- The Importance of Mineral Fertilizers for Plant Growth
- 1. Nutrient Supply
- 2. Balanced Nutrition
- 3. Increased Yield
- 4. Efficient Absorption
- 5. Targeted Nutrient Application
- 6. Cost-Effectiveness
- Debunking the Myth of Harmful Chemicals in Mineral Fertilizers
- Exploring the Benefits of Properly Applied Mineral Fertilizers
- 1. Improved Nutrient Availability
- 2. Increased Crop Yield
- 3. Nutrient Management
- 4. Cost-Effective Solution
- Understanding the Environmental Impact of Mineral Fertilizers
- 1. Nutrient Runoff
- 2. Soil Degradation
- 3. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- 4. Water Contamination
- 5. Energy Consumption and Resource Depletion
- Conclusion
- Busting the Myth of Leaching and Groundwater Contamination
- The Role of Proper Application
- The Role of Soil Nutrient Management
- The Role of Nutrient Stewardship
- Conclusion
- The Role of Mineral Fertilizers in Sustainable Agriculture
- Nutrient requirements for plant growth
- Improving soil fertility
- Increasing crop productivity
- Environmental sustainability
- Conclusion
- Dispelling the Myth of Dependency on Mineral Fertilizers
- The Importance of Soil Health
- Supplementing Natural Methods
- The Myth of Dependence
- Balancing Environmental and Productivity Goals
- The Future of Mineral Fertilizers: Innovations and Sustainable Solutions
- 1. Improving Efficiency
- 2. Developing Sustainable Production Methods
- 3. Promoting Precision Agriculture
- 4. Exploring Organic Alternatives
- “Question-Answer”
- Are mineral fertilizers harmful to the environment?
- Do mineral fertilizers deplete soil nutrients over time?
- Can mineral fertilizers harm human health?
- Do mineral fertilizers negatively affect crop quality?
- Are mineral fertilizers sustainable?
- Can mineral fertilizers contribute to water pollution?
- “Video” FERTILIZERS || ORGANIC AND INORGANIC FERTILIZERS || SCIENCE VIDEO FOR KIDS
Mineral fertilizers have long been a subject of debate when it comes to their impact on the environment and human health. Some argue that the use of these fertilizers is harmful, while others believe they are necessary for increasing crop yields and ensuring food security. In this article, we will debunk some of the myths surrounding mineral fertilizers, and shed light on their actual harm or benefit.
One of the common misconceptions about mineral fertilizers is that they are purely synthetic and contain harmful chemicals. While it is true that mineral fertilizers are manufactured using synthetic processes, they are primarily made from naturally occurring minerals or elements. These minerals, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential nutrients for plant growth and are found in the soil naturally. By supplementing these minerals through mineral fertilizers, farmers can provide plants with the nutrients they need to thrive and produce higher yields.
Another myth surrounding mineral fertilizers is that they are solely responsible for soil degradation and nutrient depletion. While it is true that excessive use of fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalance and environmental pollution, responsible and targeted application can actually improve soil fertility. When used in moderation and in combination with organic matter, mineral fertilizers can help replenish nutrients and enhance soil structure. Additionally, modern fertilizers are formulated to release nutrients slowly, reducing the risk of leaching and runoff.
In conclusion, it is important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to mineral fertilizers. While they have the potential to cause harm if misused, when used responsibly, mineral fertilizers can be a valuable tool for increasing agricultural productivity and ensuring food security. By understanding the science behind these fertilizers and adopting sustainable practices, farmers can strike a balance between maximizing yields and minimizing environmental impact.
