- Causes of Soil Salinization
- 1. Natural causes:
- 2. Human-induced causes:
- Natural Causes
- Human Activities
- Effective Methods to Improve Soil Fertility
- Organic Matter Addition
- Proper Irrigation Management
- 1. Watering techniques
- 2. Water source management
- 3. Soil moisture monitoring
- 4. Crop rotation and cover crops
- 5. Drainage and leaching
- Soil Testing and Nutrient Analysis
- The Importance of Soil Testing
- The Soil Testing Process
- Interpreting Soil Test Results
- Conclusion
- Use of Cover Crops
- Benefits of Cover Crops:
- Types of Cover Crops:
- Management of Cover Crops:
- Optimal Use of Fertilizers
- Soil Testing
- Appropriate Fertilizer Selection
- Correct Fertilizer Application
- Proper Timing
- Split Application
- Avoid Overfertilization
- Proper Nutrient Management
- Regular Monitoring
- “Question-Answer”
- What is soil salinization?
- What causes soil salinization?
- How does soil salinization affect plant growth?
- What are the effective methods to improve soil fertility?
- Can soil salinization be reversed?
- What are the long-term consequences of soil salinization?
- “Video” The easiest and most efficient way to make the soil fertile
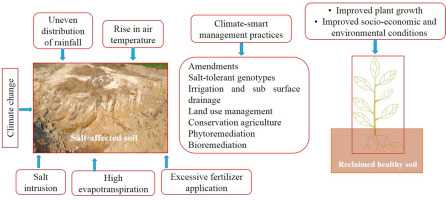
Soil salinization is a major problem in agricultural areas around the world, resulting in reduced crop yields and the degradation of soil quality. It occurs when the salt content in the soil exceeds the level that is tolerable for plant growth. There are several causes of soil salinization, including natural and human-induced factors.
Natural causes of soil salinization include the presence of salt deposits in the soil, which can be brought to the surface through natural processes such as evaporation and capillary action. Additionally, high levels of salt can be found in certain types of soils, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where rainfall is low and evaporation is high. These natural factors contribute to the accumulation of salt in the soil over time.
Human activities can also exacerbate soil salinization. The excessive use of fertilizers and irrigation water can lead to an increase in the salt content of the soil. When irrigation water contains high levels of salt, it can leave behind salt deposits in the soil as it evaporates. Similarly, the use of fertilizers that contain high concentrations of salt can contribute to the salt accumulation in the soil.
To improve soil fertility and reduce the effects of soil salinization, several effective methods can be employed. One such method is the use of drainage systems to remove excess water from the soil and prevent the buildup of salt. These systems can include open ditches, underground pipes, or tile drains, all of which help to lower the water table and improve the drainage of the soil.
Another effective method is the use of soil amendments, such as gypsum, which can help to leach out the excess salts from the soil. Gypsum works by replacing the sodium ions that are responsible for soil salinity with calcium ions, which are less harmful to plant growth. Additionally, adding organic matter to the soil can improve its structure and water-holding capacity, reducing the effects of salt accumulation.
In conclusion, soil salinization is a major issue affecting agricultural areas worldwide, and it is caused by both natural and human-induced factors. However, there are effective methods to improve soil fertility and reduce the effects of salinization, including the use of drainage systems and soil amendments. By employing these methods, farmers and landowners can mitigate the negative effects of soil salinization and maintain healthy and productive soils for sustainable agriculture.
