- Factors to Consider When Growing Cauliflower
- Choosing the Right Variety
- Consider Your Climate
- Size and Shape
- Flavor and Color
- Recommended Varieties
- Proper Watering Techniques
- 1. Watering Frequency
- 2. Timing
- 3. Watering Method
- 4. Mulching
- 5. Monitoring
- 6. Rainwater Harvesting
- 7. Avoid Overwatering
- Nutrient Tips for Healthy Growth
- 1. Balanced Fertilizer
- 2. Compost
- 3. Mulching
- 4. Micronutrients
- 5. pH Level
- 6. Water-Soluble Fertilizers
- 7. Crop Rotation
- Climate Considerations for Growing Cauliflower
- Temperature
- Sunlight
- Frost
- Humidity
- Rainfall and Watering
- Preparing the Soil for Growing Cauliflower
- 1. Soil Testing
- 2. pH Adjustment
- 3. Soil Enrichment
- 4. Weed Removal
- 5. Soil Drainage
- 6. Bed Preparation
- 7. Mulching
- Sowing Seeds and Transplanting Cauliflower
- 1. Choosing the Right Time
- 2. Preparing the Soil
- 3. Sowing the Seeds
- 4. Providing Ideal Growing Conditions
- 5. Transplanting the Seedlings
- 6. Digging the Planting Holes
- 7. Transplanting the Seedlings
- Caring for Cauliflower Plants
- 1. Planting and spacing
- 2. Watering
- 3. Mulching
- 4. Fertilizing
- 5. Pest and disease control
- 6. Harvesting
- Common Pests and Diseases Affecting Cauliflower
- Pests:
- Diseases:
- Harvesting and Storing Cauliflower
- “Question-Answer”
- What are some tips for choosing the right variety of cauliflower?
- How often should I water my cauliflower plants?
- What are some nutrient tips for growing cauliflower?
- Is it possible to grow cauliflower year-round?
- How long does it take for cauliflower to mature?
- Can I grow cauliflower in containers?
- “Video” Growing cauliflower from seed Time lapse | Home DIY planter box
Growing cauliflower can be a rewarding experience for any gardener. Not only is cauliflower a nutritious and versatile vegetable to have in your garden, but the process of growing it can also be enjoyable and fulfilling. However, like any crop, there are certain secrets to success that can help you achieve the best possible results.
First and foremost, choosing the right variety of cauliflower is crucial. There are a wide variety of cauliflower cultivars available, each with its own unique characteristics. Some varieties are better suited for specific climates or growing conditions, so it’s important to do your research and select a variety that will thrive in your specific area.
Proper watering is also essential for successful cauliflower growth. Cauliflower plants have shallow root systems, so it’s important to water them consistently and evenly. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can result in stunted growth. Finding the right balance and providing adequate moisture is key to ensuring healthy cauliflower plants.
In addition to proper watering, providing the right nutrients is vital for cauliflower growth. Cauliflower plants are heavy feeders and require a nutrient-rich soil to thrive. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil before planting can help provide the necessary nutrients. Additionally, regularly fertilizing with a well-balanced fertilizer can help promote healthy growth and strong cauliflower heads.
By choosing the right variety, providing proper watering, and ensuring adequate nutrient levels, you can set yourself up for success in growing cauliflower. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, these tips can help you cultivate healthy, delicious cauliflower in your own backyard.
Factors to Consider When Growing Cauliflower
- Climate: Cauliflower grows best in cool climates with temperatures between 60°F and 70°F (15°C and 21°C). Extreme heat can cause the heads to become small and malformed.
- Variety: Choose a cauliflower variety that is suitable for your specific climate and growing conditions. Some varieties are more tolerant to heat or cold, while others may have better disease resistance.
- Soil: Cauliflower prefers well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. The soil should have a pH level between 6.5 and 7.0. Adding compost or well-rotted manure before planting can improve soil fertility.
- Timing: The timing of planting is crucial for successful cauliflower growth. Start cauliflower seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost date, or directly sow seeds in the garden when the soil temperature reaches 50°F (10°C).
- Spacing: Cauliflower plants need enough space for their heads to develop fully. Space transplants or seedlings 18-24 inches apart in rows that are 2-3 feet apart.
