- Selecting the Best Summer Silkworm Cuttings
- 1. Choose healthy branches
- 2. Select young branches
- 3. Consider the size
- 4. Look for nodes
- 5. Avoid flowers or buds
- 6. Check for pests
- 7. Consider the source
- Choosing Healthy Branches
- 1. Select branches from a mature mulberry tree
- 2. Look for branches with a diameter of about 1/4 inch
- 3. Choose branches that are straight and healthy
- 4. Prioritize branches that have leaf nodes
- 5. Select branches with younger growth
- 6. Avoid branches that are flowering or fruiting
- Identifying Optimal Growth Indicators
- 1. Healthy Branch Appearance
- 2. Firmness of Branch
- 3. Leaf Nodes
- 4. Multiple Branch Nodes
- 5. Thickness of Branch
- 6. Seasonal Timing
- 7. Branch Orientation
- Preparing the Cuttings for Rooting
- Removing Leaves and Buds
- Trimming the Cuttings to the Right Length
- Applying Rooting Hormone
- Understanding the Benefits of Rooting Hormone
- Using Rooting Hormone Correctly
- Choosing the Right Soil for Rooting
- Question-answer:
- What are summer silkworm cuttings?
- When is the best time to take summer silkworm cuttings?
- How do you choose the best branches for summer silkworm cuttings?
- What is the process for rooting summer silkworm cuttings?
- How long does it take for summer silkworm cuttings to root?
- What are some tips for successfully rooting summer silkworm cuttings?
- Video: This One Trick Got My Hydrangea Cuttings Rooting Like Crazy! Bottom Heat to the Rescue
Summer is the perfect time to take cuttings from silkworm plants, also known as mulberry trees. These cuttings can be used to propagate new plants and expand your silk production. However, not all branches are suitable for taking cuttings. In this article, we will discuss the best branches to choose for summer silkworm cuttings and provide a step-by-step guide to rooting them successfully.
Choosing the right branches is crucial for successful silkworm cuttings. The ideal branches are young and flexible, with a diameter of about 1/2 inch (1.3 cm) and a length of at least 8 inches (20 cm). They should have a healthy appearance, without any signs of disease or pest infestation. It’s best to select branches that are six months old or younger, as older branches may not root as easily.
Once you have identified the suitable branches, you can proceed with the rooting process. Make a clean cut just below a leaf node using a sharp pruning shears. Remove any leaves from the bottom half of the cutting. Applying a rooting hormone to the cut end can increase the chances of successful rooting. Place the cuttings in a container filled with a well-draining rooting medium, such as perlite or a mix of peat moss and sand.
It’s important to keep the cuttings moist but not waterlogged. Mist the cuttings with water regularly and cover them with a plastic bag to create a humid environment.
In about 2-4 weeks, you should start seeing roots developing from the cut ends of the branches. Once the roots are about 1 inch (2.5 cm) long, you can transfer the cuttings into individual pots filled with potting soil. Provide them with bright, indirect light and keep the soil evenly moist. After a few months, the cuttings should be well-established plants ready to be transplanted into the garden or used for silk production.
In conclusion, summer silkworm cuttings can be a great way to propagate new plants and expand your silk production. By choosing the right branches and following a step-by-step rooting process, you can ensure a successful outcome. Happy gardening!
Selecting the Best Summer Silkworm Cuttings
When it comes to selecting summer silkworm cuttings, there are a few factors to consider in order to ensure successful growth and rooting. Here are some tips to help you select the best cuttings:
1. Choose healthy branches

Look for branches that are healthy and free from any signs of disease or pest infestation. Healthy branches are more likely to root successfully and produce robust plants.
2. Select young branches
Youthful branches tend to root more easily than older ones. Look for branches that are flexible and have green, tender growth. Avoid selecting branches that are woody or have excessive lignification.
3. Consider the size
Opt for branches that are neither too thin nor too thick. Thin branches may lack sufficient nutrients to support rooting, while extremely thick branches may have a more difficult time rooting due to their low flexibility.
