- Identify Phytophthora Symptoms
- Use Biofungicides for Preventive Treatment
- Apply Homemade Garlic Fungicide Spray
- Materials Needed:
- Instructions:
- Application Tips:
- Try Neem Oil as a Natural Fungicide
- Benefits of using neem oil as a fungicide:
- Precautions when using neem oil:
- Control Soil Moisture Levels
- Tips to control soil moisture:
- Rotate Crops and Practice Crop Diversity
- Enhance Soil Health with Organic Amendments
- 1. Compost
- 2. Manure
- 3. Cover Crops
- 4. Peat Moss
- 5. Worm Castings
- 6. Biochar
- 7. Bone Meal
- “Question-Answer”
- What is Phytophthora and why is it a problem?
- What are some signs that indicate a plant may be infected with Phytophthora?
- Are there any natural methods to protect plants against Phytophthora?
- How can garlic be used as a natural fungicide against Phytophthora?
- What is compost tea and how can it help protect plants against Phytophthora?
- Why is crop rotation an effective method to protect against Phytophthora?
- “Video” Top 10 Foods To Detox Your Kidneys
Phytophthora is a common plant disease that can wreak havoc on gardens, crops, and landscapes. This destructive pathogen can quickly spread and cause severe damage, leading to significant economic losses for growers. While there are chemical treatments available, many people prefer to use natural, folk remedies to protect their plants against Phytophthora.
In this article, we will explore seven effective and proven folk tips to safeguard your plants from Phytophthora. These remedies have been passed down through generations and have stood the test of time. Incorporating these tips into your gardening routine can help prevent and control the spread of this devastating disease.
1. Garlic: Add some garlic cloves to a spray bottle filled with water and let it sit overnight. The next day, spray the mixture on your plants, focusing on the leaves and stems. Garlic contains natural antimicrobial properties that can inhibit the growth of Phytophthora.
2. Baking Soda: Create a solution by mixing a tablespoon of baking soda in a gallon of water. Spray this mixture on your plants every two weeks to deter Phytophthora. Baking soda alters the pH of the plant surface, making it less hospitable to the pathogen.
3. Neem Oil: Neem oil is a natural pesticide that can be used to protect plants from various diseases, including Phytophthora. Dilute neem oil according to the instructions on the package, and apply it to your plants every two weeks. Neem oil acts as a repellent and disrupts the growth and reproduction of the pathogen.
4. Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around your plants can help prevent Phytophthora. Mulch acts as a barrier, preventing the pathogen from splashing onto the plant’s leaves and stems during rain or irrigation. Additionally, mulch helps retain moisture in the soil, promoting overall plant health.
5. Copper Sulfate: Mix copper sulfate with water according to the instructions on the package, and spray it on your plants. Copper sulfate has been used for decades as a fungicide to control numerous plant diseases, including Phytophthora.
6. Proper Planting Techniques: Planting your crops or ornamental plants at the correct depth and spacing is crucial in preventing Phytophthora. Proper spacing allows for good air circulation, which helps keep the plant’s foliage dry and reduces the risk of infection. Avoid planting too deeply, as this can increase the likelihood of pathogen attack.
7. Crop Rotation: Implementing crop rotation can break the cycle of Phytophthora. Avoid planting susceptible crops in the same location year after year. Instead, rotate crops with different plant families to disrupt the pathogen’s life cycle and reduce the risk of infection.
Disclaimer: While these folk remedies have shown effectiveness against Phytophthora, they may not completely eradicate the disease. It is always recommended to consult with a professional or experienced gardener for a comprehensive management plan.
By incorporating these seven effective folk tips into your gardening practices, you can help protect your plants from Phytophthora and promote overall plant health. Remember to be consistent and vigilant in your efforts, as prevention is key in managing this destructive pathogen.
Identify Phytophthora Symptoms
Phytophthora is a common plant disease that affects a wide range of crops and plants. It is caused by a group of water molds, which thrive in wet and humid conditions. Being able to identify the symptoms of Phytophthora early on is crucial for effective management and control. Here are some key symptoms to look out for:
- Root Rot: One of the most common symptoms of Phytophthora is root rot. Infected plants often display darkened, mushy roots that are a sign of decay. The roots may also have a foul odor.
