- The Importance of Potassium for Plant Immunity
- Understanding the Role of Potassium
- 1. Plant Health and Vitality
- 2. Plant Immunity
- 3. Disease Resistance
- 4. Nutrient Uptake
- 5. Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses
- Potassium Deficiency and Plant Vulnerability
- Signs of Potassium Deficiency
- Impact on Plant Immunity
- Interaction with Other Nutrients
- Enhancing Plant Immunity with Potassium
- The Importance of Potassium in Plant Immunity
- Signs of Potassium Deficiency in Plants
- Providing Plants with Adequate Potassium
- Potassium’s Impact on Plant Growth and Development
- Promotes Cell Division and Expansion
- Aids in Photosynthesis
- Enhances Nutrient Uptake
- Improves Water Use Efficiency
- Strengthens Plant Immunity
- Final Thoughts
- The Relationship Between Potassium and Disease Resistance
- Benefits of Potassium in Disease Resistance:
- Deficiency and Excess of Potassium:
- Conclusion:
- Potassium’s Effect on Plant Defense Mechanisms
- 1. Enhanced Cell Wall Strength
- 2. Activation of Defense Genes
- 3. Regulation of Stomatal Opening
- 4. Increased Production of Phytoalexins
- 5. Improved Nutrient Uptake and Distribution
- Optimizing Potassium Levels for Maximum Plant Immunity
- The Importance of Potassium in Plant Immunity
- Signs of Potassium Deficiency
- Optimizing Potassium Levels
- Conclusion
- “Question-Answer”
- How does potassium affect the immune system of plants?
- What are some common symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants?
- Can plants absorb potassium from the soil?
- What are some natural sources of potassium for plants?
- Are there any negative effects of excessive potassium on plants?
- “Video” Why trace minerals & micronutrients are vital to crop health, disease resistance | Regenerative Ag
Plant immunity is a vital aspect of plant health and survival, protecting them against various pathogens and diseases. Research has shown that potassium, an essential macronutrient, plays a key role in enhancing plant immunity. This article will explore the impact of potassium on plant immune response and the mechanisms behind its protective effects.
Potassium is involved in several physiological processes in plants, including osmoregulation, photosynthesis, and enzyme activation. However, recent studies have revealed its profound influence on plant defense mechanisms. Potassium ions act as signal molecules, triggering a cascade of responses that activate immune-related genes and strengthen the plant’s defense system.
One of the primary ways potassium enhances plant immunity is by regulating stomatal closure. Stomata are small openings on the surface of leaves that allow for gas exchange but also serve as entry points for pathogens. When potassium levels are optimal, plants can regulate stomatal aperture, reducing the risk of pathogen entry and infection.
Furthermore, potassium can directly inhibit the growth and colonization of some plant pathogens. It can disrupt the osmotic balance within pathogen cells, causing water loss and death. Additionally, high potassium levels in plant tissues can alter the pH, making it less favorable for pathogen growth.
In conclusion, potassium plays a crucial role in enhancing plant immunity by regulating stomatal closure, activating immune-related genes, and directly inhibiting pathogen growth. Understanding the impact of potassium on plant defense mechanisms can inform agricultural practices, leading to improved crop health and increased productivity.
The Importance of Potassium for Plant Immunity
Potassium is a vital nutrient for plants and plays a key role in their overall health and immunity. It is considered one of the essential macronutrients, along with nitrogen and phosphorus, that are required in relatively large quantities by plants.
Potassium’s role in plant immunity
Potassium is involved in various physiological and biochemical processes within plants, contributing to their ability to defend against diseases and pests. Here are some key roles that potassium plays in enhancing plant immunity:
- Activation of defense mechanisms: Potassium is essential for the activation of enzymes and biochemical processes that form the foundation of a plant’s defense mechanisms. These defense mechanisms include the production of pathogenesis-related proteins and the synthesis of phytoalexins, which can inhibit the growth of pathogens.
- Regulation of stomatal opening: Stomata are tiny openings on the surface of plant leaves that control the exchange of gases and water vapor. Potassium helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata, allowing plants to optimize their gas exchange while minimizing water loss. This regulation is crucial for balancing the plant’s need for carbon dioxide uptake and limiting pathogen entry through the stomata.
- Enhancement of plant cell integrity: Potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of plant cells. It helps regulate turgor pressure within cells, ensuring they remain rigid and resistant to deformation. This structural integrity is important for plant cells to withstand the physical pressure exerted by pathogens and pests.
- Improved nutrient uptake: Potassium aids in the absorption and transportation of other important nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, within plants. When plants have an adequate supply of potassium, they can efficiently take up these nutrients, which are essential for their growth and overall health. This improved nutrient uptake helps strengthen the plants’ defense mechanisms against pathogens.
Potassium deficiency and plant immunity
A deficiency of potassium can severely impact a plant’s immune response and make it more susceptible to diseases and pests. Some common symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants include yellowing of leaves, stunted growth, and increased susceptibility to pathogens.