- Watering: Cauliflower plants require consistent moisture throughout their growing season. Water deeply and regularly, ensuring that the soil remains evenly moist, but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering to prevent the spread of diseases.
- Fertilization: Provide cauliflower plants with the nutrients they need by fertilizing regularly. Use a balanced fertilizer that is high in nitrogen to promote healthy leaf and head development. Follow the package instructions for application rates and frequencies.
- Pest and Disease Control: Monitor cauliflower plants for common pests such as aphids, cabbage worms, and slugs. Utilize organic pest control methods like companion planting, row covers, and handpicking to prevent infestations. Additionally, practice crop rotation to minimize disease problems.
- Harvesting: Harvest cauliflower heads when they reach the desired size and have a tight, compact appearance. Cut the heads with a sharp knife, leaving about 2 inches of stem attached. Harvesting should be done before the heads begin to separate or turn yellow.
Choosing the Right Variety

When it comes to growing cauliflower, choosing the right variety is crucial for a successful harvest. Different varieties have different growth habits, flavors, and colors, so it’s important to select one that suits your preferences and growing conditions.
Consider Your Climate
Cauliflower is a cool-season crop and tends to prefer cooler temperatures. However, there are varieties available for different climate zones. If you live in a colder region, look for varieties that are cold-hardy and can withstand frost. On the other hand, if you live in a warmer climate, choose heat-tolerant varieties that can handle higher temperatures without bolting.
Size and Shape
Cauliflower varieties come in different sizes and shapes. Some produce large heads, while others are more compact. Consider your garden space and the amount of cauliflower you want to harvest. If you have limited space, go for compact varieties that don’t take up too much room. If you want large heads, choose varieties that are known for their size.
Flavor and Color
Another factor to consider when choosing a cauliflower variety is the flavor and color. Cauliflower can be white, green, orange, or purple. The flavor can also vary from mild to strong. Decide whether you prefer a specific color or if you’re open to trying different flavors. Some varieties even have a nutty or sweet taste.
Recommended Varieties
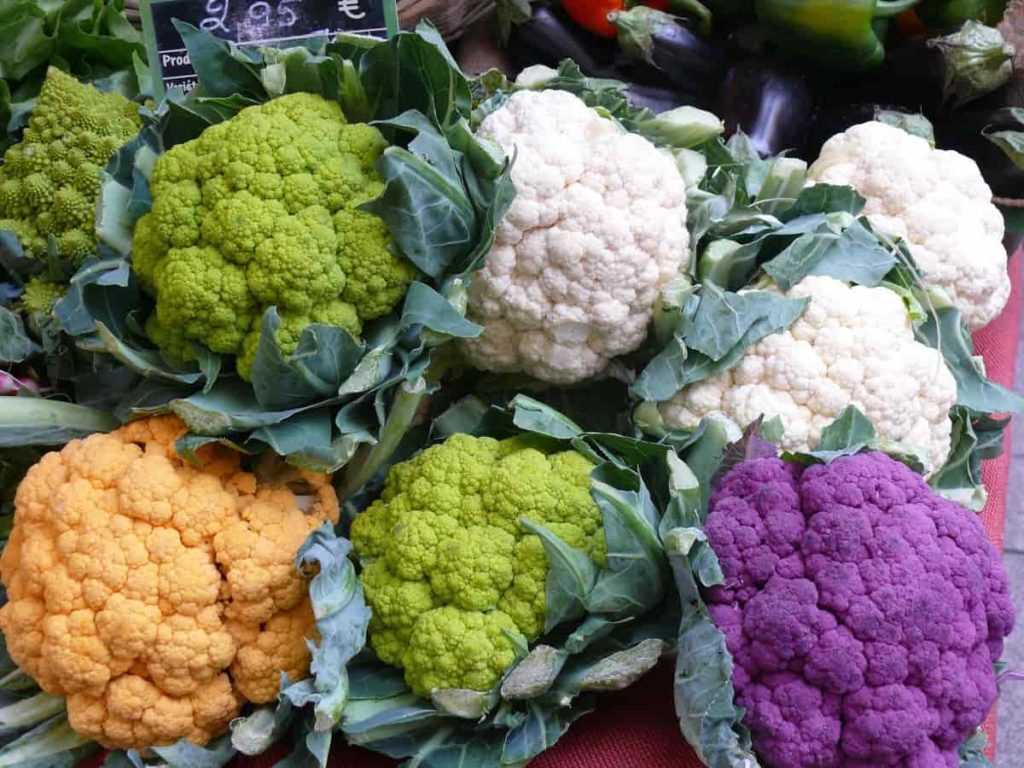

Here are some popular cauliflower varieties to consider:
- Snow Crown: This variety produces large, white heads and has a mild flavor.