- Leaf Spots: Phytophthora can also cause leaf spots, which appear as dark, water-soaked lesions on the leaves. These spots may gradually enlarge and turn brown or gray over time. In some cases, the spots can cause the leaves to wilt and die.
- Stem Canker: Another symptom of Phytophthora infection is the development of stem cankers. These cankers are sunken, discolored areas on the stem that may ooze a sticky sap. The cankers can restrict the flow of water and nutrients, leading to wilting and dieback of the affected plant parts.
- Fruit Rots: When Phytophthora affects fruit-bearing plants, it can cause fruit rot. Infected fruits may develop soft, water-soaked spots that rapidly decay and become covered in a fuzzy mold. The fruits may eventually shrivel up and drop from the plant.
In addition to these symptoms, plants affected by Phytophthora may also exhibit stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and overall decline in health. It is important to note that the symptoms may vary depending on the specific plant species and the stage of infection.
If you notice any of these symptoms on your plants, it is important to take action quickly to prevent the spread of Phytophthora. Implementing proper cultural practices such as improving drainage, avoiding over-irrigation, and practicing crop rotation can help reduce the risk of Phytophthora infection. Additionally, using resistant plant varieties and applying appropriate fungicides can also be effective management strategies.
Use Biofungicides for Preventive Treatment
One effective way to protect against Phytophthora is by using biofungicides. Biofungicides are substances derived from living organisms that are used to control plant diseases. They work by either inhibiting the growth of the pathogen or by stimulating the plant’s natural defense mechanisms.
There are different types of biofungicides available in the market, and they can be used preventively to protect plants against Phytophthora. Here are some popular biofungicides that have been proven effective:
- Bacillus subtilis: This bacterium produces antibiotics that inhibit the growth of Phytophthora pathogens. It can be applied as a foliar spray or as a soil drench.
- Trichoderma species: These fungi have the ability to parasitize and kill Phytophthora pathogens. They can be applied as a soil drench or as a seed treatment.
- Gliocladium species: These fungi produce enzymes that can break down the cell walls of Phytophthora pathogens. They can be applied as a soil drench or as a foliar spray.
When using biofungicides, it is important to read and follow the instructions on the label for proper application. In general, biofungicides should be applied preventively before the appearance of Phytophthora symptoms. Regular applications may be necessary to maintain protection.
In addition to using biofungicides, it is also important to practice good cultural practices to prevent the spread of Phytophthora. This includes proper sanitation, avoiding waterlogged conditions, and selecting resistant plant varieties.
By using biofungicides as part of an integrated disease management program, you can effectively protect your plants against Phytophthora and maintain a healthy garden.
Apply Homemade Garlic Fungicide Spray
Garlic is known for its antifungal properties and can be used as a natural fungicide to protect plants from Phytophthora. Making a homemade garlic fungicide spray is simple and can be an effective way to prevent and control fungal diseases.
Materials Needed:
- 3-4 garlic bulbs
- 1 quart of water
- Blender or food processor
- Strainer or cheesecloth
- Spray bottle
Instructions:
- Peel and chop the garlic cloves into small pieces.
- Put the chopped garlic cloves in a blender or food processor.
- Add the water to the blender or food processor.
- Blend or process the garlic and water mixture until it becomes a smooth liquid.
- Strain the liquid using a strainer or cheesecloth to remove any solid particles.
- Transfer the liquid into a spray bottle.
- Apply the homemade garlic fungicide spray to the affected plants.
Application Tips:
- Apply the garlic fungicide spray to the plants in the early morning or late afternoon to avoid the hot sun.
- Make sure to cover both sides of the plant’s leaves thoroughly with the spray.
- Repeat the application every 7-10 days or after significant rainfall.
Using a homemade garlic fungicide spray can help protect plants from Phytophthora and other fungal diseases. It is a natural and cost-effective alternative to chemical fungicides.
