- Optimal Feeding Proportions for Seedling Development
- Introduction
- Stage 1: Germination
- Stage 2: Early Vegetative Growth
- Stage 3: Root Development
- Stage 4: Pre-Transplanting
- Conclusion
- Understanding the Stages
- Germination
- Root Development
- Leaf Formation
- Stem Elongation
- Secondary Root Growth
- Vegetative Growth
- Different Nutritional Requirements
- Germination Stage
- Cotyledon Stage
- True Leaf Stage
- Transplanting Stage
- Maturity Stage
- Importance of Balanced Feeding
- Early Stage Growth
- Establishment of Root System
- Importance of a strong root system
- Phases of root system development
- Factors influencing root system development
- Care practices for promoting root system development
- Vigorous Leaf Growth
- Preparation for Transplanting
- Hardening Off
- Preparing the Planting Site
- Watering and Fertilizing
- Final Stage of Seedling Development
- Characteristics of the Final Stage
- Care during the Final Stage
- “Question-Answer”
- How often should I water seedlings at each stage of development?
- What nutrients do seedlings need during each stage of development?
- At what stage should I start fertilizing my seedlings?
- How can I ensure that my seedlings receive enough light?
- When should I transplant my seedlings into larger containers?
- Can I use compost as a growing medium for seedlings?
- What should I do if my seedlings are leggy?
- “Video” Seeds and Germination Explained
Growing seedlings is an essential part of any gardening or farming endeavor. Whether you’re looking to cultivate a backyard vegetable garden or start a nursery, understanding the stages of seedling development is crucial. One key aspect of ensuring healthy seedling growth is providing them with optimal feeding proportions.
From the moment a seed is planted, it embarks on a journey of growth and development. The first stage is germination, where the seed absorbs water and begins to sprout. At this stage, it is essential to provide the seedlings with adequate moisture to support their growth.
As the seedlings grow and develop, they enter the second stage of development known as the cotyledon stage. During this stage, the seedlings start developing their first pair of leaves, called cotyledons. Proper feeding proportions during this stage are necessary to provide the seedlings with the essential nutrients they require to develop strong roots and healthy leaves.
Finally, the seedlings enter the third stage of development – the true leaf stage. At this point, the seedlings have developed their true leaves, which differ from the cotyledons in shape and structure. It is crucial to maintain proper feeding proportions during this stage to encourage further root development and promote overall plant health.
Understanding the specific feeding proportions required at each stage of seedling development is vital for successful gardening and farming. By providing seedlings with the optimal balance of nutrients and moisture, you can ensure their healthy growth and increase their chances of thriving into mature plants.
Optimal Feeding Proportions for Seedling Development
Introduction
Proper feeding is crucial for the healthy growth and development of seedlings. Providing the right balance of nutrients at each stage of growth is essential to ensure optimal development and overall plant vigor. In this article, we will explore the different stages of seedling development and discuss the optimal feeding proportions for each stage.
Stage 1: Germination
During germination, seedlings initially rely on the energy stored in the seed. However, as soon as the cotyledons emerge, they require external nutrition to continue growth. At this stage, it is recommended to provide a balanced feeding solution containing a higher proportion of nitrogen (N) for promoting leaf and stem growth. A ratio of 3:1:2 (N:P:K) is often suitable for this stage.
Stage 2: Early Vegetative Growth
During the early vegetative growth stage, the seedlings start developing their true leaves and establish a stronger root system. A balanced feeding solution with a ratio of 1:1:1 (N:P:K) is generally recommended at this stage. This balanced ratio provides a sufficient amount of all essential nutrients for the overall growth of the seedlings.
Stage 3: Root Development

Root development is crucial for the establishment of a strong and healthy plant. At this stage, the seedlings require a higher proportion of phosphorous (P) for promoting root growth. A feeding solution with a ratio of 1:3:1 (N:P:K) is often recommended to support root development.
Stage 4: Pre-Transplanting

Pre-transplanting is the stage before transferring the seedlings to their final growing location. During this stage, it is essential to provide a well-balanced feeding solution to ensure optimal plant strength and vigor. A ratio of 2:2:2 (N:P:K) is commonly applied to promote overall plant development and establish healthy transplantable seedlings.
Conclusion
Feeding seedlings with the right proportions of nutrients at each stage of growth is crucial for their overall development. Adjusting the nutrient ratios according to the specific growth stage helps ensure that the seedlings receive the optimal nutrition they need for healthy growth, strong root development, and vigorous plant establishment.
