- Strawberries: A Comprehensive Guide to Planting and Care
- Introduction
- Choosing the Right Variety
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting
- Care
- Harvesting
- Conclusion
- Growing Strawberries from Seeds: Tips and Tricks
- 1. Choose the Right Seeds
- 2. Start Seeds Indoors
- 3. Maintain Optimal Conditions
- 4. Transplanting Seedlings
- 5. Provide Proper Care
- 6. Managing Pests and Diseases
- 7. Harvesting and Enjoying
- Choosing the Right Variety: Factors to Consider
- Climate
- Available Space
- Taste and Texture
- Harvest Time
- Disease Resistance
- Yield
- Requirements for Successful Strawberry Planting
- Soil
- Sunlight
- Temperature
- Watering
- Fertilizer
- Spacing
- Weed Control
- Pest and Disease Management
- Pruning and Runner Management
- Preparing the Soil for Strawberry Plants
- Planting Techniques for Strawberries
- Site Selection
- Prepare the Soil
- Planting Options
- Transplants:
- Seeds:
- Care and Maintenance
- Nurturing Strawberry Plants: Essential Care Tips
- 1. Planting:
- 2. Watering:
- 3. Mulching:
- 4. Fertilizing:
- 5. Pruning:
- 6. Pest and Disease Control:
- 7. Harvesting:
- Protecting Strawberry Plants from Pests and Diseases
- Pest Control
- Disease Control
- Conclusion
- Harvesting and Storing Strawberries: Best Practices
- 1. Harvesting Strawberries:
- 2. Storing Strawberries:
- 3. Preserving Strawberries:
- Question-answer:
- Can strawberries be grown from seeds?
- When is the best time to plant strawberries?
- How do I care for strawberry plants?
- Can I grow strawberries in containers?
- How long does it take for strawberry plants to bear fruit?
- Video: Simple method of growing chili tree with Aloe vera || How to grow chili tree at home
Growing strawberries in your garden can be a rewarding and delicious experience. These juicy fruits are not only packed with nutrients but also add a pop of color to your landscape. Whether you want to plant strawberries from seeds or start with seedlings, our expert tips will help you succeed in growing healthy plants.
Planting Strawberries:
When planting strawberries from seeds, it’s important to choose a sunny spot for your garden bed. Strawberries require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily to thrive. Prepare the soil by removing any weeds and loosening it with a garden fork. Mix in compost or well-rotted manure to enrich the soil with nutrients.
Care and Maintenance:
Once your strawberry plants are established, regular care and maintenance are essential for their growth. Water deeply but infrequently, aiming for about 1 inch of water per week. Mulch the soil with straw or wood chips to regulate soil moisture and prevent weed growth. Regularly inspect your plants for pests and diseases, and take appropriate measures to control them.
Strawberries: A Comprehensive Guide to Planting and Care
Introduction
Strawberries are delicious and nutritious fruits that can be easily grown in your own garden. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to successfully plant and care for strawberries.
Choosing the Right Variety
There are three main types of strawberries: June-bearing, everbearing, and day-neutral. June-bearing strawberries produce a single large crop in late spring or early summer. Everbearing strawberries produce two to three crops, one in spring, one in summer, and one in fall. Day-neutral strawberries produce small crops throughout the growing season.
When choosing a variety, consider your climate, as different varieties thrive in different conditions. It’s also important to consider the size and flavor of the strawberries you prefer.
Preparing the Soil
Strawberries prefer well-drained soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Before planting, remove any weeds and rocks from the area. Dig the soil to a depth of 8-10 inches and mix in organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve the soil’s fertility.
