- Understanding Blacklegs
- Factors contributing to blacklegs
- Preventing and managing blacklegs
- Proper Crop Rotation
- Sanitation Practices
- Clean and Disinfect Tools
- Remove and Destroy Infected Plants
- Rotate Crops
- Keep Your Garden Clean
- Selection of Resistant Varieties
- References
- “Question-Answer”
- What is blackleg and why is it harmful to seedlings?
- How can I prevent blackleg in my seedlings?
- Can I use organic methods to protect my seedlings from blackleg?
- What are the symptoms of blackleg in seedlings?
- How long can the blackleg fungus survive in the soil?
- Are there any resistant varieties of plants that are less susceptible to blackleg?
- Can I save seedlings that have been infected with blackleg?
- “Video” How to Save Seeds of All Sorts | A Complete Guide to Garden Seed Saving | Frugal Gardening
When it comes to gardening, one of the biggest challenges is protecting seedlings from diseases and pests. Blacklegs, a common fungal disease, can wreak havoc on young plants, stunting their growth and even killing them. However, there are several proven methods to protect your precious seedlings and ensure a successful harvest.
1. Sanitation: The first step in preventing blacklegs is to maintain a clean and healthy environment for your plants. Start by sterilizing your garden tools and containers before use. This can be done by soaking them in a solution of bleach and water. Additionally, make sure to remove any infected plant debris from your garden to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Crop Rotation: Another effective method to prevent blacklegs is to practice crop rotation. Since the disease can remain in the soil for several years, it is important to avoid planting susceptible crops in the same location year after year. By rotating your crops, you can disrupt the disease cycle and reduce the chances of blacklegs infecting your seedlings.
3. Fungicide Treatment: In severe cases where blacklegs is already present in your garden, using a fungicide treatment can help control the disease. Look for a fungicide specifically formulated for blacklegs and follow the instructions carefully. Remember to apply the treatment as soon as the disease is detected to prevent further spread and damage to your seedlings.
By practicing proper sanitation, implementing crop rotation, and using fungicide treatments when necessary, you can protect your seedlings from blacklegs and ensure a successful harvest. Remember to monitor your plants closely and take action at the first signs of disease. With these proven methods, you can save your harvest and enjoy a bountiful garden.
Understanding Blacklegs
Blacklegs is a common disease that affects seedlings, particularly in brassica crops such as cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. It is caused by a group of bacteria known as Pectobacterium and Erwinia. These bacteria survive in the soil and can infect plants during the germination and early growth stages.
One of the main symptoms of blacklegs is the wilting and darkening of the lower stem of the seedling. As the disease progresses, the stem may become soft and watery, eventually leading to the death of the plant. In severe cases, blacklegs can cause significant losses in crop yield.
Factors contributing to blacklegs
There are several factors that contribute to the development and spread of blacklegs:
- Contaminated soil: The bacteria that cause blacklegs can survive in the soil for several years. If the soil is contaminated with these bacteria, the risk of infection is high.
- Crowded seedlings: When seedlings are grown too closely together, it creates conditions for the rapid spread of the disease. The close proximity allows the bacteria to easily move from one plant to another.
- Poor sanitation: Failing to clean and sanitize gardening tools, pots, and trays can contribute to the spread of blacklegs. The bacteria can survive on these surfaces and infect seedlings upon contact.
Preventing and managing blacklegs
Although blacklegs can be difficult to control, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent its occurrence:
- Use disease-resistant varieties: Planting disease-resistant varieties can significantly reduce the risk of blacklegs. These varieties have been bred to have increased resistance to the bacteria that cause the disease.
- Practice crop rotation: Avoid planting brassica crops in the same area year after year. Crop rotation helps to disrupt the life cycle of the bacteria and reduces the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
- Proper sanitation: Clean and sanitize gardening tools, pots, and trays before each use. This helps to eliminate any residual bacteria that may be present.
- Monitor and remove infected plants: Regularly inspect your seedlings for symptoms of blacklegs. If any plants show signs of infection, remove them immediately to prevent the spread of the disease to healthy plants.
