- The balance between benefits and drawbacks
- Understanding Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
- Potassium Chloride Fertilizer: Nutritional Advantages
- 1. Essential Nutrient for Plant Growth
- 2. Improves Plant Health and Disease Resistance
- 3. Enhances Fruit and Flower Quality
- 4. Boosts Crop Yield
- 5. Balances Nutrient Uptake
- 6. Compatibility with Various Soil Types
- 7. Cost-Effective Option
- Impact of Potassium Chloride Fertilizer on Soil
- Positive Impacts
- Negative Impacts
- Environmental Concerns: Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
- 1. Soil Salinization
- 2. Groundwater Contamination
- 3. Negative Impact on Soil Microorganisms
- 4. Ecotoxicity
- 5. Energy Intensive Production
- Conclusion
- Alternatives to Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
- 1. Potassium Sulfate
- 2. Potassium Nitrate
- 3. Organic Fertilizers
- 4. Potassium Magnesium Sulfate
- 5. Balanced Fertilizers
- Maximizing Potassium Chloride Fertilizer Efficacy
- Soil Testing and Analysis
- Proper Application Timing
- Correct Dosage
- Proper Mixing and Distribution
- Consideration of Other Nutrients
- Monitoring and Adjustment
- User Guidelines for Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
- 1. Application rates:
- 2. Timing of application:
- 3. Mixing and distribution:
- 4. Avoid direct contact with plant foliage:
- 5. Monitor soil and plant health:
- 6. Consider alternatives:
- “Question-Answer”
- What is potassium chloride fertilizer?
- What are the benefits of using potassium chloride fertilizer?
- Are there any drawbacks of using potassium chloride fertilizer?
- What are some alternatives to potassium chloride fertilizer?
- Can potassium chloride fertilizer be used for all types of plants?
- How should potassium chloride fertilizer be applied?
- What precautions should be taken when using potassium chloride fertilizer?
- “Video” Sulfate Of Potash
Potassium chloride fertilizer is a popular choice among farmers and gardeners for its ability to provide plants with essential nutrients. It is a concentrated source of potassium, which is vital for plant growth and development. Potassium plays a key role in cell division, water regulation, and enzyme activation. It also helps plants build strong cell walls and increases their resistance to diseases and pests.
However, despite its benefits, potassium chloride fertilizer has some drawbacks that need to be considered. One of the main concerns is its impact on soil quality. Continuous use of potassium chloride can lead to an imbalanced soil pH and excessive buildup of chloride ions. This can result in a decrease in soil fertility and negatively affect the health of plants in the long run.
Another drawback of potassium chloride fertilizer is its potential environmental impact. When applied in excessive amounts or not properly managed, it can leach into groundwater and nearby bodies of water, leading to water pollution. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems and the overall quality of water resources.
The balance between benefits and drawbacks
While potassium chloride fertilizer has its drawbacks, when used judiciously and in combination with other fertilizers, its benefits can outweigh the disadvantages. It is essential to carefully monitor soil fertility levels and adjust fertilizer application rates accordingly. Additionally, implementing best management practices, such as proper irrigation and drainage systems, can help mitigate the potential negative effects on soil and water quality.
Overall, the use of potassium chloride fertilizer should be part of a comprehensive nutrient management plan, taking into account the specific needs of the plants, soil conditions, and environmental considerations. By finding the right balance, farmers and gardeners can ensure that their crops and plants receive the necessary nutrients while minimizing the potential negative impacts on the environment.
Understanding Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
Potassium chloride fertilizer is a commonly used agricultural product that provides plants with essential nutrients. It is composed of potassium and chloride ions, which are important for plant growth and development.
Function
Potassium chloride fertilizer serves as a source of potassium, which is a macronutrient required by plants for various physiological processes. It plays a crucial role in the activation of enzymes, regulation of water balance, and transportation of sugars within the plant. Additionally, potassium enhances crop yield, improves fruit quality, and increases resistance to diseases and pests.
