- Crop Rotation in the Vegetable Garden
- Benefits of Crop Rotation
- Implementing Crop Rotation
- Conclusion
- The Importance of Crop Rotation
- 1. Soil Health
- 2. Pest and Disease Management
- 3. Weed Control
- 4. Nutritional Diversity
- 5. Sustainable Farming
- Year 1: Planting for Success
- Planning the Garden Layout
- Choosing the Right Crops
- Implementing Crop Rotation
- Benefits of Year 1 Planting
- Year 2: Maximizing Nutrient Uptake
- Soil Testing and Analysis
- Planting Nitrogen Fixing Crops
- Companion Planting
- Mulching and Organic Amendments
- Record Keeping and Observations
- Year 3: Disease Prevention
- Identifying and Understanding Plant Diseases
- Implementing Disease Prevention Measures
- Monitoring and Managing Diseases
- Year 4: Weed Control
- Cover Crops
- Mulching
- Hand Weeding
- The Key to Abundant Harvests
- Benefits of Crop Rotation
- How to Practice Crop Rotation
- Tips for Successful Crop Rotation
- “Question-Answer”
- Why is crop rotation important in a vegetable garden?
- What are the benefits of crop rotation?
- How does crop rotation help with pest management?
- What types of crops are commonly rotated in a vegetable garden?
- How long should each crop stay in its designated bed?
- What can be done to improve soil health during crop rotation?
- “Video” Cover Cropping: The LAZIEST Way to Improve Your Soil

One of the keys to a successful vegetable garden is crop rotation. By implementing a strategic plan for rotating crops, gardeners can prevent soil nutrient depletion, reduce the spread of pests and diseases, and ultimately enjoy bountiful harvests year after year.
The concept of crop rotation is based on the idea that different plants have different nutrient needs and are susceptible to different pests and diseases. Therefore, by rotating crops, gardeners can ensure that each plot of soil has time to replenish its nutrients and avoid the buildup of specific pests or diseases that may target certain crops.
Experts recommend a four-year rotation plan, dividing vegetables into different groups based on their nutrient needs. In the first year, for example, gardeners may plant nitrogen-fixing legumes, such as peas or beans, which help replenish soil nitrogen levels. In the second year, leafy greens like lettuce or spinach can be planted, which have lower nutrient needs and can benefit from the nitrogen-rich soil. In the third year, root crops like carrots or radishes can be planted, as they don’t require high levels of nitrogen. Finally, in the fourth year, heavy feeders like tomatoes or cucumbers can be grown, as the soil has had time to replenish its nutrients.
By following a crop rotation plan, gardeners can not only maintain soil health and fertility but also break the disease cycle and reduce the need for chemical pesticides. This leads to healthier and more sustainable vegetable gardens, producing abundant harvests year after year. So if you want to enjoy the benefits of a thriving vegetable garden, consider implementing a four-year crop rotation plan in your own backyard.
Crop Rotation in the Vegetable Garden
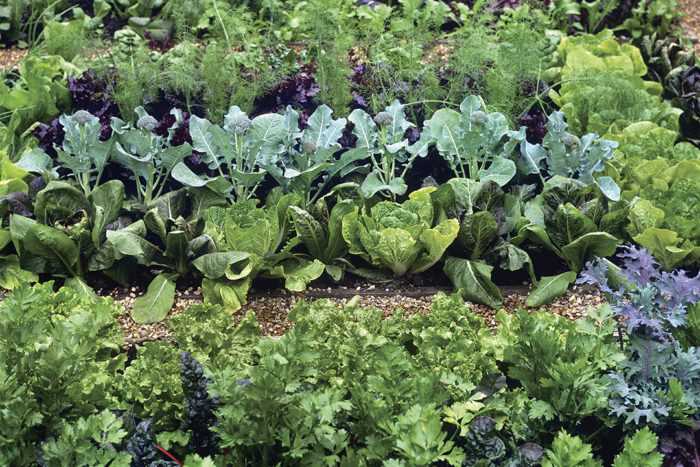


Crop rotation is a traditional farming practice that involves the systematic planting of different crops in different areas of the garden each year. This technique is used to help improve soil health, control pests and diseases, and maximize crop yields. By rotating crops, gardeners can break pest and disease cycles, reduce nutrient depletion, and promote overall garden health.
