- The Ultimate Guide: Protecting Seedlings from Black Leg Infection
- Introduction
- 1. Start with Healthy Seeds
- 2. Maintain Proper Hygiene
- 3. Provide Optimal Growing Conditions
- 4. Practice Crop Rotation
- 5. Use Biological Controls
- 6. Monitor and Remove Infected Plants
- Conclusion
- Understanding Black Leg Infection
- Symptoms
- Disease Cycle
- Management and Prevention
- Identifying Symptoms of Black Leg Infection
- 1. Dark Lesions on Stems
- 2. Wilting and Yellowing Leaves
- 3. Stunted Growth
- 4. Rotting at the Base
- 5. Foul Smell
- 6. Testing for Black Leg
- Preventing Black Leg Infection in Seedlings
- Selecting Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties
- Why Choose Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties?
- How to Identify Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties?
- Consider Crop Rotation and Integrated Pest Management
- Proper Seedling Care and Hygiene Practices
- 1. Start with Healthy Seeds
- 2. Clean Containers and Tools
- 3. Use Sterile Seed Starting Mix
- 4. Practice Proper Watering
- 5. Optimize Air Circulation
- 6. Thin Out Seedlings
- 7. Avoid Cross Contamination
- 8. Dispose of Infected Seedlings
- 9. Maintain a Clean Growing Environment
- 10. Monitor and Act Promptly
- Optimal Growing Conditions to Avoid Black Leg
- 1. Proper Lighting
- 2. Well-Drained Soil
- 3. Good Air Circulation
- 4. Maintain Proper Temperature and Humidity
- 5. Clean and Sterilize Tools and Containers
- 6. Use Disease-Resistant Varieties
- 7. Practice Crop Rotation
- Treating Black Leg Infection
- 1. Remove Infected Seedlings
- 2. Clean and Sanitize Tools
- 3. Improve Drainage
- 4. Provide Adequate Air Circulation
- 5. Apply Fungicides
- 6. Rotate Crops
- 7. Monitor and Maintain Plant Health
- Long-Term Strategies for Protecting Seedlings
- “Question-Answer”
- What is black leg infection and why is it a problem for seedlings?
- How can I prevent black leg infection in seedlings?
- What are the signs and symptoms of black leg infection in seedlings?
- Can black leg infection be treated once seedlings are infected?
- Are there any resistant varieties available to prevent black leg infection?
- Is black leg infection a common problem for seedlings?
- “Video” 10 Organic Ways to Control Pests in the Garden

Black leg is a common and destructive disease that affects seedlings and young plants. It is caused by a group of fungi called Phoma and is characterized by black lesions on the stem and roots. This infection can quickly spread and lead to the death of the plant if not properly managed.
In this ultimate guide, we will provide you with all the information you need to protect your precious seedlings from black leg infection. We will discuss the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods, as well as the treatment options available. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the health and vitality of your seedlings.
“Prevention is always better than cure.”
One of the most effective ways to prevent black leg infection is to start with healthy and disease-free seeds. It is essential to purchase seeds from reliable sources and inspect them for any signs of disease or damage. Additionally, maintaining proper hygiene in your garden and using clean tools can greatly reduce the risk of infection.
In the case of an outbreak, it is crucial to detect the symptoms of black leg infection early on. These include wilting, yellowing, and the appearance of black lesions on the stem and roots. Promptly removing and destroying infected plants can help prevent the spread of the disease to healthy seedlings.
There are various preventive measures you can take to protect your seedlings from black leg infection. These include using sterilized soil, practicing crop rotation, and providing adequate spacing between plants. Furthermore, applying fungicides and biological control agents can help suppress the growth of the fungi responsible for black leg.
In conclusion, protecting your seedlings from black leg infection requires a combination of preventive measures and prompt action. By following the ultimate guide provided, you can ensure the health and success of your seedlings, leading to a thriving garden.
The Ultimate Guide: Protecting Seedlings from Black Leg Infection
Introduction
Black Leg is a common and destructive disease that affects seedlings, especially those grown in humid and cool conditions. It is caused by the bacterium Phoma lingam and can result in the death of young plants. This guide will provide you with important information and strategies to protect your seedlings from black leg infection.
1. Start with Healthy Seeds

- Choose seeds from reputable sources to ensure they are disease-free.
