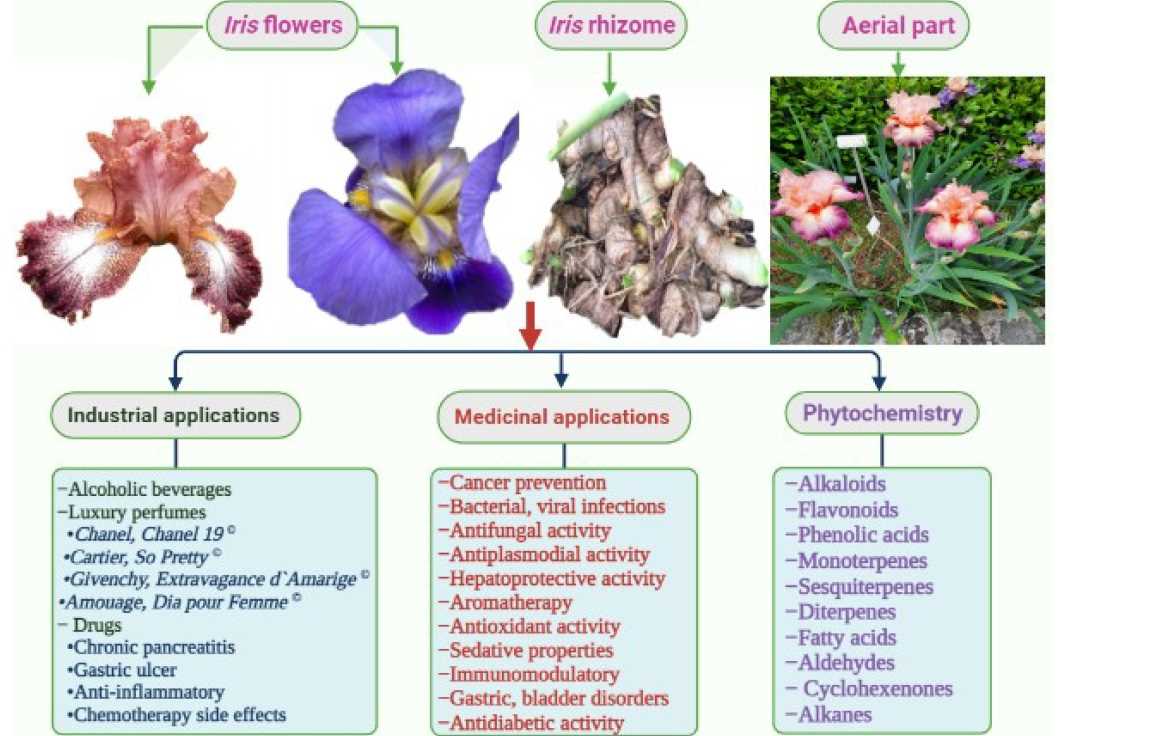
- Why roses get infected: common causes of bacterial cancer
- 1. Wounds and injuries
- 2. Poor plant hygiene
- 3. High humidity and moist conditions
- 4. Infected planting material
- 5. Lack of resistance
- Early signs of bacterial cancer: how to identify a sick rose
- Preventing bacterial cancer: essential steps for rose care
- 1. Choose disease-resistant varieties
- 2. Provide proper sunlight and air circulation
- 3. Practice good sanitation
- 4. Water roses properly
- 5. Use organic fungicides
- 6. Monitor for pests
- Conclusion
- Cutting-edge treatments for bacterial cancer: what works best
- 1. Antibiotics
- 2. Bactericides
- 3. Biocontrol agents
- 4. Plant strengthening treatments
- 5. Genetic engineering
- 6. Integrated pest management
- Natural remedies for bacterial cancer: alternatives to chemical treatments
- 1. Neem oil
- 2. Garlic spray
- 3. Copper-based fungicides
- 4. Organic compost
- 5. Proper pruning and sanitation
- Isolate and destroy: the importance of removing infected plants
- Why should you isolate infected plants?