Understanding the Stages
Germination
Germination is the first stage in the life cycle of a seedling. It is the process by which a seed begins to grow into a new plant. During germination, the seed absorbs water and swells, causing the seed coat to crack open. This allows the embryonic root, called the radicle, to emerge and anchor the seedling into the soil. The radicle also starts to absorb nutrients from the soil.
Root Development
After germination, the root system of the seedling develops. The primary root, or taproot, grows downward and anchors the seedling. From the taproot, secondary roots, also known as lateral roots, begin to emerge and spread out in the soil. The root system plays a crucial role in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, providing stability to the plant, and storing energy reserves.
Healthy root development is essential for seedling growth, as it ensures an efficient intake of nutrients and water. Proper feeding proportions should support root growth by providing an adequate supply of nutrients.
Leaf Formation
As the root system develops, the seedling starts to produce its first leaves. These initial leaves are known as cotyledons or seed leaves. They provide the seedling with energy through photosynthesis until true leaves start to emerge. True leaves are the leaves that grow after the cotyledons and resemble the leaves of the mature plant.
During this stage, the seedling relies on a sufficient supply of nutrients to support leaf formation and growth. The feeding proportions should be adjusted to meet the increasing nutritional needs of the seedling.
Stem Elongation
In the next stage, the seedling’s stem begins to elongate, allowing it to grow vertically above the soil surface. The stem provides structural support to the plant and transports water and nutrients between the roots and leaves.
To ensure optimal stem elongation, the seedling requires a balanced supply of nutrients. Proper feeding proportions should consider the specific nutrient requirements for stem growth and development.
Secondary Root Growth
During this stage, the seedling’s root system continues to develop as secondary roots grow and branch out from the primary root. These secondary roots enhance the seedling’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
Feeding proportions should be adjusted to provide adequate nutrients for secondary root growth. This stage is crucial for establishing a healthy root system that will support the plant’s growth and development.
Vegetative Growth
After the initial stages of seedling development, the plant enters the vegetative growth stage. During this stage, the plant focuses on leaf and stem development to increase its photosynthetic capacity and overall size.
Feeding proportions during the vegetative growth stage should provide an appropriate balance of nutrients to support vigorous leaf and stem growth. This stage sets the foundation for future flowering and fruit production.
Different Nutritional Requirements
As seedlings develop, their nutritional requirements change at each stage. Understanding these different requirements can help optimize feeding proportions for seedling growth and development.
Germination Stage
During the germination stage, seedlings primarily rely on stored energy within the seed. They do not require external sources of nutrients during this stage. Adequate moisture, light, and temperature are the key factors that promote germination.
Cotyledon Stage
In the cotyledon stage, seedlings start to develop their first pair of true leaves and depend on the energy stored in the cotyledons for growth. The cotyledons provide the necessary nutrients until the seedling can establish its root system and begin taking up nutrients from the soil. Providing a balanced nutrient mix during this stage can help support healthy growth.
True Leaf Stage
Once seedlings reach the true leaf stage, they have established a root system and can start absorbing nutrients from the soil. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are key macronutrients required for healthy leaf and stem development. Additionally, micronutrients such as iron, copper, and zinc are important for various metabolic processes in the seedlings.
Transplanting Stage
When seedlings are ready to be transplanted into larger containers or the ground, they may require a slightly different nutrient mix compared to earlier stages. It is important to provide a well-balanced fertilizer that includes both macro and micronutrients to support the seedling’s growth during this transitional stage.
Maturity Stage
As seedlings continue to grow and mature, their nutrient requirements may change. Depending on the specific plant species, some seedlings may require higher levels of certain nutrients to support flower and fruit development. It is important to research the specific nutritional requirements of the plant species being grown to ensure optimal feeding proportions for mature seedlings.
Understanding the different nutritional requirements at each stage of seedling development is crucial for promoting healthy growth and maximizing crop yields. By providing the right balance of nutrients, seedlings can thrive and reach their full potential.
Importance of Balanced Feeding
Balanced feeding is crucial for optimal seedling development. It involves providing the right nutrients in the correct proportions to support healthy growth and development. A well-balanced diet ensures that seedlings have the necessary elements for photosynthesis, root development, and overall plant health.
Feeding seedlings with a balanced diet promotes strong and sturdy growth. It helps seedlings grow roots that are resistant to diseases and pests, as well as improve their ability to absorb nutrients from the soil. This, in turn, leads to healthier and more productive plants in the long run.