Benefits of Crop Rotation
- Pest and Disease Control: Crop rotation can help reduce the buildup of pests and diseases that can harm vegetable plants. By moving crops to different areas each year, gardeners can disrupt the life cycle of pests and prevent them from becoming a problem.
- Nutrient Management: Different crops have different nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, gardeners can prevent the depletion of specific nutrients in the soil. For example, legumes, such as peas and beans, fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits future crops that require nitrogen.
- Weed Suppression: Some crops, such as dense leafy greens, can help suppress weeds and prevent them from taking over the garden. By rotating these crops with others, gardeners can effectively manage weed growth.
- Improved Soil Structure: Crop rotation can help improve soil structure by alternating between deep-rooted and shallow-rooted crops. Deep-rooted crops, like tomatoes, can penetrate the soil and break up compacted areas, while shallow-rooted crops, like lettuce, help keep the topsoil loose and well-aerated.
Implementing Crop Rotation


When planning crop rotation in the vegetable garden, it is important to consider the specific needs and characteristics of each crop. Here is a basic guide to help get started:
- Divide the Garden: Divide the garden into separate sections or beds.
- Rotate Based on Crop Families: Group crops based on their families, such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants belonging to the nightshade family. Rotate crops within the same family to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases that affect specific families.
- Follow a Cycle: Create a rotation cycle that moves crops through each section of the garden over several years. A common cycle is a 4-year rotation, where crops are divided into four groups and moved to a different section each year.
- Add Cover Crops: Consider adding cover crops, such as clover or buckwheat, to help improve soil health and fertility during fallow periods in the rotation cycle.
Conclusion
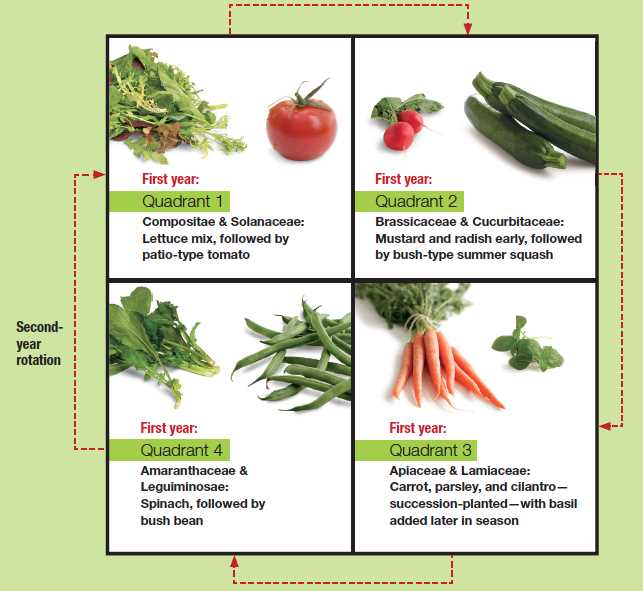

Crop rotation is a valuable technique for maintaining a healthy and productive vegetable garden. By implementing a thoughtful crop rotation plan, gardeners can reduce pest and disease pressure, manage soil fertility, and promote overall garden health. Whether it’s a small backyard garden or a larger farm, crop rotation can benefit any vegetable growing operation.
The Importance of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a systematic approach to planting different crops in different areas of the vegetable garden each year. This practice offers numerous benefits and is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of the soil, as well as preventing the build-up of pests and diseases.
1. Soil Health
One of the key benefits of crop rotation is its positive impact on soil health. Planting different crops in consecutive years helps to improve soil structure and fertility by replenishing essential nutrients and organic matter. Different crops have different nutrient requirements, so rotating crops ensures a more balanced nutrient profile in the soil. Additionally, some crops can have specific interactions with the soil, such as legumes that fix nitrogen, which can further enhance soil health.
2. Pest and Disease Management
Crop rotation plays a crucial role in managing pests and diseases in the vegetable garden. Many pests and diseases have specific host plants, and by rotating crops, you disrupt their life cycles and reduce the risk of infestations. Additionally, some crops have natural defense mechanisms that can deter pests and diseases, so rotating with these crops can provide an added layer of protection.
3. Weed Control
Crop rotation can also help with weed control. Different crops have different growth habits and shading capacities, and by rotating crops, you can disrupt the life cycle of weeds and prevent them from becoming established in the garden. Additionally, some crops, such as cover crops, can be grown specifically to suppress weeds and improve soil health.
