- Signs of Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
- 1. Stunted Growth
- 2. Pale or Yellow Leaves
- 3. Reduced Fruit Yield
- 4. Delayed Maturity
- 5. Weak and Thin Stems
- 6. Overall Poor Plant Health
- The Importance of Nitrates for Tomato Crop
- Causes of Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
- 1. Insufficient Nitrogen in the Soil
- 2. Imbalanced Fertilizer Application
- 3. Excessive Rainfall
- 4. Intense Heat and Drought
- 5. Compacted or Poorly Drained Soil
- 6. Root Diseases or Damage
- How to Test Soil Nitrate Levels
- 1. Soil Testing Kits
- 2. Laboratory Testing
- 3. Digital Nitrate Meters
- 4. Observation
- Methods to Correct Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
- 1. Soil Amendment
- 2. Foliar Fertilizers
- 3. Nitrate-Rich Fertilizers
- 4. Crop Rotation
- 5. pH Adjustment
- 6. Irrigation Management
- Effective Fertilizers to Increase Nitrate Content
- 1. Calcium Nitrate
- 2. Potassium Nitrate
- 3. Ammonium Nitrate
- 4. Organic Nitrogen Fertilizers
- 5. Controlled-Release Fertilizers
- Preventive Measures to Avoid Nitrate Deficiency
- Consult a Professional for Nitrate Deficiency Solutions
- “Question-Answer”
- What are the symptoms of nitrate deficiency in tomato plants?
- How can I determine if my tomato plants have nitrate deficiency?
- What causes nitrate deficiency in tomato plants?
- How can I treat nitrate deficiency in my tomato plants?
- Can nitrate deficiency in tomato plants be prevented?
- “Video” You’re Killing Your Tomatoes if You Do This, 5 MISTAKES You Can’t Afford to Make Growing Tomatoes

The cultivation of tomatoes is an essential agricultural activity worldwide, contributing to food security and economic stability. However, tomato plants are susceptible to various nutrient deficiencies, including nitrate deficiency, which can lead to severe crop loss. Understanding the importance of nitrates for plant growth and development is critical in preventing these losses and ensuring a successful tomato harvest.
Nitrates are the main source of nitrogen in plants, playing a crucial role in various physiological processes. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient required for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll. Without an adequate supply of nitrates, tomato plants suffer from stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, reduced fruit production, and poor overall health.
To address nitrate deficiency in tomato plants, immediate assistance is needed. Farmers and growers must be vigilant in monitoring the nutrient levels in their crops and take prompt action if deficiencies are identified. One effective method is the application of nitrogen-based fertilizers, which can provide a quick source of nitrates for the plants. However, it is essential to carefully follow application rates and timing to avoid over-application, which can lead to environmental pollution.
Additionally, organic sources of nitrogen, such as compost and manure, can help replenish nitrate levels in the soil and promote long-term soil health. These organic amendments slowly release nitrates, ensuring a sustained supply of nutrients to the tomato plants. Crop rotation and intercropping with nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes, can also enhance nitrogen availability in the soil, reducing the risk of nitrate deficiency.
In conclusion, preventing nitrate deficiency in tomato plants is crucial for maintaining crop productivity and reducing losses. Through careful monitoring, timely application of nitrogen-based fertilizers, and incorporation of organic amendments, farmers can provide immediate assistance to their crops and ensure a bountiful tomato harvest.