A balanced diet also plays a role in preventing nutrient deficiencies and imbalances, which can result in stunted growth, reduced yields, and even plant death. By providing the necessary nutrients in the right proportions, seedlings are less likely to suffer from deficiencies in essential macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese.
Furthermore, a balanced feeding approach can improve the overall resilience and stress tolerance of seedlings. When seedlings are properly nourished, they are better equipped to withstand environmental stresses, such as extreme temperatures, drought, and disease attacks. This is particularly important during the early stages of growth when seedlings are more vulnerable.
To achieve balanced feeding, it is important to understand the specific nutrient requirements of seedlings at different stages of development. This knowledge can help growers adjust their feeding programs accordingly, ensuring that seedlings receive the right nutrients at the right time. Regular monitoring and analysis of soil nutrient levels can also help identify any deficiencies or imbalances, allowing for prompt corrective measures.
In conclusion, balanced feeding is essential for optimal seedling development. By providing the right nutrients in the correct proportions, growers can support healthy growth, promote root development, prevent nutrient deficiencies, and improve overall stress tolerance. Adopting a balanced feeding approach is key to achieving successful seedling growth and ensuring the long-term productivity of plants.
Early Stage Growth
The early stage of plant growth is a critical period where the seedling is establishing its root system and developing its first leaves. During this stage, the seedling relies heavily on the nutrients stored in the seed, but it also requires additional nutrients from the surrounding soil.
At this stage, it is important to provide the seedling with a balanced diet of macro and micronutrients. Macro nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are essential for the growth and development of the seedling. Nitrogen is required for the production of proteins and other essential compounds, while phosphorus is important for energy transfer and root development. Potassium helps with water balance and overall plant growth.
In addition to macro nutrients, the seedling also requires micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese. These nutrients are required in smaller quantities but are equally important for the healthy development of the seedling. Iron is necessary for chlorophyll production and photosynthesis, while zinc and manganese are involved in various metabolic processes.
During the early stage of growth, it is important to ensure that the seedling has access to these nutrients. This can be achieved by providing a nutrient-rich soil or using a balanced fertilizer. Additionally, it is important to monitor the soil moisture and provide the seedling with adequate water as water is essential for nutrient uptake and overall plant growth.
The early stage of growth is a critical period for the seedling, and providing it with optimal feeding proportions of nutrients will help ensure its healthy development and better chances of survival.
Establishment of Root System
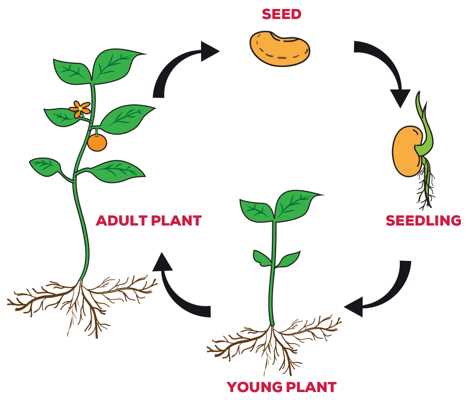
The establishment of a strong and healthy root system is crucial for the long-term success of seedling development. The root system plays a vital role in nutrient uptake, anchoring the plant in the soil, and providing stability.
Importance of a strong root system
A strong root system allows seedlings to access the necessary nutrients and water from the soil. It provides a stable foundation for the plant and enables it to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as strong winds or heavy rains. A well-developed root system also promotes efficient photosynthesis and overall plant growth.
Phases of root system development
The development of a root system can be divided into several phases:
- Germination phase: During this phase, root growth begins and a primary root, also known as a radicle, emerges from the seed. This primary root elongates and starts to explore the surrounding soil for water and nutrients.
- Root hair development phase: In this phase, the primary root continues to elongate, and fine root hairs develop. These root hairs increase the surface area of the root system, enhancing the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients.
- Secondary root growth phase: As the seedling grows, secondary roots start to develop from the primary root. These secondary roots branch out and spread in search of additional resources. This phase is crucial for establishing a strong and well-structured root system.
- Mature root system phase: After the seedling has established a well-developed root system, further growth and complexity are achieved. The root system becomes more extensive, with numerous lateral roots and root hairs, enabling optimal nutrient and water uptake.
Factors influencing root system development
Several factors can influence the development of a seedling’s root system:
- Soil structure: The physical properties of the soil, such as its texture, drainage, and fertility, can affect root growth. Loose and well-aerated soil promotes healthy root development, while compacted soil can restrict it.
