- Aquaponics: Growing Seedlings with Fish
- How does aquaponics work?
- Benefits of aquaponics
- Challenges of aquaponics
- Aeroponics: Growing Seedlings in Mist
- How Does Aeroponics Work?
- Benefits of Aeroponics
- Types of Plants Suitable for Aeroponics
- Conclusion
- Hydroponics: Growing Seedlings in Water
- Advantages of Hydroponics:
- How Hydroponics Works:
- Choosing the Right Hydroponic System:
- Conclusion:
- Vertical Farming: Growing Seedlings on Stacked Layers
- Benefits of Vertical Farming
- How Vertical Farming Works
- Applications of Vertical Farming
- Conclusion
- Urban Farming: Growing Seedlings in Cities
- Introduction
- Benefits of Urban Farming
- Alternative Methods for Growing Seedlings without Soil
- Conclusion
- Container Gardening: Growing Seedlings in Small Spaces
- Benefits of Container Gardening for Seedlings
- Tips for Growing Seedlings in Containers
- Bioponics: Growing Seedlings with Organic Nutrients
- The Benefits of Bioponics:
- Implementing Bioponics:
- Tissue Culture: Growing Seedlings in Laboratory
- Advantages Consistency: Tissue culture allows for the production of uniform and genetically identical seedlings. This eliminates variations that may arise in traditional soil-based methods. Mass production: This method enables the production of a large number of seedlings in a short period. It is particularly useful for commercial nurseries, where a high volume of seedlings is required. Disease-free: Tissue culture can produce disease-free seedlings because they are grown in a sterile environment. It eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases or contamination. Space-saving: Since tissue culture does not require soil, it takes up less space compared to traditional methods. This makes it suitable for urban areas or locations with limited space. Procedure The process of tissue culture involves several steps: Initiation: Plant tissues, such as leaf or stem pieces, are sterilized and placed in a culture medium containing nutrients and hormones. Shoot multiplication: The tissues are induced to form shoots by controlling the growth regulators in the culture medium. Root formation: The shoots are transferred to a different medium to induce root formation. Acclimatization: Once the roots have developed, the seedlings are transferred to soil or another suitable growing medium for further growth and development. Applications Tissue culture can be used for a variety of purposes: Propagation: Tissue culture allows for rapid and efficient multiplication of plants without relying on traditional methods like seeds or cuttings. Conservation of endangered species: This technique is used to preserve endangered plant species by growing them in the laboratory. Genetic modification: Tissue culture is an essential tool for genetic engineers to introduce desirable traits into plants. Research: Scientists use tissue culture to study plant physiology, investigate plant responses to different stimuli, and conduct experiments. Conclusion Tissue culture offers numerous advantages for growing seedlings in a controlled environment. It is a versatile technique that allows for the mass production of uniform and disease-free seedlings. With its applications in plant propagation, conservation, genetic modification, and research, tissue culture plays a significant role in modern agriculture and horticulture. “Question-Answer” What are alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil? There are several alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil, such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and using soilless growing media like coco coir or rockwool. How does hydroponics work? Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil by using a nutrient-rich water solution. Plants are typically grown in a container filled with an inert growing medium, such as perlite or gravel, and their roots are submerged in the water solution. What is aeroponics and how does it work? Aeroponics is a method of growing plants without soil or a growing medium. In aeroponics, plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich water solution. This allows for oxygenation and efficient nutrient absorption. What are the advantages of growing seedlings without soil? Growing seedlings without soil has several advantages. It allows for better control over nutrient intake, water usage, and pH levels. It also reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests. Additionally, it can result in faster growth and higher yields. Can any plant be grown without soil? Yes, most plants can be grown without soil using alternative methods like hydroponics or aeroponics. However, some plants may require specific environmental conditions or adaptations to thrive without soil. Is it more expensive to grow seedlings without soil? Growing seedlings without soil can initially be more expensive due to the cost of setting up the necessary equipment and purchasing nutrient solutions. However, over time, the savings in water usage and reduced need for pesticides can offset the initial costs. Are there any drawbacks to growing seedlings without soil? While there are many advantages to growing seedlings without soil, there are also some drawbacks. It requires a higher level of knowledge and expertise to properly monitor and maintain the nutrient solution and environmental conditions. There is also a higher risk of system failure if the equipment malfunctions or the nutrient solution becomes imbalanced. “Video” How to Start Seeds for Hydroponics