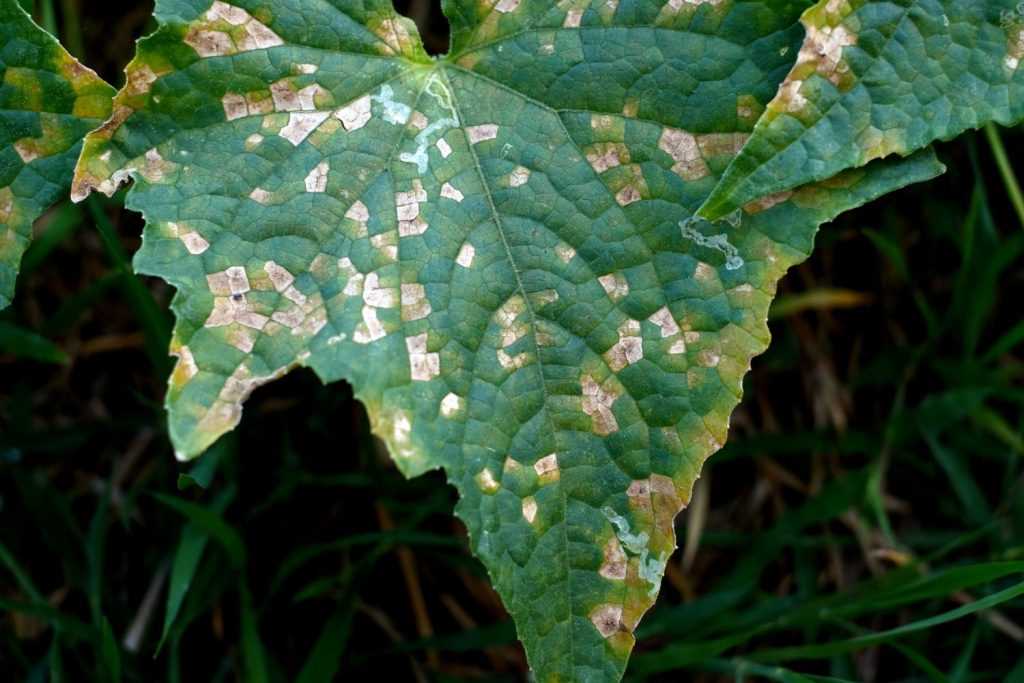
Signs of Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
Nitrate deficiency in tomato plants can have visible signs that indicate the plants are not receiving an adequate supply of nitrogen. Recognizing these signs is crucial for addressing the deficiency and preventing crop loss. Here are some common signs to look out for:
1. Stunted Growth
Tomato plants suffering from nitrate deficiency may exhibit slow or stunted growth. The plants may be smaller in size compared to healthy plants, or they may struggle to develop new leaves and branches.
2. Pale or Yellow Leaves
One of the most apparent signs of nitrate deficiency in tomato plants is the development of pale or yellow leaves. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for chlorophyll production, and its deficiency can cause a lack of green pigmentation in the leaves, resulting in a yellowish or pale appearance.
3. Reduced Fruit Yield

A lack of nitrogen can significantly impact the fruit yield of tomato plants. Nitrogen is crucial for promoting flower and fruit development, and a deficiency can lead to a lower number of fruits or smaller-sized fruits. The plants may also drop their flowers prematurely.
4. Delayed Maturity
Tomato plants with nitrate deficiency may take longer to mature compared to healthy plants. This delayed maturity can further exacerbate the effects on fruit yield and overall crop productivity.
5. Weak and Thin Stems
A lack of nitrogen can weaken the stems of tomato plants, making them thin and fragile. This can increase the risk of stem breakage and make the plants more susceptible to wind damage or disease.
6. Overall Poor Plant Health
In addition to the specific signs mentioned above, tomato plants with nitrate deficiency may exhibit overall poor health. They may appear weak, wilted, or have a general lack of vigor.
It is important to note that these signs may also be caused by other factors, such as nutrient imbalances or pest infestations. Conducting a soil test and consulting with a horticultural expert can help confirm the presence of nitrate deficiency and determine the best course of action.
The Importance of Nitrates for Tomato Crop

Nitrates are essential nutrients for the growth and development of tomato crops. They play a vital role in the formation of proteins and enzymes, which are necessary for various physiological processes in plants. Nitrogen, in the form of nitrates, is a major component of plant tissue and is required in large quantities for proper development.
1. Enhanced Growth:
Nitrates serve as a primary source of nitrogen for plants. They promote cell division, elongation, and overall growth of tomato plants. Nitrates are involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids, which are essential for DNA replication and growth.
2. Improved Leaf Development:
Nitrates have a significant impact on leaf development in tomato crops. They help in the formation of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color of leaves. Adequate levels of nitrates ensure proper leaf expansion and photosynthesis, leading to healthy plants with robust foliage.
3. Enhanced Fruit Production:
Nitrates play a key role in fruit development and yield. They contribute to the formation of auxins, which are plant hormones responsible for fruit growth and development. Adequate nitrate levels ensure the production of quality fruits and increase the overall yield of tomato crops.
4. Resistance to Diseases and Stress:
Nitrates also play a role in enhancing the resistance of tomato crops to diseases and environmental stressors. They strengthen the plant’s defense mechanisms, making it less susceptible to infections and adverse conditions. Adequate nitrate levels help plants cope with drought, temperature fluctuations, and other stressors.