Application
The application of potassium chloride fertilizer is typically done through spreading it on the soil surface or incorporating it into the soil during planting. The dosage and timing of application depend on the specific crops being cultivated. It is important to follow the recommended guidelines to avoid over or under application, which can have negative effects on plant health and productivity.
Advantages
- Potassium chloride fertilizer is readily available and affordable, making it easily accessible to farmers of all scales.
- It has a high potassium content, making it an effective source of this essential nutrient.
- It can be used for a wide range of crops, including cereals, fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
- Potassium chloride is water-soluble, allowing plants to easily absorb the nutrients.
- It improves plant drought tolerance, helping crops withstand periods of water scarcity.
Disadvantages
- Excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer can lead to soil salinity, which negatively affects soil structure and reduces water infiltration.
- It may lead to a nutrient imbalance if used in excess, particularly in soils that already have high levels of potassium.
- Potassium chloride can be harmful to some sensitive plants, such as those growing in acidic soils or prone to chloride toxicity.
- It can leach into groundwater and surface water, potentially causing environmental contamination.
Conclusion
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of potassium chloride fertilizer is crucial for farmers and agronomists to make informed decisions regarding its use. When used correctly, it can significantly improve crop yield and quality. However, careful consideration of soil conditions, crop requirements, and environmental impacts is necessary to ensure sustainable and responsible use of potassium chloride fertilizer in agricultural practices.
Potassium Chloride Fertilizer: Nutritional Advantages
Potassium chloride fertilizer, commonly known as potash, has several nutritional advantages that make it an essential component in plant fertilization. This article will outline some of the key benefits that potassium chloride fertilizer provides to crops and plants.
1. Essential Nutrient for Plant Growth
Potassium is one of the three primary macronutrients required by plants for healthy growth, along with nitrogen and phosphorus. It plays a vital role in several plant functions, including enzyme activation, photosynthesis, and protein synthesis.
2. Improves Plant Health and Disease Resistance
Potassium helps improve the overall health and disease resistance of plants. It strengthens cell walls, making plants more resistant to pests and diseases. Potassium also regulates water uptake and retention, reducing the risk of dehydration and wilting, especially during periods of drought.
3. Enhances Fruit and Flower Quality
Using potassium chloride fertilizer can lead to improved fruit and flower quality. Potassium promotes larger fruit size, better fruit coloration, and increased sugar content. In flowers, it helps enhance vibrancy, size, and overall appearance.
4. Boosts Crop Yield
Applying potassium chloride fertilizer to crops can significantly increase overall yield. Potassium plays a vital role in promoting root development, nutrient uptake, and enzyme activation, all of which contribute to higher crop productivity.
5. Balances Nutrient Uptake
Potassium chloride fertilizer helps maintain the balance of nutrients within plants. It ensures that other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are efficiently absorbed and utilized by plants. This balance is crucial for avoiding nutrient deficiencies and promoting optimum plant growth.
6. Compatibility with Various Soil Types
Potassium chloride fertilizer is compatible with a wide range of soil types, including sandy soils, loamy soils, and clay soils. It is an effective and versatile fertilizer option that can be used in various agricultural and horticultural settings.
7. Cost-Effective Option
Potassium chloride fertilizer is generally more cost-effective compared to other potassium fertilizers. Its availability and affordability make it a popular choice for farmers and gardeners looking to optimize plant nutrition without breaking the bank.
In conclusion, potassium chloride fertilizer provides several nutritional advantages that contribute to overall plant health, disease resistance, and improved crop yield. By considering these benefits, farmers and gardeners can make informed decisions regarding the use of this essential fertilizer in their agricultural and horticultural practices.
Impact of Potassium Chloride Fertilizer on Soil
Potassium chloride fertilizer is commonly used in agriculture to provide plants with the essential nutrient potassium. However, its use can have both positive and negative impacts on the soil. It is important to assess these impacts to ensure sustainable agriculture practices.
Positive Impacts
- Increased crop yield: Potassium chloride fertilizer helps to replenish potassium levels in the soil, ensuring that plants have an adequate supply of this essential nutrient. This can result in increased crop yields and improved overall plant health.