Try Neem Oil as a Natural Fungicide

When it comes to protecting your plants from phytophthora, neem oil is a natural and effective solution. Neem oil is derived from the seeds of the neem tree, which is native to India. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its antifungal properties.
Neem oil works by disrupting the life cycle of the fungi that causes phytophthora. When applied to plants, it coats the leaves and stems, creating a barrier that prevents the fungi from infecting the plant. It also has pesticidal properties, which can help control other pests that may contribute to the spread of phytophthora.
To use neem oil as a fungicide, mix it with water according to the instructions on the label. Then, spray the mixture onto the leaves and stems of the infected plants, ensuring thorough coverage. It’s important to apply neem oil at the first sign of infection and continue to apply it regularly to prevent further spread.
Neem oil is safe to use on most plants, but it’s always a good idea to test it on a small area of the plant first to make sure there are no adverse reactions. It is also important to note that neem oil can be harmful to bees and other beneficial insects, so it’s best to avoid using it when bees are actively foraging.
Benefits of using neem oil as a fungicide:

- Effective against phytophthora and other plant diseases caused by fungi
- Natural and non-toxic to humans and pets
- Can be used on a wide variety of plants
- Environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic fungicides
Precautions when using neem oil:
- Read and follow the instructions on the label carefully
- Test on a small area of the plant before applying to the entire plant
- Avoid using when bees are actively foraging
- Store neem oil in a cool, dry place away from children and pets
By using neem oil as a natural fungicide, you can protect your plants from phytophthora and other fungal diseases without resorting to harsh chemicals. Give it a try and see the difference it can make in your garden!
Control Soil Moisture Levels
Maintaining proper soil moisture levels is crucial in preventing the spread of Phytophthora. This pathogen thrives in wet and waterlogged conditions, making it essential to control the moisture content of the soil.
Tips to control soil moisture:

- 1. Use well-draining soil: Ensure that the soil you use in your garden or pots has good drainage capabilities. This allows excess water to seep away, preventing water accumulation.
- 2. Avoid overwatering: It is important to water your plants appropriately, avoiding both underwatering and overwatering. Overwatering can create an environment suitable for Phytophthora growth.
- 3. Water in the morning: Watering your plants in the morning allows excess moisture to evaporate throughout the day, reducing the chances of waterlogging.
- 4. Mulch your plants: Apply a layer of mulch around your plants to help retain soil moisture. However, make sure not to overmulch, as it can lead to excessive moisture accumulation.
By maintaining proper soil moisture levels, you can create an unfavorable environment for Phytophthora and minimize the risk of plant infections.
Rotate Crops and Practice Crop Diversity
Rotating crops and practicing crop diversity are effective methods to protect against Phytophthora. Phytophthora is a devastating plant disease that can cause severe damage to crops. By regularly rotating crops and diversifying the types of crops planted, farmers can reduce the risk of Phytophthora outbreaks and minimize its impact.
Rotating crops involves changing the type of crop planted in a particular area each growing season. This practice helps break the disease cycle by preventing the buildup of Phytophthora pathogens in the soil. When the same crop is planted in the same area year after year, the pathogens that cause Phytophthora can accumulate in the soil and infect new plants. By rotating crops, farmers can disrupt this cycle and reduce the risk of infection.
Crop diversity is another important strategy for protecting against Phytophthora. Planting a variety of crop types helps reduce the overall vulnerability of the farm to diseases. Different crops have different susceptibility to Phytophthora, so by diversifying the types of crops planted, farmers can lower the chances of a widespread outbreak.
By implementing crop rotation and practicing crop diversity, farmers can create a more resilient farming system that is less prone to Phytophthora outbreaks. These strategies can help preserve crop health and increase overall productivity.
Enhance Soil Health with Organic Amendments
Organic amendments are a great way to improve soil health and fertility. By adding organic matter to the soil, you can boost its nutrient content, water-holding capacity, and overall structure. Here are some effective organic amendments that you can use to enhance your soil health:
1. Compost
Compost is a valuable organic amendment that is rich in nutrients. It improves soil structure, enhances moisture retention, and promotes aeration. You can make your own compost by collecting kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials. Apply compost to your soil by spreading a layer of it and gently mixing it in.