- Steps to isolate infected plants:
- The importance of destroying infected plants:
- Boosting resistance: how to make your roses stronger
- 1. Choose disease-resistant varieties
- 2. Provide proper nutrition
- 3. Water properly
- 4. Prune regularly
- 5. Mulch your roses
- 6. Monitor for pests and diseases
- 7. Rotate plantings
- 8. Keep a clean garden
- 9. Use organic treatments
- 10. Seek professional advice
- Caring for your garden: tips to prevent the spread of bacterial cancer
- 1. Clean your tools
- 2. Practice good hygiene
- 3. Remove and destroy infected plants
- 4. Practice crop rotation
- 5. Avoid overhead watering
- 6. Use disease-resistant plant varieties
- 7. Monitor your plants regularly
- 8. Follow proper pruning techniques
- 9. Dispose of plant debris properly
- 10. Avoid overcrowding
- Conclusion
- Questions and Answers:
- What is bacterial cancer in roses?
- How can I identify bacterial cancer in my roses?
- What are the essential actions to take when saving roses from bacterial cancer?
- Can I prevent bacterial cancer in roses?
- Is there a cure for bacterial cancer in roses?
- What should I do if my roses have already been severely infected with bacterial cancer?
- Videos: Learn How To Keep Your Roses Forever | Simple DIY by Janine DLV
Roses are one of the most beautiful and beloved flowers in the world. They have been cherished for centuries for their vibrant colors and captivating fragrance. However, roses are not immune to diseases, and one of the most destructive ones is bacterial cancer. This deadly disease can quickly spread throughout an entire rose bush, causing irreversible damage and eventually death. To prevent the devastation of bacterial cancer, it is essential to take immediate action.
Inspect and monitor: Regularly inspecting your roses for any signs of bacterial cancer is crucial in saving them. Look for dark reddish-brown lesions on the stems, cankers that ooze a sticky sap, and wilting or stunted growth. These are telltale signs of bacterial cancer and should be treated as soon as possible. Monitoring your roses for any changes in their appearance or growth is also essential, as catching the disease early can increase the chances of successful treatment.
Prune and burn: If you find any signs of bacterial cancer on your roses, it is crucial to act quickly. Begin by pruning off all infected parts of the plant using sterilized tools. Make sure to cut at least 6 inches below the visible infection to ensure that all infected tissue is removed. After pruning, carefully dispose of the infected plant material by burning it, burying it in a deep hole, or sealing it in a plastic bag and throwing it away. This will prevent the bacteria from spreading to other plants in your garden.
Apply appropriate fungicide: After pruning, it is essential to apply an appropriate bactericide or fungicide to your roses to further prevent the spread of bacterial cancer. Consult with a professional at your local garden center to determine which product will work best for your specific rose variety and the severity of the infection. Follow the instructions carefully and make sure to reapply the product as directed.
Why roses get infected: common causes of bacterial cancer
Bacterial cancer is a serious disease that can affect roses and cause significant damage to their health. Understanding the common causes of this infection is crucial in order to prevent its occurrence and protect your roses.
1. Wounds and injuries
Roses can become susceptible to bacterial cancer if they have wounds or injuries. These wounds provide an entry point for bacteria to invade and infect the plant. Pruning, insect damage, and extreme weather conditions can all lead to wounds on rose plants.
2. Poor plant hygiene
Another common cause of bacterial cancer in roses is poor plant hygiene. When the plants are grown in unclean conditions or are not properly maintained, the chances of infection increase. Dirty tools, contaminated soil, and infected neighboring plants can all contribute to the spread of bacteria.
3. High humidity and moist conditions
Bacterial cancer thrives in humid and moist environments. Excessive rainfall or overwatering can create the perfect conditions for bacteria to grow and infect the roses. It is important to ensure proper drainage and avoid overwatering to minimize the risk of infection.
4. Infected planting material
If you are using infected planting material, the risk of bacterial cancer in roses increases. It is important to obtain healthy and disease-free plant material from reputable sources to reduce the chances of infection.