- Inspect the seeds for any signs of disease or damage before planting.
- Avoid using seeds from infected plants or areas where black leg has been previously detected.
2. Maintain Proper Hygiene
- Disinfect all gardening tools, pots, and trays before use to prevent the spread of disease-causing pathogens.
- Regularly clean and sterilize the growing area to eliminate any potential sources of infection.
3. Provide Optimal Growing Conditions
- Avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can promote the growth and spread of black leg bacteria.
- Ensure good air circulation by spacing seedlings adequately and avoiding overcrowding.
- Monitor temperature and humidity levels, as black leg thrives in cool and wet environments.
4. Practice Crop Rotation
- Avoid planting susceptible crops, such as brassicas, in the same area for consecutive growing seasons.
- Rotate crops with non-host plants to disrupt the life cycle of black leg bacteria.
5. Use Biological Controls
- Introduce beneficial microorganisms, such as Trichoderma or Bacillus species, to the growing medium to suppress black leg pathogens.
- Consider using biofungicides approved for controlling black leg, following the instructions on the product label.
6. Monitor and Remove Infected Plants
- Regularly inspect seedlings for any signs of black leg infection, such as dark lesions on stems or leaves.
- Isolate and remove infected plants immediately to prevent the spread of the disease to healthy seedlings.
Conclusion
By following these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of black leg infection in your seedlings. Remember to implement preventive measures, maintain proper hygiene, and promptly address any signs of infection to ensure the health and vitality of your young plants.
Understanding Black Leg Infection
Black Leg Infection is a common disease that affects seedlings, specifically those of the cabbage family. It is caused by the bacterium Phoma lingam and can result in severe damage and even death of the plants.
Black Leg Infection primarily affects young seedlings during the early stages of growth when they are most vulnerable. The bacterium enters the plant through wounds or natural openings, such as stomata, and then spreads throughout the plant, causing tissue decay.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Black Leg Infection can vary depending on the stage of the disease. Here are some common signs to look out for:
- Dark, sunken lesions on the stems and leaves
- Rapid wilting and stunting of the affected seedlings
- Yellowing and discoloration of the foliage
- Blackening and rotting of the root system
Disease Cycle
The disease cycle of Black Leg Infection involves several stages:
- Infection: The bacterium enters the plant through wounds or natural openings.
- Colonization: The bacterium spreads throughout the plant, causing tissue decay.
- Spore Production: Upon reaching maturity, the bacterium produces spores that can survive in the soil.
- Survival and Spread: The spores can remain viable in the soil for several years, infecting future crops and facilitating the spread of the disease.
Management and Prevention
Preventing and managing Black Leg Infection requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Crop Rotation: Avoid planting members of the cabbage family in the same location for consecutive years to minimize the risk of disease buildup in the soil.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infected seedlings and plant debris to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Seed Treatment: Soaking seeds in a fungicide solution before planting can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Proper Planting Techniques: Ensure proper spacing and avoid overcrowding to promote good airflow and reduce the likelihood of infection.
- Maintain Healthy Plants: Provide adequate water, nutrients, and sunlight to promote strong plant growth and resistance to diseases.
By understanding the basics of Black Leg Infection and implementing appropriate prevention and management strategies, you can protect your seedlings and ensure healthy plant growth.
