- The Basics of Hydroponics
- The Benefits of Hydroponics
- 1. Efficient use of water
- 2. Faster growth and higher yields
- 3. Space-saving
- 4. Reduced risk of pests and diseases
- 5. Greater control over nutrients and pH levels
- 6. Year-round cultivation
- 7. Environmentally friendly
- Types of Hydroponic Systems
- 1. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
- 2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
- 3. Aeroponics
- 4. Drip System
- 5. Wick System
- 6. Ebb and Flow System
- Choosing the Right Hydroponic System
- 1. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
- 2. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
- 3. Ebb and Flow
- 4. Aeroponics
- 5. Drip System
- Hydroponic Nutrients and Solutions
- Planting and Maintaining a Hydroponic Garden
- 1. Choose the right plants
- 2. Start with seedlings or seeds
- 3. Monitor and adjust nutrient levels
- 4. Control water and temperature
- 5. Manage pests and diseases
- 6. Harvest and replant
- Common Challenges and Solutions in Hydroponics
- 1. Nutrient Imbalances
- 2. pH Fluctuations
- 3. Algae Growth
- 4. Root Diseases
- 5. Temperature and Humidity Control
- 6. Water Quality
- 7. Pest and Disease Control
- Q&A:
- What is hydroponics?
- How does hydroponics work?
- What are the advantages of hydroponics?
- What types of plants can be grown using hydroponics?
- Is hydroponic gardening more difficult than traditional gardening?
- Can hydroponics be used to grow organic produce?
- Video: Kratky Hydroponic for Beginners – Outdoors
Hydroponics is an innovative method of gardening that is becoming increasingly popular among both professional growers and home gardening enthusiasts. Unlike traditional gardening methods that rely on soil as a growing medium, hydroponics involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without the use of soil.
This method of gardening offers numerous benefits, including faster and larger plant growth, increased yield, and the ability to grow plants in areas with poor soil quality or limited space. Additionally, hydroponics conserves water by recycling the nutrient solution, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Hydroponic systems can vary in complexity and design, but they all work on the same basic principle: providing plants with the necessary nutrients and support to grow in the absence of soil. This is typically achieved using a variety of techniques, such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), or aeroponics.
By eliminating the need for soil, hydroponics allows for precise control over the growing conditions, including pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and light exposure. This level of control allows growers to optimize plant growth and tailor the conditions to the specific needs of each plant species.
The Basics of Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without the use of soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the necessary minerals and elements for their growth. This method allows plants to grow faster and produce higher yields compared to traditional soil-based gardening.
Advantages of Hydroponics:
- Increased Growth Rate: Without the need to search for nutrients in the soil, plants can focus their energy on growing and developing. This results in faster growth rates and earlier harvests.
- Water Conservation: Hydroponics uses significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based gardening. The water used in a hydroponic system is recirculated and can be reused, reducing water waste.
- No Weeds: Since plants are not grown in soil, there is no need to deal with weeds. This reduces the time and effort required for weed control.
- Less Space Required: Hydroponics allows for vertical farming, which means plants can be stacked on top of each other. This maximizes the use of space and allows for higher plant densities.
- Controlled Environment: In a hydroponic system, the grower has full control over the environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. This allows for optimal growth and eliminates the risk of pests and diseases.
Types of Hydroponic Systems:
- Drip System: This is one of the most common and simple hydroponic systems. It involves dripping nutrient solution onto the base of each plant, allowing the excess solution to drain back into the reservoir.
- Flood and Drain System: Also known as the ebb and flow system, this method involves flooding the growing tray with nutrient solution and then draining it back into the reservoir. This cycle is repeated several times a day.
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) System: In this system, a thin film of nutrient solution continuously flows over the roots of the plants, providing a constant supply of nutrients.
- Aeroponic System: This advanced system involves growing plants in air or mist. The roots are suspended in the air and are periodically misted with a nutrient solution.