5. Lack of resistance
Some rose varieties are more susceptible to bacterial cancer than others. Varieties with a lack of resistance to this disease are more likely to get infected. It is important to choose disease-resistant varieties when planting roses to minimize the risk of bacterial cancer.
By understanding and addressing these common causes of bacterial cancer, you can take essential actions to protect your roses and promote their health and vitality.
Early signs of bacterial cancer: how to identify a sick rose
- Discoloration of leaves: One of the early signs of bacterial cancer in roses is the discoloration of leaves. Infected leaves may turn yellow, reddish, or even brown. Keep an eye out for any unusual colors on the leaves of your roses.
- Black spots: Another early sign is the appearance of black spots or lesions on the stems and leaves of the rose plant. These spots may be small at first but can grow larger over time. They may also have a slimy or oily appearance.
- Wilting or drooping: Infected roses may start to wilt or droop, even when they are properly watered. This is often due to the bacteria affecting the vascular system of the plant, preventing it from getting enough water and nutrients.
- Stunted growth: Bacterial cancer can also cause stunted growth in roses. If you notice that your rose plant is not growing as vigorously as it should be or if new shoots are dying before they have a chance to develop fully, it may be a sign of infection.
- Unusual odor: In some cases, infected roses may emit a foul or unusual odor. This can be a result of the bacteria attacking and decaying the tissues of the plant. If you notice a strange smell coming from your rose plants, it is worth investigating further.
If you observe any of these signs on your roses, it is important to take immediate action to prevent the spread of bacterial cancer. Early detection and intervention can greatly increase the chances of saving your roses and preserving their health.
Preventing bacterial cancer: essential steps for rose care
Bacterial cancer is a common and destructive disease that affects roses. It can cause severe damage to the plants, leading to stunted growth and even death. However, with proper care and attention, you can prevent bacterial cancer and keep your roses healthy and vibrant. Here are some essential steps to follow:
1. Choose disease-resistant varieties
When selecting roses for your garden, opt for disease-resistant varieties. These roses are genetically bred to be more tolerant of diseases, including bacterial cancer. Look for labels or ask for recommendations at your local garden center.
2. Provide proper sunlight and air circulation
Roses thrive in full sunlight, so make sure to plant them in a location where they can receive at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Additionally, good air circulation is essential for preventing the buildup of moisture, which can contribute to the development of bacterial cancer. Avoid planting roses too close together and prune them regularly to maintain good airflow.
3. Practice good sanitation
Remove any fallen leaves or flowers around the roses regularly, as they can harbor bacteria and promote disease spread. Clean your gardening tools before and after use to prevent contamination. Additionally, make sure to clean your pruning shears with a solution of bleach or rubbing alcohol after each use.
4. Water roses properly
Roses need regular watering, but overwatering can promote the development of bacterial cancer. Water the plants deeply and thoroughly, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between each watering. Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can facilitate the spread of diseases. Instead, water at the base of the plant.
5. Use organic fungicides
If you notice any signs of bacterial cancer on your roses, such as black or purple lesions on the stems or leaves, consider using organic fungicides to help control the disease. Consult with a local gardening expert or choose products labeled for rose diseases, and always follow the instructions on the packaging.
6. Monitor for pests
Pests can weaken roses and make them more susceptible to diseases. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests, such as aphids or mites, and take appropriate measures to control them. This can include using natural predators, applying insecticidal soaps, or manually removing the pests.
Conclusion
Preventing bacterial cancer in roses requires a combination of proper care, vigilant monitoring, and timely action. By following these essential steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of this devastating disease and keep your roses thriving for years to come.
Cutting-edge treatments for bacterial cancer: what works best
When it comes to saving roses from bacterial cancer, using cutting-edge treatments is crucial. These treatments have been developed through extensive research and have proven to be effective in combating this destructive disease.
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are one of the most common treatments for bacterial cancer in roses. They work by targeting and killing the bacteria responsible for the disease. It is important to choose the right antibiotic and follow the recommended dosage for optimal results. Regular application is necessary to prevent reoccurrence of the disease.