- Nutrient availability: A balanced availability of essential nutrients is crucial for root system development. Insufficient nutrients can lead to stunted root growth, while excess nutrients may cause damage to the roots.
- Water supply: An adequate water supply is essential for root growth and development. Adequate irrigation is important to prevent water stress, which can hinder root system establishment.
- Temperature and environmental conditions: Optimal temperature and favorable environmental conditions promote healthy root system development. Extreme temperatures, drought, or excessive moisture can negatively impact root growth.
Care practices for promoting root system development
To promote the establishment of a strong root system, the following care practices should be considered:
- Proper watering: Provide adequate water to ensure consistent soil moisture without overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
- Appropriate nutrient balance: Use a balanced fertilizer to provide essential nutrients for healthy root development. Avoid excess fertilizer application, as it can cause nutrient imbalances and root damage.
- Soil aeration: Ensure proper soil aeration by avoiding compaction and incorporating organic matter into the soil.
- Protection from extreme weather conditions: Protect seedlings from extreme weather conditions such as frost, excessive heat, or heavy rainfall to prevent stress on the developing root system.
By understanding the different stages of root system development and implementing appropriate care practices, seedlings can establish strong root systems and thrive in their environment.
Vigorous Leaf Growth
During the seedling stage, one of the critical aspects of development is achieving vigorous leaf growth. This stage is crucial for establishing a strong foundation for the plant and ensuring its ability to photosynthesize effectively.
The following factors play a significant role in promoting vigorous leaf growth:
- Proper lighting: Seedlings require adequate light to stimulate leaf growth. Providing them with the right amount of light, either natural or artificial, is essential. It is recommended to place seedlings near a south-facing window or provide them with grow lights for at least 12-14 hours a day.
- Suitable temperature: Maintaining an optimal temperature range is crucial for promoting vigorous leaf growth. Most seedlings thrive in temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). Sudden temperature fluctuations or constant exposure to extremes can hinder leaf development.
- Balanced nutrition: Providing seedlings with a balanced nutrient solution is vital for their growth. A nutrient-rich soil mix or a properly formulated fertilizer can provide the necessary nutrients for leaf development. It is essential to understand the specific nutrient requirements of the seedlings you are growing.
- Adequate water: Proper hydration is crucial for seedlings to grow healthy leaves. Overwatering or underwatering can both have negative effects on leaf growth. The key is to ensure that the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Air circulation: Seedlings benefit from good air circulation, as it helps strengthen their leaves and stems. It prevents the buildup of excess humidity, reducing the risk of fungal diseases that can hinder vigorous leaf growth. Using a small fan or keeping a gentle breeze in the growing area can promote healthy air circulation.
By providing the optimal conditions for vigorous leaf growth, you can ensure that your seedlings develop strong, healthy leaves, setting them on the path to successful plant growth.
Preparation for Transplanting
Preparing seedlings for transplantation is a crucial step in ensuring their successful growth and development. This stage involves a series of steps to make the seedlings ready for their transition from the nursery to the final planting location.
Hardening Off
Hardening off is the process of gradually acclimatizing seedlings to outdoor conditions. This step prepares them for the changes in temperature, humidity, and sunlight they will encounter once transplanted.
- Begin hardening off seedlings about 7-10 days before the planned transplanting date.
- Start by placing the seedlings in a sheltered area outdoors for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the duration over time.
- Protect the seedlings from strong winds and direct sunlight during the initial stages of hardening off.
- Gradually expose the seedlings to more sunlight and outdoor conditions as they become more resilient.
Preparing the Planting Site
Before transplanting the seedlings, it is important to prepare the planting site to ensure optimal growing conditions.
- Clear the planting area of any weeds, rocks, or debris that may hinder the growth of the seedlings.
- Amend the soil with organic matter such as compost or aged manure to improve its fertility and drainage.
- Ensure that the soil is well-drained and has a neutral pH level suitable for the specific type of seedling.
- Provide support structures like stakes or trellises if needed for certain plants to ensure proper growth and development.
Watering and Fertilizing
Proper watering and fertilizing are essential during the preparation for transplanting stage to promote healthy seedling growth.
- Water the seedlings regularly, keeping the soil moist but not waterlogged to avoid root rot.
- Apply a balanced liquid fertilizer or slow-release granular fertilizer according to the specific needs of the seedlings.
- Monitor the moisture levels in the soil and adjust the watering frequency accordingly.
