- The importance of light for plant growth
- Intensity
- Duration
- Quality
- The role of water in plant development
- Transport of nutrients
- Photosynthesis
- Turgor pressure
- Respiration
- Understanding nutrient requirements for optimal growth
- 1. Macronutrients
- 2. Micronutrients
- 3. Soil pH
- 4. Nutrient ratios
- 5. Fertilizer application
- 6. Nutrient deficiency and excess
- Temperature and its impact on plant growth
- Temperature range for plant growth
- Impact of temperature on photosynthesis
- Effects of temperature on respiration
- Temperature and plant development
- Managing temperature for plant growth
- Conclusion
- The significance of air circulation for healthy plants
- Why is air circulation important?
- How to improve air circulation
- Conclusion
- Choosing the right soil for successful plant growth
- 1. Nutrient-rich soil
- 2. Well-draining soil
- 3. Soil pH
- 4. Texture and structure
- 5. Organic matter
- 6. Fertilizer requirements
- 7. Soil sterilization
- Pruning and trimming techniques for plant maintenance
- 1. Regular maintenance pruning
- 2. Pinching
- 3. Heading back
- 4. Thinning
- 5. Structural pruning
- Pest control measures to protect plants from damage
- 1. Identifying pests
- 2. Cultural control
- 3. Natural predators
- 4. Barriers
- 5. Organic insecticides
- 6. Integrated pest management
- 7. Regular monitoring
- “Question-Answer”
- What are the optimal temperature and light conditions for seedlings?
- How often should I water seedlings?
- Can I use regular garden soil for seedlings?
- What are some common symptoms of overwatering seedlings?
- How do I know when it’s time to transplant seedlings into larger pots?
- What are the ideal growing conditions for adult plants?
- “Video” What Is Seed Germination? | SEED GERMINATION | Plant Germination | Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
Providing optimal growth conditions is essential for the healthy development of both seedlings and adult plants. Whether you are starting from seed or caring for mature plants, understanding their specific needs can make all the difference in their growth and overall productivity. This guide aims to provide comprehensive information and tips on how to create the ideal environment for your plants to flourish.
Seedlings:
Seedlings are delicate and require special attention during their early stages of growth. The key to successful seedling development is to provide them with the right combination of light, temperature, moisture, and nutrients.
Light: Most seedlings require bright, indirect light to thrive. It is recommended to place them near a south or west-facing window to ensure they receive enough sunlight. Alternatively, you can use grow lights specifically designed for seedlings to provide the necessary light intensity.
Temperature: Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for the growth of seedlings. Most common plants require temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C) during the day and slightly cooler temperatures at night. Avoid placing seedlings near cold drafts or heat sources that can cause temperature fluctuations.
Moisture: Keeping the soil consistently moist but not overly saturated is essential for seedling growth. Watering from the bottom of seedling trays or using a spray bottle to mist the soil surface can help prevent excessive moisture. It is also crucial to provide good drainage to avoid root rot.
Nutrients: Seedlings have specific nutrient requirements during their early stages. Using a balanced fertilizer with a higher concentration of phosphorus and potassium can promote healthy root and leaf development. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid overfertilization, which can harm seedlings.
Adult plants:
Once seedlings have matured into adult plants, their needs change. Factors such as light intensity, temperature, watering frequency, and nutrient requirements may differ. Understanding these changes and adjusting the growth conditions accordingly ensures the optimal health and productivity of adult plants.
Light: Adult plants have varying light requirements depending on their species. Some may need direct sunlight, while others prefer indirect or filtered light. It is important to research the light needs of your specific plants and place them in an area that provides the appropriate amount of light.
Temperature: Adult plants generally prefer stable temperatures within the range of 60-75°F (15-24°C). Avoid placing them in areas with extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can stress the plants and affect their growth.
Watering: The watering needs of adult plants can vary greatly. Some plants prefer consistently moist soil, while others prefer a dry period between waterings. It is important to monitor the soil moisture levels and adjust your watering schedule accordingly. Additionally, using a well-draining potting medium and providing proper drainage can prevent issues such as root rot.
Nutrients: Adult plants require a balanced fertilizer that matches their specific nutritional needs. Generally, a slow-release fertilizer applied every few weeks can provide the necessary nutrients for healthy plant growth. It is important to follow the recommended dosage and avoid overfertilization, which can lead to nutrient imbalances and damage the plant.
Remember, every plant species is unique and may have specific requirements that differ from the general guidelines mentioned here. It is crucial to research the specific care needs of your plants to ensure their optimal growth and development. By providing the right growth conditions, you can help your seedlings and adult plants thrive and create a beautiful, healthy garden.