- Improved plant quality: Potassium is essential for many plant processes, including photosynthesis, enzyme activation, and protein synthesis. The use of potassium chloride fertilizer can enhance the quality of plants by promoting these vital processes.
- Enhanced stress resistance: Potassium plays a crucial role in plant stress responses, such as drought and disease resistance. By providing plants with sufficient potassium, potassium chloride fertilizer can enhance their ability to withstand environmental stressors.
- Soil fertility maintenance: Continuous use of potassium chloride fertilizer can help maintain soil fertility by preventing potassium depletion. This is especially important in intensive agricultural systems where crops continually extract potassium from the soil.
Negative Impacts
- Acidity increase: Potassium chloride fertilizer is highly soluble and can contribute to soil acidification. This can negatively affect soil pH, making it less suitable for some crops and reducing overall soil fertility.
- Leaching and environmental pollution: Overuse or improper application of potassium chloride fertilizer can lead to leaching, where excess potassium is washed away from the root zone. This can contaminate groundwater and surface water, causing environmental pollution.
- Imbalanced nutrient ratio: Excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer without proper consideration of other nutrients can lead to imbalanced nutrient ratios in the soil. This can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities in plants, affecting their growth and development.
Overall, potassium chloride fertilizer can have significant impacts on soil fertility and plant growth. Proper application and management are crucial to optimize the benefits while minimizing the negative effects. It is important to consider factors such as soil type, crop requirements, and environmental considerations when deciding on the appropriate use of potassium chloride fertilizer.
Environmental Concerns: Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
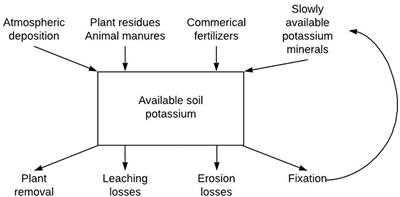
Potassium chloride fertilizer, while providing essential nutrients to plants, can also have negative impacts on the environment. Here are some environmental concerns associated with the use of potassium chloride fertilizer:
1. Soil Salinization
Excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer can lead to soil salinization. When the fertilizer is applied in high quantities or in concentrated form, it can increase the salt content in the soil, potentially damaging plant root systems and inhibiting plant growth. Soil salinization can also affect soil fertility and reduce crop yields.
2. Groundwater Contamination
Leaching is a common concern with potassium chloride fertilizer. When excess fertilizer is applied or when rainfall occurs shortly after application, the potassium and chloride ions can leach through the soil and reach groundwater. This can lead to an increase in potassium and chloride levels in groundwater, potentially impacting the quality of drinking water sources and aquatic ecosystems.
3. Negative Impact on Soil Microorganisms
Excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer can negatively impact soil microorganisms. High levels of potassium and chloride can disrupt the balance of soil microorganisms, affecting their activity and diversity. This can have long-term consequences for soil health and nutrient cycling.
4. Ecotoxicity
Potassium chloride fertilizer can have adverse effects on non-target organisms. Runoff from fields treated with potassium chloride fertilizer can reach nearby water bodies and cause imbalances in aquatic ecosystems. High concentrations of potassium and chloride can be toxic to aquatic organisms, leading to detrimental effects on fish, amphibians, and other aquatic organisms.
5. Energy Intensive Production
Potassium chloride fertilizer is primarily produced through mining and extraction processes. These processes require significant energy inputs and can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and depletion of non-renewable resources.
Conclusion
While potassium chloride fertilizer offers benefits in terms of plant nutrition, it is important to consider the potential environmental concerns associated with its use. Sustainable management practices, such as optimizing fertilizer application rates, timing, and placement, along with integrating other nutrient sources and conservation practices, can help minimize these environmental impacts.
Alternatives to Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
While potassium chloride fertilizer is widely used in agriculture due to its high potassium content, there are several alternatives that can be considered. These alternatives provide similar benefits without some of the drawbacks associated with potassium chloride.
1. Potassium Sulfate
Potassium sulfate is a commonly used alternative to potassium chloride fertilizer. It contains potassium in the form of sulfate ions, which can be more readily absorbed by plants than chloride ions. Additionally, potassium sulfate can help improve soil quality and enhance nutrient uptake by plants.