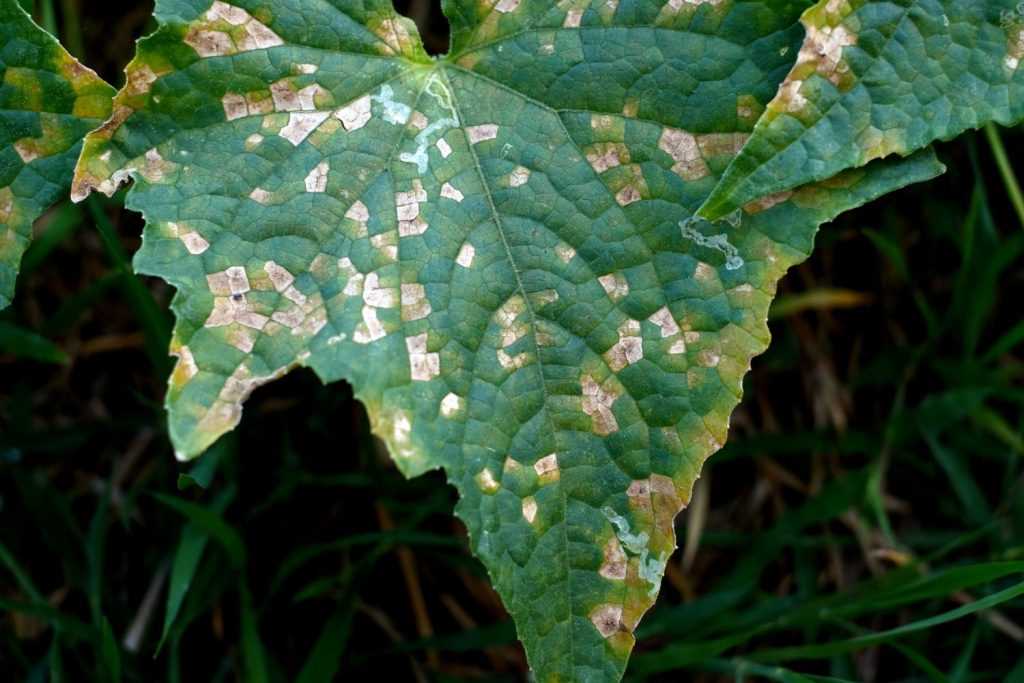
Identifying Symptoms of Black Leg Infection
Black Leg infection is a common problem that affects seedlings in the early stages of growth. It is important to be able to identify the symptoms of this disease in order to take appropriate measures to protect your plants.
1. Dark Lesions on Stems
One of the telltale signs of Black Leg infection is the presence of dark lesions on the stems of the seedlings. These lesions may start out as small spots and gradually enlarge and darken over time. They are usually sunken and may have a water-soaked appearance.
2. Wilting and Yellowing Leaves
Infected seedlings often exhibit wilting and yellowing of the leaves. This is due to the disruption of water and nutrient uptake caused by the disease. The leaves may also become soft and mushy, eventually turning brown and dying.
3. Stunted Growth
Seedlings affected by Black Leg infection may experience stunted growth. They may fail to reach their expected size and may appear smaller and weaker compared to healthy plants. This is because the disease affects the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients and can hinder its overall development.
4. Rotting at the Base
As the disease progresses, the base of the stem may start to rot and become soft. This can lead to the collapse of the entire plant. Inspect the base of the stems carefully to look for any signs of rotting.
5. Foul Smell

In some cases, Black Leg infection may produce a foul odor. This is caused by the breakdown of plant tissues and the release of volatile compounds. If you notice any unpleasant smells coming from your seedlings, it may be an indication of this disease.
6. Testing for Black Leg
If you suspect that your seedlings are infected with Black Leg, you can perform a simple tissue test. Cut a small section of the stem and observe the presence of dark discoloration or rotting. However, it is recommended to consult with a plant pathologist or a professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
By being able to identify the symptoms of Black Leg infection, you can take prompt action to protect your seedlings and prevent the spread of the disease. Early detection and effective management strategies are key to ensuring the health and survival of your plants.
Preventing Black Leg Infection in Seedlings
Black Leg is a common fungal disease that affects seedlings, causing damping-off and killing the young plants. It is important to take preventive measures to protect your seedlings from this infection. Here are some effective strategies to prevent black leg in seedlings:
- Start with clean and disease-free seeds: Use high-quality seeds that have been certified clean and disease-free by a reputable source. Avoid using seeds from plants that have shown signs of black leg infection.
- Sanitize your growing environment: Before sowing seeds, clean and disinfect all equipment, including seed trays, pots, and tools. Use a bleach solution or a commercial disinfectant to kill any fungal spores that may be present.
- Provide proper ventilation: Good air circulation is essential to prevent the buildup of humidity, which creates a favorable environment for black leg fungal growth. Place fans in the growing area to ensure adequate ventilation.
- Avoid overwatering: Excess moisture can promote the development of black leg. Water your seedlings sparingly, allowing the soil to dry out between waterings. Use a well-draining growing medium to prevent waterlogging.
- Practice crop rotation: Avoid planting seedlings in the same spot where you had black leg-infected plants in the previous season. Crop rotation helps break the disease cycle by preventing the buildup of fungal spores in the soil.
