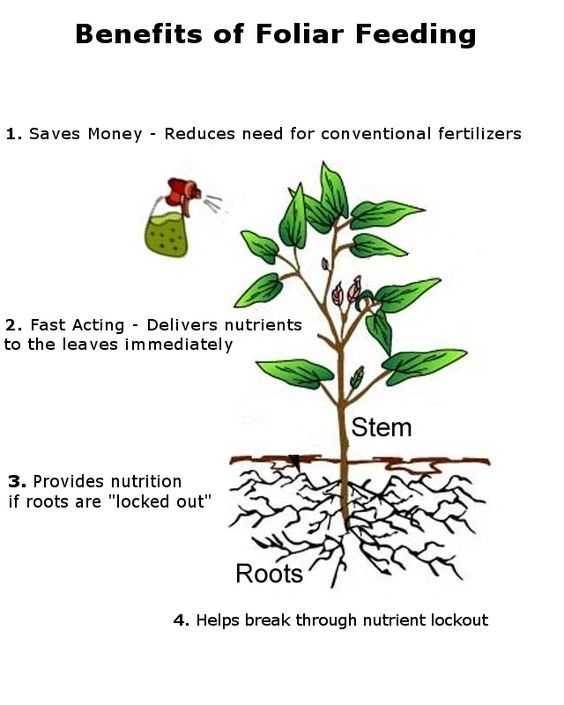
- Overview of Foliar Feeding
- Benefits and Importance of Foliar Feeding
- 1. Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
- 2. Rapid Response
- 3. Targeted Nutrition
- 4. Increased Nutrient Mobility
- 5. Supplementing Soil Fertility
- 6. Improved Plant Health and Growth
- When to Use Foliar Feeding
- 1. Nutrient Deficiencies
- 2. Poor Soil Conditions
- 3. Rapid Nutrient Delivery
- 4. Enhanced Absorption
- 5. Targeted Treatment
- Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Foliar Feeding
- 1. Nutrient Content
- 2. Solubility
- 3. pH Compatibility
- 4. Formulation
- 5. Plant Requirements
- Types of Fertilizers Suitable for Foliar Feeding
- Considerations for Choosing the Right Fertilizer
- Application Techniques for Foliar Feeding
- When to Apply:
- Application Methods:
- Tips for Effective Application:
- Proper Application Method
- Tips for Maximizing Effectiveness
- “Question-Answer”
- What is foliar feeding?
- Why would someone choose to foliar feed their plants?
- When is the best time to foliar feed plants?
- What types of nutrients can be used for foliar feeding?
- Should the nutrients be diluted when foliar feeding?
- Can any type of sprayer be used for foliar feeding?
- Are there any precautions to take when foliar feeding plants?
- “Video” Your Plants NEED This Calcium – How To Make Water Soluble Calcium Supplement – KNF – WCA
Foliar feeding is a technique used by gardeners and farmers to supply essential nutrients to plants through their leaves. While plants primarily get their nutrients from the soil, foliar feeding can provide a quick and effective way to deliver nutrients directly to the plant’s foliage, allowing for faster absorption and utilization. However, knowing when and with what to process is crucial to ensure optimum results and prevent any adverse effects on the plants.
Timing is key when it comes to foliar feeding. It is best done during the early morning or late evening when the stomata, the tiny openings on the leaves, are more receptive to the nutrients. Avoid spraying during the hotter parts of the day, as this can cause the water to evaporate quickly and reduce the effectiveness of the foliar application.
When selecting the right nutrients to use for foliar feeding, it is important to consider the specific needs of the plants. Different plants require different nutrients at various stages of growth. Generally, a balanced foliar fertilizer containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is a good option for most plants. However, some plants may require additional micronutrients like iron, magnesium, or zinc. It is recommended to consult a horticulturist or refer to specific guidelines for the plants you are growing to determine the appropriate nutrient composition.