- Consistency: Tissue culture allows for the production of uniform and genetically identical seedlings. This eliminates variations that may arise in traditional soil-based methods. Mass production: This method enables the production of a large number of seedlings in a short period. It is particularly useful for commercial nurseries, where a high volume of seedlings is required. Disease-free: Tissue culture can produce disease-free seedlings because they are grown in a sterile environment. It eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases or contamination. Space-saving: Since tissue culture does not require soil, it takes up less space compared to traditional methods. This makes it suitable for urban areas or locations with limited space. Procedure The process of tissue culture involves several steps: Initiation: Plant tissues, such as leaf or stem pieces, are sterilized and placed in a culture medium containing nutrients and hormones. Shoot multiplication: The tissues are induced to form shoots by controlling the growth regulators in the culture medium. Root formation: The shoots are transferred to a different medium to induce root formation. Acclimatization: Once the roots have developed, the seedlings are transferred to soil or another suitable growing medium for further growth and development. Applications Tissue culture can be used for a variety of purposes: Propagation: Tissue culture allows for rapid and efficient multiplication of plants without relying on traditional methods like seeds or cuttings. Conservation of endangered species: This technique is used to preserve endangered plant species by growing them in the laboratory. Genetic modification: Tissue culture is an essential tool for genetic engineers to introduce desirable traits into plants. Research: Scientists use tissue culture to study plant physiology, investigate plant responses to different stimuli, and conduct experiments. Conclusion Tissue culture offers numerous advantages for growing seedlings in a controlled environment. It is a versatile technique that allows for the mass production of uniform and disease-free seedlings. With its applications in plant propagation, conservation, genetic modification, and research, tissue culture plays a significant role in modern agriculture and horticulture. “Question-Answer” What are alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil? There are several alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil, such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and using soilless growing media like coco coir or rockwool. How does hydroponics work? Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil by using a nutrient-rich water solution. Plants are typically grown in a container filled with an inert growing medium, such as perlite or gravel, and their roots are submerged in the water solution. What is aeroponics and how does it work? Aeroponics is a method of growing plants without soil or a growing medium. In aeroponics, plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich water solution. This allows for oxygenation and efficient nutrient absorption. What are the advantages of growing seedlings without soil? Growing seedlings without soil has several advantages. It allows for better control over nutrient intake, water usage, and pH levels. It also reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests. Additionally, it can result in faster growth and higher yields. Can any plant be grown without soil? Yes, most plants can be grown without soil using alternative methods like hydroponics or aeroponics. However, some plants may require specific environmental conditions or adaptations to thrive without soil. Is it more expensive to grow seedlings without soil? Growing seedlings without soil can initially be more expensive due to the cost of setting up the necessary equipment and purchasing nutrient solutions. However, over time, the savings in water usage and reduced need for pesticides can offset the initial costs. Are there any drawbacks to growing seedlings without soil? While there are many advantages to growing seedlings without soil, there are also some drawbacks. It requires a higher level of knowledge and expertise to properly monitor and maintain the nutrient solution and environmental conditions. There is also a higher risk of system failure if the equipment malfunctions or the nutrient solution becomes imbalanced. “Video” How to Start Seeds for Hydroponics
- Procedure
- Applications
- Conclusion
- “Question-Answer”
- What are alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil?
- How does hydroponics work?
- What is aeroponics and how does it work?
- What are the advantages of growing seedlings without soil?
- Can any plant be grown without soil?
- Is it more expensive to grow seedlings without soil?
- Are there any drawbacks to growing seedlings without soil?
- “Video” How to Start Seeds for Hydroponics
In traditional gardening, seedlings are typically grown in soil. However, there are alternative methods that can be utilized to grow seedlings without soil. These methods can offer numerous benefits, such as increased control over nutrient availability, improved disease prevention, and reduced water usage. In this article, we will explore some of the alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil.