Sources of potassium
There are several natural sources of potassium that can be used to supplement a plant’s nutrient intake. Common sources include potassium-rich fertilizers, such as potassium sulfate and potassium nitrate, as well as organic materials like wood ash and compost.
| Source | Potassium content |
|---|---|
| Potassium sulfate | 50-55% K2O |
| Potassium nitrate | 37-39% K2O |
| Wood ash | 30-40% K2O |
| Compost | 0.5-3% K2O |
Conclusion
Potassium plays a crucial role in enhancing plant immunity and overall health. By understanding the importance of potassium and ensuring plants have an adequate supply of this essential nutrient, growers can help promote a stronger immune response in their plants and protect them from the damaging effects of diseases and pests.
Understanding the Role of Potassium
Potassium is an essential nutrient for plant growth and plays a key role in their overall health and development. It is one of the three primary macronutrients required by plants, along with nitrogen and phosphorus. Although potassium is required in relatively small quantities compared to other nutrients, its presence is crucial for maintaining plant immunity and defending against various diseases and infections.
1. Plant Health and Vitality
Potassium is essential for various physiological processes in plants, including enzyme activation, protein synthesis, and photosynthesis. It helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata, which are small pores on the surface of leaves that control gas exchange and water loss. A sufficient supply of potassium ensures healthy stomatal function, leading to improved water and nutrient uptake, as well as better overall plant growth and development.
2. Plant Immunity
Potassium plays a crucial role in enhancing plant immunity by strengthening its defense mechanisms. It helps activate and regulate various protective enzymes and proteins that enable plants to ward off pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. Potassium also promotes the synthesis of phenolic compounds, lignin, and other secondary metabolites that act as barriers against microbial attacks. Moreover, it helps regulate osmotic balance and water potential, allowing plants to withstand fluctuations in temperature and water availability.
3. Disease Resistance
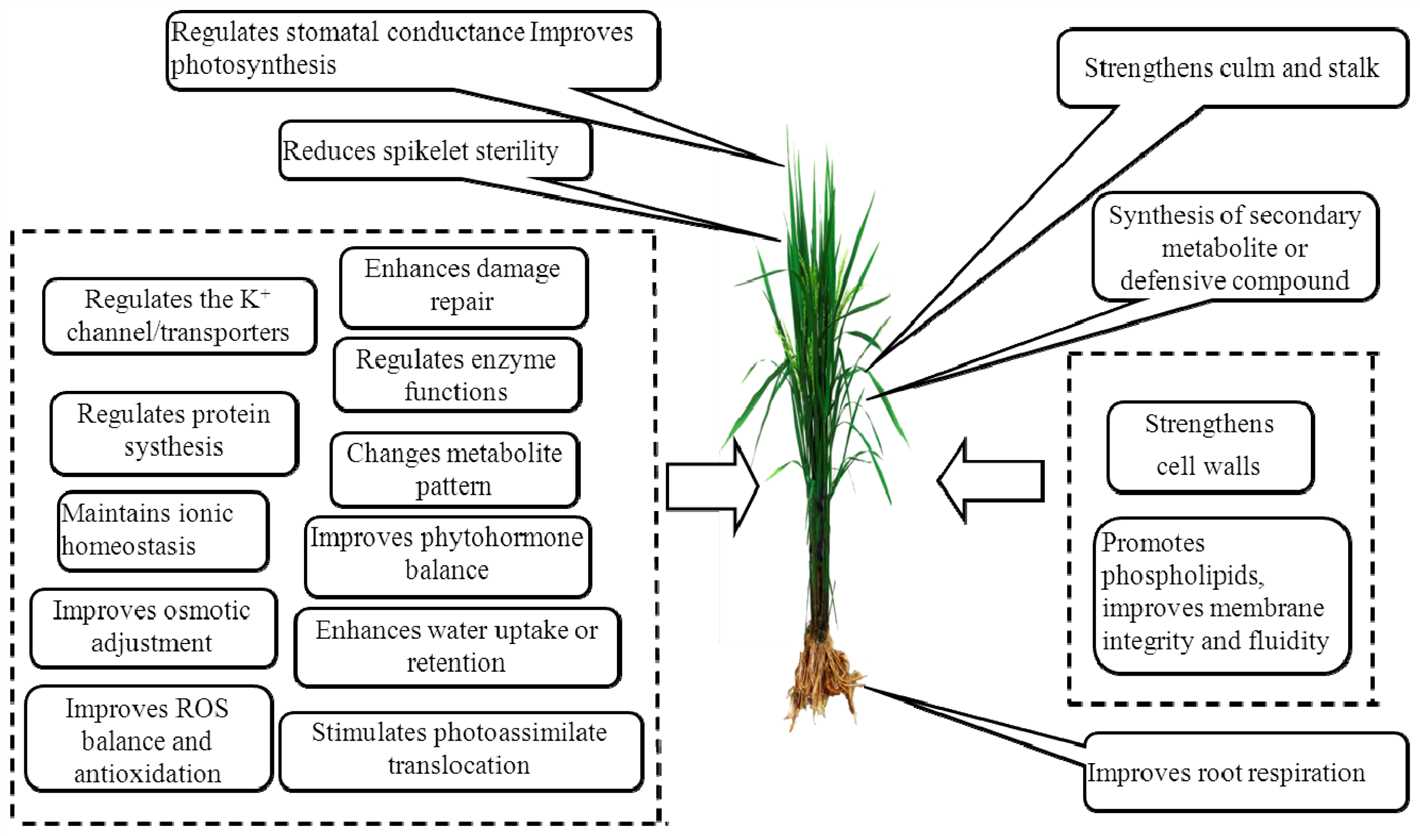
Adequate potassium levels in plants contribute to their increased disease resistance. Potassium participates in the synthesis and transportation of carbohydrates, which are vital energy sources for plants. Healthy carbohydrate levels ensure a strong defense against pathogens and minimize the potential for disease development. Additionally, potassium helps stimulate the production of phytoalexins, which are antimicrobial compounds that inhibit the growth of disease-causing organisms.