In addition to nutrients, foliar feeding can also be an effective way to supplement plants with growth stimulants and pest control solutions. Growth stimulants can promote root and shoot development, while pest control solutions can help protect plants from common pests and diseases. However, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and application instructions to avoid damage to the plants.
Overall, foliar feeding can be a beneficial technique to enhance the growth and health of plants. By understanding the timing and selecting the right nutrients or supplements, gardeners and farmers can effectively support their plants’ nutritional needs and mitigate potential issues. It is important to remember that foliar feeding should complement a well-rounded fertilization and cultivation practice for optimal plant health and yield.
Overview of Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is a technique used to supply essential nutrients to plants through their leaves. This method involves spraying a liquid fertilizer solution directly onto the foliage, allowing the plant to absorb nutrients directly through its leaves. While plants primarily obtain nutrients through their roots, foliar feeding can be an effective way to supplement nutrient uptake and address nutrient deficiencies.
Foliar feeding is particularly useful in situations where there are deficiencies in the soil or when the plants are unable to take up nutrients efficiently through their roots. It can also be valuable during periods of high nutrient demand, such as during flowering or fruiting stages, when plants require higher levels of certain nutrients.
When foliar feeding, it is important to choose a fertilizer solution that is appropriate for the specific needs of the plant. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, so it is essential to select a fertilizer that contains the necessary elements in the proper ratios.
Foliar feeding can be done using both organic and synthetic fertilizers. Organic options include compost teas, seaweed extracts, and fish emulsion, while synthetic options include water-soluble fertilizer formulations specifically designed for foliar application. These fertilizers can be dissolved in water and sprayed onto the foliage using a sprayer.
It is crucial to ensure that the fertilizer solution is properly diluted to avoid leaf damage. Concentrated solutions can burn or harm the leaves, so it is recommended to follow the instructions provided by the fertilizer manufacturer for proper dilution rates.
Foliar feeding should be done during the early morning or late evening when temperatures are cooler and the sun is less intense. This allows the plants to absorb the nutrients without the risk of leaf damage from direct sunlight or high temperatures.
Overall, foliar feeding can be a valuable tool in plant nutrition management. It provides a means of supplementing nutrient intake, addressing deficiencies, and promoting healthy growth. However, it should not be relied upon as a substitute for proper soil fertility management and regular root feeding.
Benefits and Importance of Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is the process of applying nutrients directly to the leaves of plants. While traditional fertilization methods involve applying nutrients to the soil, foliar feeding offers a number of unique benefits and plays a crucial role in maintaining plant health and growth.
1. Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
One of the key advantages of foliar feeding is that it enables plants to absorb nutrients more efficiently. When nutrients are applied directly to the leaves, they bypass the soil and enter the plant’s vascular system through the stomata, small openings on the leaf surface. This allows for quicker absorption, ensuring that the plants receive the necessary nutrients in a timely manner.
2. Rapid Response
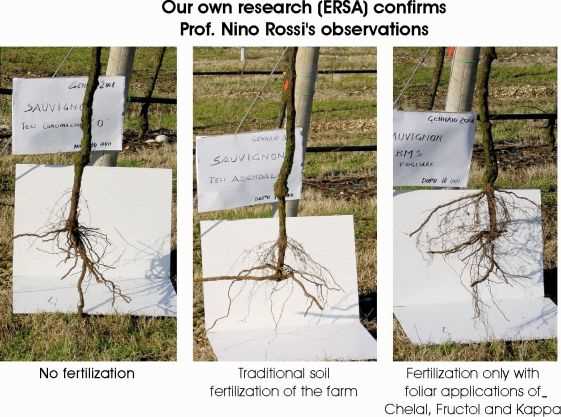

Because foliar feeding allows nutrients to be absorbed directly by the leaves, it provides a rapid response to nutrient deficiencies. When plants show signs of nutrient deficiency, foliar sprays can quickly correct the issue and restore health. This can be particularly important during critical growth phases or when plants are under stress.