- Monitor and remove infected plants: Regularly inspect your seedlings for signs of black leg infection, such as stem discoloration and wilting. If you identify any infected plants, promptly remove and destroy them to prevent the spread of the fungus.
- Apply fungicides: As a preventive measure, you can apply fungicides labeled for black leg control to your seedlings. Follow the instructions on the product label carefully and apply the fungicide as recommended.
- Optimize growing conditions: Provide your seedlings with optimal growing conditions, including proper sunlight exposure, temperature control, and balanced nutrition. Healthy, vigorous plants are less susceptible to black leg infection.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of black leg infection in your seedlings, ensuring their healthy growth and development.
Selecting Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties
When starting a garden, it is important to choose seed varieties that are resistant to diseases such as black leg. Disease-resistant seeds have been bred to have natural defense mechanisms against specific pathogens, making them less susceptible to infection.
Why Choose Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties?
By selecting disease-resistant seed varieties for your garden, you can significantly reduce the risk of plants being infected by black leg or other diseases. This can save you time, effort, and money, as you won’t have to deal with the consequences of a diseased crop.
Furthermore, disease-resistant seeds can also help minimize the use of pesticides and fungicides, as these seeds have built-in defenses against common pathogens.
How to Identify Disease-Resistant Seed Varieties?
When selecting seed varieties, look for specific information regarding disease resistance. Seed packets or online seed catalogs often provide this information. The following are some indicators to look for:
- Disease Rating: Many seed varieties are rated on a scale to indicate their resistance or susceptibility to various diseases. Look for seeds that have high ratings for black leg resistance.
- Resistance Codes: Some seed catalogs use codes to represent the diseases a variety is resistant to. Look for codes that indicate resistance to black leg.
- Seed Breeders: Certain seed breeders specialize in developing disease-resistant varieties. Research reputable breeders that focus on creating plants resistant to black leg.
Consider Crop Rotation and Integrated Pest Management
While disease-resistant seed varieties are an effective preventive measure, it is still important to practice crop rotation and integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to further protect your seedlings from black leg infection.
Crop rotation involves planting different crops in different areas of your garden each year, which can help break the disease cycle and prevent the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
IPM techniques involve using a combination of cultural, physical, and biological methods to control pests and diseases. This can include practices such as removing infected plants, improving soil drainage, and using natural predators to control pest populations.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced risk of infection | Disease-resistant seeds have built-in defenses against specific pathogens, reducing the risk of infection. |
| Less reliance on pesticides | By using disease-resistant seeds, you can minimize the need for chemical pesticides and fungicides. |
| Cost and time savings | Preventing diseases like black leg can save you time, effort, and money that would otherwise be spent on managing a diseased crop. |
| Eco-friendly gardening | By incorporating disease-resistant seed varieties, you can adopt a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening. |
Proper Seedling Care and Hygiene Practices
1. Start with Healthy Seeds
It is crucial to begin the seedling care process with high-quality, disease-free seeds. Inspect the seeds before planting and discard any that appear damaged, discolored, or moldy. Using healthy seeds provides a strong foundation for your seedlings’ growth and helps prevent the spread of diseases.
2. Clean Containers and Tools
Prior to sowing seeds, ensure that all containers, trays, and gardening tools are thoroughly cleaned and sanitized. Wash them with a mild detergent or dish soap, rinse well, and then use a diluted bleach solution to disinfect. This helps eliminate any potential pathogens that may harm your seedlings.
3. Use Sterile Seed Starting Mix

Invest in a sterile seed starting mix rather than using garden soil, which may harbor harmful pathogens. The sterile mix reduces the risk of introducing diseases to your seedlings and promotes healthy root development. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper usage and watering techniques.
4. Practice Proper Watering
Water your seedlings carefully to avoid overwatering, which can lead to fungal diseases. Use a spray bottle or a gentle shower attachment to dampen the soil surface evenly. Allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings to prevent waterlogged conditions that favor disease development.
5. Optimize Air Circulation
Adequate ventilation is essential for preventing the buildup of excess moisture around your seedlings, which can encourage disease development. Place a small fan near your seedlings to provide gentle air circulation, but avoid directing the airflow directly on the seedlings.