4. Nutrient Uptake
Potassium also plays a vital role in regulating nutrient uptake and their efficient utilization by plants. It helps facilitate the movement of other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, within the plant. Additionally, potassium improves the efficiency of nitrogen fixation and phosphorus solubilization, making these nutrients more available to plants. This enhances overall nutrient uptake and helps plants maintain a healthy nutrient balance, which is crucial for proper growth and immune response.
5. Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses
Plants with sufficient potassium levels are better equipped to withstand abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. Potassium helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata, enabling plants to conserve water during drought conditions. It also enhances the synthesis of heat shock proteins, antioxidants, and other stress-responsive molecules that protect plants against oxidative damage caused by high temperatures or excessive light. Additionally, potassium helps maintain cellular turgor pressure, ensuring optimal plant function even in salinity-stressed environments.
In conclusion, understanding the role of potassium is crucial for enhancing plant immunity and overall growth. Adequate potassium levels help plants maintain their health, defend against diseases, optimize nutrient uptake, and tolerate abiotic stresses. Therefore, it is essential to provide plants with sufficient potassium through proper fertilization and management practices to ensure their optimal wellbeing and productivity.
Potassium Deficiency and Plant Vulnerability
Potassium is an essential nutrient for plants and plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including plant immunity. When plants lack sufficient potassium, they become more vulnerable to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors. Potassium deficiency can have detrimental effects on both the quantity and quality of crop yields.
Signs of Potassium Deficiency
Identifying potassium deficiency in plants can be challenging, as the symptoms can vary depending on the plant species. However, some common signs include:
- Leaf chlorosis or yellowing
- Necrosis or tissue death at the leaf margins
- Stunted growth
- Reduced fruit or seed production
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases
Impact on Plant Immunity
Potassium is known to play a significant role in enhancing plant immunity. It helps activate various defense mechanisms that enable plants to resist attacks from pathogens and pests.
Firstly, potassium regulates the opening and closing of stomata, the tiny pores on the leaf surface. Stomata control the exchange of gases, including oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as water vapor. When plants lack potassium, stomata can remain open for longer periods, leading to increased water loss and making them more susceptible to drought stress.
Secondly, potassium contributes to the synthesis of proteins and enzymes involved in plant defense mechanisms. It helps activate and enhance the production of antimicrobial compounds, such as phytoalexins, which inhibit the growth of pathogens. Potassium also stimulates the production of pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins, which play a crucial role in the plant’s defense against a wide range of pathogens.
Interaction with Other Nutrients
Potassium deficiency can also interact with other nutrient deficiencies, further compromising plant health and immunity. For example, a lack of potassium can impair the uptake and transport of other essential nutrients, such as magnesium and calcium, which are also vital for plant growth and defense. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a balanced nutrient profile to ensure optimal plant health.
| Source | Potassium Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | 60-62% |
| Potassium sulfate (K2SO4) | 50-52% |
| Potassium nitrate (KNO3) | 44-47% |
In conclusion, potassium deficiency can significantly impact plant immunity, making them more vulnerable to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors. Maintaining an adequate supply of potassium, along with other essential nutrients, is crucial for promoting plant health, enhancing defense mechanisms, and maximizing crop yields.
Enhancing Plant Immunity with Potassium
Potassium plays a key role in enhancing plant immunity. It is an essential nutrient that participates in various physiological processes in plants, including the regulation of water balance, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates. Moreover, potassium is known to play a vital role in plant defense mechanisms against various diseases and pathogens.