The Importance of Mineral Fertilizers for Plant Growth
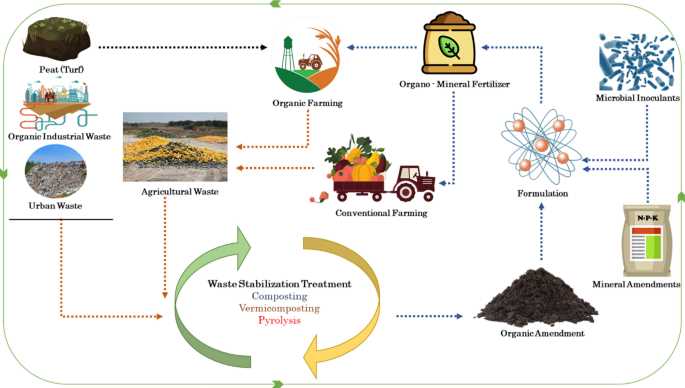
Mineral fertilizers play a crucial role in promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing crop yields. These fertilizers provide essential nutrients that are necessary for plants to thrive and develop properly. Here are some key reasons why mineral fertilizers are indispensable for plant growth:
1. Nutrient Supply
Mineral fertilizers contain a range of essential nutrients, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), also known as NPK. These nutrients are critical for plant growth as they support vital functions such as cell division, energy production, and the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. A lack of these nutrients can lead to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth.
2. Balanced Nutrition
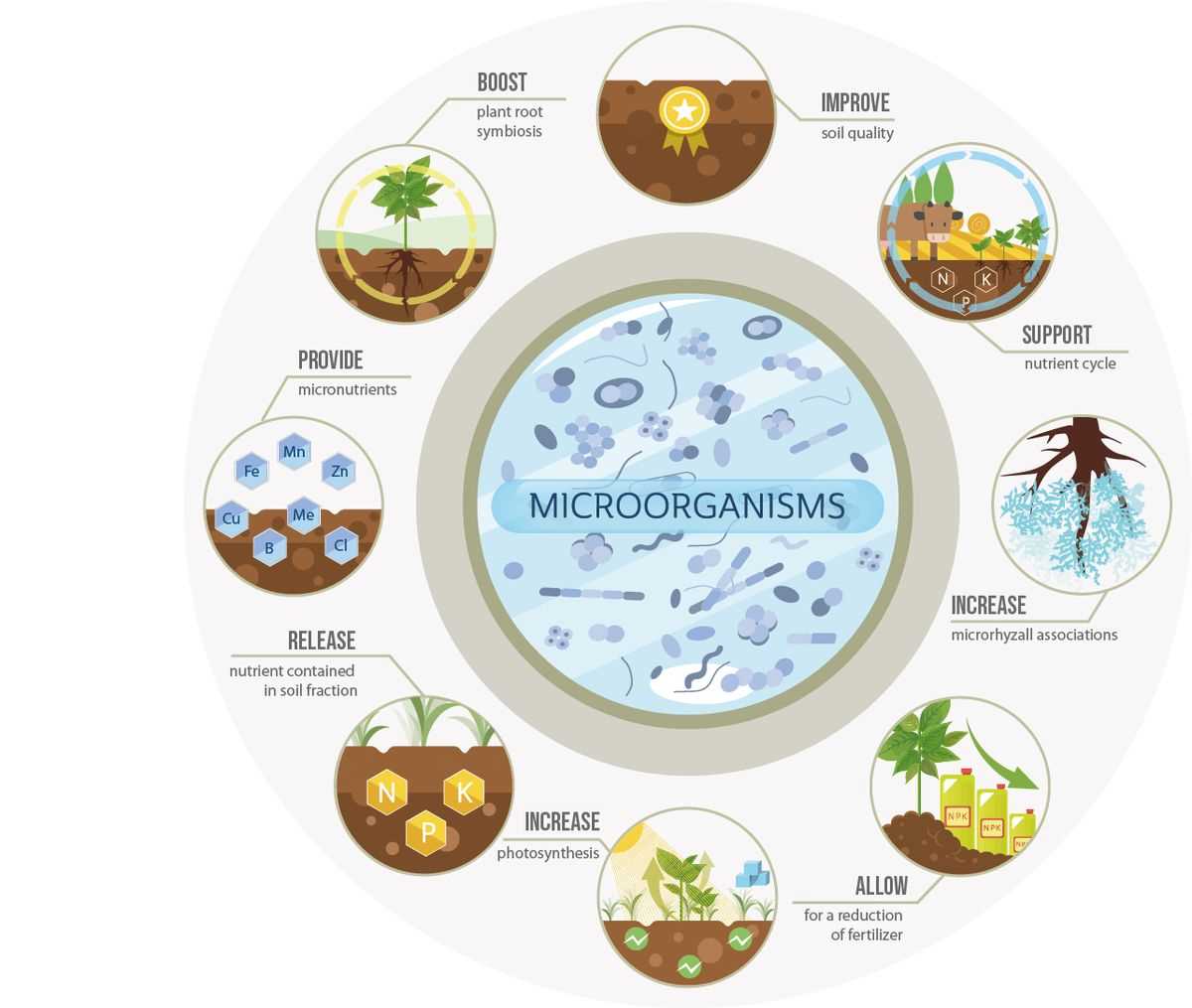
Mineral fertilizers are specially formulated to provide a balanced ratio of nutrients, ensuring that plants receive a proper and adequate supply. Different plants require varying amounts of nutrients at different stages of growth. Mineral fertilizers can be tailored to meet these specific nutritional requirements, providing plants with the right balance of NPK and other essential elements.