- Green Macerata: If you prefer a green cauliflower, this variety is an excellent choice. It has a sweet and nutty flavor.
- Purple of Sicily: Known for its vibrant purple color, this variety adds a pop of color to any dish. It has a slightly stronger flavor compared to white cauliflower.
- Cheddar: For a unique orange color, try the Cheddar variety. It has a creamy texture and a delicious mild flavor.
Remember to check the seed packet or plant label for specific information on each variety’s growing requirements. Choose a variety that matches your climate, desired size, taste, and color preferences, and you’ll be on your way to successfully growing cauliflower in your garden.
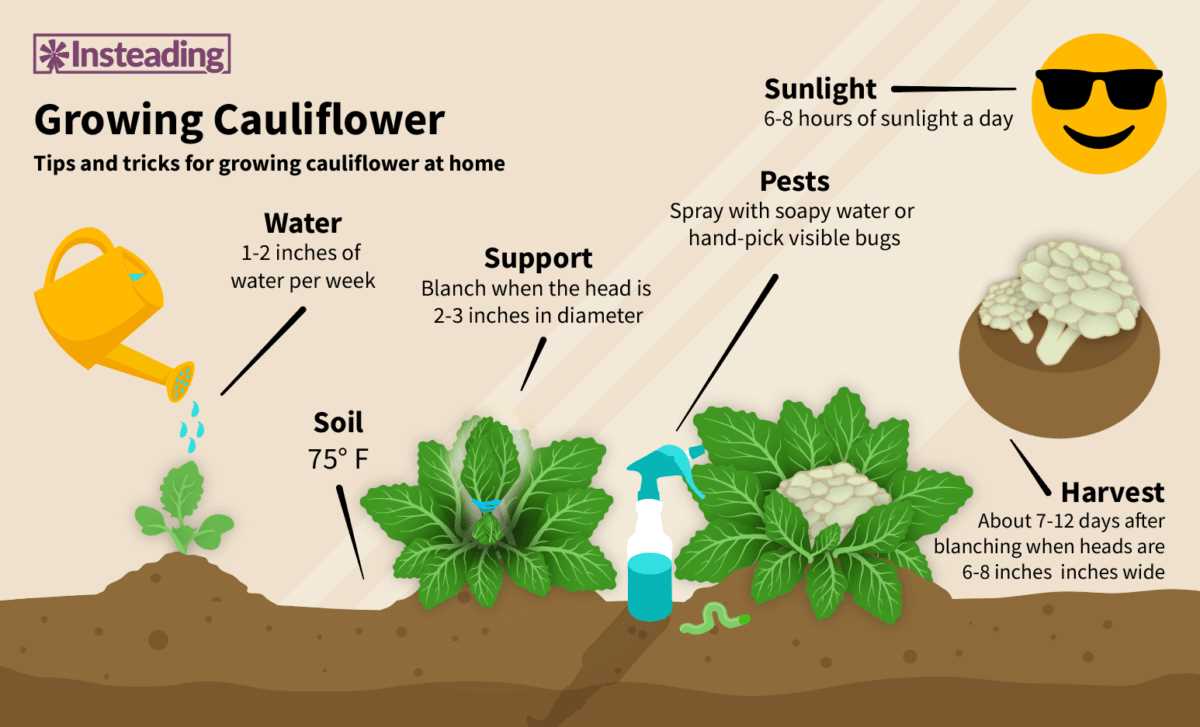
Proper Watering Techniques
Proper watering techniques are essential for the successful growth of cauliflower. This cruciferous vegetable requires consistent moisture to thrive and produce high-quality heads. Here are some tips on how to water your cauliflower plants:
1. Watering Frequency
Water your cauliflower plants deeply and evenly. Aim to provide at least 1 inch of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation. It is important to keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, to avoid root rot.
2. Timing
Water your cauliflower plants early in the morning to allow enough time for the foliage to dry before nighttime. Wet foliage during the evening can lead to disease development. Avoid watering in the late afternoon or evening to prevent prolonged moisture on the leaves.