The Importance of Potassium in Plant Immunity
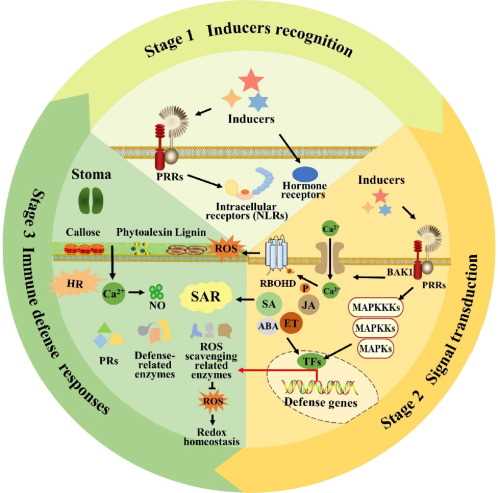
Potassium acts as a regulator in the plant’s defense response, helping it to ward off pathogens and diseases. It does so by:
- Activating Defense Genes: Potassium stimulates the expression of defense genes in plants, which are responsible for producing proteins that help fight against pathogens.
- Strengthening Cell Walls: Potassium plays a crucial role in the synthesis of cellulose, a component of plant cell walls. Cellulose provides physical protection to the plant cells, making it harder for pathogens to invade.
- Regulating Stomatal Opening: Potassium regulates the opening and closing of stomata, the tiny pores on the surface of plant leaves. By controlling stomatal aperture, potassium helps prevent the entry of pathogens through stomata.
- Boosting Antioxidant Systems: Potassium helps enhance the antioxidant defense mechanisms in plants, reducing the damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during pathogen attack.
Signs of Potassium Deficiency in Plants
A lack of potassium can weaken a plant’s immune system, making it more susceptible to diseases and pests. Some common signs of potassium deficiency in plants include:
- Yellowing Leaves: The leaves may turn yellow, starting from the edges and progressing towards the center.
- Leaf Necrosis: The tips and margins of the leaves may become brown or black and eventually die off.
- Reduced Growth: Plants lacking potassium may exhibit stunted growth and reduced fruit or flower production.
- Increased Disease Susceptibility: Potassium-deficient plants have weakened immune systems, making them more vulnerable to diseases and pests.
Providing Plants with Adequate Potassium
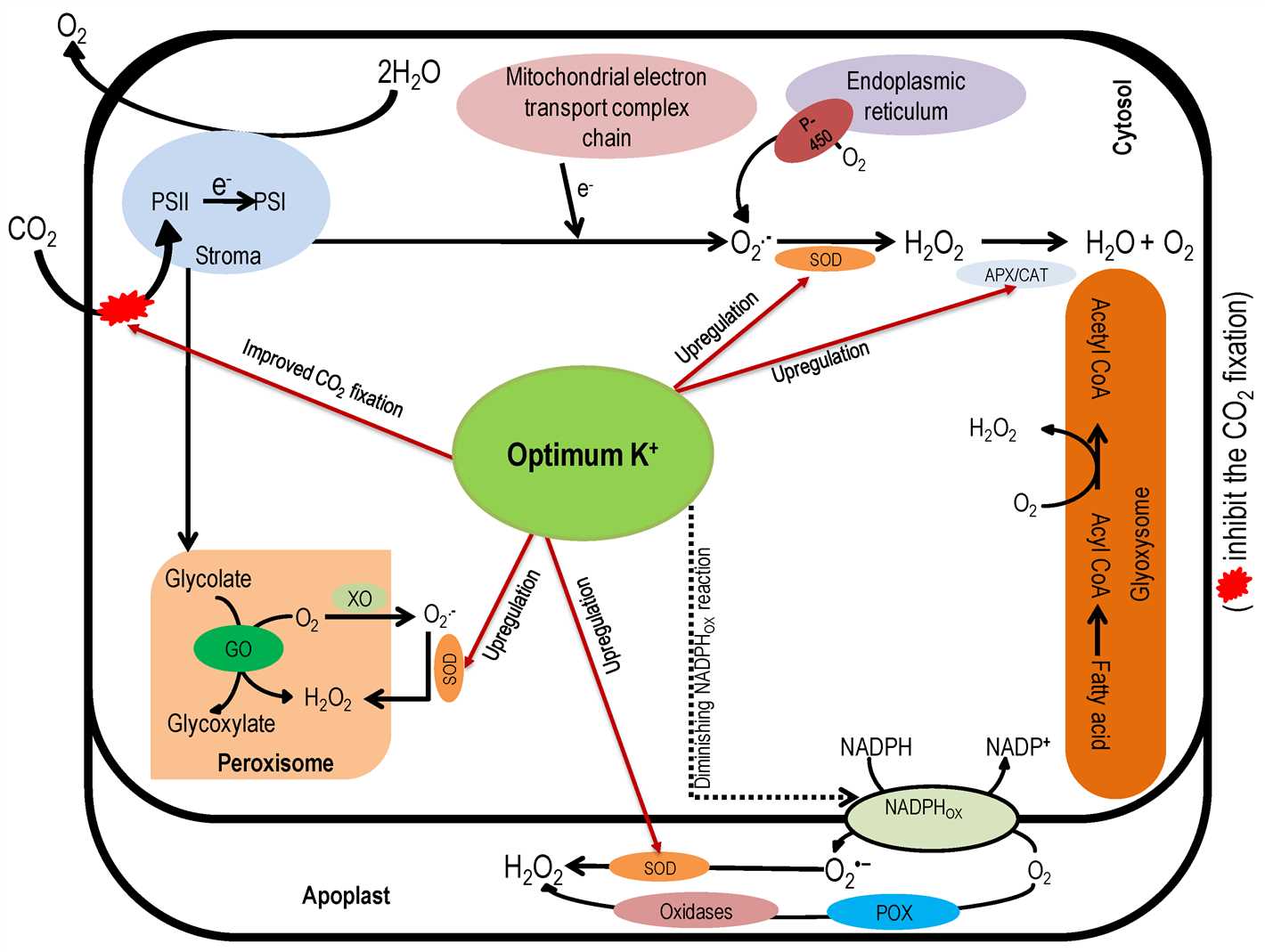
To enhance plant immunity, it is crucial to provide plants with adequate potassium. This can be achieved through:
- Fertilization: Applying potassium-rich fertilizers can help replenish the nutrient in the soil and provide plants with the necessary potassium for optimal growth and defense.