Planting
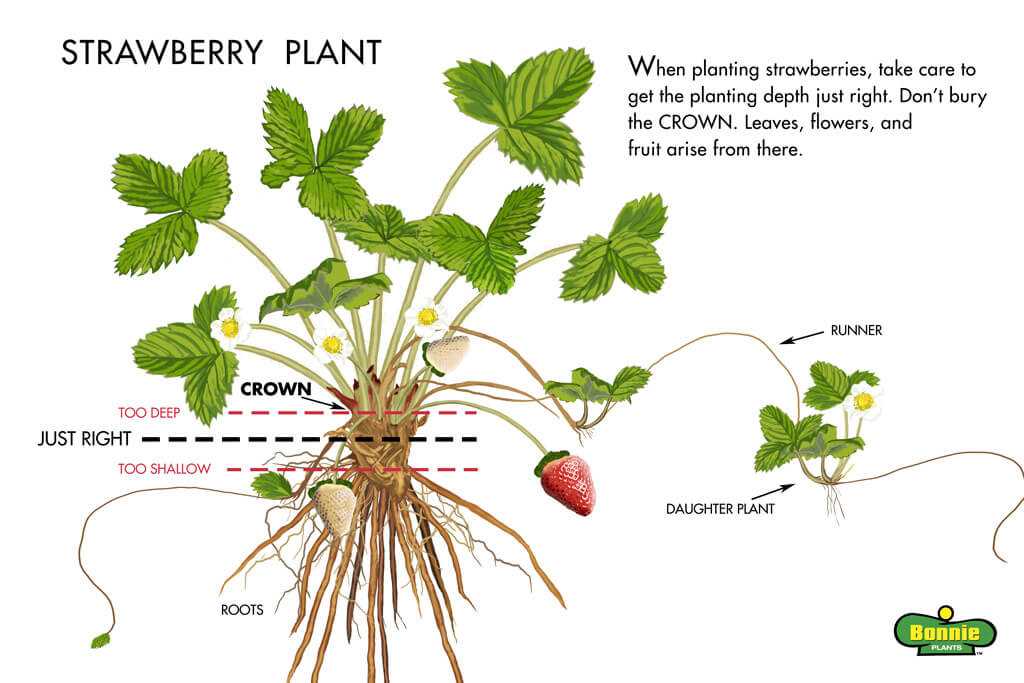
Plant strawberries in early spring or late summer, depending on your climate. Space the plants 12-18 inches apart in rows that are 2-3 feet apart. Dig a hole large enough to accommodate the roots, making sure the crown is level with the soil surface. Gently spread out the roots in the hole and cover them with soil, firming it down gently.
Care
Water the plants regularly, providing about 1-2 inches of water per week. Mulch around the plants with straw or pine needles to suppress weeds and retain moisture. Remove any weeds that do appear, as they can compete with the strawberries for nutrients and water.
Fertilize the plants with a balanced fertilizer once a month during the growing season. Prune off any runners that appear, as they can divert energy away from fruit production. Protect the plants from pests such as birds and slugs by using nets or traps.
Harvesting
Strawberries are usually ready for harvest 4-6 weeks after flowering. They should be bright red and fully ripe before picking. Gently lift the fruit from the stem, taking care not to damage the plant. Harvest the strawberries in the morning when they are cool and at their sweetest.
Conclusion
By following these planting and care tips, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious strawberries right from your own garden. With some patience and care, you will be rewarded with juicy, flavorful fruits that are perfect for eating fresh or using in a variety of recipes.
Growing Strawberries from Seeds: Tips and Tricks
Growing strawberries from seeds can be a fun and rewarding experience. While it may take a little more time and effort compared to starting from transplants, the process allows you to select the specific strawberry variety you want to grow. Here are some tips and tricks to help you successfully grow strawberries from seeds.
1. Choose the Right Seeds
When selecting strawberry seeds, make sure to choose ones that are of high quality and from a reputable source. Look for seeds that are fresh and have a high germination rate. Consider the specific variety you want to grow, as different varieties have different flavors, sizes, and growth characteristics.