2. Bactericides
Bactericides, specifically formulated to control bacterial infections, can also be effective in treating bacterial cancer in roses. These products are designed to kill the bacteria present on the plant’s surface and within the tissues. Regular application is necessary to ensure proper protection.
3. Biocontrol agents
Using biocontrol agents is an innovative approach to treat bacterial cancer in roses. These agents are living organisms, such as beneficial bacteria or fungi, that can help control the growth and spread of harmful bacteria that cause the disease. Biocontrol agents can be applied through sprays or incorporated into the soil.
4. Plant strengthening treatments
Strengthening the overall health and immune system of the rose plant can also be an effective strategy against bacterial cancer. Treatments that include plant growth regulators and nutrition supplements can help improve the plant’s ability to fight off infections and resist disease development. Additionally, proper watering, pruning, and ventilation practices contribute to overall plant health.
5. Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering is a cutting-edge approach to combating bacterial cancer in roses. Researchers are working on developing genetically modified roses that have increased resistance to the disease. By introducing specific genes into the rose plant, scientists hope to create plants that are more resilient to bacterial infections.
6. Integrated pest management
Adopting an integrated pest management (IPM) approach can help prevent and manage bacterial cancer in roses. IPM involves a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods. By implementing practices such as proper sanitation, regular monitoring, and targeted pesticide applications, rose growers can effectively manage the disease.
While these cutting-edge treatments show promise in combating bacterial cancer in roses, it is essential to consult with experts or professionals in the field for guidance on their proper use and application. Additionally, a holistic approach that includes good cultural practices, regular monitoring, and proper care is essential for the long-term health and vitality of roses.
Natural remedies for bacterial cancer: alternatives to chemical treatments
When it comes to saving roses from bacterial cancer, there are natural remedies available that can be used as alternatives to chemical treatments. These natural remedies can be just as effective in treating and preventing bacterial cancer in roses, without the side effects and potential harm that chemicals can cause.
1. Neem oil
Neem oil is a natural extract from the neem tree and is known for its antibacterial properties. It can be diluted with water and sprayed onto the infected roses to help combat bacterial cancer. Neem oil also acts as a natural fungicide, which can provide additional protection for the roses.
2. Garlic spray
Garlic has long been used for its medicinal properties, including its antibacterial and antifungal effects. To make a garlic spray, crush several garlic cloves and mix them with water. Let the mixture sit for a few hours, then strain it and apply it to the infected roses. This garlic spray can help kill the bacteria causing cancer in the roses.
3. Copper-based fungicides
Copper-based fungicides are approved for use in organic gardening and can be effective in treating bacterial cancer. These fungicides work by creating a protective barrier on the surface of the plants, preventing the bacteria from entering and causing further damage. It is important to follow the instructions for application, as too much copper can be harmful to the plants.
4. Organic compost
Using organic compost can help build the health and resilience of the roses, making them less susceptible to bacterial cancer. Organic compost provides essential nutrients and beneficial microorganisms to the soil, creating a healthy environment for the roses to grow. Regularly applying organic compost around the base of the roses can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of bacterial cancer.
5. Proper pruning and sanitation
Pruning infected rose branches and removing fallen leaves can help reduce the spread of bacterial cancer. It is important to sanitize pruning tools between cuts to prevent further contamination. By practicing proper pruning and sanitation techniques, you can minimize the risk of bacterial cancer spreading to other roses.
Overall, natural remedies can be effective alternatives to chemical treatments when it comes to saving roses from bacterial cancer. However, it is important to note that prevention is key, so maintaining the overall health of the roses through proper watering, fertilization, and monitoring for signs of disease is crucial in preventing bacterial cancer.
Isolate and destroy: the importance of removing infected plants
Once you have identified a rose plant infected with bacterial cancer, it is crucial to take immediate action to prevent the spread of the disease to other plants in your garden. Isolating and destroying the infected plants is an essential step in containing the bacteria and protecting the health of your rose garden.
Why should you isolate infected plants?
- Bacterial cancer is highly contagious and can easily spread from one plant to another through various means, including wind, rain, insects, and gardening tools.
