- Understanding the Importance of Proper Grape Planting
- The Role of Rootstocks
- Selection and Preparation of the Planting Site
- Digging the Planting Hole
- Planting the Grapevine
- Proper Training and Support
- Maintenance and Care
- Conclusion
- Benefits of Using Grafted Grape Seedlings
- Method 1: Planting Grafted Grape Seedlings
- 1. Prepare the soil
- 2. Dig a hole
- 3. Remove the graft protection
- 4. Place the seedling in the hole
- 5. Backfill the hole
- 6. Water the seedling
- 7. Install support structures
- 8. Keep the seedling well-maintained
- Selecting the Right Rootstock for Successful Grape Cultivation
- Factors to Consider
- Common Rootstock Types
- Consulting with Experts
- Preparing the Soil and Planting Grafted Grape Seedlings
- 1. Choose a suitable planting location
- 2. Clear the planting area
- 3. Test and amend the soil
- 4. Dig the planting hole
- 5. Plant the grafted grape seedling
- 6. Provide support for the grape seedling
- 7. Water thoroughly
- 8. Mulch around the grape seedling
- Method 2: Planting Rootstock Grape Seedlings
- Exploring the Advantages of Rootstock Grape Seedlings
- Increased Disease Resistance
- Improved Tolerance to Environmental Conditions
- Vigor Control
- Compatibility with Different Soil Types
- Grafted Varietal Diversity
- Step-by-Step Guide to Planting Rootstock Grape Seedlings
- Question-answer:
- What is the difference between grafted and rootstock seedlings?
- Which method is more successful for grape cultivation, grafted or rootstock seedlings?
- How do I plant grafted grape seedlings?
- Are there any specific techniques for planting rootstock grape seedlings?
- How long does it take for grafted grape seedlings to bear fruit?
- What are some tips for successful grape cultivation?
- Video: Grafting Grape Vine – How To Grafting Grape Vines/Plant Using Cleft Graft Method

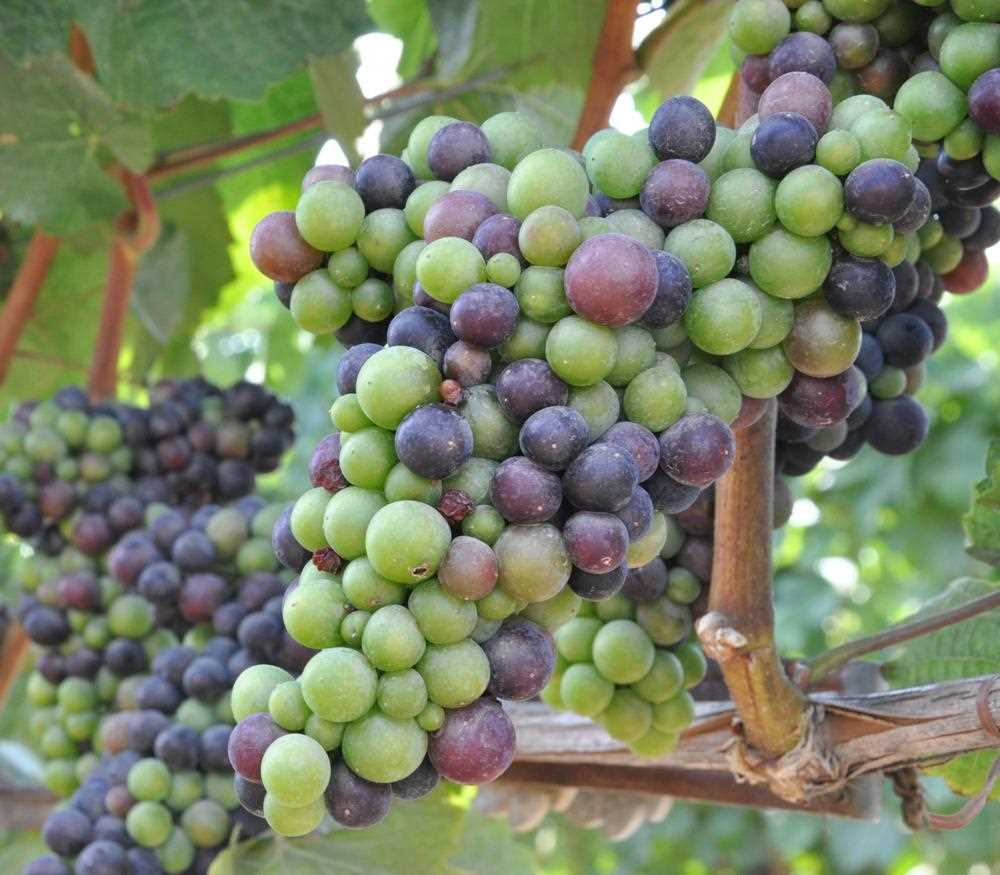
Grapes are an incredibly versatile and popular fruit, known for their delicious taste and the ability to be made into a variety of products like wine, juice, and jelly. If you’re interested in growing your own grapes, it’s important to understand the different planting methods available and which one is best for your needs.