3. Targeted Nutrition
Foliar feeding allows for targeted nutrition, as specific nutrients can be applied directly to the areas of the plant that need them the most. This precision targeting is especially useful when plants are experiencing localized nutrient deficiencies or when certain nutrients are required in higher quantities for specific growth stages or functions.
4. Increased Nutrient Mobility
Unlike nutrients that are applied to the soil, foliar-applied nutrients have the ability to move within the plant. Once absorbed through the leaves, these nutrients can be transported to various plant parts, including areas where nutrient demand is high. This increased mobility helps ensure that nutrients are distributed efficiently and effectively throughout the plant.
5. Supplementing Soil Fertility
Foliar feeding can supplement soil fertility, especially when soil conditions make it difficult for plants to access essential nutrients. By bypassing the soil, foliar spraying can provide plants with vital nutrients without relying solely on the soil’s nutrient availability. This can be particularly beneficial in cases where the soil pH, texture, or nutrient imbalances limit nutrient uptake.
6. Improved Plant Health and Growth
Overall, foliar feeding promotes improved plant health and growth. By ensuring that plants have access to vital nutrients in a form readily available for absorption, foliar feeding helps prevent nutrient deficiencies, enhances plant vigor, and supports optimal growth. Healthy plants are better able to withstand environmental stress, resist pests and diseases, and produce higher quality yields.
In conclusion, foliar feeding offers numerous benefits and plays a crucial role in plant nutrition. By providing enhanced nutrient absorption, rapid response, targeted nutrition, increased nutrient mobility, and supplementation of soil fertility, foliar feeding contributes to improved plant health and growth, ultimately leading to better agricultural outcomes.
When to Use Foliar Feeding

Foliar feeding is a technique of applying liquid fertilizers directly to the leaves of plants. It is generally done when the plants are unable to obtain enough nutrients from the soil or when there is a deficiency of certain nutrients. Foliar feeding can provide a quick and targeted nutrient boost to plants, helping them to overcome nutrient deficiencies and promote overall growth and productivity.
1. Nutrient Deficiencies
Foliar feeding is particularly useful when plants show signs of nutrient deficiencies. Common symptoms include yellowing or discoloration of leaves, stunted growth, and poor overall appearance. By applying liquid fertilizers directly to the leaves, plants can quickly absorb the necessary nutrients and overcome these deficiencies.
2. Poor Soil Conditions
In some cases, the soil may not have enough nutrients or may have poor conditions that hinder nutrient uptake by plants. Factors such as high pH levels, low organic matter, or compacted soil can limit the availability of essential nutrients. Foliar feeding can bypass these soil issues and provide plants with the nutrients they need for healthy growth and development.
3. Rapid Nutrient Delivery
Foliar feeding allows for rapid nutrient delivery to plants. Unlike soil application, where nutrients must be taken up by the plant’s roots and transported to the leaves, foliar feeding directly applies nutrients to the leaves, where they can be quickly absorbed. This can be especially beneficial during periods of rapid growth or when plants require immediate nutrient support.
4. Enhanced Absorption
The leaves of plants have tiny openings called stomata, which can absorb nutrients from the applied liquid fertilizers. The surface area of the leaves is much larger than the root surface area, leading to increased absorption efficiency. Foliar feeding can enhance nutrient uptake by directly targeting these stomata and providing nutrients in a readily available form.
5. Targeted Treatment
Foliar feeding allows for targeted treatment of specific plants or plant parts. This can be particularly helpful when dealing with nutrient deficiencies in individual plants within a larger garden or field. By directly applying liquid fertilizers to the affected plants, growers can provide them with the necessary nutrients without affecting the surrounding plants.