One method that is gaining popularity is hydroponics. Hydroponics is a soil-less growing technique that utilizes a nutrient-rich solution to provide plants with the essential elements they need for growth. The plants are typically grown in a water-based medium, such as perlite or coconut coir, and the nutrients are delivered directly to the roots through a water solution. This method allows for precise control over nutrient levels and eliminates the risk of over- or under-fertilization.
Aquaponics is another alternative method for growing seedlings without soil. Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, creating a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. The fish waste provides the nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish. This method is highly efficient, as it uses less water compared to traditional agriculture and eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Aeroponics is a soil-less growing technique that involves suspending the plant’s roots in air and misting them with a nutrient-rich mist. This method provides the plants with optimal oxygen levels, leading to faster growth and higher yields. Aeroponics is particularly useful for growing plants in limited space, as it requires less water and nutrients compared to other methods.
In conclusion, there are several alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil. Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics offer unique advantages in terms of nutrient control, water usage, and disease prevention. These methods are increasingly being adopted by gardeners and farmers looking to maximize their crop yields and minimize their environmental impact.
Aquaponics: Growing Seedlings with Fish

Aquaponics is a sustainable method of growing seedlings that combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil). This system relies on a symbiotic relationship between fish, bacteria, and plants to create a self-sustaining environment for seedling growth.
How does aquaponics work?
In an aquaponics system, fish are kept in a tank or pond. The fish produce waste, mainly in the form of ammonia. Bacteria in the system convert the ammonia into nitrates, which are then absorbed by the plants as nutrients.
The water containing the fish waste is then pumped into a grow bed, where the seedlings are planted. The plants take up the nutrients from the water, filtering it and removing harmful substances. The filtered water is then recirculated back to the fish tank, providing a clean environment for the fish.
Benefits of aquaponics
- Water efficiency: Aquaponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based farming, as the water is recirculated and reused in the system.
- No need for soil: With aquaponics, seedlings can be grown without the need for soil. This is especially beneficial in areas with poor soil quality or limited access to arable land.
- Reduced need for fertilizers: The fish waste provides a natural source of nutrients for the plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Sustainable food production: Aquaponics allows for the production of both fish and plants in one system, providing a sustainable source of food that is high in protein and fresh produce.
Challenges of aquaponics

- System maintenance: Aquaponics systems require regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure the balance between fish, bacteria, and plants is maintained. This includes monitoring water quality, feeding the fish, and pruning the plants.
- Initial setup costs: Setting up an aquaponics system can be expensive, as it requires tanks or ponds for fish, grow beds for seedlings, and a filtration system to maintain water quality.
- Learning curve: Aquaponics requires some knowledge and understanding of fish and plant biology, as well as the interactions between the different components of the system. It may take some time to learn and optimize the system for optimal growth.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Water efficiency | System maintenance |
| No need for soil | Initial setup costs |
| Reduced need for fertilizers | Learning curve |
| Sustainable food production |
Aeroponics: Growing Seedlings in Mist
Aeroponics is a method of growing seedlings without soil that utilizes a misting system to provide plants with the necessary nutrients and moisture. This innovative technique has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits and efficiency in plant growth.
How Does Aeroponics Work?
In aeroponics, plants are suspended in a chamber or tray, with their roots exposed to the air. A misting system is used to spray a nutrient-rich solution directly onto the roots, providing them with essential nutrients and moisture. The mist is fine enough to ensure that the roots receive proper airflow and do not become waterlogged.
Aeroponics systems typically consist of a reservoir for the nutrient solution, a pump to generate the mist, and a delivery system to distribute the mist to the roots. The misting intervals can be controlled to ensure that the plants receive the appropriate amount of moisture and nutrients at regular intervals.
Benefits of Aeroponics
- Increased Oxygenation: Since the roots are exposed to the air in aeroponics, they have constant access to oxygen. This promotes healthier root development and overall plant growth.
- Water Efficiency: Aeroponics systems use water more efficiently compared to traditional soil-based methods. The misting system delivers water directly to the roots, minimizing water wastage and conserving resources.
- Faster Growth: The nutrient-rich mist provides plants with everything they need for optimal growth. As a result, seedlings grown using aeroponics tend to grow faster and produce healthier plants.