- Soil Testing: Conducting regular soil tests can help determine the potassium levels in the soil, allowing for targeted fertilization strategies.
- Companion Planting: Growing potassium-rich companion plants alongside susceptible plants can help improve their overall nutrient availability and immune response.
- Foliar Sprays: Applying foliar sprays containing potassium can provide a quick boost of the nutrient to the plant, improving its defense mechanisms.
| Potassium-Rich Foods for Plants | Potassium Content per 100g |
|---|---|
| Bananas | 358mg |
| Kale | 491mg |
| Tomatoes | 237mg |
| Potatoes | 429mg |
By understanding the importance of potassium in enhancing plant immunity and actively providing plants with an adequate supply of this nutrient, growers can significantly improve the resistance of their crops to diseases and pathogens.
Potassium’s Impact on Plant Growth and Development
Potassium is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within plants, and its availability in the soil can significantly impact plant health.
Promotes Cell Division and Expansion
Potassium is involved in regulating cell division and expansion, which are essential for plant growth. It activates various enzymes that control cell division, allowing plants to develop new tissues and structures. Additionally, potassium helps maintain turgor pressure within cells, giving plants the rigidity needed for upright growth.
Aids in Photosynthesis
Plants need potassium to perform photosynthesis effectively. Potassium contributes to the opening and closing of stomata, small pores on the surface of leaves that regulate gas exchange. By controlling stomatal aperture, potassium helps optimize the uptake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen during photosynthesis.
Enhances Nutrient Uptake
Potassium plays a crucial role in nutrient uptake by plants. It increases the absorption and transportation of other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus. Furthermore, potassium improves the efficiency of nutrient utilization within plants, allowing them to fully benefit from the available nutrients in the soil.
Improves Water Use Efficiency
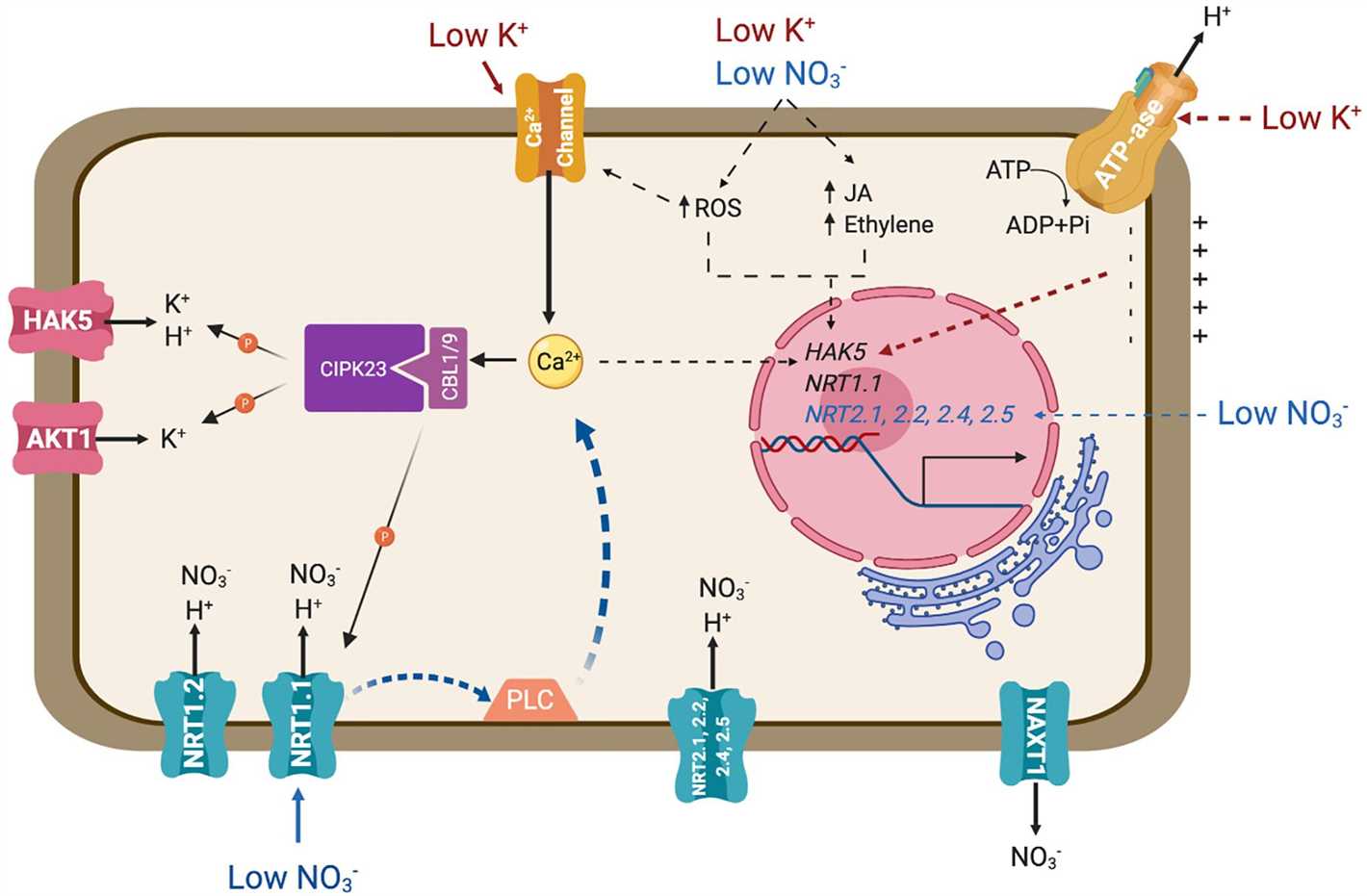
Potassium helps plants regulate water use by controlling stomatal opening and closing. By maintaining optimal stomatal aperture, potassium reduces water loss through transpiration. This enhances water use efficiency, particularly in drought conditions, as plants can conserve water while still facilitating photosynthesis.
Strengthens Plant Immunity
Potassium is closely linked to plant immunity. It enhances the synthesis of defense-related compounds, such as phytoalexins and enzymes involved in plant defense mechanisms. This helps plants effectively respond to biotic and abiotic stresses, such as pathogens, pests, and adverse environmental conditions.
Final Thoughts