4. Look for nodes
Nodes, which are points where leaves emerge from the stem, are crucial for rooting. Make sure the branches you select have multiple nodes, as this will increase the likelihood of successful rooting.
5. Avoid flowers or buds
Branches with flowers or buds are not ideal for rooting purposes. The energy of the plant is primarily focused on developing flowers and reproductive structures, making it less likely for the branch to root successfully.
6. Check for pests
Before taking the cuttings, inspect them carefully for any signs of pests. Common pests that can affect silkworm cuttings include aphids, mites, and scale insects. It is best to avoid using branches that are heavily infested.
7. Consider the source
If possible, choose branches from healthy and well-maintained silkworm plants. This increases the chances of obtaining cuttings with a high potential for successful rooting.
Remember, the success of rooting summer silkworm cuttings depends on various factors such as temperature, humidity, and the overall health of the plant. By selecting the best cuttings, you can increase the chance of successful rooting and enjoy healthy silkworm plants in your garden.
Choosing Healthy Branches
When selecting branches for summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to choose healthy branches in order to maximize the chances of successful rooting. Here are some tips to help you choose the best branches:
1. Select branches from a mature mulberry tree

The best branches for silkworm cuttings come from mature mulberry trees that are at least three years old. These trees have well-established root systems, which are essential for successful cutting rooting.
2. Look for branches with a diameter of about 1/4 inch
The branches you choose should have a diameter of approximately 1/4 inch. Thicker branches are harder to root, while thinner branches may not have enough energy to support the growth of new roots.
3. Choose branches that are straight and healthy
Avoid selecting branches that are curved or have any signs of damage or disease. Straight and healthy branches have a higher chance of success when it comes to rooting.
4. Prioritize branches that have leaf nodes
Leaf nodes are the areas where leaves emerge from the branches. Choosing branches that have leaf nodes increases the likelihood of successful rooting, as these nodes contain the necessary growth hormones for root development.
5. Select branches with younger growth
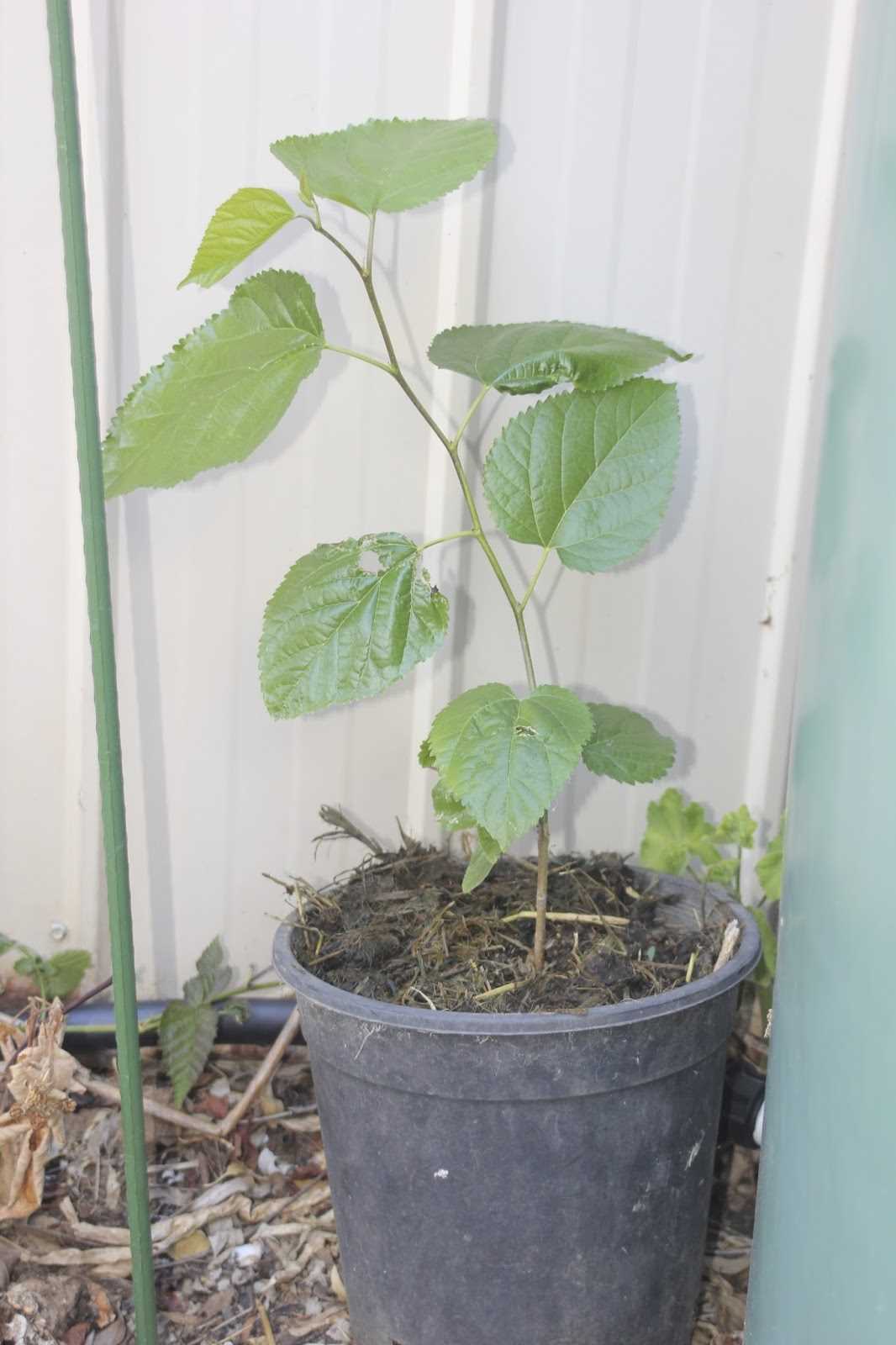