By understanding the causes and preventive measures of blacklegs, you can protect your seedlings and ensure a healthy harvest.
Proper Crop Rotation
Proper crop rotation is an effective method to prevent the spread of blackleg disease in seedlings. By rotating crops, farmers can disrupt the life cycle of the fungus that causes blackleg, reducing its presence in the soil and minimizing the risk of infection for future plantings.
What is crop rotation?
Crop rotation is the practice of planting different crops in a specific sequence on the same piece of land. This technique has been used for centuries to improve soil fertility, manage pests, and reduce the risk of diseases. By rotating crops, farmers avoid planting the same species in the same spot year after year, which can lead to the build-up of pests and diseases that specifically target those crops.
How does crop rotation help in controlling blackleg?
Blackleg is a soil-borne disease caused by the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans. This fungus can survive in the soil for several years, making it difficult to eradicate once it is established. However, by following a proper crop rotation plan, farmers can limit the disease’s impact on their seedlings.
There are several ways crop rotation can help control blackleg:
- Break the disease cycle: Blackleg fungus survives by infecting the roots and stems of brassica crops such as cabbage, broccoli, and canola. By rotating these crops with non-host plants like legumes or cereals, farmers can break the disease cycle and reduce the fungus’s population in the soil.
- Reduce inoculum: Crop rotation also helps reduce the overall inoculum of blackleg fungus in the field. By planting non-host crops, the fungus has fewer opportunities to reproduce and build up its population. This decreases the chances of blackleg infection in future plantings.
- Improve soil health: Different crops have different nutritional needs. By rotating crops, farmers can ensure the soil is not depleted of specific nutrients that are necessary for blackleg fungus survival and growth. This improves soil health and helps create an environment less favorable for the disease.