6. Thin Out Seedlings
Once your seedlings have sprouted and developed a pair of true leaves, thin them out to prevent overcrowding. Overcrowded seedlings are more susceptible to diseases and have reduced access to light and nutrients. Gently remove the weaker seedlings, leaving only the healthiest and most vigorous ones.
7. Avoid Cross Contamination

Take precautions to prevent cross contamination between seedlings. Use clean and sanitized tools when handling your seedlings, and avoid touching one seedling after handling another without washing your hands or disinfecting your tools.
8. Dispose of Infected Seedlings
If you notice any signs of black leg infection on your seedlings, such as darkened stems, roots, or damping-off symptoms, promptly remove and dispose of the infected plants. This helps prevent the spread of the disease to healthy plants.
9. Maintain a Clean Growing Environment
Regularly clean and disinfect your greenhouse, growing area, and equipment to reduce the risk of disease outbreaks. Remove any plant debris, fallen leaves, or dead seedlings from the growing area to minimize potential sources of infection.
10. Monitor and Act Promptly
Closely monitor your seedlings for any signs of stress, disease, or pests. Early detection is key to preventing the spread of diseases like black leg. Should any issues arise, take immediate action by implementing appropriate treatments or consulting a gardening expert.
Optimal Growing Conditions to Avoid Black Leg
Black Leg is a common fungal disease that affects seedlings and can lead to stunted growth or even death. However, by providing optimal growing conditions, you can greatly reduce the risk of black leg infection. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Proper Lighting
Seedlings require adequate light for proper growth and development. Place them in a well-lit area or provide artificial lights if natural lighting is insufficient. The light should be evenly distributed to prevent weak and leggy seedlings, which are more susceptible to black leg.
2. Well-Drained Soil
Black leg thrives in wet and poorly drained soil. Ensure your seedlings are planted in well-drained soil or use containers with drainage holes. Avoid excessive watering and allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings to prevent the growth of fungal spores.
3. Good Air Circulation
Proper air circulation is essential for preventing the buildup of moisture and reducing the risk of fungal diseases like black leg. Avoid overcrowding seedlings and provide enough space between them. Use a small fan to improve air movement if necessary.
4. Maintain Proper Temperature and Humidity
Black leg thrives in cool and moist conditions. Maintain a temperature range of 70 to 75°F (21 to 24°C) during the day and slightly lower at night. Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature inside your growing area. Keep the humidity level around 40 to 60% to discourage fungal growth.
5. Clean and Sterilize Tools and Containers
Fungal spores can easily spread through contaminated tools and containers. Before planting, make sure all tools and containers are clean and sterilized. This will help prevent the introduction of black leg spores to your seedlings.
6. Use Disease-Resistant Varieties
When choosing seeds or seedlings, look for varieties that are resistant to black leg. These varieties have been bred to have natural resistance to the disease, reducing the risk of infection. Check seed catalogs or consult with local gardening experts for recommended disease-resistant varieties.
7. Practice Crop Rotation
Black leg can survive in the soil for several years, so it’s important to practice crop rotation. Avoid planting susceptible crops, such as cabbage or broccoli, in the same location year after year. Instead, rotate crops to different areas of your garden to disrupt the disease’s lifecycle.
By implementing these optimal growing conditions, you can create a healthy and disease-resistant environment for your seedlings, reducing the risk of black leg and ensuring their successful growth and development.
Treating Black Leg Infection
Once black leg infection is detected, immediate action should be taken to prevent further damage to seedlings. Here are some effective measures you can take to treat black leg:
1. Remove Infected Seedlings
The first step in treating black leg infection is to remove any infected seedlings from the planting area. This will help prevent the spread of the disease to healthy plants. Carefully uproot the infected seedlings and dispose of them properly.
2. Clean and Sanitize Tools
It’s important to thoroughly clean and sanitize any gardening tools that came into contact with the infected seedlings. This will prevent the disease from spreading to other plants in the future. Use a solution of bleach and water (1:9 ratio) to clean your tools, and make sure to rinse them thoroughly.
3. Improve Drainage
Black leg infection often occurs in wet and poorly drained soil. To prevent future infections, you should improve the drainage in your planting area. Amend the soil with organic matter such as compost or peat moss to help improve water drainage. Avoid overwatering your seedlings as well.