3. Watering Method
When watering, use a gentle stream or a drip irrigation system to ensure that the water reaches the soil without splashing onto the leaves. Directing the water at the base of the plants will help the moisture reach the root zone more efficiently.
4. Mulching
Applying a layer of mulch around your cauliflower plants helps retain moisture in the soil and reduces evaporation. Mulch can also help regulate soil temperature and discourage weed growth. Use organic mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, and apply it around the base of the plants.
5. Monitoring
Regularly monitor the moisture levels in the soil around your cauliflower plants. It is crucial to maintain consistent moisture throughout the growing season. Check the soil by inserting your finger into the ground up to the second knuckle. If it feels dry, it’s time to water.
6. Rainwater Harvesting
If possible, consider collecting rainwater to use for watering your cauliflower plants. Rainwater is often preferable to tap water, as it is free of added chemicals and has a more balanced pH level. Collect rainwater using barrels or any other suitable container and use it to supplement your plants’ watering needs.
7. Avoid Overwatering
While consistent moisture is important, overwatering can be detrimental to cauliflower plants. It can lead to shallow root development, nutrient leaching, and disease issues. Avoid watering too frequently or allowing water to pool around the plants. Always allow the top few inches of soil to dry out slightly between watering sessions.
| Watering Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Sprinkler |
|
|
| Drip irrigation |
|
|
| Hand watering |
|
|
By following these proper watering techniques, you can ensure that your cauliflower plants remain healthy and productive throughout the growing season.
Nutrient Tips for Healthy Growth
Proper nutrition is crucial for the healthy growth of cauliflower plants. Here are some nutrient tips to ensure your plants thrive:
1. Balanced Fertilizer

Cauliflower requires a well-balanced fertilizer to provide essential nutrients. Look for a fertilizer with equal proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). The balanced ratio will support overall plant growth and development.
2. Compost
Incorporating compost into the soil before planting will boost nutrient availability and improve soil structure. Compost provides a rich source of organic matter that enhances the absorption of nutrients by the plants.
3. Mulching
Applying mulch around the base of cauliflower plants helps retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth. Organic mulches like straw, grass clippings, or wood chips also break down over time, adding nutrients to the soil.
4. Micronutrients

In addition to the primary nutrients, cauliflower plants also require certain micronutrients for optimal growth. These include iron, manganese, zinc, copper, and boron. Using a micronutrient fertilizer or foliar spray can ensure these trace elements are adequately supplied.
5. pH Level
Cauliflower prefers slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Test the soil pH regularly and make any necessary adjustments using lime or sulfur. Maintaining the correct pH level allows for better nutrient absorption by the plants.
6. Water-Soluble Fertilizers
Using water-soluble fertilizers during the growing season provides a quick and efficient way to deliver nutrients to the plants. Follow the package instructions for proper dilution and application rates to avoid over-fertilization.
7. Crop Rotation

To prevent nutrient imbalances and reduce the risk of diseases, practice crop rotation. Avoid planting cauliflower or other brassicas in the same spot year after year. Rotating with other plant families replenishes the soil and minimizes nutrient deficiencies.
By following these nutrient tips, you can ensure that your cauliflower plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth, leading to a bountiful harvest.
Climate Considerations for Growing Cauliflower
When it comes to growing cauliflower, climate plays a crucial role in determining its success. Cauliflower is a cool-season crop that prefers moderate temperatures and can be quite sensitive to extreme cold or heat. Here are some climate considerations to keep in mind when growing cauliflower:
Temperature
Cauliflower grows best in temperatures between 60°F (15°C) and 70°F (21°C). Temperatures that are consistently below 50°F (10°C) can stunt its growth, while temperatures above 80°F (27°C) can cause the plant to bolt and develop poor-quality heads. It is important to choose the right time of year to plant cauliflower based on your climate.
Sunlight
Cauliflower requires at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day to grow properly. A sunny location without too much shade is ideal for its development. However, in hot climates, some afternoon shade can help protect the plant from excessive heat and prevent premature bolting.
Frost
Although cauliflower can tolerate light frosts, it is not frost-resistant. Freezing temperatures can damage the plant and cause it to produce inferior heads. To protect cauliflower from frost, cover it with a frost cloth or plastic when the temperature drops below freezing.