In conclusion, foliar feeding is a useful technique for providing plants with a quick nutrient boost, overcoming deficiencies, and promoting healthy growth. It is most effective when plants show signs of nutrient deficiencies, the soil conditions are poor, rapid nutrient delivery is required, enhanced absorption is desired, or targeted treatment is needed.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is an effective way to provide nutrients to plants through their leaves. It allows for direct absorption of essential elements, resulting in quicker nutrient uptake and improved plant health. When deciding which fertilizer to use for foliar feeding, it’s important to consider several factors:
1. Nutrient Content
The nutrient content of the fertilizer is crucial in determining its suitability for foliar feeding. Look for a fertilizer that is specifically formulated for foliar application and contains a balanced ratio of essential nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Additionally, it should contain other micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) to ensure comprehensive nutrient supply.
2. Solubility

The solubility of the fertilizer is another important consideration. It should be readily soluble in water to ensure easy application and quick absorption by the plants. Avoid using fertilizers that are highly insoluble as they may clog the plant’s stomata and hinder nutrient uptake.
3. pH Compatibility
Check the pH of the fertilizer solution before using it for foliar feeding. The pH should be in the neutral to slightly acidic range (pH 6-7) to enhance nutrient availability and uptake. Avoid using fertilizers with extreme pH levels as they can potentially damage the plant’s foliage and affect overall plant health.
4. Formulation
The formulation of the fertilizer plays a significant role in its effectiveness for foliar feeding. Choose a fertilizer that is specifically designed for foliar application, as foliar fertilizers are typically formulated with smaller nutrient particles that can be easily absorbed by the plant’s leaves. Also, consider using a liquid fertilizer as it allows for easy mixing and application.
5. Plant Requirements
Lastly, consider the specific requirements of the plant you are feeding. Different plants have varying nutrient needs, so it’s important to select a fertilizer that meets those requirements. Conduct a soil or leaf analysis to determine any nutrient deficiencies and choose a fertilizer that addresses those deficiencies.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right fertilizer for foliar feeding and ensure optimal nutrient supply to your plants. Remember to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and frequency to avoid over-fertilization and potential damage to the plants.
Types of Fertilizers Suitable for Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is a method of supplying plants with essential nutrients through their leaves. This can be done by applying various types of fertilizers that are specifically formulated for foliar application. The choice of fertilizer depends on the specific needs of the plants and the desired nutrients to be supplied. Some common types of fertilizers suitable for foliar feeding include:
- Water-soluble fertilizers: These fertilizers are highly soluble in water and can be easily absorbed by the leaves. They are available in both liquid and powder forms. Water-soluble fertilizers are composed of a balanced mix of essential macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (iron, manganese, zinc, etc.). They can be quickly absorbed by the plants and provide immediate nutrient availability.
- Organic fertilizers: Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as animal manure, compost, or plant materials. They are rich in organic matter and slowly release nutrients over time. Organic fertilizers are usually less concentrated than synthetic fertilizers, but they provide long-term benefits to the plants by improving soil fertility and microbial activity. They can be used for foliar feeding by diluting them in water and spraying onto the leaves.
- Foliar fertilizers: These fertilizers are specifically formulated for foliar application and are designed to be absorbed directly by the leaves. They are usually in liquid form and contain a high concentration of essential nutrients. Foliar fertilizers are easily absorbed by the plants and can provide a quick boost of nutrients. They are commonly used for correcting nutrient deficiencies or providing a supplemental nutrient source during critical growth stages.
When choosing a fertilizer for foliar feeding, it is important to consider the specific nutrient requirements of the plants and the desired results. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for application rates and frequency to avoid over-fertilization and potential damage to the plants. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient status of the plants and identify any deficiencies that need to be addressed through foliar feeding.