4. Provide Adequate Air Circulation

Good air circulation is essential in preventing the development of black leg infection. Avoid overcrowding seedlings and provide enough space between plants. Prune any dense foliage that may restrict air flow and promote the development of humidity and moisture.
5. Apply Fungicides

In severe cases of black leg infection, it may be necessary to use fungicides to control the disease. Look for fungicides specifically labeled for black leg control and follow the instructions carefully. Apply the recommended dosage and frequency as stated on the product label.
6. Rotate Crops

To prevent the recurrence of black leg infection, it’s important to practice crop rotation. Avoid planting susceptible plants in the same location year after year. Rotating crops will help break the disease cycle and reduce the chances of reinfection.
7. Monitor and Maintain Plant Health
Regularly monitor your plants for any signs of black leg infection. If you notice any symptoms, take immediate action to treat the affected plants. Additionally, maintain overall plant health by providing adequate nutrition, proper watering, and general care practices to minimize the risk of disease.
By following these treatment measures, you can effectively manage and treat black leg infection in your seedlings, ensuring healthy and vigorous plants.
Long-Term Strategies for Protecting Seedlings
Protecting seedlings from black leg infection requires a long-term approach that includes various preventive measures and good gardening practices. By implementing the following strategies, you can minimize the risk of black leg and ensure the health and vitality of your seedlings:
- Start with healthy seeds: Use only high-quality seeds from reputable sources. Avoid using seeds that appear damaged or discolored, as they may be more prone to infections.
- Clean and disinfect equipment: Before sowing or transplanting, thoroughly clean and disinfect all gardening tools and containers. This helps to prevent the spread of pathogens that can cause black leg.
- Rotate crops: Practice crop rotation by changing the location of your seedlings each year. This helps to break the disease cycle and reduce the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
- Improve soil drainage: Ensure that the soil has good drainage to prevent waterlogging, as excess moisture can increase the risk of black leg infection. Consider adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil structure and drainage.
- Monitor watering: Avoid overwatering your seedlings, as damp conditions promote the growth of fungi that cause black leg. Water only when the top inch of soil feels dry, and use a watering can or drip irrigation to deliver water directly to the base of the plants.
- Use disease-resistant varieties: Select seed varieties that are resistant to black leg or other common diseases. These varieties have been bred to have increased resistance to certain pathogens, reducing the risk of infection.
By implementing these long-term strategies, you can create a healthier gardening environment and reduce the risk of black leg infection in your seedlings.
“Question-Answer”
What is black leg infection and why is it a problem for seedlings?
Black leg infection is a disease caused by the bacteria called Phoma lingam. It affects seedlings and can cause damping-off, stunting, wilting, and eventually death. It is a problem for seedlings because it can lead to significant crop losses and decrease the overall productivity of a garden or farm.
How can I prevent black leg infection in seedlings?
To prevent black leg infection in seedlings, you can follow several steps. Firstly, it is important to use high-quality seeds and planting materials. Secondly, practice good sanitation by cleaning and disinfecting all gardening tools and equipment. Thirdly, avoid overwatering and ensure proper drainage to prevent the spread of the disease. Additionally, crop rotation and the use of resistant varieties can also help in preventing black leg infection.
What are the signs and symptoms of black leg infection in seedlings?
The signs and symptoms of black leg infection in seedlings include dark lesions on the stems and leaves, stunted growth, wilting, and eventual death of the seedling. The lesions may also have a dark border and can ooze a black, sticky substance. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to take immediate action to prevent further spread of the disease.
Can black leg infection be treated once seedlings are infected?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for black leg infection once seedlings are infected. It is best to remove and destroy the infected seedlings to prevent the spread of the disease to other healthy plants. It is also important to take preventive measures to minimize the chances of black leg infection in future plantings.
Are there any resistant varieties available to prevent black leg infection?
Yes, there are certain varieties of plants that have been bred to be resistant to black leg infection. These resistant varieties can greatly reduce the chances of seedlings getting infected. It is recommended to plant such resistant varieties to minimize the risk of black leg infection in your garden or farm.
Is black leg infection a common problem for seedlings?
Black leg infection can be a common problem for seedlings, especially in humid and wet conditions. It can occur in various plants, including vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants. It is important to be aware of the disease and take preventive measures to protect seedlings from black leg infection.