3. Increased Yield
The use of mineral fertilizers has been proven to significantly increase crop yields. By replenishing essential nutrients in the soil, plants are able to access a rich source of nourishment, leading to improved growth, larger fruits or vegetables, and higher yields. This is particularly important in regions where the soil lacks natural fertility or where intensive agricultural practices have depleted nutrients.
4. Efficient Absorption
Mineral fertilizers are formulated to ensure optimal nutrient availability and efficient absorption by plants. Unlike organic fertilizers, which often require microbial action to release nutrients, mineral fertilizers are readily available to plants, providing a direct and immediate source of nutrients. This allows plants to quickly take up the required elements, promoting faster and more vigorous growth.
5. Targeted Nutrient Application
Mineral fertilizers can be applied in a targeted manner, allowing for precise nutrient management. Farmers and gardeners can tailor their fertilizer application based on soil tests and plant needs, ensuring that nutrients are provided in the right amount and at the right time. This helps prevent nutrient imbalances, excessive fertilizer use, and environmental pollution.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
Mineral fertilizers are generally more cost-effective compared to organic fertilizers. They are produced on a large scale and are readily available, making them a cost-efficient option for farmers and gardeners. Additionally, their precise nutrient content and easy application help optimize resource utilization and reduce waste.
In conclusion, mineral fertilizers are essential for promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing crop yields. Their nutrient supply, balanced nutrition, increased yield potential, efficient absorption, targeted application, and cost-effectiveness make them a valuable tool for farmers and gardeners alike.
Debunking the Myth of Harmful Chemicals in Mineral Fertilizers
There is a common misconception that mineral fertilizers contain harmful chemicals that can have negative effects on the environment and human health. However, this myth is based on a misunderstanding of the composition and use of mineral fertilizers.
What are mineral fertilizers?
Mineral fertilizers are synthetic or naturally occurring substances that provide essential nutrients to plants. They are made up of different combinations of mineral elements, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for plant growth and development.
Are mineral fertilizers harmful?
No, mineral fertilizers are not inherently harmful. When used correctly, they can actually have a positive impact on crop yields and soil fertility. The key is to use them in the right amounts and at the right time, following recommended application practices.
Mineral fertilizers and the environment
Contrary to popular belief, mineral fertilizers do not contribute significantly to environmental pollution. Properly managed agricultural practices, including the use of mineral fertilizers, can reduce nutrient runoff and water contamination. In fact, mineral fertilizers can help replenish soil nutrients and improve soil structure, leading to healthier ecosystems.
Human health concerns
The myth of harmful chemicals in mineral fertilizers may stem from concerns about exposure to synthetic pesticides and herbicides used in agriculture. However, mineral fertilizers themselves are not pesticides or herbicides. They are formulated to provide specific nutrients to plants and do not pose a direct risk to human health when used correctly.
Regulations and safety measures
Government regulations and industry standards ensure the safety and quality of mineral fertilizers. These regulations help to minimize any potential risks and ensure that they are manufactured and used in a responsible manner. It is important to choose fertilizers that meet these standards and guidelines.
Fertilizer labels and information
When using mineral fertilizers, it is important to read and follow the instructions provided on the fertilizer labels. These labels contain important information about the proper application rates, timing, and safety precautions to ensure the best results and minimize any potential risks.
Conclusion
The myth of harmful chemicals in mineral fertilizers is not supported by scientific evidence. When used correctly and in accordance with regulations and guidelines, mineral fertilizers are a safe and effective way to provide essential nutrients to plants and improve crop yields. It is important to base our understanding of mineral fertilizers on facts and scientific research rather than unfounded myths.