Considerations for Choosing the Right Fertilizer
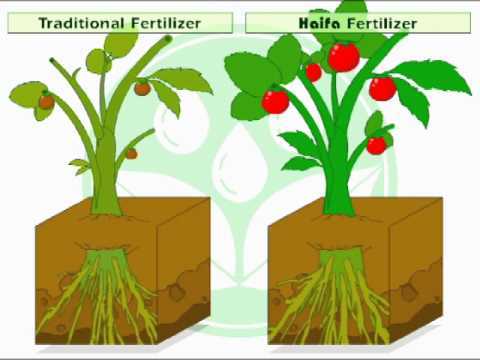
Choosing the right fertilizer for foliar feeding is crucial for the overall health and growth of plants. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when selecting a fertilizer:
- Nutrient Composition: Different plants have different nutrient requirements. It is important to choose a fertilizer that contains the necessary nutrients for the specific type of plant you are treating. Look for fertilizers that provide a balanced mix of essential nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), as well as micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese.
- Nutrient Solubility: The solubility of the nutrients in the fertilizer is important for foliar feeding. Fertilizers with high solubility can be easily absorbed by the leaves and provide quick results. Look for water-soluble fertilizers that can be easily dissolved in water for foliar application.
Absorption Efficiency: Some fertilizers have better absorption rates than others. Choose fertilizers that are known for their high absorption efficiency to ensure that the plants can efficiently take up the nutrients through their leaves. - Compatibility: It is important to consider the compatibility of the fertilizer with other products that may be used in conjunction. Some fertilizers may react negatively with other products, leading to reduced effectiveness or even damage to the plants. Always check for compatibility before mixing fertilizers with other additives.
- Formulation: Fertilizers come in different formulations such as liquid, granular, or powdered. The formulation you choose will depend on your specific application method and the ease of use you prefer. Liquid fertilizers are commonly used for foliar feeding as they can be easily applied and absorbed by the leaves.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the fertilizer and compare it with the benefits and results it offers. While it is important to invest in quality fertilizers, it is also essential to find a balance between cost and effectiveness.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right fertilizer that provides the necessary nutrients and promotes healthy growth when foliar feeding your plants.
Application Techniques for Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is a method of providing nutrients to plants by applying liquid fertilizers directly onto their leaves. It is an effective way to supplement the nutritional needs of plants, especially when they are experiencing deficiencies or stress.
When to Apply:
Foliar feeding can be done at various growth stages of the plant, but it is most effective during the early morning or late afternoon when the stomata (tiny pores on the leaves) are open. This allows for better absorption of nutrients. Avoid applying during the midday when the sun is intense as it can cause leaf burning.
Application Methods:
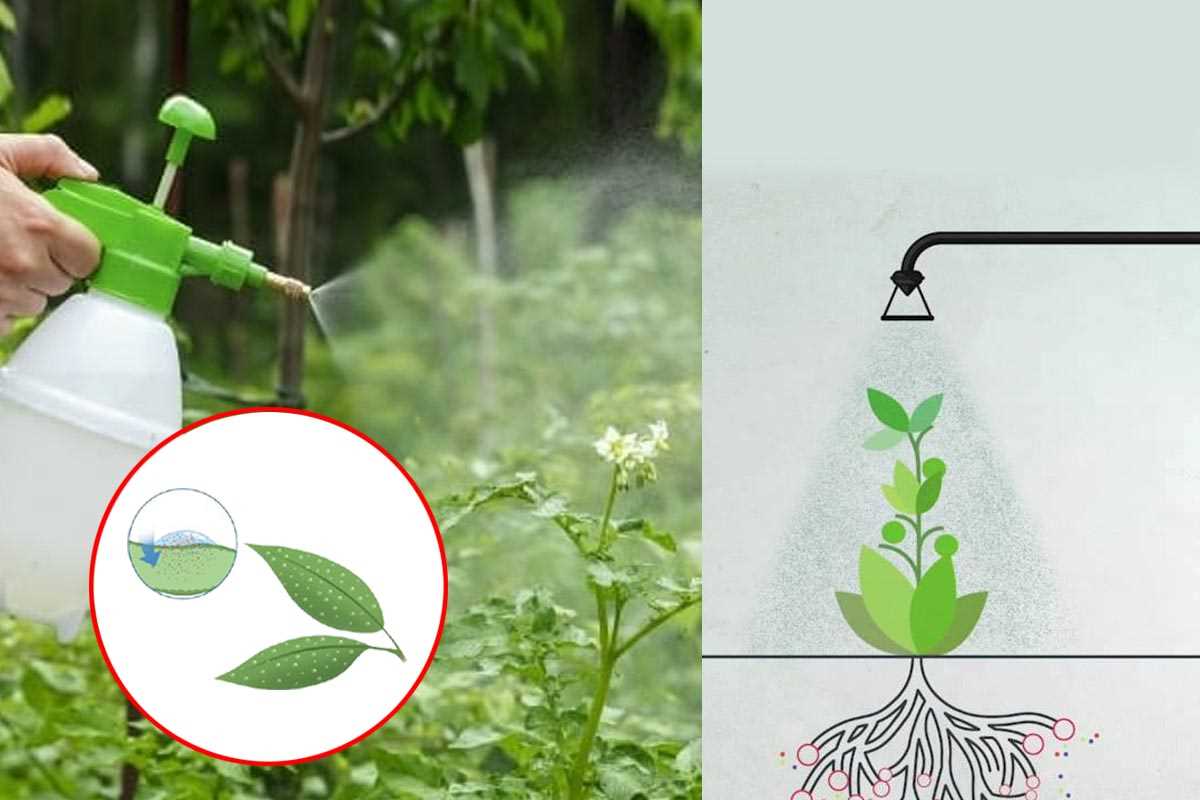