Potassium is a vital nutrient for plant growth and development. It influences various aspects of plant physiology, including cell division, photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, water regulation, and immunity. Ensuring adequate potassium availability in the soil is crucial for maintaining healthy plants and optimizing agricultural productivity.
The Relationship Between Potassium and Disease Resistance
Potassium, an essential nutrient for plant growth and development, also plays a crucial role in enhancing the plant’s immune system. Adequate potassium levels in plants promote disease resistance and overall plant health.
Benefits of Potassium in Disease Resistance:
- Strengthening Cell Walls: Potassium helps to regulate the movement of water and nutrients within plant cells, making them less susceptible to invasion by pathogens. It also strengthens the cell walls, making it more difficult for pathogens to penetrate and cause damage.
- Activation of Defense Mechanisms: Potassium is involved in the activation of various defense mechanisms in plants, such as the production of antimicrobial compounds, phytoalexins, and pathogenesis-related proteins. These defense mechanisms help plants to combat and suppress the growth of pathogens.
- Enhancing Photosynthesis: Potassium is essential for photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert sunlight into energy. Enhanced photosynthesis results in increased production of carbohydrates, which provide the energy and resources needed for the plant’s immune system to function effectively.
- Improving Nutrient Uptake: Adequate potassium levels in plants improve nutrient uptake, including the uptake of other essential minerals required for disease resistance, such as calcium and magnesium. This enables the plant to maintain optimal health and better withstand pathogen attacks.
Deficiency and Excess of Potassium:
Both deficiency and excess of potassium can have adverse effects on plant immunity and disease resistance.
A potassium deficiency can weaken the plant’s immune system, making it more susceptible to infections. It can also result in stunted growth, chlorosis, and reduced overall plant health. Monitoring and maintaining adequate levels of potassium in the soil is essential to prevent deficiencies.
On the other hand, an excess of potassium can lead to imbalances in mineral uptake and nutrient absorption. This imbalance can negatively affect plant health and make them more prone to certain diseases. It is crucial to maintain appropriate potassium levels for optimal disease resistance without causing nutrient imbalances.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, potassium plays a key role in enhancing plant immunity and disease resistance. Its ability to strengthen cell walls, activate defense mechanisms, enhance photosynthesis, and improve nutrient uptake all contribute to a healthier and more resilient plant. Adequate potassium levels and proper management are essential to ensure optimum disease resistance and overall plant health.