The importance of light for plant growth
Light is one of the most important factors for plant growth. It is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Without adequate light, plants cannot make enough food, which can lead to stunted growth and overall poor health.
There are three main aspects of light that are important for plant growth: intensity, duration, and quality.
Intensity
The intensity of light refers to the amount of light energy that reaches the plant. Different plants have different light intensity requirements, but in general, most plants require bright, indirect light. Too much or too little light can be harmful to plants.
Duration
The duration of light refers to the length of time that plants are exposed to light each day. Most plants require around 12-16 hours of light per day to grow and thrive. This can be achieved through natural sunlight or artificial lighting, such as grow lights.
Quality
The quality of light refers to the specific wavelengths of light that plants need for photosynthesis. Different wavelengths have different effects on plants, and plants have specific light requirements depending on their stage of growth. For example, blue light is important for vegetative growth, while red light is important for flowering and fruiting.
It is important for growers to provide the right balance of light intensity, duration, and quality for their plants. This can be achieved through proper placement of plants in relation to light sources, using appropriate lighting fixtures, and using light timers to ensure consistent light exposure.
Overall, light is a crucial factor for plant growth and should be carefully considered when growing plants indoors or in areas with limited sunlight. By providing the right amount and quality of light, growers can help their plants thrive and reach their full potential.
The role of water in plant development
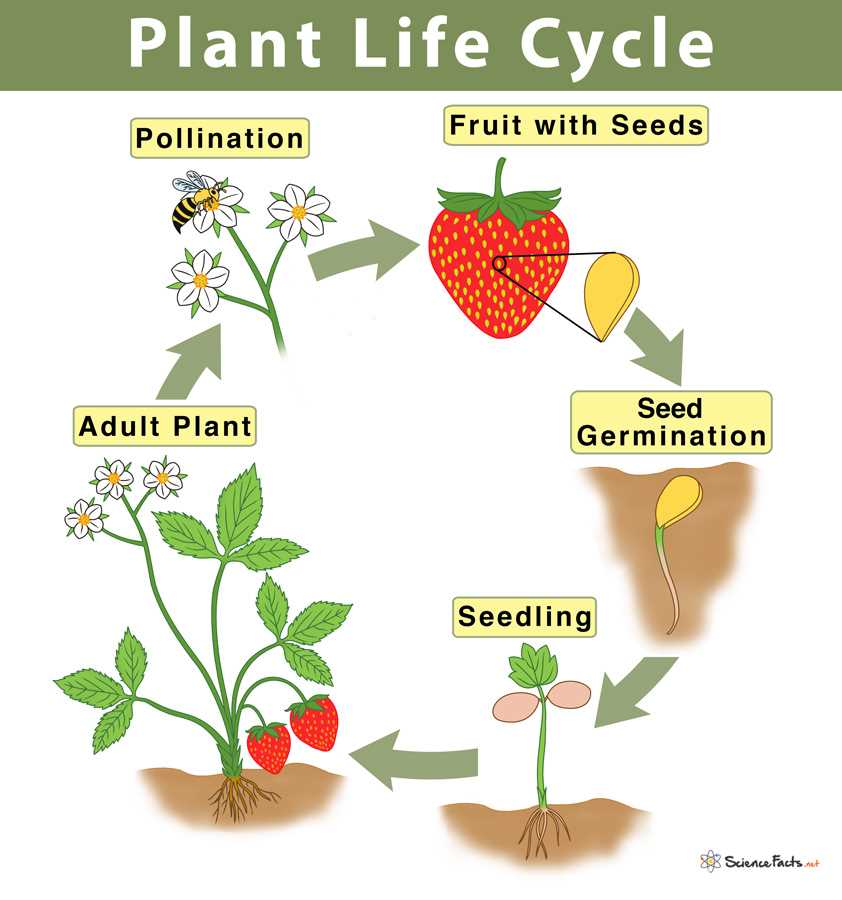
Water plays a vital role in the development of plants, as it is essential for various physiological processes. Without an adequate water supply, plants may not be able to grow and function properly.
Transport of nutrients
- Water acts as a medium for the transportation of nutrients throughout the plant.
- Through the process of transpiration, water is absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves, where it evaporates and creates a suction force that pulls up water and dissolved nutrients from the roots.
- This constant flow of water helps in the movement of essential minerals and nutrients to different parts of the plant, ensuring proper growth and development.