- Spraying: The most common method of foliar feeding is spraying the liquid fertilizer onto the leaves. Use a fine mist sprayer to ensure the fertilizer covers the entire leaf surface. It is important to spray both the top and bottom sides of the leaves for better absorption.
- Drenching: For smaller plants or potted plants, drenching can be used. This involves pouring the liquid fertilizer directly onto the soil or substrate, allowing it to be absorbed by the roots as well as through the leaves.
- Fogging: Fogging is a technique used in large-scale agricultural settings. It involves using specialized equipment to create a mist or fog of the liquid fertilizer, which is then applied to the plants. This method ensures the fertilizer reaches all parts of the plant, including hard-to-reach areas.
Tips for Effective Application:
- Choose a time when the weather is calm to minimize drift and ensure the fertilizer stays on the leaves.
- Dilute the liquid fertilizer as per the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid leaf burning or nutrient imbalances.
- Apply the fertilizer evenly, making sure to cover the entire leaf surface.
- Repeat the application at regular intervals, especially during periods of rapid growth or when nutrient deficiencies are observed.
- Monitor the plants after foliar feeding and assess their response. Adjust the application rate or frequency if necessary.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Faster nutrient uptake compared to soil application | Not a substitute for proper soil nutrition |
| Can address nutrient deficiencies quickly | Possible risk of leaf burning if not diluted properly |
| Allows targeted application of nutrients | May not provide long-term nutrient availability |
| Can improve overall plant health and productivity | Requires regular monitoring and adjustment |
Overall, foliar feeding can be a valuable tool in plant nutrition management. By understanding the appropriate application techniques and integrating it with proper soil fertility practices, growers can maximize the health and productivity of their plants.
Proper Application Method

When it comes to foliar feeding of plants, it is important to follow the proper application method to ensure maximum effectiveness and minimize any potential damage to the plants. Here are some guidelines for the proper application of foliar sprays:
- Choose the right time: The best time to apply foliar sprays is early in the morning or late in the afternoon when the temperature is cooler and the sun is not at its peak. This helps to minimize evaporation of the spray and reduce the risk of leaf burn.
- Prepare the solution: Mix the required amount of foliar spray according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It is important to use the correct dilution rate to avoid over-fertilization or chemical burn.
- Use the right equipment: Use a high-quality sprayer with a fine nozzle that can produce a fine mist. This helps to ensure even coverage and penetration of the spray on the leaves.