5. Nutrient Balance:
Nitrates are one of the primary nutrients required by tomato crops, along with phosphorus and potassium. Maintaining a proper balance of these nutrients is crucial for plant health and overall productivity. Imbalances, particularly nitrogen deficiencies, can lead to stunted growth, reduced fruit production, and poor overall crop quality.
In conclusion, nitrates are essential for the optimal growth and development of tomato crops. They promote growth, leaf development, fruit production, disease resistance, and nutrient balance. Monitoring and ensuring adequate nitrate levels in the soil is crucial to prevent nitrate deficiency and maximize crop productivity.
Causes of Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
Nitrate deficiency in tomato plants can occur due to several factors. Understanding these causes is crucial in preventing crop loss and ensuring the overall health and productivity of tomato plants.
1. Insufficient Nitrogen in the Soil
Nitrate is a form of nitrogen that plays a vital role in plant growth and development. If the soil lacks an adequate nitrogen supply, tomato plants may experience nitrate deficiency. This can happen in both natural and cultivated environments.
2. Imbalanced Fertilizer Application
An improper balance of fertilizers can also contribute to nitrate deficiency in tomato plants. Fertilizers that do not provide enough nitrogen or are applied in incorrect proportions can lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil, affecting the availability of nitrates to the plants.
3. Excessive Rainfall
Excessive rainfall can wash away nitrates from the soil, leading to their depletion. This is particularly significant in areas with heavy and prolonged rainfall, as it can leach out a considerable amount of nitrates from the root zone of tomato plants.
4. Intense Heat and Drought

High temperatures and extended periods of drought can also contribute to nitrate deficiency in tomato plants. These stress conditions can limit the uptake and assimilation of nitrates, further exacerbating the problem.
5. Compacted or Poorly Drained Soil
Soil compaction and inadequate drainage can impede the root development of tomato plants. This can limit their ability to access nitrates present in the soil, leading to nitrate deficiency.
6. Root Diseases or Damage
Root diseases or physical damage to the roots can interfere with the uptake of nitrates by tomato plants. This can result in reduced nitrate availability and subsequent deficiency symptoms.
By addressing these causes of nitrate deficiency and implementing appropriate cultivation practices, farmers and gardeners can ensure the optimal growth and productivity of tomato plants, ultimately preventing crop loss.
How to Test Soil Nitrate Levels
Testing the nitrate levels in your soil is an important step in determining the health of your plants and preventing crop loss. Here are a few methods you can use to test for nitrate deficiencies in your soil:
1. Soil Testing Kits

Soil testing kits are readily available and can be a convenient option for testing nitrate levels in your soil. These kits typically come with instructions and all the necessary tools for collecting a soil sample and performing the test. Follow the instructions provided with the kit to accurately measure the nitrate levels in your soil.
2. Laboratory Testing
If you prefer a more precise and accurate method, you can send a soil sample to a laboratory for testing. Many agricultural extension offices or private laboratories offer soil testing services. Collect a soil sample following their instructions and send it to the laboratory for analysis. The results will provide you with detailed information on the nitrate levels in your soil.
3. Digital Nitrate Meters
For a more advanced and instant reading, you can use digital nitrate meters. These devices use electrical conductivity to measure the nitrate levels in the soil. They are easy to use and provide quick results. Simply insert the metal probe into the soil and wait for the meter to display the nitrate levels.
4. Observation
While not a direct testing method, observation can help you identify some signs of nitrate deficiency in your plants. Look for stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or general poor plant health. These symptoms may indicate a nitrate deficiency in the soil. However, it is important to note that other factors can also cause similar symptoms, so it is always best to confirm with a proper soil test.
By regularly testing the nitrate levels in your soil, you can take appropriate measures to address any deficiencies and ensure the health and productivity of your plants.
Methods to Correct Nitrate Deficiency in Tomato Plants
If your tomato plants are showing signs of nitrate deficiency, it is important to take immediate action to prevent crop loss. Here are some methods you can use to correct nitrate deficiency in tomato plants:
1. Soil Amendment
One of the main causes of nitrate deficiency is low levels of nitrogen in the soil. To correct this, you can amend the soil with organic matter or nitrogen-rich fertilizers. This will increase the nitrogen content in the soil and provide the tomato plants with the necessary nutrients.