4. Nutritional Diversity
Crop rotation promotes nutritional diversity in the vegetable garden. By planting a variety of crops, you can ensure a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals in your diet. Different crops have different nutritional profiles, so by rotating crops, you can maximize the nutritional benefits of your harvest.
5. Sustainable Farming
Crop rotation is an essential practice in sustainable farming. By diversifying crop types and using natural pest control methods, you reduce reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This not only benefits the environment but also contributes to the long-term viability of your vegetable garden.
| Year | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | Tomatoes | Carrots | Peppers |
| Year 2 | Peppers | Tomatoes | Carrots |
| Year 3 | Carrots | Peppers | Tomatoes |
| Year 4 | Spinach | Peppers | Carrots |
A simple crop rotation plan like the one shown above can help you get started with implementing crop rotation in your vegetable garden. However, it’s important to note that the specific crop rotation plan will vary depending on your location, climate, and specific crop requirements.
In conclusion, crop rotation is a vital practice for maintaining soil health, managing pests and diseases, controlling weeds, promoting nutritional diversity, and practicing sustainable farming in the vegetable garden. By implementing a well-thought-out crop rotation plan, you can enjoy years of abundant harvests and a thriving garden ecosystem.
Year 1: Planting for Success
Planning the Garden Layout
The first year of implementing crop rotation in your vegetable garden is crucial for setting a strong foundation for future years. Before planting, it’s important to plan out the layout of your garden to ensure proper rotation of crops. This involves dividing your garden into sections or beds and assigning a specific group of crops to each section.
Consider the following factors when planning your garden layout:
- Group crops based on their botanical families.
- Consider the nutrient needs and disease susceptibility of each crop.
- Designate separate sections for high-demand crops and low-demand crops.
- Ensure proper spacing between each crop for optimal growth.
Choosing the Right Crops
Once you have planned your garden layout, it’s time to select the crops that you will be planting. It’s important to choose a diverse range of crops from different botanical families to promote healthy soil and prevent the buildup of pests and diseases.
Consider the following when choosing crops:
- Select crops that are suitable for your climate and growing conditions.
- Include a mix of leafy greens, root vegetables, legumes, and fruiting crops.
- Rotate heavy feeders with light feeders to maintain soil fertility.
- Consider companion planting to maximize the health and productivity of your crops.
Implementing Crop Rotation
With the garden layout planned and crops selected, it’s time to start implementing crop rotation in your vegetable garden.
Follow these steps to implement crop rotation:
- Start by allocating each crop to its designated section or bed.
- Plant crops according to the recommended spacing and depth.
- Keep track of the location and rotation of each crop using a journal or garden planner.
- After each harvest, replace the harvested crop with a different crop from the same group.
- Amend the soil with organic matter and nutrients as needed.
Benefits of Year 1 Planting
By properly planning and implementing crop rotation in the first year, you lay the foundation for years of abundant harvests and healthy plants.
Benefits of Year 1 Planting:
- Prevents the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
- Maintains soil fertility and prevents nutrient depletion.
- Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Promotes a diverse range of crops for a balanced diet.
- Improves overall garden productivity and success.
| Section/Bed | Crop Group |
|---|---|
| Section 1 | Leafy Greens (e.g., lettuce, spinach, kale) |
| Section 2 | Root Vegetables (e.g., carrots, beets, radishes) |
| Section 3 | Legumes (e.g., peas, beans, lentils) |
| Section 4 | Fruiting Crops (e.g., tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers) |
Year 2: Maximizing Nutrient Uptake
In the second year of implementing crop rotation in the vegetable garden, our focus shifted to maximizing nutrient uptake. By strategically planning the placement of our crops, we aimed to optimize nutrient availability and minimize nutrient depletion in the soil.
Soil Testing and Analysis


Before starting the planting season, we conducted a comprehensive soil test to assess the nutrient levels in our garden beds. This analysis provided valuable insights into the deficiencies and excesses of various nutrients in the soil. Armed with this information, we were able to tailor our crop rotation plan to address specific nutritional needs.