Younger branches have a higher concentration of growth hormones, which can enhance the rooting process. Look for branches that have new, green growth at the tips.
6. Avoid branches that are flowering or fruiting
Flowering or fruiting branches are actively using their energy for reproduction, making it less likely for them to root successfully. It’s best to choose branches that are not currently producing flowers or fruits.
By following these guidelines, you can increase the chances of successfully rooting summer silkworm cuttings and growing healthy mulberry trees to support your silkworms.
Identifying Optimal Growth Indicators

To ensure successful rooting of summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to identify optimal growth indicators. These indicators will help you select the best branches for propagation and determine the right conditions for rooting.
1. Healthy Branch Appearance
Select branches that appear healthy and vigorous. Look for branches that have smooth bark, vibrant green leaves, and no signs of damage or disease. Healthy branches are more likely to root successfully.
2. Firmness of Branch
Gently squeeze the branch to determine its firmness. Opt for branches that are firm but not overly rigid. This indicates that the branch is still actively growing and has the potential to develop new roots.
3. Leaf Nodes

Pay attention to the presence of leaf nodes on the branch. Leaf nodes are the points where leaves emerge from the branch and are essential for rooting. In general, branches with more leaf nodes have a higher chance of successful rooting.
4. Multiple Branch Nodes
Choose branches that have multiple branch nodes within the selected cutting. Multiple nodes provide more opportunities for root development and increase the chances of successful propagation.
5. Thickness of Branch
Consider the thickness of the branch when selecting cuttings. Thicker branches have a greater nutrient supply and are more likely to successfully develop roots. Avoid using very thin or extremely thick branches.
6. Seasonal Timing
Take into account the optimal time for propagating summer silkworm cuttings. Summer is the ideal season for rooting, as the warm temperatures and increased humidity promote root growth. Avoid propagating during extreme weather conditions.
7. Branch Orientation
Pay attention to the orientation of the branches when selecting cuttings. Choose branches that have a vertical orientation, as this allows for better water and nutrient absorption, leading to successful rooting.
