Remember to be patient and attentive to the needs of your passion fruit plants for the best results.
Achieving Consistent Yields: Importance of Regular Artificial Pollination
Passion fruit production relies heavily on successful pollination to achieve consistent yields. While passiflora incarnata, or passion fruit vine, is capable of self-pollination, artificial pollination is crucial to ensure the best quality and quantity of fruit.
1. Maximizing Fruit Set
Regular artificial pollination helps maximize fruit set, ensuring a higher number of fruits per vine. This is particularly important for commercial passion fruit growers who rely on high yields to meet market demands.
By manually transferring pollen from the male parts (anthers) to the female parts (stigma) of the flower using a small brush or cotton swab, growers can control and optimize the pollination process.
2. Overcoming Pollinator Limitations
Passion fruit vine relies on pollinators like bees and butterflies to transfer pollen naturally. However, in some areas or during certain seasons, natural pollinators may be limited or absent. In such cases, artificial pollination becomes essential to ensure successful pollination and fruit development.
By taking matters into their own hands and manually transferring pollen, growers can continue the pollination process even when natural pollinators are not present or insufficient. This helps overcome pollination limitations and promotes consistent fruit production.
3. Ensuring Fruit Quality
Artificial pollination allows growers to select and control the pollen used for pollination, ensuring better fruit quality. By choosing healthy and superior pollen sources, growers can enhance the genetic traits of the resulting fruit, such as taste, size, and color.
This level of control is especially important for farmers who produce passion fruit that is targeted towards specific markets or customers with specific preferences.
4. Managing Flowering Patterns
Passion fruit vines have irregular and intermittent flowering patterns, with flowers typically blooming in batches. By implementing regular artificial pollination, growers can manage and optimize the timing and consistency of flower pollination.
This helps ensure that all flower batches are treated with enough pollen for consistent fruit set. It also enables growers to control the fruit ripening cycle and ensure a more even distribution of fruit throughout the growing season.
5. Increasing Crop Yield Potential
Regular artificial pollination increases the overall yield potential of passion fruit vines. By ensuring consistent pollination and fruit set, growers can achieve higher yields and improve the profitability of their passion fruit farming operation.
Furthermore, increased crop yield potential allows growers to meet market demands, establish long-term contracts, and expand their business.
| Benefits of Regular Artificial Pollination |
|---|
| Maximizes fruit set |
| Overcomes pollinator limitations |
| Ensures fruit quality |
| Manages flowering patterns |
| Increases crop yield potential |
The Future of Passion Fruit Production: Artificial Pollination Innovations
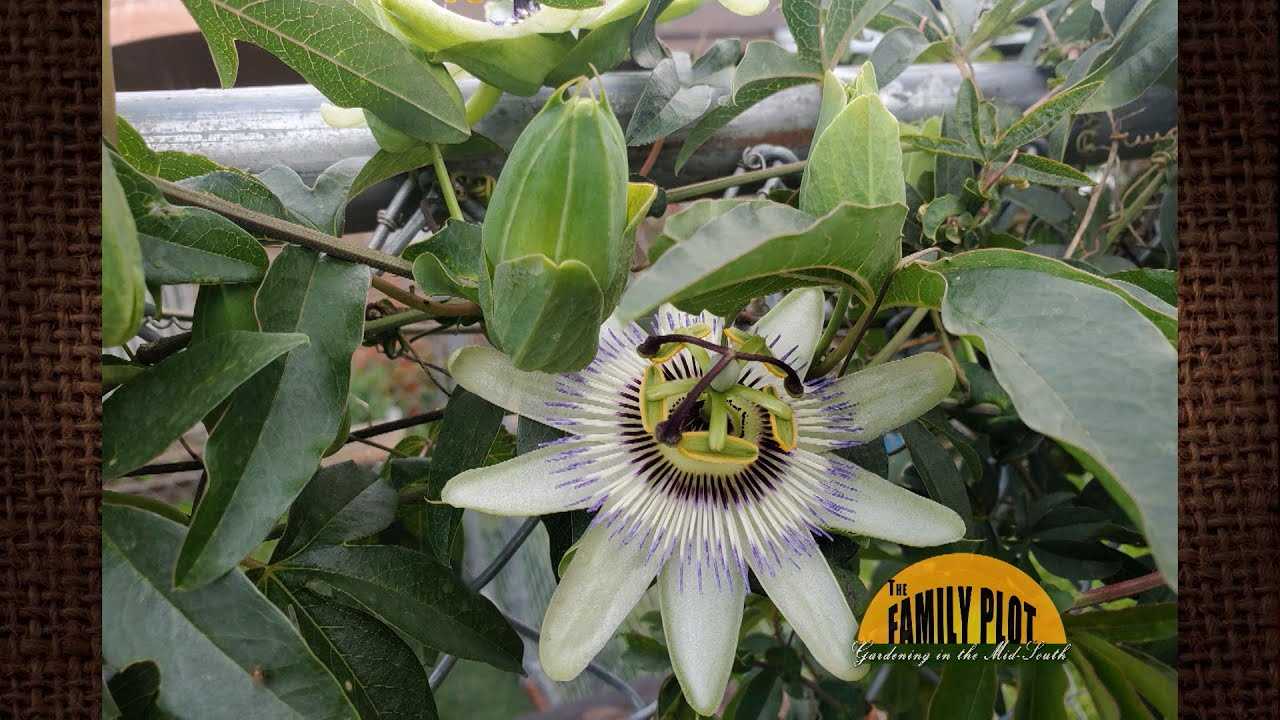

Passion fruit production plays a significant role in the global fruit market. However, the traditional methods of pollination used in passion fruit cultivation have limitations and can be labor-intensive. As a result, researchers and experts in the industry are exploring artificial pollination innovations to enhance passion fruit production for the future.