- Space Saving: Aeroponics systems can be set up vertically, allowing for efficient use of space. This makes them ideal for urban gardening or indoor cultivation, where space is often limited.
- No Soil-Borne Diseases: Growing seedlings without soil eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, reducing the need for pesticides and making the plants healthier.
Types of Plants Suitable for Aeroponics
Aeroponics can be used to grow a wide variety of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, vegetables, and even flowers. However, it is especially popular for growing delicate plants that require careful moisture control, such as orchids and other epiphytic plants.
Conclusion

Aeroponics offers an efficient and effective method of growing seedlings without soil. With its numerous benefits and ability to produce healthier plants in less time, it is becoming an increasingly popular choice for both small-scale and commercial cultivation. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, aeroponics is definitely worth considering for your next growing project.
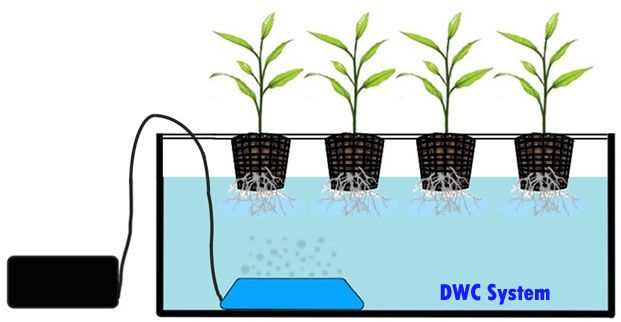
Hydroponics: Growing Seedlings in Water
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, instead using a nutrient-rich water solution to support root growth. This method offers several benefits, including faster growth, increased yields, and the ability to control nutrient levels.
Advantages of Hydroponics:
- Increased Growth Rate: Because plants have direct access to nutrients, they can grow up to 50% faster than traditional soil-based methods.
- Conservation of Water and Space: Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based gardening and requires less space.
- Efficient Nutrient Absorption: The nutrient solution in hydroponics can be precisely controlled, ensuring plants receive the optimal levels of nutrients required for their growth.
- No Weeds or Soil-borne Diseases: Since plants are not grown in soil, there is no need to worry about weeds or soil-borne diseases that can harm the plants.
How Hydroponics Works:
In hydroponics, plants are grown in a growing medium, such as perlite, coconut coir, or Rockwool, which provides mechanical support to the roots. The roots are regularly immersed in a nutrient-rich water solution, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients for growth.
The water solution is typically recirculated through a system that consists of a reservoir, a pump, and a network of tubes or channels that deliver the solution to the roots. This allows for efficient nutrient absorption and prevents water waste.
Choosing the Right Hydroponic System:
There are various types of hydroponic systems available, each offering specific advantages and suiting different plant varieties. Some common types include:
- Drip System: This system uses a timer to periodically drip nutrient solution onto the growing medium or roots.
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique): In NFT, a thin film of nutrient solution continuously flows through a sloped channel, allowing the roots to take up nutrients.
- Ebb and Flow: Also known as flood and drain, this system periodically floods the growing area with nutrient solution, which then drains back into the reservoir.
- Aeroponics: Plants are suspended in the air and have their roots misted with a nutrient-rich water solution.
Conclusion:

Hydroponics offers an efficient and controlled method for growing seedlings in water without the need for soil. Its benefits include accelerated growth, water and space conservation, efficient nutrient absorption, and freedom from soil-borne diseases. With various hydroponic systems available, growers can choose the one that suits their needs and plant varieties best.
Vertical Farming: Growing Seedlings on Stacked Layers
Vertical farming is a method of growing plants in vertically stacked layers. It is an innovative technique that allows for maximum space utilization and increased crop production. This method has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits.
Benefits of Vertical Farming

1. Space Efficiency: By growing seedlings on stacked layers, vertical farming makes the most efficient use of limited space. This is especially beneficial in urban areas where space is limited.
2. Increased Crop Yield: Vertical farming allows for multiple layers of plants, which significantly increases the number of plants that can be grown in the same area compared to traditional farming methods.