One of the most proven and effective methods of planting grapes is using grafted and rootstock seedlings. Grafting is the process of combining the rootstock of one grapevine with the scion of another, creating a new plant with the desired qualities of both varieties. This technique allows for the propagation of grapevines that are resistant to diseases and pests, as well as having high-quality fruit.
When planting grafted grapevines, it’s important to prepare the soil properly to ensure healthy growth. The soil should be well-drained and enriched with organic matter, such as compost or manure. The planting hole should be large enough to accommodate the root system of the grapevine, with the graft union placed just above the soil level.
Rootstock seedlings, on the other hand, are grapevines that have been grown from seeds collected from wild grape species. These seedlings are known for their strong root systems, which make them more resistant to certain soil conditions and diseases. When planting rootstock seedlings, it’s important to choose varieties that are well-adapted to your climate and soil conditions, as well as being compatible with the scion you plan to graft onto them.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Grape Planting
Grape planting is a crucial step in the cultivation process and plays a significant role in the overall success of grape production. Proper planting techniques ensure healthy growth, optimal fruit production, and longevity of the grapevine.
The Role of Rootstocks
Rootstocks are an essential component of grape planting as they provide the foundation for the grapevine. They are selected for their specific attributes such as disease resistance, tolerance to soil conditions, and ability to regulate vine vigor. Choosing the right rootstock can significantly impact the quality and quantity of the grapes produced.
Selection and Preparation of the Planting Site
Before planting, it is crucial to carefully select the planting site. Grapes require full sunlight exposure, well-drained soil, and good air circulation to thrive. The pH level of the soil should also be considered, as grapes prefer a slightly acidic to neutral range (pH 6-7).
Once the planting site is chosen, proper preparation is necessary. Clear the area of any weeds, rocks, or debris. If the soil is compacted, it should be loosened with a shovel or tiller to allow for proper root growth.
Digging the Planting Hole
The planting hole should be large enough to accommodate the root system without crowding it. The depth of the hole should be such that the graft union (if present) is slightly above the soil surface. This helps prevent crown rot and ensures that the scion receives sufficient air and water.
Planting the Grapevine
Gently place the grapevine into the planting hole, spreading the roots out evenly. Ensure that the vine is straight, with the graft union (if present) slightly above the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the roots to remove any air pockets.
Proper Training and Support
After planting, it is essential to provide proper training and support to the grapevine. This involves establishing a trellis system for the vine to climb on and pruning the vine to encourage lateral growth and fruit production. Adequate support ensures that the vine grows in the desired direction and allows for easier maintenance and harvesting.