Causes of Soil Salinization
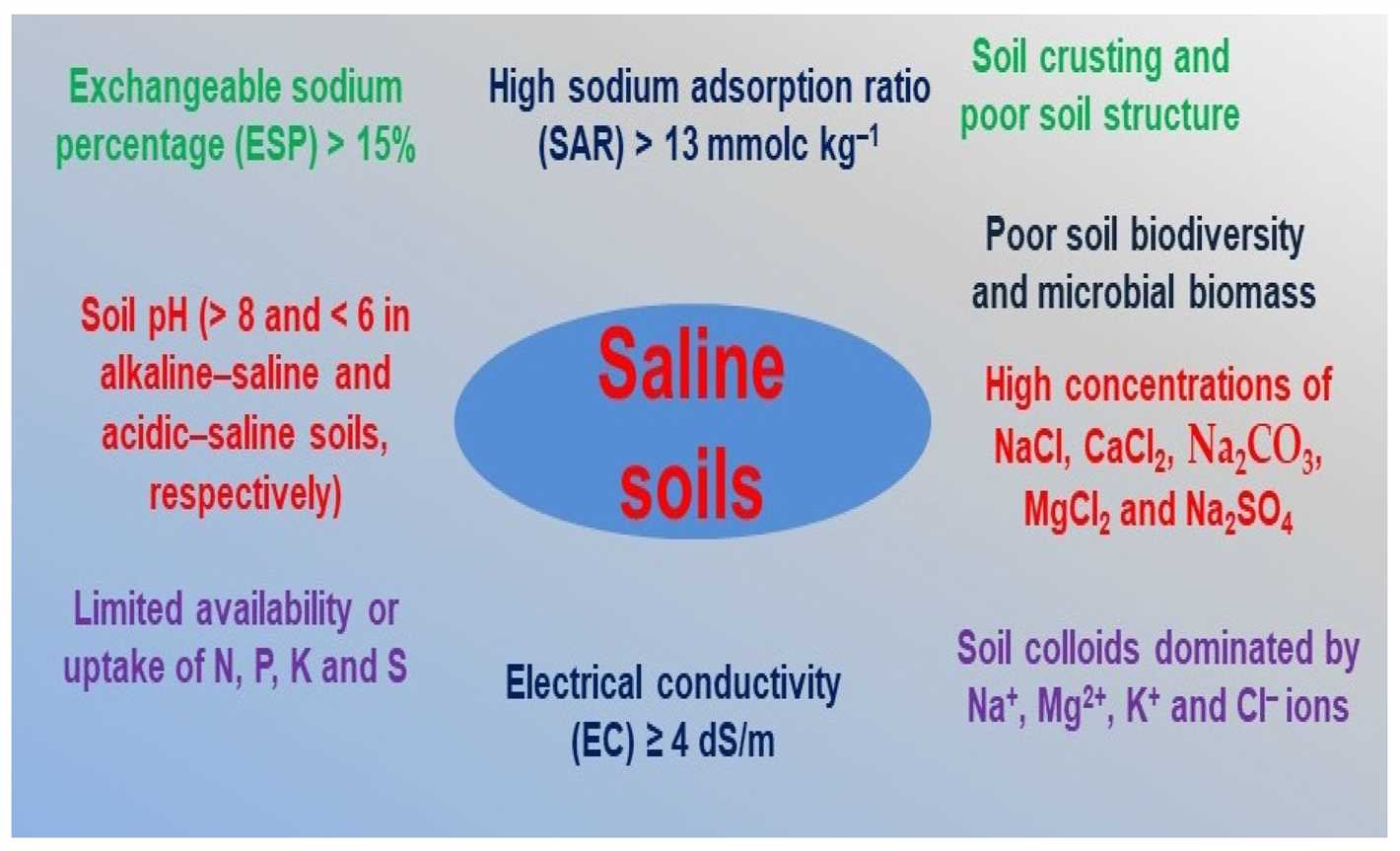
Soil salinization refers to the accumulation of salts in the soil, which can have detrimental effects on soil fertility and plant growth. There are several main causes of soil salinization:
1. Natural causes:
- Geological factors: Some soils naturally contain high levels of salts due to geological processes such as weathering of rocks and minerals.
- Climate: Arid and semi-arid regions with low rainfall and high evaporation rates are prone to soil salinization. As water evaporates, salts are left behind, gradually accumulating in the soil.
2. Human-induced causes:
- Improper irrigation practices: Over-irrigation or poor drainage can lead to waterlogging, which brings salts to the soil surface. As the water evaporates, salts are left behind, contributing to soil salinity.
- Use of saline water for irrigation: The use of saline water for irrigation can introduce high levels of salts into the soil.
- Excessive use of fertilizers: Improper use of fertilizers, especially those that contain high levels of salts, can contribute to soil salinity.
- Deforestation and vegetation removal: Removing vegetation cover from an area can disrupt the natural water cycle, leading to increased soil salinity.
- Industrial activities: Certain industries produce waste materials that contain high levels of salts. Improper disposal of these wastes can result in soil salinization.