2. Foliar Fertilizers

In addition to amending the soil, you can also use foliar fertilizers to provide a quick boost of nitrogen to the tomato plants. These fertilizers are applied directly to the leaves of the plants, allowing them to quickly absorb the nutrients and alleviate the nitrate deficiency.
3. Nitrate-Rich Fertilizers
Using fertilizers that are specifically high in nitrates can help correct the deficiency in tomato plants. Look for fertilizers that have a high percentage of nitrogen, particularly in the form of nitrates. Apply the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure the plants receive an adequate amount of nitrates.
4. Crop Rotation
Crop rotation can also help correct nitrate deficiency in tomato plants. By rotating the tomato crop with other nitrogen-fixing plants or crops that were grown with high nitrogen levels, you can improve the overall nitrogen content in the soil. This will help prevent future nitrate deficiencies and promote healthy tomato growth.
5. pH Adjustment
Monitoring and adjusting the pH of the soil can also play a role in preventing nitrate deficiency. Tomato plants prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 6.8. If the soil pH is too high or too low, it can affect nutrient availability and uptake. Test the soil pH regularly and make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal nutrient absorption.
6. Irrigation Management
Proper irrigation management is essential for preventing nitrate deficiency in tomato plants. Overwatering or underwatering can affect nutrient uptake and lead to deficiencies. Ensure that the tomato plants receive consistent and adequate irrigation, taking into account factors such as weather conditions, soil moisture levels, and the specific needs of the plants.
By implementing these methods, you can correct nitrate deficiency in your tomato plants and ensure their healthy growth and development. It is important to regularly monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies and take immediate action to address any issues that arise.
Effective Fertilizers to Increase Nitrate Content
Nitrate deficiency in tomato plants can lead to significant crop loss. To prevent this, it is essential to provide the plants with an adequate supply of nitrates through effective fertilizers. Here are some fertilizers that can effectively increase the nitrate content in tomato plants:
1. Calcium Nitrate

Calcium nitrate is a widely used fertilizer for increasing nitrate levels in plants. It contains a high concentration of both calcium and nitrogen, which are essential nutrients for plant growth. When applied as a fertilizer, calcium nitrate helps to improve the absorption and utilization of nitrates by tomato plants, leading to higher nitrate content and healthier growth.
2. Potassium Nitrate

Potassium nitrate is another effective fertilizer for increasing nitrate content in tomato plants. It provides a balanced combination of potassium and nitrogen, which are important for plant development. Potassium nitrate helps to promote the production of nitrates within the plants by supplying them with the necessary nutrients. Regular application of potassium nitrate can help prevent nitrate deficiency and improve overall plant health.
3. Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a commonly used nitrogen fertilizer that can effectively increase nitrate content in tomato plants. It provides both ammonium and nitrate forms of nitrogen, which are readily available for plant uptake. The ammonium form of nitrogen is quickly absorbed by the plant roots, while the nitrate form is slowly released, providing a sustained supply of nitrates to the plants.
4. Organic Nitrogen Fertilizers
Organic nitrogen fertilizers, such as compost and manure, can also be used to increase nitrate content in tomato plants. These fertilizers release nitrogen slowly and continuously, providing a steady supply of nitrates to the plants. Additionally, organic fertilizers help improve soil fertility and enhance the overall health of the plants.
5. Controlled-Release Fertilizers
Controlled-release fertilizers are designed to release nutrients gradually over an extended period. These fertilizers can be formulated with a high concentration of nitrates, providing a sustained supply to tomato plants. The slow release of nitrates ensures that the plants receive a constant source of this essential nutrient, reducing the risk of nitrate deficiency.
In conclusion, using effective fertilizers is crucial for increasing nitrate content in tomato plants and preventing crop loss. Calcium nitrate, potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, organic nitrogen fertilizers, and controlled-release fertilizers are some of the fertilizers that can effectively boost nitrate levels in plants. Regular and proper application of these fertilizers can help ensure healthy growth and maximize tomato crop productivity.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Nitrate Deficiency
Preventing nitrate deficiency in tomato plants is crucial to ensure healthy growth and a good yield. Here are some preventive measures that farmers can take:
- Regular soil testing: Conduct regular soil tests to determine the nutrient levels, including nitrates, in the soil. This will help farmers identify any deficiencies and take appropriate actions.