Maintenance and Care
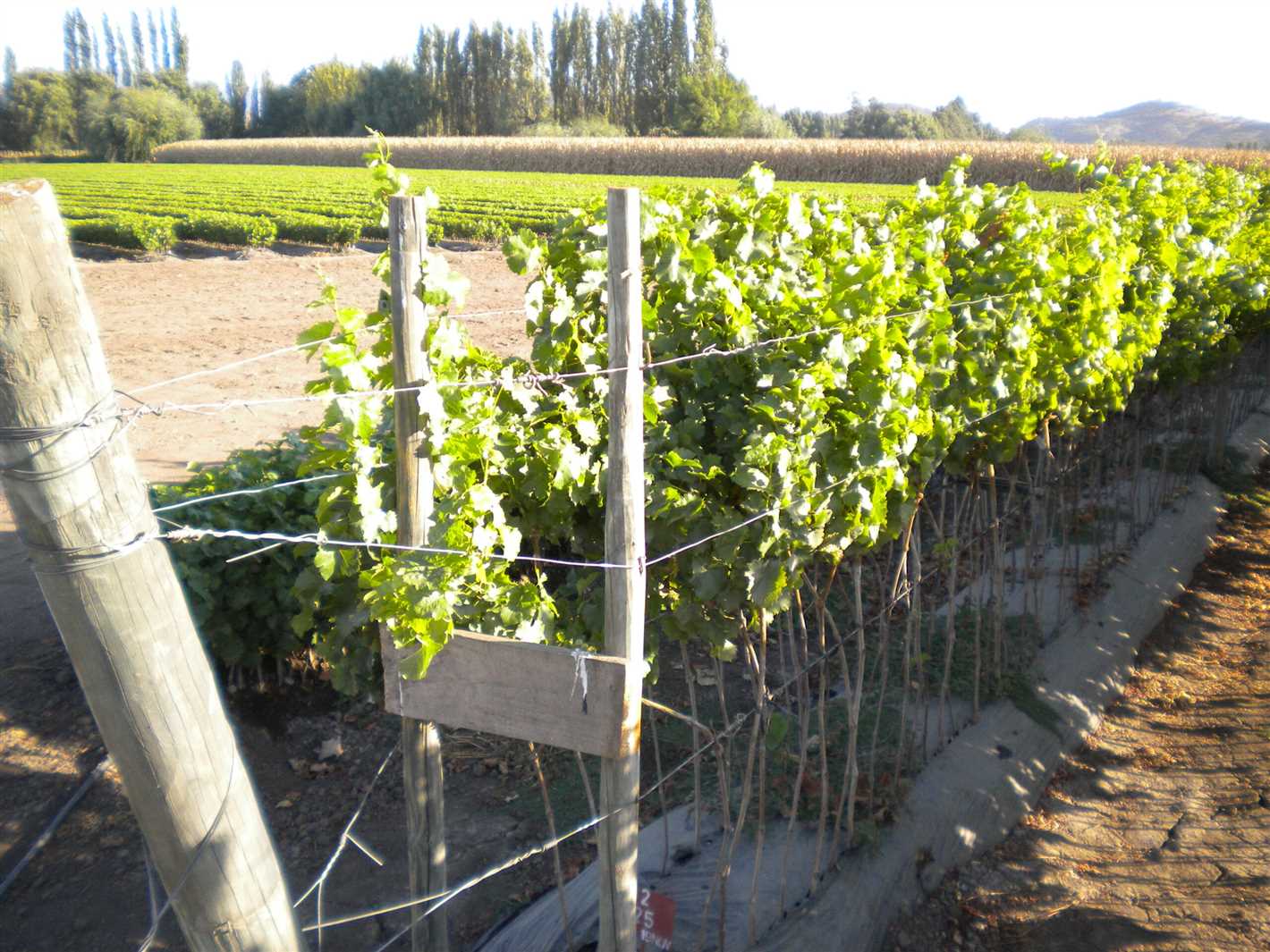


Regular maintenance and care, such as watering, fertilizing, and pest control, are necessary for the healthy growth of the grapevine. Mulching around the base of the vine helps retain moisture, control weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Additionally, regular pruning and thinning of the grape clusters promote better airflow and prevent diseases.