Photosynthesis
- Water is also a crucial component for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- During photosynthesis, water is absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves, where it combines with carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
- This glucose serves as the main source of energy for the plant, while oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
Turgor pressure
- Water is responsible for maintaining turgor pressure, which gives rigidity and structure to plant cells.
- When a plant absorbs water, it fills the vacuoles within the cells, creating a pressure that helps the plant maintain its shape.
- Without sufficient water, plants may wilt and become floppy, as the lack of turgor pressure causes the cells to lose their shape.
Respiration
- Water is involved in the respiration process of plants, allowing them to release energy from glucose.
- During respiration, plants break down glucose molecules to release energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
- This process occurs in the presence of oxygen, and water plays a vital role in facilitating the chemical reactions involved in respiration.
In conclusion, water is essential for various aspects of plant development, including nutrient transportation, photosynthesis, maintenance of turgor pressure, and respiration. Providing plants with an adequate and regular water supply is necessary to ensure their healthy growth and overall well-being.
Understanding nutrient requirements for optimal growth
Proper nutrient supply is essential for the optimal growth and development of plants. Understanding the nutrient requirements of seedlings and adult plants can help ensure their healthy growth and productivity. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the essential elements required in relatively large quantities for plant growth. They include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). These nutrients play crucial roles in various biochemical processes and are necessary for the formation of proteins, enzymes, and structural components of plants.
2. Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential elements required in small amounts, but they are equally vital for plant growth. They include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), and chlorine (Cl). Although plants need these nutrients in smaller quantities, their deficiency can severely affect plant growth and development.
3. Soil pH

The pH level of the soil has a significant impact on nutrient availability. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH (around 6.0 to 7.0), as this range allows for optimal nutrient uptake. However, some plants may have specific pH requirements, so it’s important to consider the target plant’s preferences when adjusting soil pH.
4. Nutrient ratios
The balance between different nutrients is crucial for optimal plant growth. The ratios of macronutrients and micronutrients can vary depending on the specific plant species and stage of growth. It’s important to provide a balanced nutrient solution or soil amendment to meet the plant’s requirements at different growth stages.
5. Fertilizer application

Fertilizers can be applied in various forms, including granular, liquid, or foliar application. The choice of fertilizers depends on the nutrient requirements of the plants and the desired method of application. It’s essential to follow recommended application rates and schedules to prevent nutrient toxicity or deficiency.
6. Nutrient deficiency and excess
Monitoring plant health and observing any symptoms of nutrient deficiencies or excess is crucial for providing appropriate remedial measures. Symptoms of nutrient deficiencies can include stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or abnormal leaf color. On the other hand, excess nutrients can cause leaf burn, root rot, or other detrimental effects on plant health.
By understanding the nutrient requirements of plants, you can create optimal growing conditions and promote healthy growth. Regular monitoring, appropriate fertilization, and maintaining a balanced nutrient supply will help your plants thrive and reach their fullest potential.
Temperature and its impact on plant growth
Temperature plays a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. It affects various physiological processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration. Different plants have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth, and understanding these requirements is essential for successful cultivation.
Temperature range for plant growth
Each plant species has its own temperature range for optimal growth. Generally, most plants prefer temperatures between 65°F and 75°F (18°C and 24°C). However, this range can vary depending on the plant’s origin and adaptation to different environments. Some plants, such as tropical species, thrive in higher temperatures, while others, like cool-season crops, prefer cooler temperatures.
Impact of temperature on photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, heavily relies on temperature. As temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis generally increases as well. However, extreme high temperatures can inhibit photosynthesis and damage the plant. On the other hand, low temperatures can slow down photosynthesis and limit plant growth. Maintaining an optimal temperature range allows plants to maximize their photosynthetic activity and optimize their growth.
Effects of temperature on respiration
Respiration, the process by which plants convert stored energy into a usable form, is also influenced by temperature. Warmer temperatures generally increase the rate of respiration, while colder temperatures slow it down. This means that during hot weather, plants may require more energy and nutrients to support their increased respiration rates. It is crucial to provide adequate resources to meet these increased demands.
Temperature and plant development
Temperature plays a vital role in determining the rate of plant development. Warmer temperatures generally accelerate plant growth and development, while colder temperatures slow it down. This can have implications for seed germination, flowering, and fruit set. Understanding the ideal temperature ranges for specific plant stages can help manage the timing and growth of plants.
Managing temperature for plant growth
To create optimal temperature conditions for plant growth, it is important to consider various factors. Providing proper insulation and ventilation in greenhouse environments can help regulate temperature and prevent extreme fluctuations. Additionally, using shade cloth or adding mulch can help protect plants from excessive heat. Monitoring temperature levels regularly and making necessary adjustments can ensure plants have the ideal conditions for growth.