Humidity
Cauliflower prefers moderate humidity levels, around 50% to 70%. High humidity can promote the development of diseases, such as fungal infections, while low humidity can result in poor head formation. Adequate air circulation and spaced-out planting can help minimize humidity-related issues.
Rainfall and Watering
Irrigation is essential for cauliflower growth, especially during its early stages. The soil should be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases, while underwatering can cause the heads to become dry and stunted. Providing the right amount of water, whether through rain or irrigation, is crucial for a healthy cauliflower crop.
By understanding and considering these climate factors, you can create the optimal growing conditions for your cauliflower plants. This will ensure that they thrive and produce high-quality, tasty heads that can be enjoyed in various culinary dishes.
Preparing the Soil for Growing Cauliflower
Proper soil preparation is crucial for successful growth of cauliflower. By ensuring the right soil conditions, you can provide the necessary nutrients and optimal environment for the plants to thrive. Here are a few steps to prepare the soil for growing cauliflower:
1. Soil Testing
Before planting cauliflower, it is important to test the soil to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Cauliflower prefers a slightly acidic soil with a pH range between 6.0 and 7.0. A soil test will also help you identify any deficiencies or excesses of nutrients.
2. pH Adjustment
If the soil test reveals that the pH level is not within the preferred range, you can adjust it by adding amendments. To lower the pH level, you can incorporate organic materials like compost, peat moss, or sulfur. If the soil is too acidic, you can increase the pH level by adding lime.
3. Soil Enrichment
Cauliflower plants require nutrient-rich soil to grow well. To enrich the soil, you can add organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold. These additions will provide essential nutrients, improve soil structure, and promote microbial activity.
4. Weed Removal
Before planting cauliflower, it is important to remove any weeds or grass from the designated area. Weeds compete with the cauliflower plants for nutrients and water, which can hinder their growth. Regular weeding throughout the growing season is also recommended to prevent weed interference.
5. Soil Drainage
Cauliflower plants prefer well-drained soil. To ensure proper drainage, you can amend the soil by adding sand or organic matter. This will prevent waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases.
6. Bed Preparation
Prepare the planting bed by loosening the soil to a depth of 12-18 inches using a garden fork or tiller. Remove any large clumps or rocks that may hinder root growth. Level the soil surface using a rake to create a smooth and even bed for planting.
7. Mulching
After planting the cauliflower seedlings, it is beneficial to apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plants. Mulching helps to maintain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and insulate the plants’ roots.
By following these steps and providing proper soil preparation, you can create an ideal environment for growing healthy and productive cauliflower plants.
Sowing Seeds and Transplanting Cauliflower
Starting cauliflower from seeds is the most common method for growing this vegetable. Follow these steps to successfully sow seeds and transplant cauliflower:
1. Choosing the Right Time

Cauliflower is a cool-season crop and prefers cool temperatures for optimum growth. Start sowing your cauliflower seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost date in your area. This will allow the seedlings to establish before transplanting them into the garden.
2. Preparing the Soil
Cauliflower plants thrive in well-draining, fertile soil. Before planting, prepare the soil by loosening it with a garden fork or tiller. Remove any rocks or debris and amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve its nutrient content.
3. Sowing the Seeds
Fill seed trays or pots with a seed-starting mix. Moisten the mix before sowing the seeds to ensure good germination. Plant the cauliflower seeds about ¼ inch deep and space them 2-3 inches apart. Cover the seeds lightly with more seed-starting mix and gently press them down.
4. Providing Ideal Growing Conditions
Place the seed trays in a warm location with ample sunlight or under grow lights. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Maintain a temperature range of 60-70°F (15-21°C) for optimal germination. The seeds should sprout within 7-10 days.
5. Transplanting the Seedlings
Once the cauliflower seedlings have grown 2-3 true leaves, they are ready to be transplanted into the garden. Harden off the seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions over a span of 7-10 days. Choose a cloudy or overcast day for transplanting to minimize transplant shock.
6. Digging the Planting Holes
Dig planting holes in the garden bed that are slightly larger than the root ball of the seedlings. Space the holes 18-24 inches apart to provide adequate room for the mature cauliflower heads to develop. Ensure the planting holes are evenly spaced in rows.