Implementing crop rotation for blackleg control:
When implementing crop rotation to control blackleg, farmers should consider the following guidelines:
- Plan a crop rotation schedule that includes non-host plants for blackleg, such as corn, soybeans, or wheat.
- Avoid planting brassica crops in the same field for at least three years to break the disease cycle.
- Ensure proper sanitation practices, such as removing crop debris and cleaning machinery, to prevent the spread of blackleg between fields.
- Monitor the field regularly for signs of blackleg infection and take appropriate action if necessary.
Conclusion
Proper crop rotation is a proven method to protect seedlings from blackleg disease. By implementing a well-planned rotation schedule and following sanitation practices, farmers can effectively reduce the impact of blackleg on their crops, ensuring a healthy harvest.
Sanitation Practices
Sanitation practices are essential for preventing the spread of blacklegs, a common disease that affects seedlings. By implementing proper sanitation practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection and ensure the health of your plants.
Clean and Disinfect Tools
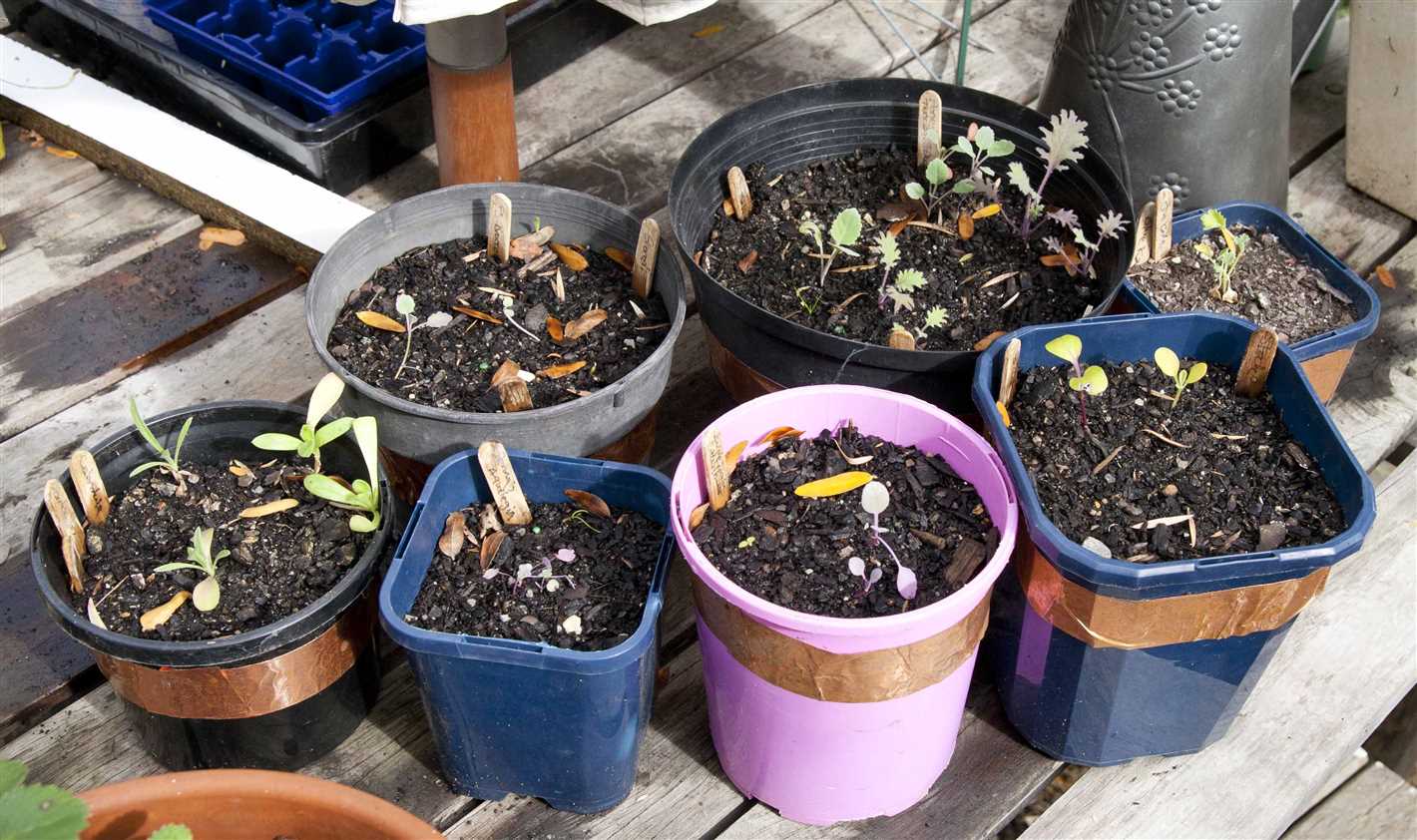

Start by cleaning and disinfecting all of your gardening tools regularly. This includes shovels, pruners, and any other tools that come into contact with the soil or plants. Use a mild detergent or soapy water to remove dirt and debris, and then sanitize the tools with a bleach solution. Mix one part bleach with nine parts water, and use this solution to wipe down the tools thoroughly.
Remove and Destroy Infected Plants
If you notice any signs of blacklegs on your seedlings, it’s important to act quickly. Remove the infected plants from your garden immediately, taking care not to touch any healthy plants in the process. Bag up the infected plants and dispose of them properly, either by burning them or sealing them in a plastic bag and throwing them away. This will help prevent the disease from spreading to other plants.