3. Water Efficiency: Vertical farming uses a closed-loop irrigation system, which recirculates water and reduces water wastage. This makes it more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
4. Reduced Pesticide Use: With vertical farming, plants are grown in a controlled environment, minimizing the need for pesticides and herbicides. This reduces the risk of contamination and ensures healthier, pesticide-free seedlings.
How Vertical Farming Works
Vertical farming typically involves shelves or racks that are stacked vertically to create multiple layers for growing plants. Each layer is equipped with artificial lighting, irrigation systems, and temperature control mechanisms to create an optimal growing environment.
Seedlings are grown in trays or containers filled with an inert growth medium, such as coconut coir or rockwool. Nutrient-rich water is circulated through the trays, providing the necessary nutrients for plant growth.
The artificial lighting, usually LED lights, mimic sunlight and provide the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis. Temperature and humidity levels can be adjusted to optimize plant growth.
Applications of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming can be used for a range of applications, including:
- Commercial agriculture: Vertical farming can be used to grow a variety of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, and even fruits. It allows for year-round production and reduces the dependency on seasonal availability.
- Urban farming: Vertical farming is particularly helpful in urban areas where space is limited. It enables local food production and reduces transportation costs, making fresh produce more accessible.
- Research and development: Vertical farming provides an ideal environment for plant research and experimentation. Scientists can control various factors, such as light intensity and nutrient levels, to study plant growth and improve crop yields.
Conclusion
Vertical farming offers a promising solution for growing seedlings without soil, providing various benefits such as space efficiency, increased crop yield, water efficiency, and reduced pesticide use. It has the potential to revolutionize the way we grow plants and address the challenges of food production in urban areas.
Urban Farming: Growing Seedlings in Cities
Introduction
Urban farming is a practice that allows people to grow plants and vegetables in urban environments, such as cities. With limited space and soil availability in cities, alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil have gained popularity. These methods provide a solution for individuals and communities who are interested in growing their own food in urban settings.
Benefits of Urban Farming
- Space optimization: Urban farming allows for efficient use of limited space by utilizing vertical growing systems and rooftop gardens.
- Food security: By growing seedlings in cities, people can have access to fresh and nutritious produce, reducing their reliance on external food sources.
- Sustainability: Urban farming promotes sustainability by utilizing recycled materials, practicing water conservation, and reducing food miles.
- Community engagement: Urban farms provide a platform for community engagement and education, fostering a sense of togetherness among residents.
Alternative Methods for Growing Seedlings without Soil
Traditional soil-based gardening is not always feasible in urban environments, leading to the development of alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil. Some of these methods include:
- Hydroponics: In hydroponic systems, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution instead of soil. This method allows for precise control over nutrient intake and water delivery, resulting in faster growth and higher yields.
- Aquaponics: Aquaponic systems combine hydroponics with fish farming. The fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water, creating a symbiotic relationship between the two.
- Aeroponics: Aeroponic systems suspend plants in the air and mist their roots with a nutrient solution. This method promotes rapid growth and allows for efficient use of space.
- Vertical farming: Vertical farming involves growing plants in vertically stacked layers, utilizing artificial lighting and controlled environments. This method maximizes space utilization and reduces the need for soil.
Conclusion
Urban farming offers a sustainable and efficient solution for growing seedlings in cities. By utilizing alternative methods that do not rely on soil, individuals and communities can have access to fresh and nutritious produce, even in limited urban spaces. Urban farming promotes self-sufficiency, community engagement, and environmental sustainability, making it an increasingly popular practice in cities around the world.
Container Gardening: Growing Seedlings in Small Spaces
Container gardening is an excellent solution for individuals who have limited space or live in urban areas. This method allows you to grow seedlings and plants in containers, such as pots, buckets, or even recycled materials like plastic bottles or old tires. Here are some benefits and tips for growing seedlings in small spaces using container gardening:
Benefits of Container Gardening for Seedlings
- Space-saving: Container gardening is perfect for small spaces, such as balconies, patios, or even window sills. You can maximize your available space by using vertical gardening techniques or hanging containers.
- Portability: Containers are portable, which means you can move them around to find the ideal amount of sunlight or shade for your seedlings.