7. Transplanting the Seedlings
Gently remove the cauliflower seedlings from their containers, being careful not to disturb the roots. Place each seedling in a planting hole and backfill with soil. Firmly press the soil around the roots to eliminate any air pockets. Water the seedlings immediately after transplanting to help them establish in their new environment.
Following these steps will help you successfully sow cauliflower seeds and transplant the seedlings into your garden. With proper care and attention, you will soon be able to enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious and nutritious cauliflower heads.
Caring for Cauliflower Plants
Cauliflower plants require special care to ensure healthy growth and a bountiful harvest. Here are some important tips for caring for your cauliflower plants:
1. Planting and spacing
When planting cauliflower, make sure to choose a location with full sun exposure and well-draining soil. Cauliflower plants need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. Space the plants about 18-24 inches apart to allow for proper airflow and prevent overcrowding.
2. Watering
Proper watering is crucial for cauliflower plants. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. The best way to water cauliflower is deeply and infrequently. Water thoroughly, allowing the water to penetrate the soil to a depth of 6-8 inches. A regular watering schedule, especially during dry periods, will help prevent stress and promote healthy growth.
3. Mulching
Mulching around cauliflower plants can help conserve moisture, reduce weed growth, and maintain a more even soil temperature. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, around the base of the plants, taking care not to cover the crown. This will also help prevent soil from splashing onto the leaves, reducing the risk of disease.
4. Fertilizing
Cauliflower plants are heavy feeders and require a steady supply of nutrients. Before planting, incorporate well-rotted compost or aged manure into the soil to improve fertility. Once the plants are established, you can apply a balanced fertilizer every 3-4 weeks. Avoid using high-nitrogen fertilizers, as this can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of the cauliflower heads.
5. Pest and disease control
Cauliflower plants can be susceptible to various pests and diseases, including cabbage worms, aphids, and fungal diseases. Monitor your plants regularly for signs of infestation or infection. Handpick any insects you find or use organic insecticides if necessary. To prevent diseases, practice crop rotation and avoid planting cauliflower or other brassicas in the same location year after year.
6. Harvesting
Knowing when to harvest cauliflower is crucial to ensure the best flavor and texture. The heads should be firm, compact, and creamy white. Avoid overmature heads with loose curds or signs of discoloration. Cut the head off with a sharp knife, leaving a few outer leaves attached to protect the curd. Harvesting should be done in the morning when the heads are cool and the dew has dried.
By following these care tips, you can enjoy a successful cauliflower harvest and delicious homegrown cauliflower from your garden.
Common Pests and Diseases Affecting Cauliflower
Cauliflower plants are susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases, which can hinder their growth and overall health. It is important to be aware of these common issues and take proactive measures to prevent or treat them. Below are some of the most common pests and diseases that can affect cauliflower plants:
Pests:
- Cabbage Worms: These green caterpillars feed on cauliflower leaves, causing damage to the foliage. To prevent cabbage worms, use row covers, apply organic insecticides, or handpick the worms.
- Aphids: Aphids are small insects that suck sap from the leaves, causing them to turn yellow and stunt the growth of the cauliflower plants. Regularly inspect the plants for signs of aphids and use insecticidal soap or neem oil sprays to control the infestation.
- Cabbage Loopers: These caterpillars create holes in cauliflower leaves and can cause significant damage. Handpicking and using organic insecticides can help manage cabbage looper infestations.
- Cabbage Root Flies: The larvae of these flies feed on cauliflower roots, causing stunted growth and wilting. To prevent cabbage root fly infestations, use row covers and keep the soil well-drained.
- Slugs and Snails: These slimy creatures can feed on cauliflower leaves, leaving behind large holes. Use organic slug and snail controls, such as copper barriers or iron phosphate baits, to protect cauliflower plants from these pests.
Diseases:
- Clubroot: Clubroot is a soil-borne disease that causes swelling and deformity in the roots, inhibiting the plant’s ability to take up nutrients. To prevent clubroot, practice crop rotation, improve soil drainage, and avoid over-watering.
- Black Rot: Black rot is a bacterial disease that affects the leaves, causing yellowing, wilting, and blackening of the veins. To prevent black rot, ensure good air circulation around the plants and promptly remove and destroy infected plants.