Conclusion
Proper grape planting is vital for successful grape cultivation. By choosing the right rootstock, preparing the planting site, digging the planting hole correctly, and providing the necessary support and care, growers can ensure healthy and productive grapevines that produce high-quality grapes.
Benefits of Using Grafted Grape Seedlings
Grafted grape seedlings offer several advantages over planting grapevines from non-grafted rootstock seedlings. These benefits include:
- Disease resistance: Grafted grape seedlings are typically grafted onto rootstock that is resistant to common grape diseases such as phylloxera and powdery mildew. This can help protect the grapevines from potential damage and reduce the need for chemical treatments.
- Improved soil adaptation: Rootstock used for grafting is often selected for its ability to adapt to a wide range of soil conditions. This means that grafted grape seedlings are more likely to thrive in different soil types, allowing for greater flexibility in grape cultivation.
- Better yield and quality: Grafting grapevines onto selected rootstock can lead to increased yield and improved grape quality. Rootstock can influence the growth, vigor, and nutrient uptake of the grapevines, resulting in healthier plants and better grapes.
- Earlier fruit production: Grafted grape seedlings tend to start producing fruits earlier compared to non-grafted seedlings. This can be advantageous for commercial grape growers who want to harvest grapes sooner and start generating revenue.
- Greater vine longevity: Grafted grapevines are often more durable and long-lasting compared to non-grafted vines. The rootstock used for grafting can provide additional support and resilience to the grapevines, allowing them to withstand various environmental stresses and diseases.
In conclusion, using grafted grape seedlings offers a range of benefits that can contribute to successful grape cultivation. These advantages include disease resistance, improved soil adaptation, better yield and quality, earlier fruit production, and greater vine longevity. It is worth considering grafting as a proven method for planting grapes and maximizing their potential in terms of growth, health, and productivity.
Method 1: Planting Grafted Grape Seedlings
Grafted grape seedlings are a popular choice for grape cultivation due to their improved disease resistance and increased vigor. Follow these steps to successfully plant grafted grape seedlings:
1. Prepare the soil
Choose a well-draining location for your grape vines. Clear the area of any weeds or grass and loosen the soil using a garden fork or tiller.
2. Dig a hole
Dig a hole that is deep and wide enough to accommodate the entire root system of the grape seedling. The hole should be approximately twice the size of the root ball.
3. Remove the graft protection
Before planting, carefully remove any graft protection material from the grape seedling. This may include wax, plastic, or other materials used to protect the graft union during transportation and storage.
4. Place the seedling in the hole
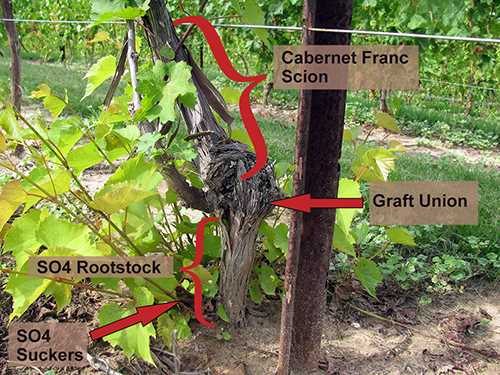
Gently place the grape seedling into the hole, ensuring that the graft union is positioned above the soil line. The graft union is the swollen area where the scion (above-ground portion) meets the rootstock (below-ground portion).
5. Backfill the hole
Fill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots of the grape seedling. Avoid packing the soil too tightly, as this can restrict root growth.