Conclusion
Temperature significantly impacts plant growth and development. Each plant has specific temperature requirements for optimal growth, and understanding these requirements is crucial for successful cultivation. By managing temperature levels and providing the appropriate conditions, gardeners and farmers can help plants thrive and maximize their potential.
The significance of air circulation for healthy plants
Air circulation is a crucial factor in maintaining the health and vitality of plants. In enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces, stagnant air can create a host of problems for plants, including reduced growth, increased susceptibility to pests and diseases, and poor nutrient absorption.
Why is air circulation important?
Proper air circulation is essential for a number of reasons:
- Prevents moisture buildup: Adequate air circulation helps to prevent excess moisture from accumulating around plants, which can lead to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and root rot. It also helps to dry out the leaves faster after watering, reducing the chances of fungal or bacterial growth.
- Regulates temperature: Air circulation helps to regulate the temperature around plants by dissipating excess heat and preventing cold spots. This is particularly important for plants that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
- Stimulates transpiration: Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water through their leaves. Good air circulation helps to increase transpiration, which in turn aids in the uptake of nutrients by the roots. It also helps to strengthen the plant’s vascular system.
- Reduces pest infestations: Proper air circulation can help to discourage pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites, as they prefer still air environments. It also makes it harder for these pests to travel between plants, reducing the risk of infestations.
How to improve air circulation
There are several ways to improve air circulation around your plants:
- Prune and thin: Regularly prune your plants to remove any dead or crowded foliage, as well as any branches that are blocking airflow. Thinning out dense vegetation can also help to improve air circulation.
- Use fans: Place fans strategically to promote air movement throughout your growing area. Oscillating fans are particularly effective at maintaining a constant flow of air.
- Space plants appropriately: Give your plants enough room to grow by spacing them accordingly. Crowding plants can impede air circulation and increase the risk of disease.
- Choose the right containers: Opt for containers with drainage holes to prevent water from pooling around the roots, which can lead to waterlogged soil and poor air circulation.
Conclusion
Air circulation plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of plants. By ensuring proper air circulation, you can create an environment that is conducive to growth, disease prevention, and optimal nutrient uptake. Implementing the strategies mentioned above will help to promote healthy plants and improve their overall resilience.
Choosing the right soil for successful plant growth
Growing healthy plants starts with choosing the right soil. The soil you use can greatly affect the growth and development of your plants. Here are a few factors to consider when selecting soil for successful plant growth:
1. Nutrient-rich soil
Plants require a variety of nutrients to grow properly. Choose a soil that is rich in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are often represented by the NPK ratio, which indicates the concentration of these elements in the soil.
2. Well-draining soil

Proper drainage is crucial for plant growth. Soil that retains too much water can lead to root rot and other plant diseases. Look for soil that allows water to drain easily, preventing waterlogged conditions.
3. Soil pH
The pH level of the soil is another important factor to consider. Different plants thrive in different pH levels. Some prefer acidic soil, while others prefer alkaline soil. It’s important to know the preferred pH range for your plants and choose soil that matches those requirements.
4. Texture and structure
The texture and structure of the soil can greatly affect root development. Sandy soils provide good drainage but may not retain enough water. Clay soils retain water well but may not drain properly. Loamy soils, which have a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, are generally the best choice as they provide good drainage and moisture retention.
5. Organic matter
Addition of organic matter can greatly improve soil quality. Compost, manure, and other organic materials can enhance soil structure, increase nutrient content, and improve water retention. Incorporating organic matter into your soil can create a healthy environment for plant growth.
6. Fertilizer requirements
Consider the fertilizer needs of your plants when choosing soil. Some plants may require additional fertilizers to meet their nutrient requirements. If your chosen soil lacks certain nutrients, you may need to supplement with fertilizers.
7. Soil sterilization
If you’re starting seedlings, it’s important to use sterilized soil to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi. Sterilized soil reduces the risk of disease and promotes healthy plant growth.
By considering these factors and choosing the right soil, you can create optimal growing conditions for your plants and set them up for successful growth and development.
Pruning and trimming techniques for plant maintenance
Pruning and trimming are important techniques for maintaining the health and shape of plants. By removing dead or overgrown branches, you can stimulate new growth and improve the overall appearance of your plants. Here are some key techniques to consider when pruning and trimming:
1. Regular maintenance pruning
- Regularly inspect your plants for any dead or damaged branches. Use clean pruning shears to remove them at the base of the branch, making a clean diagonal cut.