- Urbanization: Urban development can lead to soil salinization due to the construction of impermeable surfaces, which disrupts natural drainage patterns.
Understanding the causes of soil salinization is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and mitigate its effects. By addressing these causes, it is possible to improve soil fertility and ensure sustainable agriculture practices.
Natural Causes
Soil salinization can occur naturally due to various factors. Some of the natural causes of soil salinization include:
- Geological Factors: Some areas are naturally prone to high levels of salt in the soil due to geological factors. These areas may have salt deposits, such as salt flats or salt lakes, which can result in saline soils.
- Climate: Arid and semi-arid regions that receive low rainfall and high temperatures are more prone to soil salinization. In such regions, the limited rainfall is not sufficient to leach the salts from the soil, leading to their accumulation over time.
- Topography: The topography of an area can also influence the occurrence of soil salinization. Areas with poor drainage, such as low-lying regions or areas with high water tables, are at a higher risk of salinization as the water carrying the salts tends to accumulate instead of draining away.
- Groundwater: The quality of groundwater can also contribute to soil salinization. If the groundwater is high in salt content, it can seep into the soil and gradually increase the salt levels, especially in areas with shallow groundwater tables.
- Natural Disturbance: Natural disturbances like floods or tidal waves can introduce saltwater into the soil. This saltwater intrusion can lead to a temporary increase in soil salinity, affecting the fertility of the soil.
Understanding the natural causes of soil salinization is crucial in developing effective methods to improve soil fertility and prevent further salinization.
Human Activities
Human activities are significant contributors to soil salinization and can have detrimental effects on soil fertility. These activities include:
- Excessive irrigation: Over-irrigation or improper irrigation techniques can lead to the accumulation of salt in the soil. When water evaporates, it leaves behind the salts, which can gradually build up over time and increase soil salinity.
- Poor drainage systems: Inadequate drainage can cause water to accumulate in the soil, leading to waterlogging and the subsequent increase in salt concentration. The excessive presence of water restricts plant root growth and function, affecting their ability to take up essential nutrients.
- Improper fertilization practices: The misuse or excessive use of fertilizers can contribute to soil salinization. Fertilizers contain high levels of salts, which can accumulate in the soil if not properly managed. Additionally, using fertilizers without considering soil nutrient content can lead to imbalances and reduced fertility.
- Deforestation: Clearing of forests and vegetation can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and result in increased soil salinity. The roots of plants and trees help anchor the soil and maintain its structure, preventing erosion and promoting healthy soil composition.
- Overgrazing: Intensive or excessive grazing by livestock can lead to soil compaction and erosion, making the soil more susceptible to salinization. The trampling of animals and removal of vegetation cover can disturb the soil structure, increase soil exposure to salt, and reduce water infiltration.
It is crucial to address these human activities to prevent further soil salinization and maintain soil fertility. Implementing proper irrigation techniques, promoting effective drainage systems, practicing sustainable fertilization methods, and protecting natural vegetation are essential steps to improve soil quality and prevent salinization.
Effective Methods to Improve Soil Fertility
Soil fertility is a crucial aspect of agriculture as it directly affects the productivity and quality of crops. Here are some effective methods to improve soil fertility:
Organic Matter Addition:
Adding organic matter, such as compost or manure, to the soil can significantly increase its fertility. Organic matter improves soil structure, enhances water retention capacity, and provides essential nutrients to plants.
Cover Crops:
Planting cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, during fallow periods can help improve soil fertility. Cover crops prevent erosion, suppress weed growth, and add organic matter to the soil when they are incorporated.
Crop Rotation:
Practicing crop rotation can prevent the depletion of specific nutrients in the soil. Different crops have different nutrient requirements, so rotating crops helps maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the soil.
Green Manure:
Green manure refers to crops that are grown specifically to be incorporated into the soil as organic matter. These crops, such as clover or rye grass, improve soil structure, add nutrients, and enhance microbial activity.
Soil Testing and Nutrient Management:
Regular soil testing is essential to assess nutrient levels in the soil. Based on the test results, appropriate fertilizers can be applied to ensure adequate nutrient availability for optimal plant growth.
Conservation Tillage:
Implementing conservation tillage practices, such as no-till or reduced tillage, can help improve soil fertility. Reduced disturbance of the soil minimizes erosion, retains organic matter, and promotes beneficial soil organisms.