- Accessibility: With container gardening, you can easily reach your seedlings without the need for excessive bending or kneeling. This makes it convenient for individuals with physical limitations.
- Pest control: Container gardening allows you to isolate your seedlings from the ground, which can help prevent pests or soil-borne diseases from attacking your plants.
- Flexibility: Containers offer flexibility in terms of soil type and watering needs. You can choose a specific potting mix that suits your seedlings’ requirements, and adjust watering based on their individual needs.
Tips for Growing Seedlings in Containers

- Choose suitable containers: Select containers with adequate drainage holes to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Consider the size of your seedlings and choose containers that provide enough space for their roots to grow.
- Use quality potting mix: Avoid using garden soil in containers as it may not provide the necessary nutrients and drainage. Instead, opt for a high-quality potting mix specifically formulated for container gardening.
- Provide proper sunlight: Most seedlings require at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. Place your containers in areas that receive adequate sunlight or use artificial grow lights if natural light is limited.
- Water consistently: Containers tend to dry out faster than traditional garden beds, so it’s essential to monitor the moisture levels regularly. Water your seedlings when the top inch of soil feels dry, but avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
- Fertilize regularly: Seedlings in containers may require additional nutrients compared to those in the ground. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer or slow-release granules according to the package instructions.
- Protect from extreme weather: Container plants are more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations, so take precautions during extreme heat or cold spells. Move your containers to a sheltered area or provide shade during scorching summer days.
Container gardening offers a versatile and convenient option for growing seedlings in small spaces. With proper care and attention, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest even in the tiniest of areas.
Bioponics: Growing Seedlings with Organic Nutrients
Bioponics is an alternative method for growing seedlings without soil that utilizes organic nutrients. This innovative approach combines elements of hydroponics and organic farming to provide plants with all the necessary nutrients they need to thrive.
In bioponics, plants are grown in a soilless medium, such as coconut coir or peat moss, which provides support while allowing for the free flow of water and nutrients. The nutrients are derived from organic sources, such as compost or organic fertilizers, ensuring that the plants receive a rich mix of essential minerals and trace elements.
One of the main advantages of bioponics is its sustainability. Unlike traditional farming methods that rely on chemical fertilizers, bioponics promotes the use of organic and renewable resources. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also produces healthier and more natural seedlings.
The Benefits of Bioponics:
- Increased Nutrient Availability: Bioponics allows for precise control over nutrient levels, ensuring plants receive exactly what they need for optimal growth and development.
- Water Efficiency: As the plants are grown in a soilless medium, water can be recycled and reused more efficiently. This reduces water usage and conserves this valuable resource.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By utilizing organic nutrients, bioponics minimizes the use of synthetic chemicals, reducing soil and water pollution.
- Year-Round Production: Bioponics can be implemented indoors or in controlled environments, allowing for year-round production of seedlings regardless of the climate or weather conditions.
- Healthy Seedlings: The organic nutrients used in bioponics result in healthier seedlings with stronger roots and increased resistance to pests and diseases.
Implementing Bioponics:
Implementing bioponics requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some key components to consider:
- Choosing the Right Soilless Medium: Select a soilless medium that provides adequate support and drainage for the plants while allowing for the easy flow of water and nutrients.
- Selecting Organic Nutrients: Choose organic fertilizers or compost that provide a balanced mix of essential nutrients. Consider the specific requirements of the seedlings being grown.
- Monitoring Nutrient Levels: Regularly test the nutrient levels in the system to ensure they are at the appropriate levels for optimal plant growth.
- Proper Irrigation: Set up a reliable irrigation system that provides the plants with a steady supply of water and nutrients while preventing waterlogging.
- Maintaining a Controlled Environment: Depending on the specific requirements of the seedlings, maintain an appropriate temperature, humidity, and lighting conditions to promote healthy growth.
In conclusion, bioponics offers a sustainable and organic approach to growing seedlings without soil. By utilizing organic nutrients and soilless mediums, bioponics provides plants with the necessary elements for healthy growth while minimizing the environmental impact. Implementing bioponics requires careful planning and attention to detail, but the benefits outweigh the initial effort, resulting in healthier and more sustainable seedling production.