Choosing a Medium:
When growing plants hydroponically, a medium is used to provide physical support to the plants’ roots and retain moisture and nutrients. Some common hydroponic media include:
| Medium | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Rockwool | Excellent water retention, good airflow, reusable |
| Coco Coir | Good water retention, environmentally friendly, excellent root aeration |
| Perlite | Lightweight, good drainage, provides good root aeration |
| Expanded Clay Pellets | Excellent drainage, reusable, pH-neutral |
In conclusion, hydroponics is a modern and efficient method of growing plants that offers numerous advantages over traditional soil-based gardening. With the ability to control environmental conditions and maximize space utilization, hydroponics is becoming increasingly popular for both commercial and hobbyist growers.
The Benefits of Hydroponics
1. Efficient use of water
One of the major benefits of hydroponics is its efficient use of water. Traditional soil-based gardening requires a significant amount of water to maintain plant growth. In hydroponics, water is recirculated in a closed system, resulting in up to 90% less water usage compared to traditional gardening methods.
2. Faster growth and higher yields
Hydroponic plants tend to grow faster and produce higher yields compared to traditional soil-based gardening. This is due to the fact that plants grown hydroponically have easy access to nutrients, resulting in improved nutrient uptake and faster growth. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for optimal conditions, resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
3. Space-saving
Hydroponics is an ideal gardening method for environments with limited space. Since hydroponic systems don’t rely on soil, plants can be grown vertically or in compact spaces, maximizing the use of available area. This makes hydroponics a great option for urban gardening or indoor cultivation.
4. Reduced risk of pests and diseases
Traditional gardening methods can be susceptible to pests and diseases that live in the soil. With hydroponics, plants are grown in a soil-less medium, significantly reducing the risk of pest infestations and soil-borne diseases. This allows for a cleaner and healthier growing environment for plants.
5. Greater control over nutrients and pH levels
Hydroponics provides precise control over nutrient and pH levels, allowing growers to optimize plant nutrition and growth. By monitoring and adjusting nutrient solutions and pH levels, growers can ensure that plants receive the ideal balance of nutrients, resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