Potassium’s Effect on Plant Defense Mechanisms
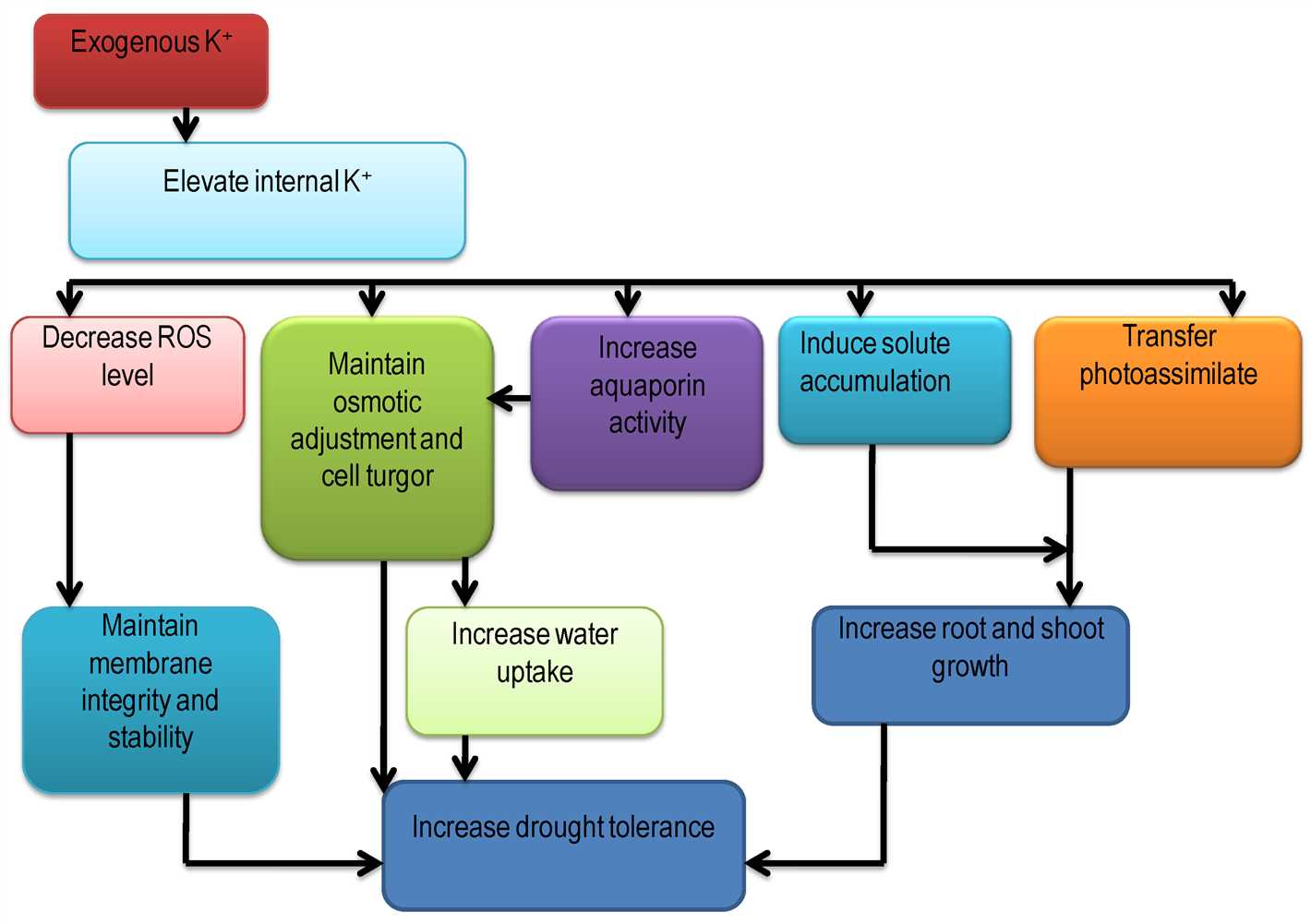
Potassium is an essential nutrient for plants, playing a key role in their overall health and growth. However, its importance goes beyond just supporting basic plant functions. Potassium also has a significant impact on plant defense mechanisms, helping to protect plants from various diseases and pests.
1. Enhanced Cell Wall Strength
Potassium is involved in the synthesis of cell wall components, including cellulose and lignin. These structural components play a crucial role in forming a protective barrier around plant cells. An adequate supply of potassium strengthens the cell walls, making it more difficult for pathogens to penetrate and invade the plant.
2. Activation of Defense Genes
Potassium is involved in the activation of genes that are responsible for triggering defense responses in plants. When a plant is attacked by a pathogen or insect, these defense genes are activated, leading to the production of various antimicrobial compounds and defense proteins. Potassium plays a vital role in the signaling pathways that activate these defense genes, enabling the plant to mount a strong immune response.