2. Start Seeds Indoors

It is recommended to start your strawberry seeds indoors to provide optimal growing conditions. Fill seed trays or pots with a well-draining potting mix, and place one or two seeds in each pot. Cover the seeds lightly with soil and provide adequate moisture.
3. Maintain Optimal Conditions
After sowing the seeds, make sure to provide the right growing conditions for your strawberry plants. Keep the soil evenly moist, but not overly wet. Place the seed trays or pots in a warm location with plenty of sunlight or under grow lights. Optimal temperatures for germination range from 60°F to 75°F (15°C to 24°C).
4. Transplanting Seedlings
Once the seedlings have developed a few sets of true leaves and are strong enough to handle, you can transplant them into larger pots or into your garden. Be careful not to damage the delicate roots when transplanting.
5. Provide Proper Care
Strawberry plants require regular watering to keep the soil moist, especially during dry periods. Mulching around the plants can help retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth. Additionally, apply a balanced fertilizer according to the specific needs of your strawberry variety.
6. Managing Pests and Diseases
Keep an eye out for common pests and diseases that can affect strawberry plants, such as aphids, slugs, and powdery mildew. Regularly inspect your plants and take appropriate measures to control and prevent infestations and diseases.
7. Harvesting and Enjoying
Once your strawberry plants start producing fruits, it’s time to enjoy the delicious rewards of your hard work. Harvest your strawberries when they are fully ripe and red. Enjoy them fresh, use them in desserts, or preserve them for later use.
By following these tips and tricks, you can successfully grow strawberries from seeds and enjoy the satisfaction of seeing your plants thrive and produce sweet and juicy strawberries.
Choosing the Right Variety: Factors to Consider

When selecting a variety of strawberries to plant, there are several factors that you should consider. The right variety will depend on your climate, available space, and personal preference.
Climate
One of the most important factors to consider is your climate. Some varieties of strawberries thrive in cooler climates, while others are better suited for warmer regions. Make sure to choose a variety that is well-suited for the temperature and weather conditions in your area.
Available Space
The amount of available space you have will also play a role in selecting the right variety. Some varieties of strawberries are more compact and are better suited for small gardens or containers. If you have limited space, look for varieties that are specifically bred for compact growth.
Taste and Texture
Another factor to consider is the taste and texture of the strawberries. Different varieties have different levels of sweetness and acidity. Some strawberries also have a firmer texture, while others are softer. Consider your personal preference and choose a variety that suits your taste.
Harvest Time
The timing of the harvest is also something to keep in mind. Some varieties of strawberries ripen earlier in the season, while others have a longer maturation period. If you have a specific timeframe in which you want to enjoy your strawberries, select a variety that will be ready for harvest during that time.
Disease Resistance
If you’re concerned about diseases that can affect strawberries, look for varieties that are known for their disease resistance. These varieties are bred to be more resistant to common strawberry diseases, which can help ensure a successful harvest.
Yield
The yield of strawberries can vary between varieties. Some varieties produce a higher quantity of strawberries, while others may have smaller yields. Consider how many strawberries you want to harvest and choose a variety that will meet your needs.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right variety of strawberries that will thrive in your specific conditions, provide you with delicious fruit, and give you a successful harvest year after year.
Requirements for Successful Strawberry Planting
Soil
Choose a well-draining soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Strawberries prefer sandy loam or loamy soils that are rich in organic matter. Avoid heavy clay soils, as they can retain too much moisture and cause root rot.
Sunlight
Strawberries thrive in full sunlight, so choose a location that receives at least 8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Without adequate sunlight, the plants may not produce as many fruits or the fruits may not develop their full flavor.
Temperature
Strawberries prefer a cool climate and do best in areas where the average temperature ranges from 60°F (15°C) to 75°F (24°C) during the growing season. They can tolerate slightly higher temperatures, but prolonged periods of heat can stress the plants and reduce fruiting.