6. Year-round cultivation
With hydroponics, plants can be cultivated year-round, regardless of seasonal limitations. The controlled environment of hydroponics allows for the manipulation of temperature, lighting, and humidity, enabling plants to grow at any time of the year. This makes hydroponics a great option for those who want to enjoy fresh produce throughout the year.
7. Environmentally friendly
Hydroponics is an environmentally friendly gardening method. The reduced water usage of hydroponics helps conserve water resources, and the absence of soil significantly reduces the need for pesticides and other chemical treatments. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for optimized resource usage, resulting in reduced waste and environmental impact.
Overall, hydroponics offers numerous benefits for growers, including efficient water usage, faster growth, space-saving capabilities, reduced risk of pests and diseases, precise control over nutrients and pH levels, year-round cultivation, and environmental friendliness. These advantages make hydroponics an attractive option for modern gardening.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems can vary in design and complexity, but they all aim to provide plants with the necessary nutrients and water without the use of soil. Here are some of the most common types of hydroponic systems:
1. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
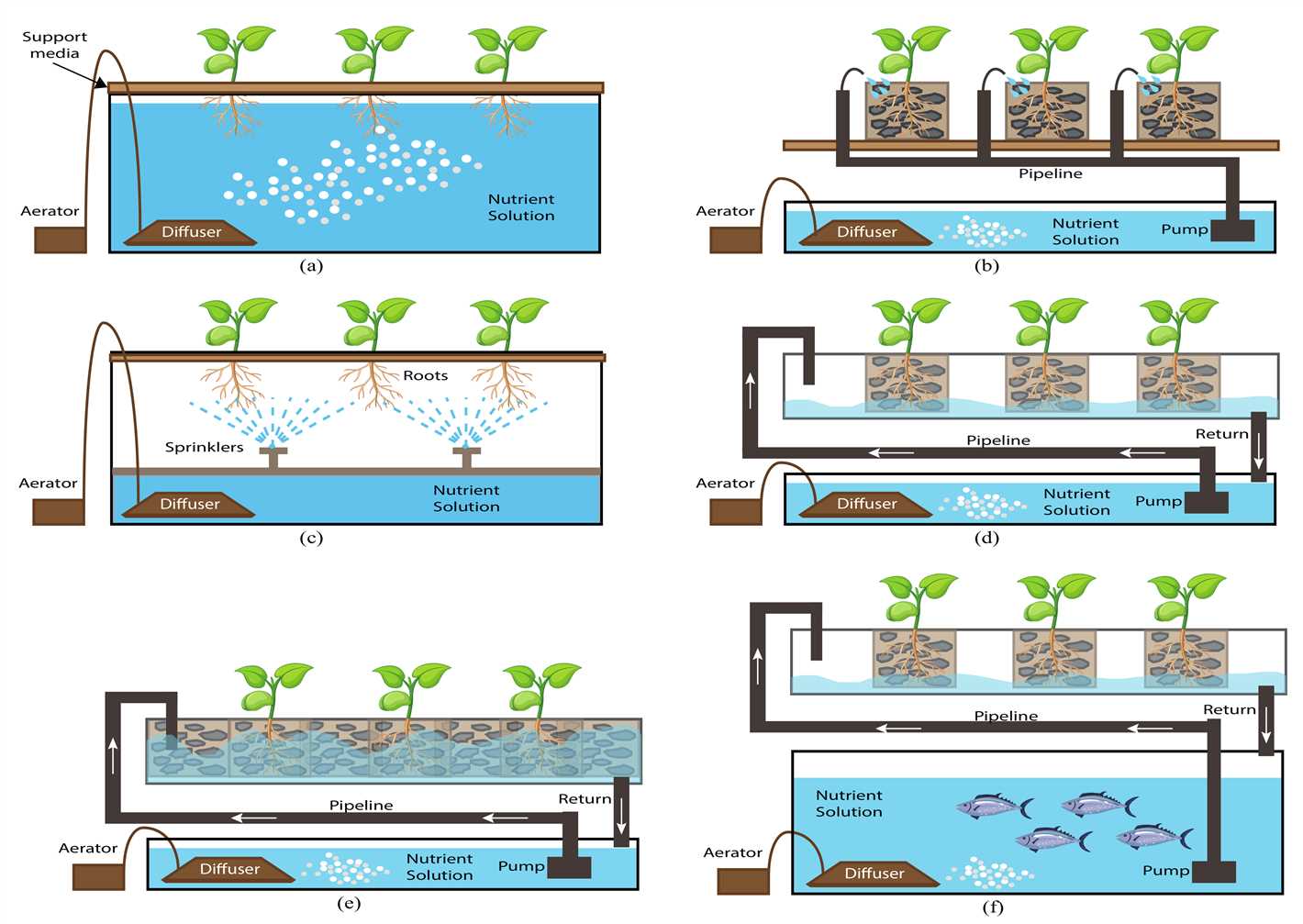
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) system is one of the simplest and most popular hydroponic systems. In this system, a thin film of nutrient-rich water flows over the roots of the plants, providing them with the necessary nutrients. The excess water then flows back into the reservoir and is recirculated through the system.
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
The Deep Water Culture (DWC) system is another popular hydroponic system. In this system, the plants’ roots are suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution. The roots are exposed to high levels of oxygen because they are not submerged in water. Air stones or air pumps are often used to oxygenate the water and promote healthy root growth.
3. Aeroponics
Aeroponics is an advanced hydroponic system that involves suspending the plant roots in the air and misting them with a nutrient-rich water solution. This method allows for increased oxygenation of the roots and can result in faster growth and higher yields. Aeroponic systems often use misters or foggers to deliver the water and nutrients to the roots.