2. Potassium Nitrate
Potassium nitrate is another alternative that provides potassium to plants. It contains both potassium and nitrogen, which are essential nutrients for plant growth. Potassium nitrate has a quick release rate, allowing plants to absorb the nutrients rapidly. It can be particularly beneficial for crops that require a quick supply of potassium.
3. Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, can also be used as alternatives to potassium chloride fertilizer. These natural sources of potassium not only provide essential nutrients but also contribute to the overall health and fertility of the soil. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, ensuring a continuous supply of potassium for plant growth.
4. Potassium Magnesium Sulfate
Potassium magnesium sulfate, commonly known as langbeinite, is another alternative that contains potassium. It also provides magnesium and sulfur, which are important secondary nutrients for plant growth. Langbeinite can be beneficial for crops that require a balanced supply of these nutrients.
5. Balanced Fertilizers
Using balanced fertilizers that contain a combination of macronutrients can also be an effective alternative to potassium chloride. These fertilizers provide a well-rounded nutrient profile, ensuring that plants receive all the necessary nutrients in the right proportions.
While considering alternatives, it is important to evaluate the specific requirements of the crops being grown, as well as the soil conditions and nutrient deficiencies. Consulting with agricultural experts or soil testing laboratories can help determine the most suitable alternative fertilizer for a particular situation.
Maximizing Potassium Chloride Fertilizer Efficacy
Potassium chloride fertilizer is a valuable resource for farmers and gardeners alike due to its high potassium content. However, maximizing its efficacy requires careful consideration and proper usage. Here are some key factors to consider when using potassium chloride fertilizer:
Soil Testing and Analysis
Before applying any fertilizer, it is important to conduct soil testing and analysis. This will help determine the current nutrient levels in the soil, including potassium. By knowing the soil’s nutrient status, it is possible to use potassium chloride fertilizer more effectively and avoid over- or under-application.
Proper Application Timing
The timing of potassium chloride fertilizer application plays a significant role in its efficacy. Generally, the best time to apply potassium chloride is in early spring or fall, before the growing season begins. This allows the potassium to be readily available to plants when they need it most.
Correct Dosage
Using the correct dosage of potassium chloride fertilizer is crucial for its effectiveness. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution, while under-application may not provide sufficient potassium for optimal plant growth. Soil testing can help determine the appropriate dosage based on the specific nutrient needs of the plants being grown.
Proper Mixing and Distribution
When applying potassium chloride fertilizer, it is important to ensure proper mixing and distribution within the soil. This can be achieved by spreading the fertilizer evenly across the target area and incorporating it into the soil through gentle tilling or watering. Uneven distribution may result in localized nutrient imbalances and reduced fertilizer efficacy.
Consideration of Other Nutrients
Potassium chloride fertilizer is primarily used for its potassium content, but it is important to consider the overall nutrient balance in the soil. High potassium levels can negatively affect the uptake of other essential nutrients, such as magnesium and calcium. It is essential to maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the soil for optimal plant growth.
Monitoring and Adjustment
After applying potassium chloride fertilizer, it is important to monitor the nutrient levels in the soil and adjust future fertilizer applications accordingly. Regular soil testing can help determine the effectiveness of the fertilizer and identify any nutrient deficiencies or excesses that need correction.
By considering these factors and adjusting fertilizer usage accordingly, farmers and gardeners can maximize the efficacy of potassium chloride fertilizer and promote healthy plant growth.
User Guidelines for Potassium Chloride Fertilizer
Potassium chloride fertilizer, also known as muriate of potash, is a widely used source of potassium for plants. It contains high levels of potassium, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. However, it is important to use potassium chloride fertilizer properly to maximize its benefits and minimize any potential drawbacks.
1. Application rates:
It is important to apply potassium chloride fertilizer at the correct rate to avoid over-applying or under-applying. The recommended application rate will depend on the specific crop or plant being grown. Follow the instructions provided on the fertilizer label or consult with an agricultural expert to determine the appropriate application rate.