6. Water the seedling
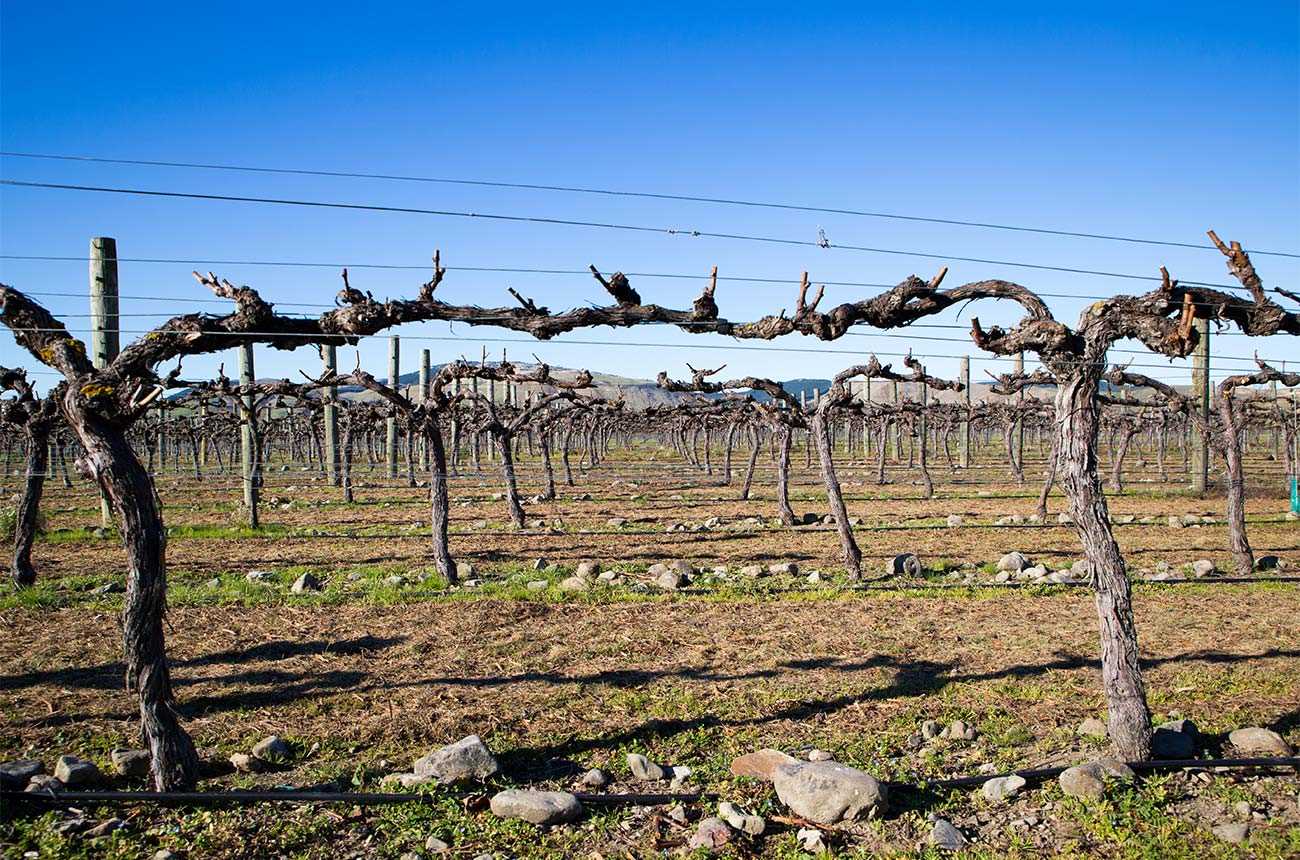


After planting, thoroughly water the grape seedling to ensure that the soil is evenly moist. This will help settle the soil and encourage root establishment.
7. Install support structures
Depending on the grape variety and training system you plan to use, install support structures such as trellises, stakes, or wires to provide stability and guidance for the growing vines.
8. Keep the seedling well-maintained
Monitor the growth of the grafted grape seedling and provide regular care and maintenance, including proper irrigation, fertilization, and pruning.