Tissue Culture: Growing Seedlings in Laboratory
Tissue culture is an alternative and innovative method for growing seedlings without the use of soil. This technique involves growing plant cells or tissues in a laboratory setting, under controlled conditions.
Advantages- Consistency: Tissue culture allows for the production of uniform and genetically identical seedlings. This eliminates variations that may arise in traditional soil-based methods.
- Mass production: This method enables the production of a large number of seedlings in a short period. It is particularly useful for commercial nurseries, where a high volume of seedlings is required.
- Disease-free: Tissue culture can produce disease-free seedlings because they are grown in a sterile environment. It eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases or contamination.
- Space-saving: Since tissue culture does not require soil, it takes up less space compared to traditional methods. This makes it suitable for urban areas or locations with limited space.
Procedure
- Consistency: Tissue culture allows for the production of uniform and genetically identical seedlings. This eliminates variations that may arise in traditional soil-based methods.
- Mass production: This method enables the production of a large number of seedlings in a short period. It is particularly useful for commercial nurseries, where a high volume of seedlings is required.
- Disease-free: Tissue culture can produce disease-free seedlings because they are grown in a sterile environment. It eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases or contamination.
- Space-saving: Since tissue culture does not require soil, it takes up less space compared to traditional methods. This makes it suitable for urban areas or locations with limited space.
Procedure
The process of tissue culture involves several steps:
- Initiation: Plant tissues, such as leaf or stem pieces, are sterilized and placed in a culture medium containing nutrients and hormones.
- Shoot multiplication: The tissues are induced to form shoots by controlling the growth regulators in the culture medium.
- Root formation: The shoots are transferred to a different medium to induce root formation.
- Acclimatization: Once the roots have developed, the seedlings are transferred to soil or another suitable growing medium for further growth and development.
Applications
Tissue culture can be used for a variety of purposes:
- Propagation: Tissue culture allows for rapid and efficient multiplication of plants without relying on traditional methods like seeds or cuttings.
- Conservation of endangered species: This technique is used to preserve endangered plant species by growing them in the laboratory.
- Genetic modification: Tissue culture is an essential tool for genetic engineers to introduce desirable traits into plants.
- Research: Scientists use tissue culture to study plant physiology, investigate plant responses to different stimuli, and conduct experiments.
Conclusion
Tissue culture offers numerous advantages for growing seedlings in a controlled environment. It is a versatile technique that allows for the mass production of uniform and disease-free seedlings. With its applications in plant propagation, conservation, genetic modification, and research, tissue culture plays a significant role in modern agriculture and horticulture.
“Question-Answer”
What are alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil?
There are several alternative methods for growing seedlings without soil, such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and using soilless growing media like coco coir or rockwool.
How does hydroponics work?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil by using a nutrient-rich water solution. Plants are typically grown in a container filled with an inert growing medium, such as perlite or gravel, and their roots are submerged in the water solution.
What is aeroponics and how does it work?
Aeroponics is a method of growing plants without soil or a growing medium. In aeroponics, plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich water solution. This allows for oxygenation and efficient nutrient absorption.
What are the advantages of growing seedlings without soil?
Growing seedlings without soil has several advantages. It allows for better control over nutrient intake, water usage, and pH levels. It also reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests. Additionally, it can result in faster growth and higher yields.
Can any plant be grown without soil?
Yes, most plants can be grown without soil using alternative methods like hydroponics or aeroponics. However, some plants may require specific environmental conditions or adaptations to thrive without soil.
Is it more expensive to grow seedlings without soil?
Growing seedlings without soil can initially be more expensive due to the cost of setting up the necessary equipment and purchasing nutrient solutions. However, over time, the savings in water usage and reduced need for pesticides can offset the initial costs.
Are there any drawbacks to growing seedlings without soil?
While there are many advantages to growing seedlings without soil, there are also some drawbacks. It requires a higher level of knowledge and expertise to properly monitor and maintain the nutrient solution and environmental conditions. There is also a higher risk of system failure if the equipment malfunctions or the nutrient solution becomes imbalanced.