By considering these optimal growth indicators, you can increase the chances of successful rooting and growth of your summer silkworm cuttings. Remember to provide appropriate care and monitoring throughout the rooting process to ensure healthy plant development.
Preparing the Cuttings for Rooting

Before you start rooting summer silkworm cuttings, it’s important to properly prepare the branches. Follow these steps to ensure the best chances of success:
- Choose healthy branches: Select branches that are strong and disease-free. Avoid branches that have signs of pest damage or disease.
- Cut the branches: Use sharp pruning shears to make clean cuts. Cut the branches to a length of about 6-8 inches, just below a node or bud.
- Remove leaves: Strip off the lower leaves of the cutting, leaving just a few pairs of leaves at the top. This will help prevent the cutting from losing too much moisture during rooting.
- Remove flowers and buds: If there are any flowers or buds on the cutting, remove them. This will redirect the plant’s energy towards root development instead of flower production.
- Apply rooting hormone: Dip the base of the cutting in a rooting hormone powder or gel. This will help stimulate root growth and increase the chances of successful rooting.
- Prepare the planting medium: Fill a clean container with a well-draining potting mix. Moisten the soil slightly so that it is evenly damp but not soaking wet.
By following these preparatory steps, you will be on your way to successfully rooting summer silkworm cuttings and growing new plants for your garden.
Removing Leaves and Buds

When taking summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to remove any leaves and buds that may interfere with the rooting process. This ensures that the cuttings can focus their energy on developing roots rather than supporting foliage and flowers.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to properly remove leaves and buds from your silkworm cuttings:
- Select a healthy cutting: Choose a branch that is free from disease and damage. Look for a branch that is approximately 6-8 inches long.
- Inspect the cutting: Examine the cutting for any leaves or buds that may be present. These can be easily identified as small leaf and bud clusters along the branch.
- Remove the leaves: Use a sharp pair of pruning shears to carefully trim off all the leaves from the cutting. Start at the base of the cutting and work your way up towards the tip. Be careful not to damage the stem while removing the leaves.
- Trim the buds: Next, locate any buds that may be present on the cutting. These are typically small oval-shaped structures that will develop into leaves or flowers. Use the pruning shears to remove these buds by making a clean cut just above the bud.
- Clean the cutting: After removing the leaves and buds, gently brush off any excess debris or sap from the cutting. This will help promote a clean and healthy rooting process.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your summer silkworm cuttings are free from excess foliage and can focus their energy on developing strong and healthy roots. Remember, the healthier the roots, the better chance your cuttings have to take root and grow into beautiful silk-producing mulberry trees.
Trimming the Cuttings to the Right Length
Once you have selected the branches for your summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to trim them to the right length. Trimming the cuttings correctly will help promote healthy root growth and increase the chances of successful propagation.
Step 1: Gather the necessary tools
- Pruning shears or a sharp knife
- Tape measure or ruler
Step 2: Measure the desired length
Using the tape measure or ruler, determine the length at which you want to trim your cuttings. The recommended length is typically around 4-6 inches, but you can adjust this based on your personal preference or specific guidelines for the type of silkworm you are propagating.
Step 3: Make a clean cut
Using the pruning shears or sharp knife, make a clean cut just below a node on the branch. Nodes are the point on the stem where leaves, buds, or flowers grow. This is where the roots will eventually form.
Step 4: Remove excess leaves and branches
If your cuttings have excessive leaves or branches, carefully remove them using the pruning shears or knife. Removing excess foliage can help conserve energy and focus the plant’s resources on root development.
Step 5: Optional: Apply rooting hormone
If desired, you can apply a rooting hormone to the cut end of the stem. Rooting hormones can help stimulate root growth and increase the success rate of propagation. Follow the instructions provided with the rooting hormone product for best results.
Step 6: Set the cuttings in a rooting medium
After trimming the cuttings, you can set them in a rooting medium such as water, perlite, or a mixture of vermiculite and peat moss. This will provide a suitable environment for root growth.