By following these steps, you can ensure the successful planting and establishment of grafted grape seedlings, setting the stage for healthy growth and abundant grape harvests.
Selecting the Right Rootstock for Successful Grape Cultivation


When it comes to grape cultivation, selecting the right rootstock is crucial for the success of the vineyard. Rootstocks are an important consideration because they directly influence the vine’s resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental conditions. Choosing the right one can significantly impact the overall health and productivity of the grape plants.
Factors to Consider
Several factors should be taken into account when selecting a rootstock for grape cultivation:
- Soil Type: Different rootstocks thrive in different soil conditions. It’s important to choose a rootstock that is well-suited to the specific soil type of the vineyard. Factors such as drainage, fertility, pH levels, and salt tolerance should be considered.
- Climate: Rootstocks vary in their ability to tolerate extreme temperatures, frost, and drought. Understanding the climate of the vineyard site is essential for selecting a rootstock that can withstand those conditions.
- Pest and Disease Resistance: Certain rootstocks are resistant to specific pests and diseases, such as phylloxera or nematodes. It’s crucial to choose a rootstock that is resistant to the prevalent pest and disease pressures in the vineyard area.
- Graft Compatibility: The rootstock selected should be compatible with the scion (the desired grape variety). Compatibility ensures successful grafting, allowing the scion to grow and thrive on the rootstock.
Common Rootstock Types
There are several common rootstock varieties used in grape cultivation:
- SO4 (Selection Oppenheim 4): This rootstock is known for its vigor and adaptability to different soil conditions. It is resistant to phylloxera and nematodes and tolerates high salinity.
- Riparia Gloire: It is a rootstock that excels in wet, heavy clay soils. It provides good resistance to phylloxera and nematodes and is well-suited for cool climates.
- 5C (Selection Couderc 5): This rootstock is resistant to phylloxera and drought, making it suitable for dry climates. It is known for its good vigor and adaptability to various soil types.
- 3309 (Schwarzmann): It is a widely used rootstock known for its resistance to phylloxera and nematodes. It thrives in well-drained soils and is suitable for moderate climates.
Consulting with Experts
Choosing the right rootstock for grape cultivation can be a complicated process. It is always advisable to consult with local experts, such as agricultural extension services or grapevine nurseries, to get specific recommendations based on the vineyard’s location and requirements. These experts can provide valuable insights and advice that will help optimize the selection process and ensure the success of the grape cultivation.
Preparing the Soil and Planting Grafted Grape Seedlings


Before planting grafted grape seedlings, it is important to properly prepare the soil to ensure optimal growth and productivity. Here are the steps to prepare the soil and plant grafted grape seedlings:
1. Choose a suitable planting location
Choose a well-drained location with full sun exposure for planting grafted grape seedlings. The soil should have a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0, which is ideal for grape cultivation.
2. Clear the planting area
Remove any existing vegetation, rocks, or debris from the planting area. This will provide a clear space for the grape seedlings to grow without competition.
3. Test and amend the soil


Conduct a soil test to determine its nutrient levels and composition. Based on the test results, amend the soil with organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve its fertility and structure.
4. Dig the planting hole
Dig a hole in the prepared soil that is deep and wide enough to accommodate the root system of the grafted grape seedling. Make sure the hole is deep enough to allow the graft union to be planted at the same level as it was in the nursery.
5. Plant the grafted grape seedling
Place the grafted grape seedling into the planting hole, making sure that the graft union is at the same level as the surrounding soil. Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots to remove any air pockets.
6. Provide support for the grape seedling
Install a trellis system or stakes near the planted grape seedling to provide support as it grows. This will help train the grapevines to grow upward and allow for better air circulation.
7. Water thoroughly
After planting, water the grafted grape seedling thoroughly to ensure good root-to-soil contact. Maintain a regular watering schedule during the establishment period to promote healthy growth.
8. Mulch around the grape seedling

Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the grafted grape seedling to help conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. Avoid placing the mulch directly against the trunk of the grapevine.