4. Drip System
The Drip System is one of the most versatile and widely used hydroponic systems. In this system, nutrient-rich water is dripped onto the base of each plant through a network of tubes and emitters. Excess water is collected and recycled back into the reservoir. Drip systems can be automated and are suitable for a wide range of plants.
5. Wick System
The Wick System is one of the simplest and least expensive hydroponic systems. In this system, a wick is used to deliver the nutrient-rich water to the plants’ roots. The wick is usually made of a porous material that allows the water to travel from the reservoir to the plants. The Wick System is suitable for small-scale gardening and is often used for herbs and small plants.
6. Ebb and Flow System
The Ebb and Flow System, also known as the Flood and Drain System, is a popular hydroponic system for growing larger plants. In this system, the plants are periodically flooded with nutrient-rich water from a reservoir and then drained back. This cycle provides the plants with water and nutrients, as well as oxygenation during the draining phase.
These are just a few examples of the many types of hydroponic systems available. Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of system will depend on factors such as the type of plants being grown, available space, and budget.
Choosing the Right Hydroponic System
When it comes to hydroponic gardening, there are several different systems to choose from. Each system has its own unique features and benefits, so it’s important to understand the different options before making a decision. Here are some of the most popular hydroponic systems:
1. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
DWC is one of the simplest and most popular hydroponic systems for beginners. In this system, plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich solution with their roots submerged in water. Oxygen is delivered to the roots through an air pump and air stone. DWC systems are known for their ease of use and low maintenance requirements.
2. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT systems involve a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water across a sloped growing channel. Plants are placed in small pots or trays, and their roots are exposed to the thin film of nutrient solution flowing through the channel. NFT systems are highly efficient and allow for maximum oxygenation of the roots.
3. Ebb and Flow
Ebb and flow, also known as flood and drain, involves periodically flooding the growing area with nutrient solution and then draining it away. This system uses a timer to control the flooding and draining cycles. Ebb and flow systems are versatile and can accommodate various types of plants.
4. Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a high-tech hydroponic system that involves suspending plants in the air and spraying their roots with a fine mist of nutrient-rich water. This allows for maximum oxygenation and nutrient uptake. Aeroponic systems are highly efficient but require more specialized equipment and maintenance.
5. Drip System
Drip systems deliver a slow and steady drip of nutrient solution directly to the base of each plant. This allows for precise control over the nutrient delivery, making it suitable for a wide range of plants. Drip systems can be automated and are relatively low maintenance.
When choosing a hydroponic system, consider factors such as your level of experience, available space, budget, and the types of plants you want to grow. It’s also important to consider the maintenance requirements and the level of control you want over nutrient delivery. With the right system in place, you’ll be on your way to successful hydroponic gardening.
Hydroponic Nutrients and Solutions
One of the key advantages of hydroponic gardening is the ability to carefully control the nutrient levels that plants receive. In traditional soil gardening, plants obtain nutrients from the soil, but in a hydroponic system, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich solution. This allows for precise control over the nutrients that plants receive, ensuring optimal growth and yield.
Hydroponic nutrient solutions are typically made up of a mixture of water and various fertilizers that provide essential nutrients to plants. These nutrients include macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc. The specific composition of the nutrient solution will depend on the type of plants being grown and their nutrient requirements.
There are two main types of hydroponic nutrient solutions: liquid concentrates and dry powders. Liquid concentrates are pre-mixed solutions that can be easily diluted with water to create the desired nutrient strength. Dry powders, on the other hand, require mixing with water to create a liquid solution. Both types of nutrient solutions are readily available and can be purchased from hydroponic supply stores or online.
When using hydroponic nutrient solutions, it is important to closely monitor and adjust the nutrient levels as needed. Plants may require different nutrient strengths at different stages of growth, and factors such as temperature and pH can also affect nutrient uptake. Regularly testing the nutrient solution and adjusting the levels accordingly will help ensure that plants receive the proper nutrients for optimal growth.