3. Regulation of Stomatal Opening
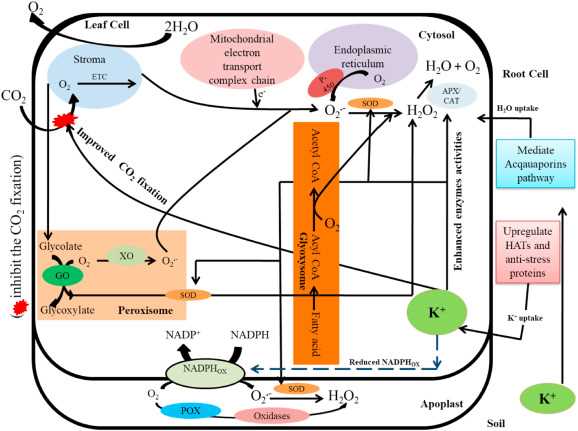
Stomata are small openings on the surface of leaves that regulate gas exchange and water loss in plants. Potassium helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata. When a plant detects the presence of pathogens, it can close its stomata to prevent the entry of pathogens. Additionally, by regulating stomatal opening, potassium helps minimize water loss during pathogen attack, enabling the plant to conserve resources and maintain its overall health.
4. Increased Production of Phytoalexins
Phytoalexins are natural compounds produced by plants in response to pathogen attack. These compounds have antimicrobial properties and play a crucial role in limiting the spread of pathogens within plant tissues. Potassium is involved in the production and accumulation of phytoalexins, enhancing the plant’s ability to fight off harmful pathogens.
5. Improved Nutrient Uptake and Distribution
Potassium is involved in the transport of nutrients within a plant. It helps in the uptake and distribution of essential nutrients, including micronutrients that are important for plant defense against diseases. Adequate potassium levels ensure that plants have access to the necessary nutrients, enabling them to maintain optimal health and strengthen their defense mechanisms.
In conclusion, potassium plays a crucial role in enhancing plant defense mechanisms. From strengthening cell walls to activating defense genes and regulating stomatal opening, potassium ensures that plants have the necessary tools to fight off diseases and pests. By understanding the impact of potassium on plant immunity, farmers and gardeners can optimize their nutrient management practices to promote healthier, more resilient plants.
Optimizing Potassium Levels for Maximum Plant Immunity
Potassium is an essential nutrient for plants that plays a key role in their overall health and immune response. By optimizing potassium levels in plants, growers can help promote maximum plant immunity and increase their resistance to diseases and pests.
The Importance of Potassium in Plant Immunity
Potassium is involved in numerous physiological processes in plants, including the synthesis of proteins, the regulation of osmotic balance, and the activation of enzymes involved in plant defense mechanisms. Adequate potassium levels can enhance a plant’s ability to withstand biotic and abiotic stresses, such as insect attacks, fungal infections, drought, and extreme temperatures.
Signs of Potassium Deficiency
A deficiency in potassium can lead to reduced plant immunity and make plants more susceptible to diseases and pests. Some common signs of potassium deficiency in plants include:
- Yellowing or browning of leaf margins
- Stunted growth
- Weaker stems that are prone to lodging
- Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests
Monitoring plants for these signs can help growers identify potassium deficiencies and take corrective measures to optimize levels.
Optimizing Potassium Levels
To optimize potassium levels for maximum plant immunity, growers should consider the following practices:
- Soil Testing: Conduct regular soil tests to determine the potassium levels in the soil. This will help growers identify any deficiencies and allow them to adjust fertilization practices accordingly.
- Fertilization: Add potassium-rich fertilizers, such as potassium sulfate or potassium nitrate, to the soil to increase potassium levels. It is important to follow recommended application rates to avoid nutrient imbalances.
- Foliar Sprays: Apply potassium-rich foliar sprays to provide a quick boost of potassium to plants during times of stress or when deficiencies are observed. This method can often provide faster results than soil applications.
- Irrigation: Ensure proper irrigation practices to prevent water stress, as potassium uptake can be affected by water availability. Maintaining consistent soil moisture levels can help plants efficiently absorb potassium.
Conclusion
Optimizing potassium levels in plants is crucial for promoting maximum plant immunity and increasing resistance to diseases and pests. By monitoring for deficiencies and implementing appropriate practices, growers can ensure that their plants have the necessary levels of potassium to thrive and defend against various stresses.
“Question-Answer”
How does potassium affect the immune system of plants?
Potassium plays a key role in enhancing the immune system of plants. It helps activate enzymes that are involved in the defense mechanisms of the plant, making them more resistant to diseases and pathogens.
What are some common symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants?
Some common symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants include yellowing or browning of the edges of leaves, stunted growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests.
Can plants absorb potassium from the soil?
Yes, plants can absorb potassium from the soil through their roots. However, the availability of potassium in the soil can vary depending on factors such as soil pH and composition.
What are some natural sources of potassium for plants?
Some natural sources of potassium for plants include banana peels, wood ash, and composted manure. These can be added to the soil to improve potassium levels and enhance plant immunity.
Are there any negative effects of excessive potassium on plants?
Yes, excessive potassium can have negative effects on plants. It can lead to nutrient imbalances, affecting the uptake of other essential nutrients. It can also cause salt buildup in the soil, which can harm plant roots and reduce their ability to absorb water.