- By isolating infected plants, you create a physical barrier that prevents the bacteria from coming into contact with healthy roses, reducing the risk of further infections.
- Isolation also allows you to closely monitor the infected plants, making it easier to observe any changes in the disease progression and take necessary steps accordingly.
Steps to isolate infected plants:
- Identify the infected rose plant by looking for symptoms such as cankers, distorted growth, oozing sap, or blackened stems.
- Mark the infected plant using a brightly colored ribbon or a stake to ensure it is easily distinguishable from healthy plants.
- Set up a physical barrier around the infected plant using a plastic sheet or a temporary fence. Make sure the barrier extends a few inches above and below the soil surface to prevent any accidental contact.
- Regularly inspect the isolated plant for any signs of disease progression or new infections. Remove any dead or infected plant material promptly.
The importance of destroying infected plants:
Mere isolation may not be sufficient to completely eradicate the bacteria from your garden. It is essential to destroy the infected plants to eliminate the source of the infection and reduce the risk of reinfection. Proper disposal methods include:
- Burning the infected plants
- Bagging and sealing the plants before disposing of them in a landfill
- Burying the plants in a deep hole away from any future gardening activities
Remember, removing infected plants from your garden not only helps in controlling the spread of bacterial cancer but also promotes the overall health and well-being of your rose plants.
Boosting resistance: how to make your roses stronger
Having strong and healthy roses is crucial for preventing and combating bacterial cancer. By boosting their resistance, you can ensure that your roses are better equipped to fight off diseases and pests. Here are some essential actions to take:
1. Choose disease-resistant varieties
Start by selecting roses that are naturally resistant to diseases, such as bacterial cancer. Look for varieties that have been bred to withstand common pests and diseases, as they will have a higher chance of survival.
2. Provide proper nutrition
Ensure that your roses receive adequate nutrition by using a balanced fertilizer. Fertilizers rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium will help boost your roses’ immune system and overall health.
3. Water properly
Water your roses deeply and consistently, ensuring that the soil is moist but not overly saturated. This will help prevent stress and keep your roses healthy, making them less susceptible to diseases.
4. Prune regularly
Regular pruning helps maintain the shape and health of your roses. Remove any dead or diseased branches to prevent the spread of bacteria. Pruning also allows for better air circulation, reducing the chances of disease development.
5. Mulch your roses
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of your roses to help retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Mulch also acts as a barrier, preventing disease-causing bacteria from splashing onto the leaves.
6. Monitor for pests and diseases
Regularly inspect your roses for signs of pests or diseases. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevents the spread of infections. Remove any affected leaves or branches immediately.
7. Rotate plantings
Rotate the location of your roses every few years to prevent the buildup of disease-causing organisms in the soil. This practice helps disrupt the life cycle of pests and diseases, reducing the risk of infection.
8. Keep a clean garden
Maintain good garden hygiene by removing fallen leaves, debris, and spent flowers. Clearing away organic matter reduces the chances of pathogens overwintering and affecting your roses.
9. Use organic treatments
Consider using organic treatments, such as neem oil or insecticidal soaps, to combat pests and diseases. These options are safer for the environment and less likely to harm beneficial insects.
10. Seek professional advice
If you’re facing persistent issues with bacterial cancer or other diseases, it’s advisable to seek the help of a professional horticulturist or plant pathologist. They can provide expert guidance and recommend specific treatment methods.
By following these steps, you can significantly boost the resistance of your roses and help protect them from bacterial cancer and other diseases. Remember, prevention is key, so it’s important to incorporate these practices into your regular rose care routine.
Caring for your garden: tips to prevent the spread of bacterial cancer
1. Clean your tools
One of the most important steps in preventing the spread of bacterial cancer in your garden is to regularly clean your gardening tools. Bacteria can easily transfer from an infected plant to a healthy one through contaminated tools. After each use, make sure to clean your tools with soap and water or a disinfecting solution.
2. Practice good hygiene
Bacterial cancer can spread through contact, so it’s crucial to practice good hygiene when working in your garden. Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling plants, especially if you suspect any of them might be infected. This will help prevent cross-contamination between plants and reduce the risk of spreading the disease.