Following these steps will help set the foundation for successful growth and development of grafted grape seedlings. Continued care, such as regular pruning, fertilization, and pest management, will be necessary for the long-term health and productivity of the grape vines.
Method 2: Planting Rootstock Grape Seedlings
Growing grapes from rootstock seedlings is another proven and effective method for successful grape cultivation. Rootstock seedlings are grape plants that have been grafted onto a rootstock, which provides the plant with improved disease resistance, increased vigor, and better adaptability to different soil conditions. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to plant rootstock grape seedlings:
- Choose a suitable planting site: Select a location with well-drained soil, good sunlight exposure, and proper air circulation.
- Prepare the soil: Make sure the soil is loose and rich in organic matter. Remove any weeds or debris and loosen the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches.
- Dig a planting hole: Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the root system of the seedling. The hole should be about 2 feet wide and 2 feet deep.
- Remove the seedling from its container: Gently remove the rootstock grape seedling from its container, being careful not to damage the roots. If the roots are tightly packed, loosen them slightly.
- Place the seedling in the planting hole: Position the seedling in the hole, making sure the crown is level with or slightly above the soil surface. Spread the roots out in a natural position.
- Backfill with soil: Add soil back into the hole, gently firming it around the roots to eliminate air pockets. Avoid covering the crown of the seedling with soil.
- Water the seedling: Water the newly planted seedling thoroughly to settle the soil and eliminate any remaining air pockets.
- Install support stakes: If necessary, install support stakes near the seedling to provide stability and support as it grows.
- Apply mulch: Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the seedling to conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and insulate the soil.
- Prune and train the seedling: As the seedling grows, prune and train it according to the specific grape variety’s requirements. This includes removing suckers, training the main shoot, and pruning for shape and structure.
- Monitor and maintain: Regularly monitor the seedling for pests, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies. Provide regular irrigation and fertilization to support healthy growth.
By following this method, you can successfully plant and grow rootstock grape seedlings, setting the stage for a productive and thriving grape vineyard.
Exploring the Advantages of Rootstock Grape Seedlings
Rootstock grape seedlings have gained popularity among grape cultivators due to their numerous advantages. These seedlings are produced by grafting the desired grape variety onto a specific rootstock, resulting in a plant that combines the desirable traits of both the scion and the rootstock.
Increased Disease Resistance
One of the main advantages of rootstock grape seedlings is their increased resistance to various diseases. Different rootstock varieties have been bred to have resistance against specific diseases, such as phylloxera, powdery mildew, and crown gall. By incorporating disease-resistant rootstocks into grape cultivation, growers can reduce the need for chemical treatments and ensure healthier plants.
Improved Tolerance to Environmental Conditions
Rootstock grape seedlings also offer improved tolerance to environmental conditions, such as drought, high salinity, and extreme temperatures. This is particularly beneficial in regions with challenging growing conditions where traditional grape varieties might struggle to survive. By using rootstock seedlings, growers can overcome these challenges and achieve successful grape cultivation.
Vigor Control


Rootstock grape seedlings allow growers to control the vigor of the plant. Different rootstock varieties have different growth habits, ranging from low vigor to high vigor. This gives growers the flexibility to choose a rootstock that matches the desired growth characteristics for their specific growing conditions. By selecting a rootstock with moderate vigor, for example, growers can achieve a good balance between canopy development and fruit production.
Compatibility with Different Soil Types
Rootstock grape seedlings are often chosen based on their compatibility with different soil types. Some rootstock varieties are known to perform well in sandy soils, while others excel in clay or loamy soils. By selecting the appropriate rootstock for their specific soil conditions, growers can optimize the grapevine’s root development and nutrient uptake, leading to healthier plants and improved grape quality.