Remember to keep the cuttings moist and provide adequate light and temperature conditions during the rooting process. With proper care, your trimmed cuttings should eventually develop strong roots and grow into healthy summer silkworm plants.
Applying Rooting Hormone
Rooting hormone can be a valuable tool in the process of propagating silkworm cuttings. It contains plant hormones, usually auxins, which help stimulate root growth and improve the chances of successful rooting. Here are the steps to apply rooting hormone:
- Prepare the cutting: Before applying rooting hormone, make sure the cutting is clean and free from any diseases or pests. Trim the cutting to a length of 4-6 inches, ensuring that it has at least 3-4 nodes.
- Dip the cutting: Take the prepared cutting and dip the base, or the portion that will be buried in the rooting medium, into the rooting hormone. Make sure to cover the base with a thin layer of the hormone.
- Tap off excess: Gently tap off any excess rooting hormone from the cutting. This helps to prevent excessive hormone application, which can actually hinder root development.
- Plant the cutting: Immediately after applying the rooting hormone, plant the cutting into a moist rooting medium. This could be a potting mix, vermiculite, or perlite. Make a small hole in the rooting medium and gently insert the cutting, ensuring that it is planted upright and the hormone-covered base is covered with the medium.
- Mist the cutting: After planting, mist the cutting with water to provide some moisture and reduce wilting. Avoid saturating the cutting, as this can lead to rot.
- Care for the cutting: Place the cutting in a warm and bright location, but avoid direct sunlight. Keep the cutting moist, but not overly wet, by misting it regularly. Monitor the cutting for signs of root development, such as new growth or resistance when tugged gently.
By following these steps and applying rooting hormone, you can increase the chances of successful root development and ensure the propagation of healthy silkworm cuttings.
Understanding the Benefits of Rooting Hormone
When it comes to propagating plants from cuttings, using rooting hormone can greatly increase your chances of success. Rooting hormone is a substance that helps to stimulate root growth in plant cuttings, making it easier for them to establish roots and grow into healthy, thriving plants. Here are some of the benefits of using rooting hormone:
- Improved Root Development: Rooting hormone contains synthetic or natural plant hormones that help to stimulate root growth in cuttings. These hormones promote the development of new roots and encourage the growth of existing root structures.
- Faster Rooting: By applying rooting hormone to your plant cuttings, you can speed up the process of rooting. The hormone helps to encourage the growth of roots, allowing the plants to establish themselves more quickly.
- Increased Success Rate: Using rooting hormone significantly increases the chances of success when propagating plants from cuttings. The hormone provides the nutrients and hormonal support necessary for the cuttings to develop strong, healthy roots.
- Greater Adaptability: Rooting hormone can help cuttings to form roots in a wider range of conditions. Whether you’re propagating plants in a greenhouse or outdoor garden, using rooting hormone can give your cuttings a better chance of survival and growth.
- Protection from Disease: Rooting hormone contains anti-fungal properties, which can protect your cuttings from diseases and infections that can hinder root development. It helps to create a protective barrier around the cuttings, ensuring their health and well-being.
In conclusion, using rooting hormone when propagating plants from cuttings provides numerous benefits. It improves root development, speeds up rooting, increases success rates, enhances adaptability, and protects against disease. By incorporating rooting hormone into your propagation process, you can ensure the success and vitality of your plant cuttings.
Using Rooting Hormone Correctly
When propagating summer silkworm cuttings, using rooting hormone can significantly increase your chances of success. Rooting hormone contains plant hormones that stimulate root growth and can help the cuttings establish themselves more easily.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use rooting hormone correctly:
- Prepare the cuttings by making sure they are clean and healthy. Remove any damaged or diseased leaves.
- Fill a small container with rooting hormone. You can find rooting hormone powders or gels at your local garden center.
- Dip the base of the cutting into the rooting hormone, making sure to coat the entire area where roots will form.
- Tap the cutting gently to remove any excess hormone. This step is important as too much hormone can actually inhibit root growth.