- Apply to the undersides of leaves: When spraying, make sure to target the undersides of leaves as well as the tops. The stomata, which are responsible for nutrient absorption, are primarily located on the undersides of leaves.
- Avoid over-saturation: Apply the foliar spray until the leaves are evenly wet, but avoid excessive runoff or dripping. Over-saturation can lead to wastage of the spray and may cause the solution to puddle, increasing the risk of leaf burn.
- Repeat as necessary: Depending on the type of foliar spray and the specific needs of your plants, you may need to repeat the application at regular intervals. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for the recommended frequency of application.
By following these proper application methods, you can ensure that your plants receive the maximum benefits from foliar feeding while minimizing any potential risks. Remember to always read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the foliar spray for the best results.
Tips for Maximizing Effectiveness
- Choose the right time: Leaves are most receptive to foliar application in the morning or late afternoon when the stomata are open. Avoid treating plants during the hottest part of the day.
- Ensure proper coverage: Make sure to thoroughly spray all sides of the leaves, including the undersides, to ensure maximum absorption of nutrients.
- Use the right concentration: Follow the product instructions for the recommended application rate and dilution. Using too high a concentration may damage the plant, while using too low a concentration may not provide enough nutrients.
- Avoid spraying in extreme weather conditions: Avoid applying foliar sprays if rain or strong winds are expected. This will prevent the solution from being washed away or blown off the leaves.
- Combine with other treatments: Foliar feeding is most effective when used in conjunction with a balanced fertilization program and proper soil care. It should not be used as a substitute for proper soil nutrient management.
Keep in mind that foliar feeding is not a cure-all solution for plant nutrition. It should be used as a supplement to a balanced fertilization program and to provide targeted nutrient correction for specific deficiencies.
“Question-Answer”
What is foliar feeding?
Foliar feeding is a method of supplying nutrients to plants by spraying a liquid fertilizer or nutrient solution onto their leaves.
Why would someone choose to foliar feed their plants?
There are several reasons why someone might choose to foliar feed their plants. Firstly, it allows for faster nutrient absorption, as the leaves can quickly take up the nutrients. Secondly, it can help to correct nutrient deficiencies in plants that are already growing in nutrient-poor soils. Lastly, foliar feeding can be beneficial for plants that have difficulty absorbing nutrients from the soil, such as plants with damaged or compacted roots.
When is the best time to foliar feed plants?
The best time to foliar feed plants is early in the morning or late in the evening, when the temperatures are cooler and the sun is not as intense. This helps to prevent the leaves from burning or drying out. It is also important to avoid foliar feeding when the plants are under stress, such as during hot, dry weather or during periods of heavy rainfall.
What types of nutrients can be used for foliar feeding?
A wide range of nutrients can be used for foliar feeding, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and trace elements. These nutrients are usually supplied in the form of water-soluble fertilizers or nutrient solutions that can be easily absorbed by the leaves.
Should the nutrients be diluted when foliar feeding?
Yes, it is important to dilute the nutrients before foliar feeding to avoid burning or damaging the leaves. The exact dilution ratio will depend on the type and concentration of the nutrient solution being used, as well as the specific needs of the plants. It is best to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult with a gardening expert for the appropriate dilution ratio.
Can any type of sprayer be used for foliar feeding?
While any type of sprayer can technically be used for foliar feeding, it is best to use a sprayer that produces a fine mist or droplets. This helps to ensure an even distribution of the nutrient solution on the leaves. Backpack sprayers, handheld pump sprayers, or even spray bottles can be used for foliar feeding.
Are there any precautions to take when foliar feeding plants?
Yes, there are a few precautions to take when foliar feeding plants. Firstly, it is important to test the nutrient solution on a small area of the plants before applying it to the entire plant. This helps to ensure that the plants are not sensitive or allergic to the solution. Secondly, it is important to avoid foliar feeding during periods of high humidity, as this can increase the risk of fungal diseases. Lastly, it is important to clean the sprayer after each use to prevent cross-contamination between plants.