2. Timing of application:
The timing of potassium chloride fertilizer application is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. It is generally recommended to apply the fertilizer before planting or during the early stages of plant growth. This allows the plants to take up the potassium when they need it most. Avoid applying the fertilizer too close to harvest as it may result in an accumulation of chloride ions in the plant tissues.
3. Mixing and distribution:
Properly mix the potassium chloride fertilizer with the soil to ensure even distribution of potassium. This can be done by spreading the fertilizer evenly across the soil surface and then incorporating it into the top layer of soil using a rake or a tiller. Avoid applying the fertilizer in concentrated piles as this may lead to localized nutrient imbalances.
4. Avoid direct contact with plant foliage:
Potassium chloride fertilizer can be corrosive and can cause damage to plant foliage if it comes into direct contact. When applying the fertilizer, be careful to avoid any contact with the leaves or stems of the plants. If any fertilizer particles accidentally contact the foliage, rinse them off with water immediately to minimize any potential harm.
5. Monitor soil and plant health:
Regularly monitor the soil and plant health to assess the effectiveness of the potassium chloride fertilizer. This can be done by testing the soil for nutrient levels and monitoring the plant’s growth and overall health. If any deficiencies or excesses are detected, adjustments to the fertilizer application may be necessary.
6. Consider alternatives:
While potassium chloride fertilizer is commonly used, there are alternative sources of potassium available, such as potassium sulfate or potassium nitrate. These alternatives may be more suitable depending on the specific needs of the plants or the soil conditions. Consider consulting with a professional agronomist to determine the best potassium source for your specific situation.
By following these user guidelines for potassium chloride fertilizer, you can optimize its benefits for plant growth while minimizing any potential drawbacks. Remember to always read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and consult with a professional if needed.
“Question-Answer”
What is potassium chloride fertilizer?
Potassium chloride fertilizer is a type of fertilizer that contains potassium in the form of chloride. It is commonly used in agriculture to provide plants with an essential nutrient for growth and development.
What are the benefits of using potassium chloride fertilizer?
Using potassium chloride fertilizer can provide several benefits to plants. It helps in improving plant growth, increasing crop yield, and enhancing plant resistance to disease and pests. Additionally, it aids in osmoregulation and improving plants’ overall health and vigor.
Are there any drawbacks of using potassium chloride fertilizer?
Yes, there are some drawbacks of using potassium chloride fertilizer. One of the main concerns is its high salt content, which can lead to soil salinization over time. It can also negatively impact soil structure and microbial activity. Furthermore, excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer can cause environmental pollution, especially if not used properly and in recommended doses.
What are some alternatives to potassium chloride fertilizer?
There are several alternatives to potassium chloride fertilizer that can be used depending on specific plant needs and soil conditions. Some of these alternatives include potassium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and organic sources of potassium such as compost or manure. These alternatives provide potassium in different forms, which can have varying effects on plants and soil.
Can potassium chloride fertilizer be used for all types of plants?
Potassium chloride fertilizer can be used for a wide range of plants, including both crops and ornamental plants. However, it is important to consider the specific requirements of each plant species and the characteristics of the soil. Some plants may require higher or lower levels of potassium, and certain soil conditions may affect the availability and uptake of potassium from potassium chloride fertilizer.
How should potassium chloride fertilizer be applied?
Potassium chloride fertilizer can be applied to the soil in several ways. It can be broadcasted by spreading it evenly over the soil surface, or it can be banded along the rows or around the plant’s root zone. The application method can vary depending on the crop or plant being grown and the machinery or tools available for fertilizer application.
What precautions should be taken when using potassium chloride fertilizer?
When using potassium chloride fertilizer, it is important to follow the recommended application rates and timings. Excessive use of potassium chloride fertilizer can lead to negative impacts on the soil and the environment. It is also advisable to conduct regular soil testing to monitor the nutrient levels and adjust fertilizer application accordingly. Additionally, proper storage and handling of potassium chloride fertilizer should be ensured to prevent accidents or spills.