Watering
Provide consistent moisture to the strawberries, especially during the growing season. Water deeply and regularly to keep the soil evenly moist, but avoid over-watering, as saturated soil can lead to root diseases. Mulching around the plants can help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
Fertilizer

Before planting, it’s recommended to amend the soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve fertility. During the growing season, feed the strawberries with a balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks to ensure they have an adequate supply of nutrients. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of fruit production.
Spacing
When planting strawberries, allow enough space between the plants for air circulation and to prevent overcrowding. Generally, strawberry plants should be spaced about 12-18 inches (30-45 cm) apart in rows that are 3-4 feet (90-120 cm) apart. This spacing allows the plants to receive sufficient sunlight and helps prevent the spread of diseases.
Weed Control
Keep the area around the strawberries weed-free, as weeds can compete with the plants for nutrients and water. Regularly remove any weeds that emerge and consider using mulch or landscape fabric to suppress weed growth. Be careful when weeding to avoid damaging the shallow strawberry roots.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor the strawberry plants regularly for signs of pests and diseases, such as aphids, slugs, or powdery mildew. Take prompt action if any issues are detected, using organic pest control methods when possible. Removing any infected or damaged plants can help prevent the spread of diseases to healthy plants.
Pruning and Runner Management
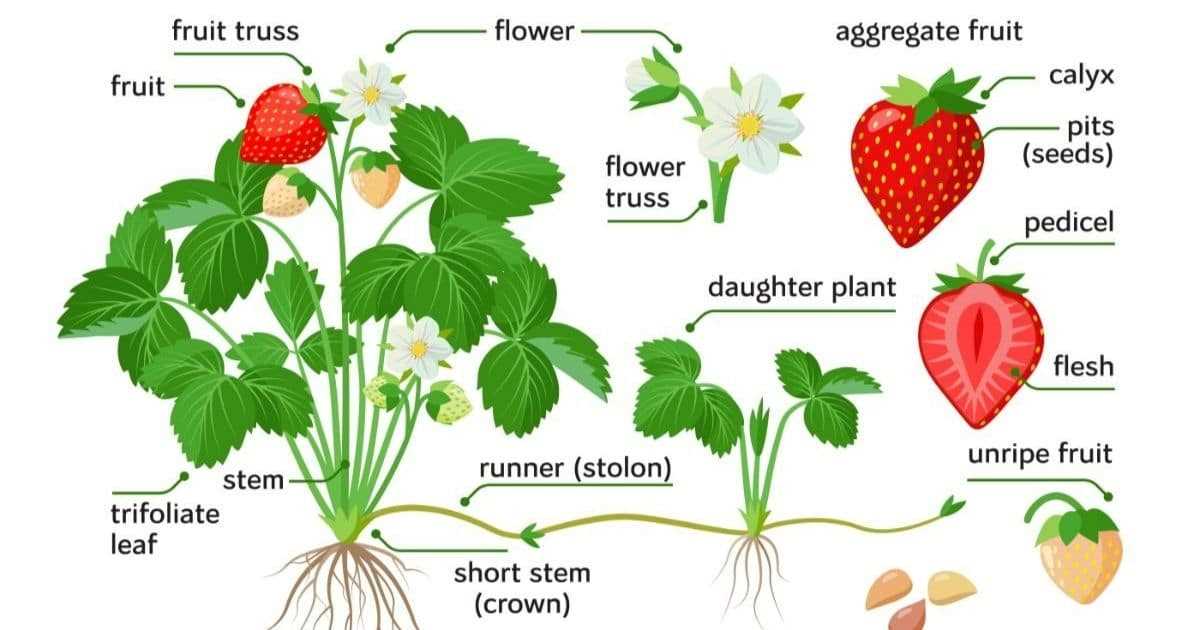
Regularly prune the strawberry plants to maintain their shape, remove old or diseased leaves, and promote better airflow. Additionally, manage the runners (long, horizontal stems) by either allowing them to root and form new plants or cutting them off to prevent energy depletion from the mother plant.