It is also worth noting that some hydroponic systems, such as deep water culture or nutrient film technique, recirculate the nutrient solution. This means that the solution is continuously reused, resulting in potential nutrient depletion over time. In these cases, it is important to regularly replenish or replace the nutrient solution to maintain proper nutrient levels.
In conclusion, hydroponic nutrient solutions play a crucial role in the success of a hydroponic garden. By providing plants with the necessary nutrients in a controlled and precise manner, hydroponic gardening allows for efficient and productive plant growth.
Planting and Maintaining a Hydroponic Garden
Once you have set up your hydroponic system, you are ready to start planting and maintaining your hydroponic garden. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Choose the right plants
Not all plants are suitable for hydroponic gardening. Some plants that are commonly grown hydroponically include lettuce, tomatoes, peppers, herbs, and strawberries. Choose plants that have a compact growth habit and do not require a lot of space to spread their roots.
2. Start with seedlings or seeds
You can either start with seedlings or sow seeds directly into the hydroponic growing medium. Seedlings are a good option if you want to get a head start, as they are already partially grown. Sow the seeds according to the instructions on the seed packet or transplant the seedlings into the hydroponic system.
3. Monitor and adjust nutrient levels
Since hydroponic plants rely on nutrient solutions, it is important to monitor and adjust the nutrient levels regularly. Use a pH meter to check the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution. Adjust the pH using pH up or pH down solutions as needed. Also, check the nutrient concentration using an electrical conductivity (EC) meter and adjust the nutrient solution accordingly.
4. Control water and temperature
Ensure that your hydroponic system maintains consistent water levels. The roots of your plants should be submerged in the nutrient solution at all times. Check the water levels regularly and top up as needed. Also, monitor the temperature of the nutrient solution and aim to keep it within the optimal range for your plants.
5. Manage pests and diseases
Just like traditional gardening, hydroponic gardens can be prone to pests and diseases. Inspect your plants regularly for signs of pests such as aphids, mites, or whiteflies. Use organic or targeted treatments to control pest populations. Additionally, practice good hygiene and maintain cleanliness in your hydroponic system to prevent the spread of diseases.
6. Harvest and replant
Harvest your hydroponic crops when they are mature and ready to eat. Use a sharp pair of scissors or pruners to avoid damaging the plants. After harvesting, replant new seedlings or sow new seeds to ensure a continuous harvest. This will maximize the productivity of your hydroponic garden.
By following these steps, you can successfully plant and maintain a hydroponic garden. Enjoy the benefits of growing plants without soil and experiment with different crops to find what works best for you.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Hydroponics
1. Nutrient Imbalances
One common challenge in hydroponics is maintaining the correct balance of nutrients in the nutrient solution. Imbalances can lead to stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, and lower crop yield. To address this challenge, it is important to regularly test the nutrient solution and adjust the nutrient levels accordingly. This can be done by adding or reducing specific nutrient solutions, depending on the needs of the plants.
2. pH Fluctuations
pH fluctuations can occur in hydroponic systems, affecting nutrient uptake and overall plant health. Low pH levels can result in nutrient lockout, while high pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies. To combat pH fluctuations, it is necessary to regularly monitor and adjust the pH levels of the nutrient solution using pH testing kits or meters. pH adjusting solutions can be used to balance the pH levels and maintain optimal growing conditions.
3. Algae Growth

Algae growth is a common issue in hydroponic systems, especially those exposed to light. Algae can compete with plants for nutrients and block light, hindering plant growth. To prevent algae growth, it is important to keep the nutrient solution and growing environment clean and sterile. This can be achieved by regularly cleaning the system, using light-blocking materials, and implementing algae prevention methods such as UV sterilization or hydrogen peroxide treatments.