Planting Nitrogen Fixing Crops
To enhance the overall fertility of the soil, we incorporated nitrogen-fixing crops in our rotation plan for the second year. Legumes such as peas and beans have the ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that is readily available to other plants. By growing these crops in designated areas, we were able to naturally boost nitrogen levels in the soil, benefiting subsequent crops that require this nutrient for vigorous growth.
Companion Planting
In addition to incorporating nitrogen-fixing crops, we practiced companion planting to maximize nutrient uptake. Certain plants have symbiotic relationships that benefit each other when grown together. For example, planting lettuce alongside carrots can help deter pests and improve soil structure, leading to healthier and more productive crops. By strategically pairing compatible plants in our garden beds, we aimed to optimize nutrient uptake and overall plant health.
Mulching and Organic Amendments
To further support nutrient uptake, we applied organic mulch and amendments to the soil. Mulching not only helps retain moisture and suppress weeds but also contributes to the slow release of nutrients as the organic matter decomposes. Additionally, we incorporated well-aged compost and other organic fertilizers to provide a balanced nutritional boost to the soil.
Record Keeping and Observations
Throughout the second year of implementing crop rotation, we diligently kept records and made observations to assess the effectiveness of our strategies. By noting the growth and overall health of each crop, we were able to refine our rotation plan for future seasons. This valuable data allowed us to identify trends, understand specific plant preferences, and make informed decisions for future improvements.
Overall, our second year of implementing crop rotation in the vegetable garden focused on maximizing nutrient uptake. Through soil testing, strategic planting, companion planting, mulching, and record keeping, we aimed to optimize the health and productivity of our crops. These practices not only contribute to sustainable gardening but also result in abundant harvests year after year.
Year 3: Disease Prevention
In the third year of implementing crop rotation in the vegetable garden, our focus was on disease prevention. By rotating our crops strategically, we aimed to reduce the incidence of plant diseases and ensure healthier plants overall.
Identifying and Understanding Plant Diseases
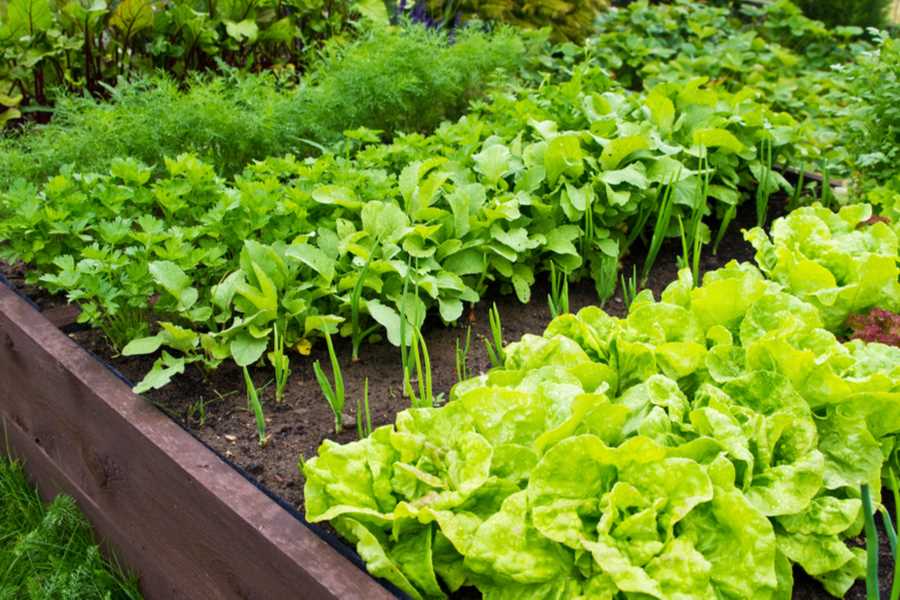


- Before implementing disease prevention measures, it is crucial to identify and understand common plant diseases that affect your vegetable garden.
- Common plant diseases include blights, mildews, rots, and viruses.
- Research and learn about the specific diseases that commonly affect the crops you are growing.
Implementing Disease Prevention Measures
1. Crop Rotation:
- Continue following the crop rotation plan established in the previous years.
- Rotate crops in a way that minimizes the buildup of disease-causing organisms in the soil.
- Avoid planting the same crop or crops from the same family in consecutive years in the same location.
2. Resistant Varieties:
- Choose plant varieties that are resistant to common diseases in your area.