Preparing the Soil for Strawberry Plants
Before planting strawberry plants, it is important to prepare the soil properly. By doing so, you can ensure that the plants will have the best conditions to grow and produce healthy fruits. Here are some steps to follow when preparing the soil for strawberry plants:
- Choose a sunny location: Strawberry plants thrive in full sun, so select a spot in your garden that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
- Clear the area: Remove any weeds, rocks, or debris from the planting area. This will help provide a clean environment for the strawberry plants.
- Test the soil: It is essential to know the pH level of your soil. Strawberry plants prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. You can use a soil testing kit or send a sample to a local agricultural extension office for analysis.
- Amend the soil: If the pH level is not within the ideal range, you may need to amend the soil to adjust it. For example, if the soil is too alkaline, you can add sulfur to lower the pH or add lime if the soil is too acidic. Additionally, you can improve the soil’s fertility by adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure.
- Loosen the soil: Using a garden fork or tiller, loosen the soil to a depth of about 8-10 inches. This will help loosen compacted soil and improve drainage.
- Remove any perennial weeds: Dig out any perennial weeds such as dandelions or bindweed, as they can compete with the strawberry plants for nutrients and water.
Once you have prepared the soil, you can proceed with planting the strawberry plants. Follow the instructions provided with the plants or seeds to ensure proper spacing and depth. It is also important to water the plants regularly and provide them with adequate nutrients throughout the growing season. By preparing the soil correctly, you can give your strawberry plants a healthy start and increase the chances of a bountiful harvest.
Planting Techniques for Strawberries
Growing strawberries can be a rewarding experience, especially if you follow proper planting techniques. Whether you are growing strawberries from seeds or transplants, here are some tips to help you get started:
Site Selection
- Choose a sunny location for your strawberry patch, as strawberries require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Avoid areas with poor drainage, as strawberries prefer well-draining soil to prevent root rot.
- Make sure the site is free from weeds and other competitive plants.
Prepare the Soil
- Before planting strawberries, prepare the soil by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris.
- Work organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, into the soil to improve its fertility and drainage.
- Aim for a soil pH of 5.5 to 6.5, as strawberries prefer slightly acidic soil.
Planting Options
You have two primary options for planting strawberries: using transplants or starting from seeds.
Transplants:
- Choose healthy transplants with green leaves and no signs of disease or pests.
- Dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots without bending or crowding them.
- Place the transplant in the hole, making sure the crown is level with the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil and gently firm it around the roots.
- Water the transplants thoroughly after planting to help them establish.
Seeds:
- Start strawberry seeds indoors about 8-10 weeks before the last frost date in your area.
- Sow the seeds in a seed tray filled with moist seed starting mix.
- Cover the tray with a plastic dome or plastic wrap to create a mini greenhouse environment.
- Place the tray in a warm location with indirect sunlight.
- Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Transplant the seedlings into individual pots once they have grown their first set of true leaves.
- Harden off the seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them into the garden.
Care and Maintenance
| Watering | Weeding |
|---|---|
| Strawberries need regular watering, especially during dry periods. Keep the soil evenly moist but not saturated. | Regularly remove weeds from your strawberry patch to prevent competition for nutrients and reduce the risk of disease. |
| Fertilizing | Mulching |
| Fertilize strawberries with a balanced organic fertilizer once a month during the growing season, following the manufacturer’s instructions. | Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around the plants to help conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and protect the fruits from direct contact with the soil. |
| Pruning | Pest Control |
| Remove any damaged or diseased leaves and runners to promote healthy growth and airflow. | Monitor your strawberry plants for pests, such as slugs, snails, and aphids. Use organic methods, such as handpicking or insecticidal soaps, to control pests if necessary. |
By following these planting techniques and providing proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious strawberries. Remember to refer to specific variety and climate guidelines for the best results in your garden.