- Place the cutting into a pot filled with well-draining potting soil. Make a hole in the soil beforehand to avoid rubbing off the hormone.
- Lightly press the soil around the base of the cutting to ensure good contact between the hormone and the soil.
- Water the cutting thoroughly, ensuring that the soil is evenly moist. Do not overwater, as this can lead to root rot.
- Cover the cutting with a clear plastic bag or a humidity dome to create a greenhouse effect. This will help retain moisture and create a favorable environment for root development.
- Place the cutting in a warm, well-lit area, but avoid direct sunlight. Indirect light will help the cutting produce energy through photosynthesis without causing it to overheat.
- Check on the cutting regularly and mist it with water if the soil starts to dry out. Be patient, as it can take several weeks for roots to develop.
- Once the cutting has established roots, you can gradually acclimate it to its final growing location by removing the plastic bag or humidity dome for short periods each day.
Using rooting hormone correctly can greatly increase your success rate when rooting summer silkworm cuttings. However, it is important to follow the instructions on the rooting hormone packaging and not to use too much, as this can have negative effects on root development.
Choosing the Right Soil for Rooting
When rooting summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to choose the right soil that will provide the necessary nutrients and moisture for successful root development. Here are some factors to consider when selecting the soil:
- Well-draining: The soil should have good drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. A well-draining soil allows excess water to drain away, keeping the roots healthy and preventing diseases.
- Loose and friable: The soil should be loose and friable to allow the roots to easily penetrate and spread. A compacted soil can impede root growth and lead to stunted plants. Adding organic matter, such as compost, can help improve the soil structure.
- Nutrient-rich: The soil should be rich in nutrients to support healthy root development. It should contain a good balance of essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients. Adding organic fertilizers or compost can help enrich the soil.
- pH level: The soil’s pH level can affect nutrient availability to the roots. Most plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral pH levels. It is recommended to test the pH level of the soil and make any necessary adjustments using pH modifiers if needed.
- Pathogen-free: The soil used for rooting should be free from pathogens, pests, and weed seeds that can harm the newly formed roots. Using sterile or pasteurized soil can help minimize the risk of diseases and pests.
It is also important to remember to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can drown the roots, while underwatering can lead to dehydration. Regularly check the moisture level of the soil and adjust watering accordingly.
Question-answer:
What are summer silkworm cuttings?
Summer silkworm cuttings are branches or shoots taken from a silkworm tree during the summer season. These cuttings are used for propagation, or rooting, to create new trees.
When is the best time to take summer silkworm cuttings?
The best time to take summer silkworm cuttings is during the summer season when the tree is actively growing. You should wait until the tree has finished flowering and the new shoots have started to harden off before taking the cuttings.
How do you choose the best branches for summer silkworm cuttings?
To choose the best branches for summer silkworm cuttings, look for healthy branches that are free from disease or damage. Select branches that are around 6-8 inches long and have a diameter of about 1/4 inch. The branches should have at least 3-4 nodes, which are the points where the leaves grow from the stem.
What is the process for rooting summer silkworm cuttings?
The process for rooting summer silkworm cuttings involves removing the leaves from the lower half of the cutting and cutting off any excess stem or branches. The bottom of the cutting should then be dipped in rooting hormone to promote root growth. The cutting is then planted in a pot filled with well-draining soil and kept in a warm and humid environment until roots develop.
How long does it take for summer silkworm cuttings to root?
The time it takes for summer silkworm cuttings to root can vary depending on the type of tree and the environmental conditions. Generally, it takes about 4-6 weeks for the cuttings to develop roots. However, it’s important to note that not all cuttings will successfully root.
What are some tips for successfully rooting summer silkworm cuttings?
To increase the chances of successfully rooting summer silkworm cuttings, it is important to choose healthy branches, use rooting hormone, provide the cuttings with a warm and humid environment, and make sure the soil is well-draining. It is also helpful to mist the cuttings with water regularly and monitor them for any signs of disease or pests.