- Proper fertilization: Provide balanced fertilization to the plants to maintain adequate nitrate levels. This can be achieved by using fertilizers that are rich in nitrates or by implementing organic farming practices.
- Crop rotation: Practice crop rotation to avoid continuous cultivation of tomatoes in the same field. Nitrate deficiency can occur when the soil becomes depleted of nutrients due to repetitive cultivation of the same crop. Growing other nitrogen-fixing crops like legumes can help replenish nitrates in the soil.
- Use of cover crops: Planting cover crops like clover or alfalfa in between tomato seasons can help improve nitrogen content in the soil. These cover crops can be later incorporated into the soil, providing a natural source of nitrates.
- Mulching: Apply organic mulch around tomato plants to help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature. Mulch can also help improve soil structure and prevent nutrient loss, including nitrates, through leaching.
- Water management: Proper watering practices are essential to avoid nitrate deficiency. Irrigate tomato plants adequately, ensuring that the water reaches the root zone and is not wasted through runoff.
- Pest and disease management: Monitor and control pests and diseases that can affect tomato plants. Infections and infestations can reduce the plant’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients, leading to nitrate deficiency.
- Cultivar selection: Choose tomato cultivars that are known to be more resistant to nitrate deficiency. Some cultivars are naturally better at absorbing and utilizing nitrates, which can help prevent deficiencies.
- Regular plant monitoring: Keep a close eye on tomato plants for any signs of nutrient deficiencies, including yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Early detection can help farmers take immediate corrective actions.
By implementing these preventive measures, farmers can proactively avoid nitrate deficiency in tomato plants and promote healthy growth, ensuring a successful and bountiful tomato crop.
Consult a Professional for Nitrate Deficiency Solutions
If you have determined that your tomato plants are suffering from nitrate deficiency and are unsure how to proceed, it is advisable to consult a professional for assistance. A professional will have the necessary knowledge and experience to diagnose the issue accurately and recommend appropriate solutions.
Here are a few reasons why you should consider consulting a professional:
- Expertise: Professionals in the field of agriculture and horticulture have in-depth knowledge of plant nutrition and can accurately identify the underlying cause of nitrate deficiency in your tomato plants.
- Diagnosis: A professional will conduct a thorough analysis of your plants and soil, taking into account factors such as pH levels, nutrient composition, water quality, and environmental conditions. This detailed assessment will enable them to diagnose the specific cause of the deficiency.
- Customized Solutions: Depending on the severity of the nitrate deficiency and the overall health of your tomato plants, a professional will be able to provide customized solutions that address the specific needs of your crop. This may involve adjusting fertilization practices, modifying watering schedules, or implementing soil amendments.
- Prevention Strategies: In addition to addressing the current nitrate deficiency, a professional can also provide guidance on preventive measures to avoid future deficiencies and maintain the long-term health and productivity of your tomato crop. These strategies may include the use of nitrogen-fixing cover crops, regular soil testing, and proper crop rotation practices.
Remember, seeking professional advice can save you time, money, and potential crop losses in the long run. By working with an expert, you can ensure that you are implementing the most effective solutions for addressing nitrate deficiency in your tomato plants.
“Question-Answer”
What are the symptoms of nitrate deficiency in tomato plants?
The symptoms of nitrate deficiency in tomato plants include stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced fruit production.
How can I determine if my tomato plants have nitrate deficiency?
You can determine if your tomato plants have nitrate deficiency by conducting a soil test and measuring the nitrate levels. Additionally, you can look for symptoms such as stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
What causes nitrate deficiency in tomato plants?
Nitrate deficiency in tomato plants can be caused by insufficient soil nutrients, high temperatures, excessive watering, or poor soil drainage. It can also be caused by pests or diseases that affect the root system.
How can I treat nitrate deficiency in my tomato plants?
To treat nitrate deficiency in tomato plants, you can apply a nitrate fertilizer according to the recommended dosage. Additionally, you can improve soil drainage, adjust watering practices, and manage pest and disease issues to prevent further nutrient deficiency.
Can nitrate deficiency in tomato plants be prevented?
Yes, nitrate deficiency in tomato plants can be prevented by regularly testing the soil and maintaining proper nutrient levels. Proper watering practices, soil improvement, and pest and disease management can also help prevent nitrate deficiency.