Nurturing Strawberry Plants: Essential Care Tips
Growing strawberries can be a rewarding experience, but it’s important to provide the right care to ensure healthy and productive plants. Here are some essential care tips for nurturing your strawberry plants:
1. Planting:
Choose a sunny spot in your garden with well-draining soil. Prepare the soil by removing any weeds and adding organic matter to improve its fertility. Plant the strawberry plants with the crown level with the soil surface, and make sure to space them at least 12 to 18 inches apart.
2. Watering:
Strawberries need regular watering, especially during dry periods. Water the plants deeply and consistently, making sure the soil is moist but not saturated. Use a soaker hose or drip irrigation system to deliver water directly to the roots and avoid wetting the foliage, which can promote disease.
3. Mulching:
Apply a layer of mulch around the strawberry plants to help conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use straw, pine needles, or shredded leaves as mulch, and apply it in a layer about 2 to 3 inches thick. Ensure that the mulch is pulled away from the crowns of the plants to prevent rotting.
4. Fertilizing:
Strawberries benefit from regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and fruit production. Apply a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 formula, according to the package instructions. Start fertilizing when the plants begin to show new growth in the spring and continue every 4 to 6 weeks throughout the growing season.
5. Pruning:
Regular pruning helps maintain the health and productivity of strawberry plants. Remove any dead or damaged leaves to prevent disease and improve air circulation. Trim off runners, which are long stems that grow from the main plant, to direct the plant’s energy towards fruit production.
6. Pest and Disease Control:
Keep a close eye on your strawberry plants for signs of pests or diseases. Common pests include slugs, snails, and aphids. Use organic pest control methods, such as handpicking or applying natural repellents, to protect your plants. To prevent diseases, water the plants in the morning to allow the foliage to dry quickly, and avoid overcrowding by providing adequate spacing between plants.
7. Harvesting:

Finally, enjoy the fruits of your labor by harvesting ripe strawberries regularly. Pick the berries when they are fully red and plump, but still firm. Twist and pull the berries gently to avoid damaging the plants. Harvesting regularly encourages the production of more berries and ensures that you enjoy them at their peak flavor.
By following these essential care tips, you can ensure the success of your strawberry plants and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious fruits. Happy growing!
Protecting Strawberry Plants from Pests and Diseases
Strawberries are delicious and highly sought-after fruit, attracting not only humans but also a variety of pests and diseases. To ensure a healthy strawberry crop, it is essential to protect the plants from these potential threats. Here are some effective methods to prevent and control pests and diseases that commonly affect strawberry plants.
Pest Control
1. Aphids: These small, soft-bodied insects can cause significant damage to strawberry plants by sucking sap from the leaves and stems. To control aphids, regularly inspect the plants and remove any infested leaves or stems. Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings, which feed on aphids. Applying insecticidal soap or spraying a mixture of water and dish soap can also help eliminate aphids.
2. Slugs and Snails: These slimy creatures feed on the leaves and fruits of strawberry plants, leaving behind holes and damage. To deter slugs and snails, create a barrier around the plants using copper tape or diatomaceous earth. Handpicking and disposing of the pests can also be effective. Additionally, maintaining a clean garden by removing debris can discourage their presence.
3. Spider Mites: These tiny pests can cause extensive damage to strawberry plants by sucking the plant’s juices. Regularly inspect the plants for signs of mite infestation, such as yellowing leaves or webbing. Applying a natural miticide or spraying the plants with a strong blast of water can help control spider mites.
Disease Control
1. Gray Mold (Botrytis cinerea): This fungal disease thrives in moist conditions and can rapidly spread throughout a strawberry patch. To prevent gray mold, ensure proper air circulation by spacing the plants adequately and removing any debris or overcrowding. Avoid watering the plants from above, as this can promote fungal growth. If gray mold is detected, remove and destroy affected plant parts to stop the spread.