Rotate Crops
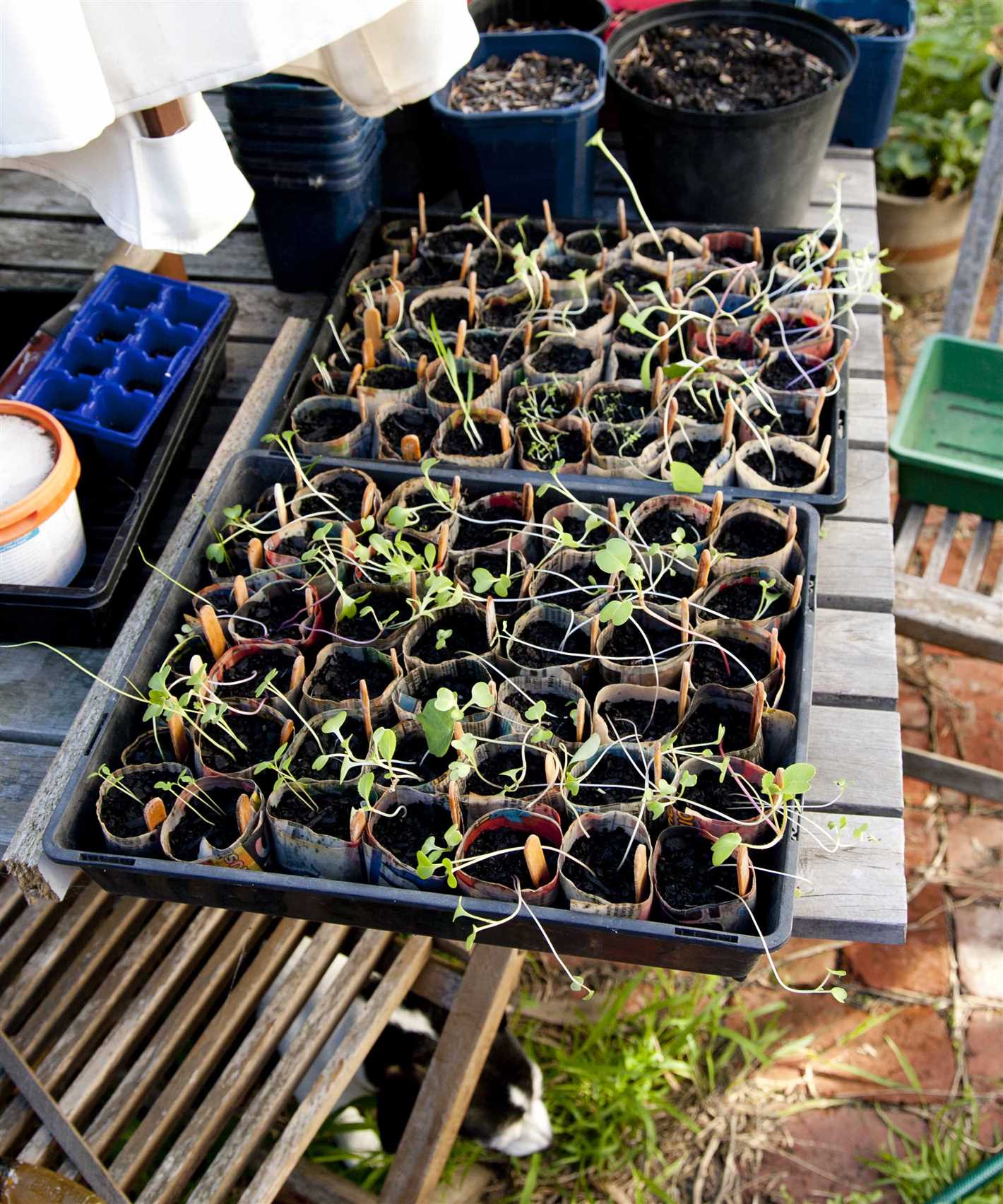

Rotating crops is another effective sanitation practice for preventing blacklegs. Avoid planting crops from the same family in the same location year after year, as this can increase the risk of disease. Instead, rotate your crops by planting different types of vegetables or flowers in the same area on a yearly basis. This helps break the disease cycle and reduces the likelihood of blacklegs affecting your seedlings.
Keep Your Garden Clean

Maintaining a clean and tidy garden is crucial for preventing the spread of blacklegs. Remove any fallen leaves, plant debris, or weeds that could harbor disease-causing pathogens. Regularly inspect your garden for signs of blacklegs or other diseases, and take action immediately if you spot any issues. By keeping your garden clean, you create a healthier environment for your seedlings and reduce the risk of infection.
Implementing proper sanitation practices is an essential part of protecting your seedlings from blacklegs. By following these guidelines and maintaining a clean and healthy garden, you can ensure the success of your harvest and enjoy vibrant, disease-free plants.
Selection of Resistant Varieties

To protect seedlings from blacklegs, one effective method is to select and plant resistant varieties. Resistant varieties are plants that have been bred to have natural defenses against blackleg disease. These plants are less susceptible to infection and can withstand the damaging effects of the disease.