Microbial Inoculants:
Applying microbial inoculants, such as mycorrhizal fungi or beneficial bacteria, can enhance soil fertility. These microorganisms form symbiotic relationships with plants, promoting nutrient uptake and improving soil structure.
Water Management:
Proper water management is crucial for maintaining soil fertility. Over-irrigation can lead to leaching of nutrients, while under-irrigation can cause nutrient deficiencies. Balancing irrigation and drainage helps optimize soil fertility.
Integrated Nutrient Management:
Using a combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers, along with other soil fertility practices, can be an effective approach. Integrated nutrient management aims to optimize nutrient availability while minimizing environmental impacts.
Soil Erosion Control:
Preventing soil erosion is essential for maintaining soil fertility. Erosion control measures, such as contour plowing or terracing, can help reduce soil loss and preserve the nutrient-rich topsoil.
By implementing these effective methods, farmers and gardeners can improve soil fertility, enhance crop productivity, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Organic Matter Addition
Organic matter addition is an effective method to improve soil fertility and reduce soil salinization. Adding organic matter to the soil helps to increase the organic carbon content and improves the soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability.
There are various sources of organic matter that can be added to the soil, such as compost, manure, cover crops, and crop residues. These organic materials provide a range of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth.
When organic matter is added to the soil, it acts as a sponge, absorbing and holding water, preventing excessive evaporation and helping to maintain a consistent soil moisture level. This is especially important in areas with high salt concentrations, as salt accumulates more easily in dry soils.
Moreover, organic matter addition promotes the development of beneficial soil microorganisms that help break down organic matter, release nutrients, and improve soil structure. These microorganisms aid in reducing the levels of salt in the soil by converting soluble salts into insoluble forms that are less harmful to plants.
It is recommended to apply organic matter before planting or during crop rotation to ensure its maximum benefits. The amount of organic matter to be added depends on various factors, including the soil type, crop requirements, and nutrient content. Farmers can conduct soil tests to determine the appropriate amount of organic matter needed for their specific conditions.
Overall, organic matter addition is an essential practice for maintaining soil fertility and combating soil salinization. It not only improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil but also helps to reduce the negative effects of salinity on crop growth and yield.
Proper Irrigation Management

Proper irrigation management is crucial for preventing soil salinization and maintaining soil fertility. Here are some effective methods to improve soil fertility through proper irrigation:
1. Watering techniques
- Use drip irrigation: Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and reducing the risk of soil salinization.
- Avoid over-watering: Excess irrigation can lead to waterlogged soil, which can increase salt concentration and hinder plant growth. Monitor soil moisture levels to determine the right amount of water to be applied.
- Apply water evenly: Uneven irrigation can result in localized salt accumulation. Ensure that water is distributed evenly across the entire field.
2. Water source management
- Monitor water quality: Saline water sources can contribute to soil salinization. Regularly test the water quality to assess its suitability for irrigation.
- Use low-salt water sources: Whenever possible, utilize low-salt water sources for irrigation to minimize the risk of salt accumulation in the soil.
- Treat saline water: If using saline water is unavoidable, consider adopting water treatment technologies such as desalination or reverse osmosis to remove excess salts before irrigation.
3. Soil moisture monitoring
- Install soil moisture sensors: Soil moisture sensors can provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, enabling precise irrigation scheduling.
- Implement irrigation scheduling: Develop an irrigation schedule based on crop water requirements and soil moisture readings to ensure optimal water use efficiency and prevent over-irrigation.
4. Crop rotation and cover crops
- Practice crop rotation: Crop rotation helps break the cycle of salt accumulation in the soil. Growing salt-tolerant crops in rotation with other crops can help mitigate soil salinization.
- Plant cover crops: Cover crops help reduce soil evaporation, prevent salt build-up in the topsoil, and improve soil structure and fertility.
5. Drainage and leaching
- Implement proper drainage: Poor drainage can lead to waterlogged conditions and promote salt accumulation in the root zone. Ensure that fields have adequate drainage systems to allow excess water to drain away.
- Practice leaching: Leaching involves applying excess water to flush out salts from the soil profile. It is particularly effective in areas with high rainfall or with naturally leachable soils.