- Remove any crossing or rubbing branches to prevent injury and improve air circulation.
- Trim back any long or overgrown branches to maintain the desired shape and size of the plant.
2. Pinching

- Pinching is a technique commonly used on herbaceous plants, such as annual flowers and herbs. Using your fingers or pruning shears, pinch off the top few inches of the plant to encourage branching and stimulate new growth.
- This technique is especially useful for promoting bushiness and preventing leggy growth.
3. Heading back
- Heading back is a more severe form of pruning that involves cutting back the entire branch to a specific point, usually above a bud or lateral branch.
- This technique is often used to rejuvenate old or overgrown plants and can stimulate new growth.
- Be careful not to remove too much foliage at once, as this can stress the plant.
4. Thinning
- Thinning involves selectively removing entire branches or stems to reduce density and promote better air circulation and light penetration.
- This technique is commonly used on trees and shrubs to maintain their natural shape and prevent overcrowding.
5. Structural pruning
- Structural pruning is important for young trees and shrubs and involves the removal of any weak or poorly positioned branches.
- This technique helps shape the plant’s overall structure and prevents future problems, such as branch breakage.
- It’s best to consult a professional arborist or horticulturist for guidance on structural pruning.
Remember to always use clean and sharp pruning tools to make clean cuts and minimize damage to the plant. It’s also important to prune and trim during the appropriate season for each specific plant, as timing can vary depending on the species. Regular maintenance pruning and proper technique can help keep your plants healthy, vigorous, and looking their best.
Pest control measures to protect plants from damage
Pests can cause significant damage to plants, affecting their growth and overall health. Implementing effective pest control measures is essential to protect plants and ensure their successful growth. Here are some strategies and techniques to combat common garden pests:
1. Identifying pests
Before implementing any control measures, it is important to identify the pests infesting your plants. Different pests may require specific control methods, and misidentifying them can lead to ineffective treatment.
2. Cultural control
Implementing cultural practices can help prevent pest infestations. These include measures such as proper watering, regular pruning, and maintaining healthy soil conditions. Healthy plants are less susceptible to pest damage.
3. Natural predators
Encouraging natural predators in your garden can help control pests. Ladybugs, lacewings, and birds are beneficial insects and animals that feed on many common garden pests. Providing habitat and food sources for these creatures can help keep pest populations under control.
4. Barriers
Physical barriers can be effective at preventing pest damage. These include fencing, netting, and row covers. They can be used to keep out larger pests like rabbits or birds or to protect plants from insect infestations.
5. Organic insecticides
If the pest population becomes too large to control using natural methods, organic insecticides can be used. These products are derived from natural sources and are less harmful to the environment and beneficial organisms. However, care should be taken to follow the instructions and use them sparingly.
6. Integrated pest management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an effective and environmentally friendly approach to pest control. It involves combining various pest control methods to minimize pest populations. This may include cultural control, natural predators, and targeted use of insecticides only when necessary.
7. Regular monitoring
Regularly inspecting your plants for signs of pests or damage is crucial for early detection and control. The sooner you identify a pest problem, the easier it is to manage and prevent further damage.
By implementing these pest control measures, you can protect your plants from damage and ensure their healthy growth and development.
“Question-Answer”
What are the optimal temperature and light conditions for seedlings?
For most seedlings, the optimal temperature range is between 65-75°F (18-24°C). In terms of light, seedlings require about 14-16 hours of bright, indirect light per day.
How often should I water seedlings?
It is important to keep the soil evenly moist, but not waterlogged. Water the seedlings when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. This usually translates to watering every 2-3 days.
Can I use regular garden soil for seedlings?
No, regular garden soil is usually too heavy and may contain pathogens or weed seeds. It is best to use a specialized seed-starting mix, which provides a lighter texture and is sterilized to prevent disease.
What are some common symptoms of overwatering seedlings?
Overwatering seedlings can cause the roots to rot and the plants to become weak and susceptible to diseases. Some common symptoms include wilting, yellowing leaves, and a foul smell coming from the soil.
How do I know when it’s time to transplant seedlings into larger pots?
Seedlings are typically ready for transplanting when they have developed their first set of true leaves and their roots start to fill the current pot. It is important to handle the seedlings gently to avoid damaging their delicate roots during the transplanting process.
What are the ideal growing conditions for adult plants?
The ideal growing conditions for adult plants depend on the specific species, but in general, they require a stable temperature range, adequate lighting, proper watering, and well-draining soil. It is important to research the specific needs of each plant to ensure optimal growth.