2. Powdery Mildew (Podosphaera aphanis): This fungal disease appears as a white, powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and fruits of strawberry plants. To prevent powdery mildew, plant resistant strawberry varieties and ensure proper air circulation. Prune or remove infected plant parts as soon as they are noticed, and apply a fungicide if necessary.
3. Verticillium Wilt (Verticillium spp.): This soil-borne fungal disease can cause wilting, stunted growth, and yellowing leaves in strawberry plants. To prevent verticillium wilt, avoid planting strawberries in soil that has previously been affected by this disease. Practice crop rotation and remove and destroy infected plants to minimize its spread.
Conclusion
Protecting strawberry plants from pests and diseases is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive crop. By following these preventive measures and promptly addressing any issues that arise, you can enjoy bountiful harvests of delicious strawberries.
Harvesting and Storing Strawberries: Best Practices
When it comes to harvesting and storing strawberries, there are a few important things to keep in mind in order to ensure the best results. Follow these expert tips to make the most of your strawberry crop:
1. Harvesting Strawberries:
- Pick strawberries when they are fully ripe. Look for berries that are bright red, plump, and have a glossy appearance.
- Gently grasp the stem above the strawberry and pull it off with a slight twisting motion. Alternatively, you can use clean scissors or pruning shears to cut the stem just above the berry.
- Avoid pulling or tugging on the berries, as this can damage the plant and affect future fruit production.
- Harvest strawberries in the morning when the temperatures are cooler. This helps to preserve the fruit’s flavor, texture, and nutritional content.
2. Storing Strawberries:
- After harvesting, sort through your strawberries and remove any damaged, overripe, or moldy berries. This prevents the spread of rot and preserves the quality of the remaining fruit.
- Do not wash the strawberries until you are ready to use them, as excess moisture can speed up spoilage.
- Store strawberries in a single layer in shallow containers or on a paper towel-lined tray. This allows for proper air circulation and helps to prevent the berries from becoming bruised or crushed.
- Keep the strawberries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. They can be stored in the refrigerator, ideally at a temperature of 32-36 degrees Fahrenheit (0-2 degrees Celsius).
- Strawberries are best consumed within a few days of harvesting, as they tend to lose flavor and texture over time. However, if stored properly, they can last for up to a week.
3. Preserving Strawberries:
If you have an abundance of strawberries and want to preserve them for longer periods, there are a few preservation methods you can try:
- Freezing: Wash and hull the strawberries, then place them in a single layer on a baking sheet and freeze until firm. Once frozen, transfer the berries to airtight containers or freezer bags and store in the freezer. They can be kept frozen for up to 8-12 months.
- Jam or Jelly: Cook down the strawberries with sugar and lemon juice to make a delicious homemade jam or jelly. Follow a trusted recipe for best results and store the finished product in sterilized jars.
By following these harvesting and storing practices, you can enjoy the sweet, juicy taste of freshly picked strawberries for as long as possible.
Question-answer:
Can strawberries be grown from seeds?
Yes, strawberries can be grown from seeds. However, it is more common and easier to grow strawberries from transplants or runners.
When is the best time to plant strawberries?
The best time to plant strawberries depends on the climate and region. In general, it is recommended to plant strawberries in the early spring or late summer to early fall.
How do I care for strawberry plants?
To care for strawberry plants, you need to provide them with enough water, regular feeding, and protection from pests and diseases. It is also important to remove any weeds and provide proper mulching.