Exploring the Benefits of Properly Applied Mineral Fertilizers
Mineral fertilizers have long been an integral part of modern agriculture and play a vital role in increasing crop productivity. When properly applied, they offer several benefits that contribute to the growth and development of plants.
1. Improved Nutrient Availability
- Mineral fertilizers are formulated to provide essential nutrients that are necessary for plant growth. These nutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), also known as NPK. By applying mineral fertilizers, farmers can ensure that plants have access to a consistent supply of these nutrients.
- Properly balanced NPK fertilizers can supply the necessary macronutrients required for plant growth, ensuring that plants have the nutrients they need to carry out essential functions such as photosynthesis, root development, and overall health.
2. Increased Crop Yield
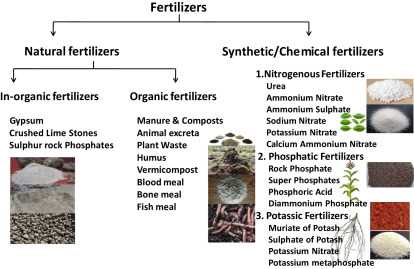
- Mineral fertilizers provide the necessary nutrients to plants in a readily available form, ensuring optimal growth and development. When plants have access to a balanced supply of nutrients, they are better equipped to produce higher yields.
- Proper application of mineral fertilizers helps plants to achieve their full genetic potential, leading to increased crop productivity. This is especially important in areas where natural soil fertility may be low, allowing farmers to maximize their harvests and meet the growing demand for food.
3. Nutrient Management
- Mineral fertilizers can be tailored to meet the specific nutrient requirements of different crops, allowing for efficient nutrient management. By utilizing soil testing and crop nutrient requirements, farmers can apply fertilizers in precise amounts and ratios, minimizing nutrient waste and potential environmental harm.
- Properly applied mineral fertilizers can also help improve soil fertility over time. By replenishing nutrient levels, they contribute to the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems and ensure that soils remain fertile for future generations.
4. Cost-Effective Solution

- Mineral fertilizers are a cost-effective solution for farmers. By providing essential plant nutrients, they help to maximize crop yield, leading to increased revenue.
- In contrast to organic fertilizers that need time to decompose and release nutrients, mineral fertilizers provide nutrients immediately and in a predictable manner. This allows farmers to precisely control the timing and availability of nutrients to match the crop’s demand, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced wastage.
In conclusion, properly applied mineral fertilizers offer numerous benefits to agricultural systems. They improve nutrient availability, increase crop yield, enable efficient nutrient management, and provide a cost-effective solution for farmers. However, it is essential that mineral fertilizers are used responsibly, following recommended application rates and practices to minimize their environmental impact and ensure sustainable agriculture.
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Mineral Fertilizers
Mineral fertilizers play a crucial role in modern agriculture, boosting crop productivity and ensuring food security. However, their use has raised concerns about their environmental impact. This article aims to explore and evaluate the environmental effects of mineral fertilizers.
1. Nutrient Runoff
One of the primary concerns associated with mineral fertilizers is nutrient runoff into water bodies. When excess fertilizers are applied to the soil, rainwater or irrigation can carry these nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into nearby rivers, lakes, and oceans. This can result in eutrophication, an excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, which depletes oxygen levels and harms aquatic life.
2. Soil Degradation
Overuse of mineral fertilizers without proper nutrient management practices can lead to soil degradation. Excessive application of nitrogen and phosphorus can cause imbalances, altering the soil pH and depleting essential micronutrients. This can affect soil fertility, reduce microbial activity, and disrupt the overall ecosystem functioning.
3. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The production and use of mineral fertilizers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process of fertilizers requires large amounts of energy, often derived from fossil fuels. Additionally, the application of these fertilizers can lead to nitrogen oxide emissions, which are potent greenhouse gases and contribute to climate change.
4. Water Contamination
The improper use or storage of mineral fertilizers can contaminate groundwater and drinking water sources. Leakage from storage facilities or improper application can introduce harmful pollutants, such as nitrates, into the water supply, posing a risk to human health.