- Research and select varieties known for their disease resistance.
- Consider disease-resistant rootstocks for grafted plants.
3. Sanitation:
- Practice good sanitation practices in the garden to prevent the spread of diseases.
- Remove and destroy any infected plants immediately.
- Clean tools, containers, and equipment regularly to prevent the transfer of pathogens.
4. Proper Irrigation:
- Overhead watering can lead to the spread of foliar diseases.
- Consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the plant roots.
Monitoring and Managing Diseases
1. Regular Inspection:
- Inspect plants regularly for signs of diseases.
- Look for wilting, yellowing leaves, rot, or any other unusual symptoms.
- Early detection is crucial for managing diseases effectively.
2. Organic Pest Control:
- Implement organic pest control methods to minimize pest populations.
- Pests can weaken plants and make them more susceptible to diseases.
- Use natural predators, biological controls, and organic pest repellents as needed.
3. Cultural Practices:
- Practice proper spacing between plants to allow for good air circulation.
- Weeds can harbor diseases, so practicing good weed control is essential.
Incorporating disease prevention measures into our crop rotation plan during the third year helped us maintain healthier plants and minimize the impact of diseases. By being proactive and implementing these practices, we were able to enjoy another year of abundant harvests in our vegetable garden.
Year 4: Weed Control
Weed control is an essential aspect of maintaining a successful vegetable garden, and in the fourth year of our crop rotation plan, we implemented several effective strategies to keep weeds at bay.
Cover Crops
One of the main ways we tackled weed control in our vegetable garden was by planting cover crops during the fallow periods. Cover crops, such as clover or winter rye, help to suppress weed growth by competing for nutrients, light, and space.
By planting cover crops strategically between vegetable plantings, we were able to keep weed populations to a minimum. After a cover crop reached maturity, we would mow or till it into the soil to add organic matter and improve soil fertility.
Mulching
Another effective method we used for weed control in the fourth year was mulching. We applied a thick layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around our vegetable plants.
The mulch acted as a natural barrier, preventing weed seeds from germinating and competing with our vegetable plants for resources. Additionally, mulch helps to conserve soil moisture and reduce evaporation, creating an optimal growing environment for our crops.
Hand Weeding
While cover crops and mulching kept weed populations under control, we still needed to perform occasional hand weeding to address any persistent or hard-to-reach weeds.
We made it a regular practice to walk through our vegetable garden, inspecting each bed carefully for any signs of weeds. By removing weeds by hand, we could prevent them from spreading and robbing our crops of nutrients and water.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cover Crops |
|
|
| Mulching |
|
|
| Hand Weeding |
|
|
Overall, by implementing a combination of cover crops, mulching, and hand weeding, we were able to maintain excellent weed control in our vegetable garden during the fourth year of our crop rotation plan. These strategies not only reduced weed competition but also improved soil health and fertility, resulting in abundant harvests of healthy vegetables.
The Key to Abundant Harvests
When it comes to having a successful vegetable garden, one of the most important factors to consider is crop rotation. Crop rotation is the practice of planting different crops in different areas of the garden each year. This simple technique is the key to maintaining soil fertility, minimizing the risk of pests and diseases, and ultimately ensuring abundant harvests year after year.
Benefits of Crop Rotation
- Soil Fertility: Different crops have different nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, you can prevent the depletion of specific nutrients in the soil. For example, legumes, such as peas and beans, have the ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and enrich the soil. Planting legumes in a specific area one year, and then planting a heavy feeding crop like tomatoes in that area the following year, ensures that the tomatoes will have access to a nutrient-rich soil.
- Pest and Disease Management: Crop rotation helps prevent the buildup of pests and diseases that target specific crops. By changing the planting location of crops, you disrupt the life cycle of pests and make it harder for them to establish themselves. In addition, some crops have the ability to repel pests or attract beneficial insects, further enhancing pest management efforts.
- Weed Suppression: Rotating crops can help control weeds. Different crops have different growth habits and can outcompete weeds in different ways. For example, tall growing crops like corn can shade out weeds, while root crops like carrots can break up compacted soil and make it harder for weeds to establish.
- Improved Soil Structure: Crop rotation can also improve the structure of the soil. Different crops have different root systems and affect the soil in different ways. For example, deep-rooted crops like potatoes can help break up compacted soil, while shallow-rooted crops like lettuces can help improve drainage in heavy clay soil.