2. Manure
Animal manure is an excellent source of organic matter and nutrients. It adds nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to the soil, which are essential for plant growth. Before applying manure, it is important to compost it or let it age for several months to reduce the risk of introducing pathogens to your plants.
3. Cover Crops
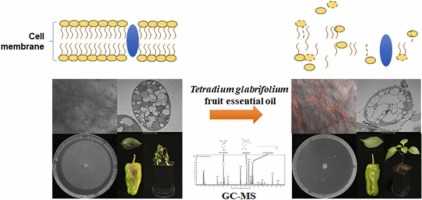
Cover crops are crops that are grown specifically to improve soil health. They are usually grown during periods when the main crop is not growing. Cover crops help to prevent soil erosion, increase organic matter content, and fix nitrogen in the soil. Examples of cover crops include clover, buckwheat, and vetch.
4. Peat Moss
Peat moss is a lightweight organic amendment that improves soil structure and water retention. It is particularly beneficial for sandy soils, which tend to drain quickly. Peat moss can be added to the soil by spreading a layer and mixing it in thoroughly.
5. Worm Castings
Worm castings, also known as vermicompost, are nutrient-rich organic amendments that enhance plant growth. They improve soil structure, increase nutrient availability, and suppress diseases. Worm castings can be applied to the soil by mixing them in or by using them as a top dressing.
6. Biochar
Biochar is a type of charcoal that is made from burning organic material in a low-oxygen environment. It improves soil fertility by increasing nutrient retention and enhancing microbial activity. Biochar can be incorporated into the soil by mixing it in or by using it as a soil amendment.
7. Bone Meal
Bone meal is a natural source of phosphorus and calcium. It is derived from animal bones and is commonly used to improve soil fertility. Bone meal can be added to the soil before planting or as a side dressing during the growing season.
When using organic amendments, it is important to follow recommended application rates and ensure that they are properly incorporated into the soil. Regular application of organic amendments will help to maintain and improve soil health over time.
“Question-Answer”
What is Phytophthora and why is it a problem?
Phytophthora is a type of fungus-like organism that can cause diseases in plants. It thrives in moist conditions and can cause significant damage to crops, gardens, and trees. It is a problem because it can lead to reduced yields, loss of plants, and economic losses for farmers and gardeners.
What are some signs that indicate a plant may be infected with Phytophthora?
Some signs that indicate a plant may be infected with Phytophthora include wilting, yellowing or browning of leaves, root rot, and stunted growth. Plants may also show discoloration on the stems or have water-soaked lesions. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to take action to prevent the spread of the disease.
Are there any natural methods to protect plants against Phytophthora?
Yes, there are several natural methods that can help protect plants against Phytophthora. Some folk tips include using garlic as a natural fungicide, applying compost tea to boost plant immunity, and practicing crop rotation to reduce the risk of disease. These methods have been proven to be effective in preventing and controlling Phytophthora infections.
How can garlic be used as a natural fungicide against Phytophthora?
Garlic contains compounds that have antifungal properties and can help protect plants against Phytophthora. To make a garlic spray, you can crush several cloves of garlic and steep them in water overnight. Then, strain the mixture and spray it on the plants. This can help prevent the spread of the disease and protect the plants from infection.
What is compost tea and how can it help protect plants against Phytophthora?
Compost tea is a liquid fertilizer that is made by steeping compost or vermicompost in water. It contains beneficial microorganisms that can enhance plant immunity and protect against diseases like Phytophthora. To use compost tea, you can apply it to the soil around the plants or spray it on the foliage. This can help boost the plant’s defenses and reduce the risk of infection.
Why is crop rotation an effective method to protect against Phytophthora?
Crop rotation is an effective method to protect against Phytophthora because it helps prevent the buildup of pathogens in the soil. By rotating crops and not planting susceptible plants in the same area year after year, the risk of infection can be greatly reduced. This breaks the disease cycle and limits the opportunity for Phytophthora to multiply and spread.
“Video”
Top 10 Foods To Detox Your Kidneys
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PxXacC4C1WE