5. Energy Consumption and Resource Depletion
The production of mineral fertilizers is energy-intensive, requiring the extraction and processing of natural resources, such as phosphate rock, potash, and natural gas. The excessive use and extraction of these resources can lead to environmental degradation and contribute to resource depletion.
Conclusion
While mineral fertilizers are essential for ensuring food production, it is vital to recognize and address their environmental impact. Sustainable practices, such as precision agriculture, nutrient management planning, and the use of organic amendments, can help minimize the negative effects. By balancing the benefits of mineral fertilizers with responsible use and environmental stewardship, we can strive for a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.
Busting the Myth of Leaching and Groundwater Contamination
One of the most persistent myths surrounding mineral fertilizers is the belief that they contribute to leaching and contamination of groundwater. However, scientific studies and research have consistently debunked this myth, showing that when used properly, mineral fertilizers pose minimal risk to groundwater quality.
The Role of Proper Application
It is important to note that the potential for leaching and groundwater contamination is not inherent to mineral fertilizers themselves, but rather to their improper use and application. When mineral fertilizers are not used according to recommended guidelines, such as applying excessive amounts or at inappropriate times, the risk of nutrient runoff and leaching is increased.
However, when mineral fertilizers are used responsibly and in accordance with best practices, the risk of leaching and groundwater contamination is greatly diminished. Farmers and gardeners can minimize the potential for nutrient runoff by carefully considering factors such as soil type, weather conditions, and nutrient requirements of the plants being grown.
The Role of Soil Nutrient Management
Another important aspect to consider when debunking the myth of groundwater contamination is the role of proper soil nutrient management. By regularly testing the soil and applying fertilizers based on the specific nutrient needs of the crops being grown, farmers can ensure that nutrients are efficiently utilized, reducing the risk of excess nutrients leaching into groundwater.
Furthermore, the use of precision agriculture techniques and technologies, such as variable rate application and site-specific nutrient management, can further enhance nutrient efficiency and minimize the risk of leaching and contamination.
The Role of Nutrient Stewardship
Lastly, it is crucial to highlight the role of nutrient stewardship in preventing groundwater contamination. Nutrient stewardship refers to the responsible use and management of fertilizers to optimize nutrient efficiency, minimize environmental impact, and protect water resources.
This involves adopting practices such as soil testing, utilizing nutrient management plans, implementing conservation practices, and following recommended fertilizer application rates and timing. By embracing nutrient stewardship principles, farmers and gardeners can significantly reduce the potential for leaching and groundwater contamination.
Conclusion
Contrary to popular belief, mineral fertilizers do not inherently contribute to leaching and groundwater contamination. When used responsibly, following best practices and adopting nutrient stewardship principles, mineral fertilizers can be safely and effectively utilized to enhance crop productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
The Role of Mineral Fertilizers in Sustainable Agriculture
Mineral fertilizers play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by providing essential nutrients to crops, improving soil fertility, and increasing crop productivity. Contrary to popular myths, mineral fertilizers are not harmful to the environment when used correctly and in appropriate quantities. In fact, they can contribute to environmental sustainability and help reduce the negative impacts of agriculture on natural ecosystems.
Nutrient requirements for plant growth
Plants require certain nutrients, known as macronutrients and micronutrients, for their growth and development. These nutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and others. While some of these nutrients are naturally present in the soil, their availability may not be sufficient to support optimal plant growth. Mineral fertilizers provide a convenient and efficient way to supplement these nutrients, ensuring that plants have an adequate supply for their needs.
Improving soil fertility

Mineral fertilizers can enhance soil fertility by replenishing essential nutrients that may be depleted over time due to continuous cropping. The application of fertilizers can balance nutrient levels in the soil, preventing nutrient deficiencies and maintaining soil health. Additionally, some mineral fertilizers, such as those containing organic matter, can improve soil structure, water holding capacity, and microbial activity, further enhancing soil fertility and sustainability.
Increasing crop productivity
By providing essential nutrients to crops, mineral fertilizers significantly contribute to increased crop productivity. Properly nourished plants are more resistant to diseases, pests, and environmental stresses, resulting in higher yields and better crop quality. This increased productivity helps meet the growing demands for food, feed, fiber, and bioenergy without the need for extensive agricultural expansion, which can lead to deforestation and habitat loss.