3. Remove and destroy infected plants
If you notice any signs of bacterial cancer in your garden, such as blackened or discolored leaves, wilting, or cankers, it’s important to act quickly. Remove the infected plants from your garden immediately and destroy them to prevent the spread of bacteria to other plants. Do not compost infected plants as this can contribute to the spread of the disease.
4. Practice crop rotation
Crop rotation is an effective strategy to prevent bacterial cancer and other diseases in your garden. By rotating your crops each year, you can disrupt the lifecycle of bacteria and reduce their population in the soil. This will help prevent the re-infection of plants and keep your garden healthy.
5. Avoid overhead watering
Overhead watering can create a moist environment that promotes the growth and spread of bacteria. To prevent the spread of bacterial cancer, water your plants at the base instead of using overhead sprinklers. This will help keep the foliage dry and reduce the risk of infection.
6. Use disease-resistant plant varieties
When selecting plants for your garden, choose varieties that are resistant to bacterial cancer and other common diseases. Disease-resistant plants have been specifically bred to have increased resistance to certain pathogens, reducing the risk of infection and the need for chemical treatments.
7. Monitor your plants regularly
Regular monitoring is essential to catch any signs of bacterial cancer early on. Inspect your plants regularly for any unusual symptoms, such as discoloration, wilting, or oozing. Prompt action can prevent the spread of the disease and help save your garden from extensive damage.
8. Follow proper pruning techniques
Pruning is an important part of maintaining healthy plants, but it can also create entry points for bacteria. When pruning your plants, make sure to use clean and sharp tools, and prune during dry weather to minimize the risk of introducing bacteria into open wounds.
9. Dispose of plant debris properly
Proper disposal of plant debris is crucial to prevent the spread of bacterial cancer. Do not leave infected leaves, stems, or other plant material in your garden as they can harbor bacteria. Bag them securely and dispose of them with your regular trash to ensure that the disease does not spread.
10. Avoid overcrowding
Overcrowded plants create a favorable environment for the spread of diseases, including bacterial cancer. To prevent the spread of the disease, make sure to space your plants properly and allow for good air circulation. This will help keep the foliage dry and reduce the risk of infection.
Conclusion
Preventing the spread of bacterial cancer in your garden requires a combination of good hygiene practices, regular monitoring, and proper plant care techniques. By following these tips, you can create a healthy environment for your plants and minimize the risk of infection.
Questions and Answers:
What is bacterial cancer in roses?
Bacterial cancer, also known as Crown Gall, is a plant disease caused by the bacteria Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It leads to the formation of galls or abnormal growths on the roots, stems, and branches of roses.
How can I identify bacterial cancer in my roses?
Bacterial cancer can be identified by the presence of galls on the roots, stems, and branches of roses. These galls are usually rough and irregular in shape. Additionally, infected plants may exhibit stunted growth, wilting, and yellowing of the leaves.
What are the essential actions to take when saving roses from bacterial cancer?
When saving roses from bacterial cancer, it is essential to first remove and destroy any infected plant material, including galls. It is recommended to prune the infected branches and apply a topical treatment containing a copper-based fungicide. Additionally, improving overall plant health through proper watering, fertilization, and soil management is crucial.
Can I prevent bacterial cancer in roses?
While it may be difficult to completely prevent bacterial cancer in roses, there are certain measures that can reduce the risk. These include choosing disease-resistant rose varieties, practicing good hygiene in the garden, avoiding mechanical injuries to the plants, and maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Is there a cure for bacterial cancer in roses?
Currently, there is no cure for bacterial cancer in roses. However, with proper management and timely intervention, it is possible to control the disease and minimize its impact on the plants.
What should I do if my roses have already been severely infected with bacterial cancer?
If your roses have already been severely infected with bacterial cancer, it may be necessary to remove and destroy the entire plant to prevent the spread of the disease to other plants. It is also a good idea to disinfect any tools or equipment that have come into contact with the infected plant.