How to Practice Crop Rotation


Crop rotation is best practiced on a 4-year cycle, but can be adapted to fit the needs of your specific garden. The basic idea is to divide your garden into four areas and rotate the crops between these areas each year. Here’s a simple rotation plan to get you started:
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leafy Greens | Root Vegetables | Fruit and Legumes | Brassicas |
| Spinach, Lettuce, Swiss Chard | Carrots, Potatoes, Onions | Tomatoes, Peppers, Beans | Cabbage, Broccoli, Cauliflower |
Remember to amend the soil with compost or organic matter before planting each crop to replenish nutrients and maintain soil health.
By practicing crop rotation, you can create a healthy and productive vegetable garden for years to come. The benefits of crop rotation are numerous and will reward you with abundant harvests, improved soil health, and reduced pest and disease problems.
Tips for Successful Crop Rotation
Proper crop rotation is essential for maintaining soil health and maximizing yields in a vegetable garden. Here are some tips to help you implement successful crop rotation:
- Plan your rotation: Before planting, make a detailed plan of your garden beds and the crops you will be growing each year. This will help you keep track of which crops have been planted where and ensure a proper rotation schedule.
- Group crops by family: Crops that belong to the same family are often affected by the same pests and diseases. By grouping these crops together, you can effectively control pests and diseases and prevent their buildup in the soil.
- Follow a crop rotation schedule: Rotate your crops on a regular schedule, ideally every year or two. This will help break pest and disease cycles and prevent nutrient depletion in the soil.
- Include cover crops: Consider planting cover crops in between vegetable rotations. Cover crops help improve soil fertility, suppress weed growth, and prevent erosion.
- Avoid planting the same crop in the same location: Try to avoid planting the same crop in the same location for at least two years. This will help prevent the buildup of pests and diseases that are specific to that crop.
- Rotate root crops: Root crops, such as carrots and radishes, should be rotated to prevent soil-borne diseases from affecting the new crop. Ideally, rotate root crops to a different bed each year.
- Keep records: Maintain a record of your crop rotations and any pests or diseases you encounter. This will help you make informed decisions in the future and track the success of your rotation schedule.
By implementing these tips, you can create a successful crop rotation plan that will benefit your vegetable garden for years to come.
“Question-Answer”
Why is crop rotation important in a vegetable garden?
Crop rotation is important in a vegetable garden because it helps with pest and disease management, prevents nutrient imbalances in the soil, and improves overall soil health.
What are the benefits of crop rotation?
Crop rotation has several benefits. It helps reduce pest and disease problems by interrupting the life cycles of pests and pathogens, it prevents nutrient imbalances in the soil by alternating nutrient-demanding crops with nutrient-building ones, and it improves soil health and fertility by enhancing organic matter content and reducing erosion.
How does crop rotation help with pest management?
Crop rotation helps with pest management by interrupting the life cycles of pests. Different pests are often specific to certain crops, so by rotating crops, you can reduce the population of pests that attack a particular vegetable. Additionally, rotating crops can disrupt the habitat and food sources of pests, making it more difficult for them to survive and reproduce.
What types of crops are commonly rotated in a vegetable garden?
In a vegetable garden, crops are commonly rotated based on their plant families. For example, nightshades like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants are often grouped together, while brassicas like cabbage, broccoli, and kale are grouped together. Other common plant families include legumes (beans and peas), cucurbits (cucumbers, squash, and melons), and root vegetables (carrots, radishes, and potatoes).
How long should each crop stay in its designated bed?
The length of time each crop should stay in its designated bed can vary depending on the specific crop and the rotation schedule. Typically, crops are rotated on a yearly basis, so each crop would stay in its designated bed for one growing season. However, in some cases, crops may stay in a bed for multiple years if they are part of a longer rotation cycle.
What can be done to improve soil health during crop rotation?
There are several things that can be done to improve soil health during crop rotation. First, incorporating organic matter, such as compost or cover crops, into the soil can enhance its structure and fertility. Second, practicing cover cropping can help reduce erosion and improve soil biology. Third, avoiding the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides can promote a more balanced and diverse soil ecosystem. Finally, rotating crops that have different nutrient needs can help prevent nutrient imbalances in the soil.