Environmental sustainability
Contrary to claims against them, mineral fertilizers can contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. Firstly, by improving soil fertility, fertilizers help reduce the need for excessive chemical inputs, such as pesticides and herbicides, as healthy plants are naturally more resistant to pests and diseases. Moreover, by increasing crop productivity, mineral fertilizers can minimize the need for agricultural expansion into pristine ecosystems, thereby preserving biodiversity and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with land conversion.
It is worth noting that the environmental impacts of mineral fertilizers largely depend on their proper and responsible use. Careful nutrient management, taking into account soil conditions, crop requirements, and climatic factors, can minimize nutrient losses, nutrient runoff, and the risk of water pollution.
Conclusion
Mineral fertilizers play a vital role in sustainable agriculture by providing essential nutrients, improving soil fertility, and increasing crop productivity. They are not inherently harmful to the environment when used responsibly. By relying on mineral fertilizers, farmers can optimize resource use, reduce environmental impacts, and contribute to a more sustainable and food-secure future.
Dispelling the Myth of Dependency on Mineral Fertilizers
There is a common misconception that once farmers start using mineral fertilizers, they become dependent on them and cannot go back to using natural methods. However, this is far from the truth. In fact, mineral fertilizers can be used in conjunction with organic practices to enhance overall soil fertility and productivity.
The Importance of Soil Health
Before diving into the discussion of dependence on mineral fertilizers, it is essential to understand the importance of soil health. Healthy soil is the foundation of a productive agricultural system. It provides the necessary nutrients, water holding capacity, and environment for plant roots to grow and thrive.
Therefore, maintaining soil health and fertility is of utmost importance for farmers. While natural methods, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting, play a crucial role in achieving this, mineral fertilizers also have their place.
Supplementing Natural Methods
Mineral fertilizers should not be seen as a replacement for natural methods but rather as a tool to supplement them. These fertilizers provide essential nutrients that may be lacking in the soil or required in higher quantities for optimal plant growth.
However, their use should be guided by soil testing and nutrient analysis to determine the specific deficiencies and needs. By using mineral fertilizers strategically and in conjunction with organic practices, farmers can achieve a balance that promotes healthy soil and minimizes negative environmental impacts.
The Myth of Dependence
The myth of dependency on mineral fertilizers arises from the misconception that their use leads to depleted soil fertility over time. This argument fails to consider that modern fertilizers are carefully formulated to provide the necessary nutrients without causing long-term harm.
Moreover, with proper soil management practices, including cover cropping and reduced tillage, farmers can enhance soil organic matter, improve nutrient retention, and minimize the need for excessive fertilizer application.
Balancing Environmental and Productivity Goals
It is important to acknowledge that there are both benefits and limitations to the use of mineral fertilizers. While they can increase crop yield and quality, their misuse can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution.
Therefore, the key lies in striking a balance between environmental stewardship and productivity goals. Through the integration of natural methods, precision agriculture techniques, and responsible fertilizer use, farmers can minimize their dependency on mineral fertilizers while maintaining and improving soil health in the long term.
The Future of Mineral Fertilizers: Innovations and Sustainable Solutions

As the global population continues to grow and the demand for food increases, the need for sustainable agricultural practices becomes even more critical. One of the key components of sustainable agriculture is the use of efficient and environmentally friendly fertilizers. Mineral fertilizers play a vital role in providing essential nutrients to crops, but there is a need for innovative solutions to make their production and use more sustainable.
1. Improving Efficiency
One of the main challenges faced by mineral fertilizers is their low efficiency. Traditional fertilizers often have a low nutrient conversion rate, resulting in much of the nutrients being wasted and causing environmental pollution. To address this issue, researchers and companies are working on developing new formulations and methods to enhance the efficiency of mineral fertilizers.
One approach is the development of slow-release fertilizers that release nutrients gradually over time, minimizing nutrient loss and improving crop uptake. These fertilizers are designed to match the nutrient requirements of plants at different growth stages, reducing the need for multiple applications and minimizing waste.
2. Developing Sustainable Production Methods

The production of mineral fertilizers can be resource-intensive and environmentally damaging. The extraction and processing of raw materials, such as phosphate rock and potash, can result in habitat destruction and water pollution. Additionally, the high energy requirements for fertilizer production contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
To address these challenges, sustainable production methods are being developed. One example is the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to power fertilizer plants. Another approach is the utilization of waste streams from other industries, such as food processing or wastewater treatment, as sources of nutrients for fertilizer production.