By implementing these proper irrigation management practices, farmers and land managers can effectively prevent soil salinization and improve soil fertility, resulting in healthier crops and increased agricultural productivity.
Soil Testing and Nutrient Analysis
Soil testing is an essential tool for understanding the fertility levels and nutrient status of the soil. It provides valuable information that can guide farmers and land managers in making informed decisions about soil management practices.
The Importance of Soil Testing
- Assessing Soil Fertility: Soil testing allows farmers to determine the nutrient content of their soil and identify any deficiencies or imbalances that may affect plant growth.
- Optimizing Fertilizer Use: By knowing the nutrient status of the soil, farmers can apply fertilizers more efficiently, ensuring that plants receive the necessary nutrients without over-application.
- Preventing Environmental Contamination: Soil testing helps prevent the excessive use of fertilizers, which can lead to nutrient runoff and water pollution.
- Monitoring Soil Health: Regular soil testing provides a long-term record of soil fertility and enables land managers to monitor changes in soil health over time.
The Soil Testing Process
The soil testing process typically involves the following steps:
- Sample Collection: Soil samples are collected from various locations throughout the field, ensuring representative samples from different soil types and management zones.
- Sample Preparation: The soil samples are air-dried, crushed, and sieved to remove large particles and ensure uniformity.
- Laboratory Analysis: The prepared soil samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Various tests are conducted to determine the nutrient levels, pH, organic matter content, and other important soil properties.
- Data Interpretation: The laboratory provides a report with the analysis results. This information is then interpreted to understand the nutrient status of the soil and make appropriate recommendations for soil management.
Interpreting Soil Test Results
Soil test results are typically presented in tables or graphs, with recommended fertilizer application rates based on the nutrient levels in the soil. These recommendations take into account the specific crops being grown and the desired yield goals.
The interpretation of soil test results involves comparing the nutrient levels in the soil to appropriate nutrient sufficiency ranges. If the nutrient levels are below the sufficiency ranges, fertilizer application may be necessary. If the nutrient levels are above the sufficiency ranges, it may indicate potential nutrient imbalances or excessive fertilizer application.
Conclusion
Soil testing and nutrient analysis are crucial for effective soil management and optimizing crop production. By understanding the nutrient status of the soil, farmers can make informed decisions about fertilizer use, prevent environmental contamination, and monitor soil health over time.
Use of Cover Crops
Cover crops, also known as green manure or living mulch, are crops that are grown specifically to protect and improve the soil. They are typically planted between main crops and provide a number of benefits for soil fertility, erosion prevention, and weed control.
Benefits of Cover Crops:
- Soil erosion prevention: Cover crops help reduce soil erosion by providing a protective cover for the soil. The roots of these crops hold the soil in place, preventing it from being washed away by heavy rain or blown away by wind.
- Nutrient cycling: Some cover crops, such as legumes, have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a form that can be easily used by plants. When the cover crop is incorporated into the soil, it releases nitrogen, improving the soil’s nutrient content.
- Organic matter addition: Cover crops add organic matter to the soil when they are incorporated. This organic matter improves the soil’s structure and moisture-holding capacity, as well as providing nutrients for plant growth.
- Weed suppression: The dense canopy formed by cover crops shades out weeds, preventing them from receiving sunlight and competing with main crops for nutrients and water.
- Improved water management: Cover crops help to improve water infiltration and reduce runoff, allowing soil to retain more water. This can be especially beneficial in areas with limited water availability.
- Disease and pest control: Some cover crops have natural pest and disease suppressive properties. They can help reduce populations of harmful organisms by acting as trap crops or by releasing chemicals that repel pests and pathogens.
Types of Cover Crops:
There are several types of cover crops that can be used depending on soil conditions, climate, and the specific goals of the farmer. Some common cover crops include:
- Legumes: Leguminous cover crops, such as clover, vetch, and cowpeas, have nitrogen-fixing abilities and are often used to improve soil fertility.
- Grasses: Grass cover crops, such as rye, oats, and barley, are known for their ability to scavenge nutrients and build organic matter.
- Brassicas: Brassica cover crops, such as radishes and mustards, have deep taproots that help break up compacted soil and improve drainage.
- Forbs: Forb cover crops, such as buckwheat and phacelia, attract beneficial insects and provide pollen and nectar resources.