- Provide adequate spacing between seedlings to prevent overcrowding, which can lead to competition for resources.
| Steps | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Hardening Off | Gradually expose seedlings to outdoor conditions before transplanting. |
| Preparing the Planting Site | Clear the area, amend the soil, and provide necessary support structures. |
| Watering and Fertilizing | Maintain proper moisture levels and provide adequate nutrients for healthy growth. |
Final Stage of Seedling Development
The final stage of seedling development is a critical period where the seedling is fully established and ready to be transplanted into the field or a larger container for further growth. During this stage, the seedling should have a well-developed root system, strong stems, and healthy leaves.
Characteristics of the Final Stage
- Root System: The seedling’s root system should be well-developed, with numerous fine roots that are capable of absorbing water and nutrients efficiently. The roots should be strong, healthy, and free from diseases or damages.
- Stem: The stem of the seedling should be sturdy and able to support the weight of the plant. It should be straight, without any signs of bending or twisting.
- Leaves: The leaves of the seedling should be fully expanded, green, and healthy-looking. They should not show any signs of wilting, yellowing, or discoloration.
- Height: The seedling should have reached its desired height, which is determined by the specific plant species. This indicates that the seedling has achieved the necessary growth to proceed to the next stage of its life cycle.
Care during the Final Stage
During the final stage of seedling development, it is crucial to provide proper care to ensure the seedling’s successful transition to the next growth phase. Here are some important care practices:
- Watering: Continue to water the seedling, ensuring the soil remains moist but not overly saturated. Be careful not to overwater, as this can lead to root diseases or rot.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer to provide the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Use a slow-release fertilizer or follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the appropriate dosage and frequency.
- Lighting: Ensure the seedling receives adequate light. If grown indoors, provide a source of artificial light or place near a bright window. If grown outdoors, make sure it is located in a spot with sufficient sunlight.
- Protection: Protect the seedling from extreme weather conditions, such as strong winds, excessive heat, or cold temperatures. Use shade cloth or provide a temporary shelter if necessary.
- Transplantation: Once the seedling has reached the desired size and strength, it can be transplanted into its final location, whether it’s a field, garden bed, or a larger container. Be gentle during the transplant process to avoid damaging the roots.
By providing proper care and monitoring during the final stage of seedling development, you can ensure that the seedling is ready for successful growth and establishment in its new environment.
“Question-Answer”
How often should I water seedlings at each stage of development?
The frequency of watering seedlings depends on the stage of development. During the germination stage, it is important to keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Once the seedlings have sprouted, they should be watered whenever the top inch of soil feels dry. As the plants grow larger, they will require more frequent watering.
What nutrients do seedlings need during each stage of development?
Seedlings require different nutrients at each stage of development. During the germination stage, they mainly need phosphorus to support root development. As the seedlings grow, they require more nitrogen for leaf and stem growth. Once the seedlings have started producing true leaves, they also need potassium for overall plant health.
At what stage should I start fertilizing my seedlings?
You can start fertilizing your seedlings once they have developed their first true leaves. This typically happens a few weeks after germination. Use a diluted liquid fertilizer or a slow-release granular fertilizer, following the instructions on the packaging for proper application and dosage.
How can I ensure that my seedlings receive enough light?
To ensure that your seedlings receive enough light, place them in a location where they can get at least 12-16 hours of bright, indirect light per day. If you are growing seedlings indoors, you can use fluorescent or LED grow lights to supplement natural light. Keep the lights 2-4 inches above the seedlings and adjust the height as the plants grow.
When should I transplant my seedlings into larger containers?
You should transplant your seedlings into larger containers once they have developed a strong root system and their true leaves have fully formed. This is typically around 2-4 weeks after germination. Use a well-draining potting mix and gently remove the seedlings from their current containers, being careful not to damage the roots. Plant them at the same depth as they were growing before.
Can I use compost as a growing medium for seedlings?
While compost is a great source of nutrients, it is not recommended to use it as a sole growing medium for seedlings. Compost can be too nutrient-rich and heavy, which can lead to over-fertilization and poor drainage. Instead, mix compost with a high-quality potting mix or seed starting mix to create a well-balanced growing medium for your seedlings.
What should I do if my seedlings are leggy?
If your seedlings are leggy, it means they are reaching for more light. To prevent leggy seedlings, make sure they are receiving enough light by placing them in a sunny location or using grow lights. You can also try brushing your hand gently over the seedlings a few times a day to simulate a breeze, which can help strengthen their stems. If the seedlings are already leggy, you can transplant them deeper into the soil, burying the stem up to the first set of leaves.