3. Promoting Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture techniques, such as remote sensing and precision application technologies, are revolutionizing farming practices. By using data-driven approaches, farmers can optimize the use of fertilizers and reduce their environmental impact.
Through the use of sensors and satellite imagery, farmers can monitor crop health and nutrient requirements in real time. This allows for the precise application of fertilizers, targeting only the areas and amounts needed, thereby minimizing waste and environmental contamination.
4. Exploring Organic Alternatives
While mineral fertilizers are essential for supporting high crop yields, there is also a growing demand for organic alternatives. Organic fertilizers, such as compost or manure, provide nutrients while improving soil health and structure.
Research is being conducted to develop organic fertilizers that can match the nutrient content and release patterns of mineral fertilizers. This would allow farmers to combine the benefits of mineral and organic fertilizers, promoting sustainable soil management practices.
| Benefits of Innovative Mineral Fertilizers | Challenges and Considerations |
|---|---|
|
|
In conclusion, the future of mineral fertilizers lies in their innovation and sustainable practices. Through improving efficiency, developing sustainable production methods, promoting precision agriculture, and exploring organic alternatives, mineral fertilizers can continue to play a vital role in supporting global food production while reducing their environmental impact.
“Question-Answer”
Are mineral fertilizers harmful to the environment?
Contrary to popular belief, mineral fertilizers are not inherently harmful to the environment. When used responsibly and in the proper amounts, mineral fertilizers can actually have positive effects on crop productivity and soil health. However, overuse or misuse of mineral fertilizers can lead to negative impacts such as nutrient runoff, water pollution, and soil degradation. It is important for farmers and gardeners to follow recommended guidelines and best practices to minimize potential harm to the environment.
Do mineral fertilizers deplete soil nutrients over time?
No, mineral fertilizers do not deplete soil nutrients over time. In fact, they can help replenish nutrient levels in soils that are deficient in essential elements. The key is to use mineral fertilizers in a balanced and targeted manner, based on soil tests and crop nutrient requirements. This ensures that the necessary nutrients are replenished without causing an imbalance or excess accumulation. To maintain soil health in the long term, it is also important to incorporate organic matter and practice proper crop rotation.
Can mineral fertilizers harm human health?
When used correctly, mineral fertilizers do not pose significant risks to human health. The nutrients present in mineral fertilizers, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for plant growth and are not typically harmful to humans when consumed through food. However, improper handling or excessive exposure to concentrated mineral fertilizers can be detrimental. It is important to follow safety guidelines and use protective measures when working with these substances to minimize any potential health risks.
Do mineral fertilizers negatively affect crop quality?
No, mineral fertilizers do not negatively affect crop quality. In fact, when used appropriately, mineral fertilizers can enhance crop quality by providing essential nutrients that may be lacking in the soil. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to poor growth, reduced yields, and lower quality crops. By supplying the necessary nutrients in the right amounts, mineral fertilizers help promote healthy plant growth, improve crop yields, and enhance overall crop quality.
Are mineral fertilizers sustainable?
The sustainability of mineral fertilizers depends on various factors, including their production methods, application practices, and environmental impacts. While the extraction and manufacturing processes of mineral fertilizers can have negative environmental consequences, their use can also contribute to sustainable agriculture. By supplying essential nutrients to plants, mineral fertilizers help improve crop productivity and food security. However, sustainable fertilizer management requires responsible use, resource efficiency, and adherence to environmental regulations to minimize negative impacts and promote long-term sustainability.
Can mineral fertilizers contribute to water pollution?
Improper use and overuse of mineral fertilizers can contribute to water pollution. When excessive fertilizer is applied to fields, the nutrients can leach into groundwater or runoff into nearby water bodies, leading to environmental problems such as algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and degradation of aquatic ecosystems. It is important for farmers and gardeners to use fertilizers judiciously, considering nutrient requirements, soil conditions, and weather patterns. Applying fertilizers at the right time, in the right amounts, and using appropriate application techniques can help minimize nutrient losses and reduce the risk of water pollution.