When selecting resistant varieties, it is important to choose ones that are specific to your growing region. Different regions may have different strains of blackleg disease, so it is crucial to choose varieties that are resistant to the specific strains in your area.
One way to determine the resistance of a variety is to look for the “R” rating. This rating is assigned to varieties that have been tested and found to be resistant to blackleg disease. The higher the R rating, the more resistant the variety is.
It is also important to consider other factors when selecting resistant varieties. Look for varieties that have desirable traits such as high yield, good taste, and a long shelf life. Consider the specific needs and preferences of your growing operation and choose varieties that will fit well into your overall planting strategy.
Once you have selected the resistant varieties that are best suited for your growing region, be sure to follow proper planting and care practices to maximize their disease resistance. This includes providing adequate spacing between plants, ensuring proper soil nutrition and moisture levels, and implementing a regular monitoring and scouting program to catch any signs of disease early.
In conclusion, selecting resistant varieties is an effective way to protect seedlings from blacklegs. By choosing varieties that have been bred to have natural defenses against the disease, you can increase your chances of a successful and healthy harvest.
References

Alvarez, R. (2019). Blackleg Disease of Crucifers. The Plant Health Instructor. DOI: 10.1094/PHI-I-2019-0912-01
Dixon, G. (2020). Managing Blackleg in Canola and Mustard Crops. Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. Retrieved from https://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/crops/facts/08-049w.htm
Patel, V. (2021). Tips for Protecting Seedlings from Blackleg. Gardening Know How. Retrieved from https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/edible/vegetables/vgen/blackleg-disease.htm
University of Minnesota Extension (2022). Blackleg of Crucifers. Retrieved from https://extension.umn.edu/diseases/blackleg-crucifers
“Question-Answer”
What is blackleg and why is it harmful to seedlings?
Blackleg is a severe disease caused by a fungus that affects seedlings and young plants. It can cause the plants to wilt, turn black, and eventually die. Blackleg can be harmful to seedlings because it can lead to significant loss of crops and decrease overall productivity.
How can I prevent blackleg in my seedlings?
There are several proven ways to protect seedlings from blackleg. Firstly, you can start by using disease-free seeds and seedlings from reputable sources. Secondly, you should practice crop rotation, as blackleg can survive in the soil for several years. Lastly, you can use fungicides or biological control methods to suppress the growth of the blackleg-causing fungus.
Can I use organic methods to protect my seedlings from blackleg?
Yes, there are organic methods available to protect seedlings from blackleg. One approach is to use biocontrol agents, such as beneficial bacteria or fungi, which can compete with the blackleg-causing fungus and prevent its growth. Additionally, practicing good cultural practices, such as proper spacing between plants and adequate drainage, can help create a healthier growing environment for the seedlings.
What are the symptoms of blackleg in seedlings?
The symptoms of blackleg in seedlings can vary, but common signs include wilting, dark discoloration at the base of the stem, and stunted growth. The leaves may also turn yellow or brown, and the plants may eventually collapse and die. It is important to regularly inspect seedlings for any signs of blackleg and take appropriate measures to prevent its spread.
How long can the blackleg fungus survive in the soil?
The blackleg fungus can survive in the soil for several years. This is why crop rotation is an important practice to prevent the buildup of the blackleg-causing pathogen in the soil. By rotating crops and not planting susceptible plants in the same area for consecutive years, you can help reduce the risk of blackleg infection in your seedlings.
Are there any resistant varieties of plants that are less susceptible to blackleg?
Yes, there are some plant varieties that have been bred to be resistant or less susceptible to blackleg. These varieties have genetic traits that make them more resistant to the blackleg-causing fungus. When selecting seeds or seedlings, it is a good idea to look for varieties that are specifically labeled as resistant to blackleg.
Can I save seedlings that have been infected with blackleg?
If your seedlings have been infected with blackleg, it is difficult to save them. The best course of action is to remove and destroy the infected plants to prevent further spread of the disease. It is important to practice good sanitation and clean any tools or equipment that came into contact with the infected seedlings to minimize the risk of reinfection in future plantings.