Grafted Varietal Diversity
Rootstock grape seedlings offer a wide range of possibilities for grafted varieties. Since the desired grape variety is grafted onto the rootstock, growers have the freedom to choose from a vast selection of grape varieties with different characteristics, such as flavor, color, and yield. This allows growers to experiment with new varieties and adapt their grape cultivation to market demands and consumer preferences.
In conclusion, rootstock grape seedlings present several advantages for successful grape cultivation. They provide increased disease resistance, improved tolerance to environmental conditions, vigor control, compatibility with different soil types, and grafted varietal diversity. By utilizing these advantages, growers can enhance the productivity, sustainability, and profitability of their grape vineyards.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planting Rootstock Grape Seedlings
Planting rootstock grape seedlings is an important step towards successful grape cultivation. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure the proper planting of rootstock grape seedlings:
- Choose a suitable location for planting the seedlings. The area should have good drainage, full sunlight exposure, and adequate space for the grape vines to spread out.
- Prepare the soil by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris. Loosen the soil using a tiller or garden fork to a depth of at least 12 inches to create a suitable planting bed for the seedlings.
- Test the soil to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Grapes prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. Adjust the soil pH if necessary using lime or sulfur.
- Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the root system of the seedling. The hole should be at least twice the size of the root ball.
- Place the rootstock grape seedling in the hole, making sure to spread out the roots. Position the plant so that the bud union, where the top part of the grape vine is grafted onto the rootstock, is slightly above the soil line.
- Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots to eliminate any air pockets. Water the newly planted seedling thoroughly to settle the soil.
- Install a trellis system or support structure for the grape vines. This will help guide the growth of the vines and provide necessary support as they mature.
- Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around the base of the seedling to suppress weed growth, retain moisture, and regulate soil temperature.
- Regularly water the seedling, especially during dry periods, to keep the soil evenly moist. Avoid overwatering, as grape vines prefer well-drained soil.
- Monitor the growth of the rootstock grape seedling and provide regular care, including fertilization, pruning, and protection from pests and diseases.
Following these step-by-step instructions will help ensure the successful establishment of rootstock grape seedlings and set the foundation for a healthy and productive grape vineyard.
Question-answer:
What is the difference between grafted and rootstock seedlings?
Grafted seedlings are created by joining the scion, which carries the desired grape variety, with the rootstock, which provides the plant’s roots. Rootstock seedlings, on the other hand, are grown from seeds and do not have a specific variety grafted onto them.
Which method is more successful for grape cultivation, grafted or rootstock seedlings?
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Grafted seedlings allow you to have a specific grape variety, which is great if you have a favorite or if you want to grow a particular type for commercial purposes. Rootstock seedlings, on the other hand, can provide better resistance to diseases and pests. Ultimately, the success of grape cultivation depends on various factors such as climate, soil conditions, and proper care.
How do I plant grafted grape seedlings?
To plant grafted grape seedlings, first, choose a sunny location with well-drained soil. Dig a hole large enough to accommodate the roots of the seedling. Place the seedling in the hole and backfill with soil, making sure the graft union is above ground. Water the plant thoroughly after planting and provide adequate support for the vine to grow.
Are there any specific techniques for planting rootstock grape seedlings?
When planting rootstock grape seedlings, it is important to choose a location with good soil drainage. Dig a hole deep enough to accommodate the entire root system. Gently place the seedling in the hole and backfill with soil, firming it around the roots. Water the plant well after planting and provide proper trellising or support for the vine to grow.
How long does it take for grafted grape seedlings to bear fruit?
The time it takes for grafted grape seedlings to bear fruit can vary depending on various factors such as the grape variety, growing conditions, and care. Generally, it can take 2 to 4 years for grafted grape seedlings to produce their first harvest.
What are some tips for successful grape cultivation?
Some tips for successful grape cultivation include selecting the right grape variety for your climate, providing proper support for the vines to grow, ensuring good soil drainage, watering the plants adequately, and regularly pruning and fertilizing the vines. It is also important to monitor for pests and diseases and take appropriate measures to prevent or treat them.