- Downy Mildew: Downy mildew is a fungal disease that causes yellow or brown spots on cauliflower leaves. To prevent downy mildew, plant disease-resistant varieties, provide adequate spacing between plants, and avoid overhead watering.
- Fusarium Yellows: Fusarium yellows is a fungal disease that causes stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and wilting. Use disease-resistant varieties and practice good sanitation to prevent the spread of fusarium yellows.
- White Mold: White mold is a fungal disease that forms white fuzzy growth on cauliflower leaves and stems. To prevent white mold, provide good air circulation, avoid overhead watering, and remove infected plants.
By taking preventive measures, monitoring your plants regularly, and promptly treating any pest or disease issues, you can help ensure the health and successful growth of your cauliflower plants.
Harvesting and Storing Cauliflower
Harvesting:
- Timing: Cauliflower is ready to be harvested when the heads are compact, firm, and reach their full size. This usually occurs around 65-75 days after transplanting.
- Cutting the head: To harvest cauliflower, use a sharp knife to cut the head off the plant, leaving a few inches of stem attached to the head. It is important to cut the head before the florets start to loosen or open up.
- Leaves: Remove the outer leaves of the plant and discard them. The inner leaves can be left attached to the head.
Storing:
- Cooling: Cauliflower should be cooled immediately after harvest to maintain its freshness and flavor. Place the heads in the refrigerator at a temperature of around 32-36°F (0-2°C).
- Moisture: Cauliflower heads should be stored in perforated plastic bags or wrapped in a damp cloth or paper towel to maintain moisture levels. This will prevent the heads from drying out.
- Shelf life: Properly stored cauliflower can last for up to 2 weeks in the refrigerator.
Tips for Quality Storage:
- Avoid washing: Do not wash cauliflower before storing it, as the moisture can promote rotting.
- Separate heads: If you have multiple cauliflower heads, store them separately to avoid bruising or crushing.
- Check regularly: Check stored cauliflower regularly for any signs of spoilage, such as mold or soft spots. Remove any affected heads to prevent the spread of rot.
“Question-Answer”
What are some tips for choosing the right variety of cauliflower?
When choosing a variety of cauliflower, it is important to consider factors such as the time of year, climate, and personal preferences. If you are growing cauliflower in a colder climate, look for varieties that are cold-hardy. For warmer climates, choose heat-tolerant varieties. Consider the size and color of the cauliflower head as well, as there are varieties that produce larger heads or have different colors like purple or green.
How often should I water my cauliflower plants?
Cauliflower plants require a consistent supply of moisture to grow properly. It is recommended to water them deeply once a week, providing about 1 to 1.5 inches of water. However, you should adjust the frequency and amount of watering based on the weather conditions. During hot and dry periods, you may need to water more frequently to keep the soil moist.
What are some nutrient tips for growing cauliflower?
Cauliflower plants benefit from a balanced supply of nutrients. Before planting, it is important to amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve its fertility. During the growing season, you can provide additional nutrients by using a slow-release fertilizer or applying water-soluble fertilizers every 3-4 weeks. Pay attention to the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels, as cauliflower plants require these nutrients in different amounts during different stages of growth.
Is it possible to grow cauliflower year-round?
While cauliflower is typically grown as a cool-season crop, it is possible to extend the growing season and have cauliflower year-round by using different techniques. This can be done by starting seeds indoors and transplanting them outside at the appropriate time, or by using protective coverings such as row covers or cold frames to shield the plants from extreme temperatures. Additionally, some varieties are more tolerant of heat or cold, so choosing the right variety can also help in growing cauliflower year-round.
How long does it take for cauliflower to mature?
The time it takes for cauliflower to mature can vary depending on the variety and growing conditions. On average, cauliflower takes about 55-100 days from transplanting to reach maturity. However, some varieties may mature faster or slower than this. Keep in mind that cauliflower heads should be harvested when they are firm and compact, as leaving them on the plant for too long can result in a bitter taste or the formation of loose curds.
Can I grow cauliflower in containers?
Yes, cauliflower can be successfully grown in containers. When choosing a container, make sure it is at least 12-16 inches deep to accommodate the root system. Use a well-draining potting mix and provide regular watering to keep the soil moist. Keep in mind that container-grown cauliflower may require more attention and care compared to plants grown in the ground, as they may dry out more quickly and require more frequent feeding.