Management of Cover Crops:

The management of cover crops depends on the specific crop and the goals of the farmer. In general, cover crops are grown for a specific period of time, usually between main crop seasons. They are then terminated by mechanical means, such as mowing or tilling, or by natural factors such as frost or drought. The terminated cover crop is then incorporated into the soil, providing organic matter and nutrients for the next crop.
It is important to choose cover crops that are suitable for the specific soil and climate conditions. A rotation of different cover crops throughout the year can help to maximize soil health and fertility.
| Cover Crop | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Clover | Nitrogen fixation, weed suppression |
| Rye | Nutrient scavenging, erosion prevention |
| Radishes | Compaction alleviation, improved drainage |
| Buckwheat | Attracts beneficial insects, quick growth |
Optimal Use of Fertilizers
Applying fertilizers in the right quantity and at the right time is crucial for optimizing their effectiveness and minimizing environmental damage. Here are some guidelines for the optimal use of fertilizers:
Soil Testing
Before applying any fertilizer, it is important to conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels and pH of the soil. This helps in identifying the specific nutrient deficiencies and adjusting the fertilizer application accordingly.
Appropriate Fertilizer Selection
Choosing the appropriate fertilizer based on the nutrient requirements of the crops is essential. Different crops have different nutrient requirements, so it is important to select a fertilizer that matches those requirements.
Correct Fertilizer Application
Fertilizers should be applied evenly and at the recommended rates to ensure optimal nutrient distribution. The application method can vary depending on the type of fertilizer (granular, liquid, or foliar). It is advisable to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for the best results.
Proper Timing
Timing plays a crucial role in fertilizer application. Applying fertilizers too early or too late can result in nutrient loss or inefficient uptake by plants. It is important to consider the crop growth stage and the nutrient availability in the soil when deciding the timing of fertilizer application.
Split Application
In some cases, it may be beneficial to apply fertilizers in multiple doses throughout the growing season. This helps in supplying nutrients to the plants when they need them the most and reduces the risk of nutrient leaching. Split application can also improve nutrient use efficiency.
Avoid Overfertilization
Overfertilization can lead to nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, and increased production costs. It is important to apply fertilizers judiciously, considering the nutrient requirements of the crops and the existing nutrient levels in the soil.
Proper Nutrient Management
Efficient nutrient management involves ensuring a balance between the macro and micronutrients required by the plants. It is important to monitor the nutrient levels in the soil and adjust the fertilizer application accordingly. Additionally, incorporating organic matter into the soil can improve nutrient availability and soil fertility.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of soil nutrient levels and plant growth is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of fertilizer application. This helps in making informed decisions about fertilizer adjustments and optimizing nutrient use efficiency.
By following these guidelines, farmers and gardeners can ensure optimal use of fertilizers, improve soil fertility, and minimize negative environmental impacts.
“Question-Answer”
What is soil salinization?
Soil salinization is the process by which salt accumulates in the soil, reducing its fertility and plant growth.
What causes soil salinization?
Soil salinization can be caused by natural processes such as weathering of rocks and minerals containing salt, or by human activities such as irrigation with saline water or excessive use of fertilizers.
How does soil salinization affect plant growth?
Soil salinization affects plant growth by increasing the concentration of salt in the soil, which makes it more difficult for plants to take up water from the soil. This can lead to osmotic stress and dehydration in plants, resulting in stunted growth or even death.
What are the effective methods to improve soil fertility?
There are several effective methods to improve soil fertility, including proper irrigation management to prevent waterlogging and salt accumulation, leaching the soil with freshwater to flush out excess salts, and using organic matter or soil amendments to improve soil structure and nutrient content.
Can soil salinization be reversed?
In some cases, soil salinization can be reversed through the implementation of appropriate management practices. This may involve leaching the soil with freshwater, applying gypsum to displace salt ions, and adopting salt-tolerant plant species. However, the success of these methods depends on the severity of salinization and site-specific conditions.
What are the long-term consequences of soil salinization?
The long-term consequences of soil salinization include reduced crop yields, loss of soil fertility, and degradation of ecosystems. It can also lead to increased soil erosion, water pollution, and economic losses for farmers and communities that rely on agriculture.