Benefits of Artificial Pollination
Artificial pollination offers several advantages over traditional methods:
- Increased efficiency: Artificial pollination enables a higher rate of pollination, ensuring a greater number of fruit set.
- Cost-effectiveness: By reducing the reliance on manual labor, artificial pollination can help lower production costs.
- Predictability: With artificial pollination, farmers have better control over the pollination process, leading to more consistent fruit production.
- Enhanced crop quality: Artificial pollination allows for targeted cross-pollination, resulting in improved fruit quality and desired traits.
Innovative Artificial Pollination Techniques
Researchers and farmers are experimenting with various techniques to facilitate artificial pollination in passion fruit production:
- Electrostatic pollination: This technique involves the use of electrostatic charges to attract pollen to the flowers, enhancing pollination rates.
- Drone-assisted pollination: Drones equipped with pollen dispensers are being tested as a means to efficiently distribute pollen across passion fruit fields.
- Insect-like robots: Robotic devices resembling insects are being developed to mimic natural insect pollinators, providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution for artificial pollination.
- Pollen dispensing machines: Automated machines capable of dispensing pollen precisely onto the stigmas of passion fruit flowers are being designed to optimize the pollination process.
The Future Outlook
The advancements in artificial pollination techniques offer a promising future for passion fruit production. With increased efficiency and reduced labor costs, farmers can achieve higher yields and improve the overall quality of passion fruit crops. Furthermore, these innovations also contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by minimizing the environmental impact associated with traditional pollination methods.
As technology continues to advance, it is likely that artificial pollination methods will become more refined and widely implemented in passion fruit cultivation. This will not only benefit farmers but also ensure a steady supply of passion fruits to meet the growing demand of consumers worldwide.
Q&A:
What is Passiflora Incarnata?
Passiflora Incarnata, commonly known as Maypop, is a species of passionflower native to the southeastern United States. It is a perennial vine with unique and beautiful flowers.
How do you identify Passiflora Incarnata?
Passiflora Incarnata can be identified by its distinctive purple flowers and three-lobed leaves. The flowers have a complex structure with a central disk, radial filaments, and a fringe of purple or white petals.
Why is artificial pollination important for Passion Fruit production?
Artificial pollination is important for Passion Fruit production because the Passiflora Incarnata flowers have a unique structure that makes it difficult for natural pollinators, such as bees, to access the pollen. By manually transferring the pollen from the male to female flowers, farmers can ensure a higher fruit set and increase their overall yield.
How do you perform artificial pollination on Passiflora Incarnata?
To perform artificial pollination on Passiflora Incarnata, you can use a small brush or cotton swab to transfer the pollen from the anthers of the male flower to the stigma of the female flower. It is important to do this early in the morning when the flowers are open and before any natural pollinators have visited them.
What are the benefits of Passion Fruit production?
Passion Fruit production has several benefits. Firstly, Passion Fruits are highly nutritious and rich in vitamins and minerals. They are also in high demand in many markets due to their unique flavor and versatility in culinary uses. Additionally, Passion Fruit vines can be grown on vertical structures, allowing farmers to save space and improve land productivity.
Video:
How to pollinate passion fruit flowers