4. Root Diseases
Root diseases, such as root rot or pythium, can occur in hydroponic systems due to the presence of excess moisture or inadequate oxygen levels. These diseases can lead to root damage and plant death. To prevent root diseases, it is important to maintain a well-ventilated system with proper oxygenation and drainage. Regularly checking the roots for any signs of disease and promptly addressing them can also help mitigate the risk of root diseases.
5. Temperature and Humidity Control
Temperature and humidity control are crucial in hydroponic systems as they can greatly affect plant growth and productivity. Maintaining the optimal temperature and humidity levels for specific plant varieties can be a challenge, especially in indoor setups. Using heaters, fans, humidifiers, or dehumidifiers can help regulate and control the temperature and humidity levels within the growing environment, ensuring optimal conditions for plant growth.
6. Water Quality

Water quality is important in hydroponics as it directly affects the health and productivity of the plants. Issues such as high mineral content, chlorine, or other contaminants in the water can negatively impact plant growth. It is essential to use high-quality, filtered water or to treat the water properly to remove any harmful substances. Regularly testing the water for pH, nutrient levels, and any potential contaminants can help maintain optimal water quality for hydroponic systems.
7. Pest and Disease Control
Pests and diseases can pose a significant challenge in hydroponics, as they can quickly spread and damage crops. Implementing proper pest and disease control measures, such as regular monitoring, biological controls, and integrated pest management strategies, can help prevent and manage pests and diseases in hydroponic systems. Quarantine measures for new plants or seedlings, as well as maintaining a clean and sterile growing environment, can also reduce the risk of pest and disease outbreaks.
Q&A:
What is hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a gardening method that involves growing plants without soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the essential minerals and nutrients they need to grow. This method allows for precise control over growing conditions and can result in faster growth and higher yields.
How does hydroponics work?
In hydroponics, plants are grown in a soil-less medium such as perlite, vermiculite, or coconut coir. The roots of the plants are then submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution that is constantly delivered to the plants. This allows the plants to take up the nutrients they need more efficiently than in traditional soil-based gardening. The water solution is typically circulated through the system using pumps and timers to ensure proper oxygenation and nutrient distribution.
What are the advantages of hydroponics?
Hydroponics offers several advantages over traditional soil-based gardening. Firstly, it allows for more efficient use of resources such as water and nutrients, as they can be delivered directly to the plants. This can result in significant water savings compared to traditional gardening methods. Additionally, hydroponics allows for precise control over growing conditions, including temperature, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations. This can lead to faster growth, higher yields, and the ability to grow plants in environments that are not suitable for traditional gardening, such as urban areas or regions with poor soil quality.
What types of plants can be grown using hydroponics?
Almost any type of plant can be grown using hydroponics. From leafy greens and herbs to fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers, the hydroponic method can support a wide range of plant species. However, certain plants may have specific requirements or may be more challenging to grow in a hydroponic system. It is important to research the specific needs of the plants you wish to grow and ensure that your hydroponic setup meets those requirements.
Is hydroponic gardening more difficult than traditional gardening?
Hydroponic gardening can be more complex than traditional gardening, as it requires a greater understanding of plant nutrition and the use of specialized equipment to maintain optimal growing conditions. However, with proper research, planning, and attention to detail, hydroponic gardening can be just as successful as traditional gardening, if not more so. Additionally, hydroponic systems can be tailored to fit a wide range of scales, from small home setups to large commercial operations.
Can hydroponics be used to grow organic produce?
Yes, hydroponic systems can be used to grow organic produce. However, there is ongoing debate within the organic farming community about whether hydroponics should be considered a truly organic method, as it does not involve the use of soil. Some organic certifying bodies allow for hydroponic farming practices to be certified as organic, while others do not. It is important to check the requirements of your specific organic certification program if you wish to grow hydroponic organic produce.
Video:
Kratky Hydroponic for Beginners – Outdoors