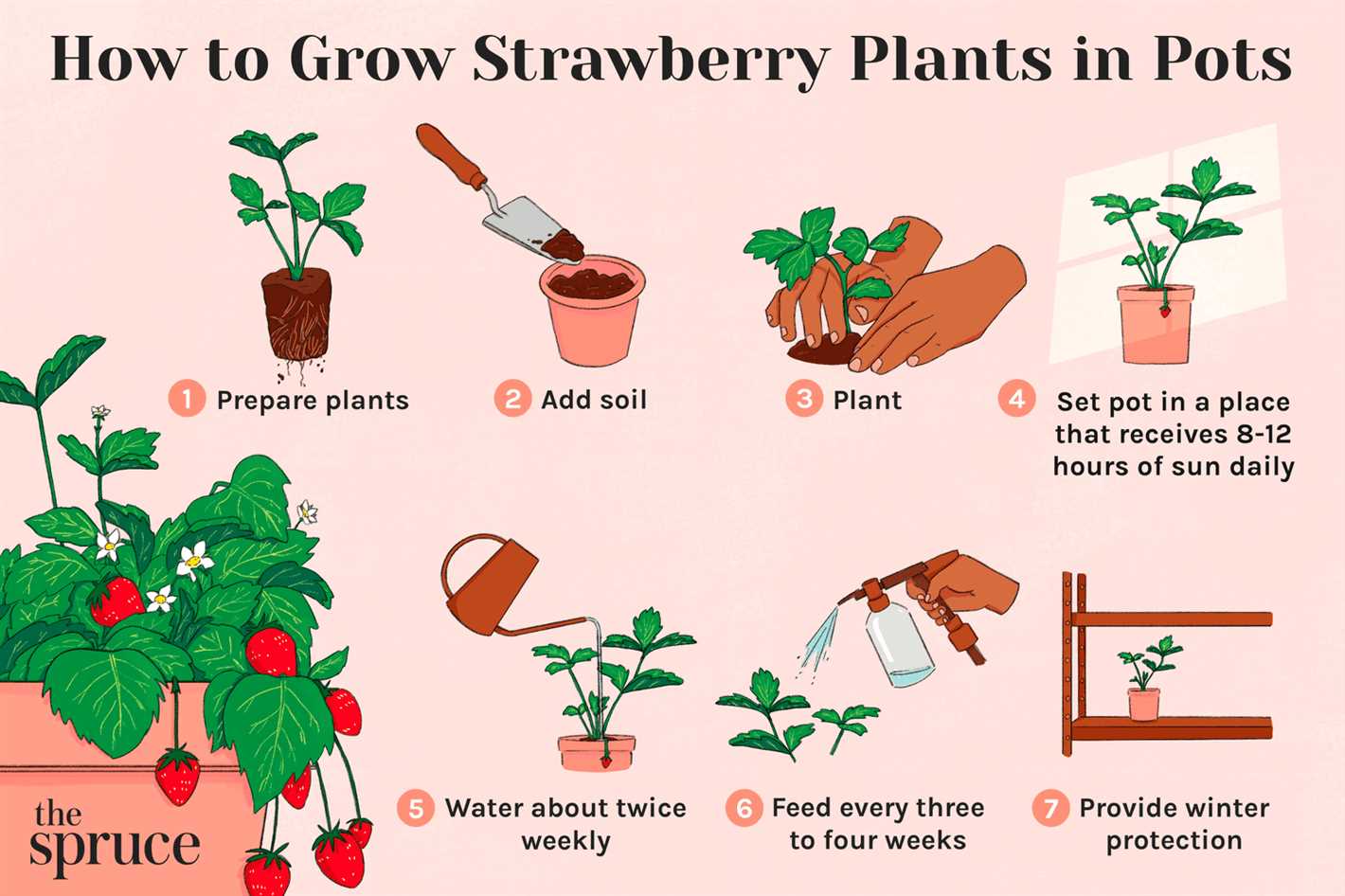
Can I grow strawberries in containers?
Yes, strawberries can be successfully grown in containers. Make sure to choose a large enough container, provide proper drainage, and use well-draining soil. Regular watering and fertilization are also important for container-grown strawberries.
How long does it take for strawberry plants to bear fruit?
The time it takes for strawberry plants to bear fruit can vary depending on various factors, such as the variety of strawberries and the growing conditions. Generally, it takes about 4 to 6 weeks for the plants to start producing strawberries after planting.







