- Why use mineral-organic fertiliser?
- Benefits of manure for gardening
- Preparing Mineral-Organic Fertiliser
- Steps to Prepare Mineral-Organic Fertiliser:
- Choosing the right manure
- Composting process
- 1. Collect organic materials
- 2. Prepare composting area
- 3. Layer the organic materials
- 4. Ensure moisture and aeration
- 5. Monitor the compost
- 6. Use the finished compost
- Adding minerals for optimal fertility
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
- Secondary nutrients and micronutrients
- Application in Year-Long Gardening
- 1. Preparing the Soil
- 2. Seedlings and Transplants
- 3. Top Dressing
- 4. Composting
- 5. Testing and Monitoring
- Preparing the garden bed
- 1. Clear the area
- 2. Loosen the soil
- 3. Amend the soil
- 4. Level the bed
- 5. Create rows or planting areas
- 6. Add mulch
- Applying the fertiliser throughout the year
- Spring
- Summer
- Fall
- Winter
- “Question-Answer”
- What is mineral-organic fertiliser?
- How can I prepare mineral-organic fertiliser from manure?
- What are the benefits of using mineral-organic fertiliser?
- Can I use mineral-organic fertiliser for all types of plants?
- How often should I apply mineral-organic fertiliser?
- Are there any alternatives to mineral-organic fertiliser?
- “Video” Creating Fermented Complete Organic Fertilizer | Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium | Super Easy!
Gardening is a rewarding hobby that can enhance the beauty of your surroundings and provide you with fresh, healthy produce. However, to achieve success in gardening, it is crucial to have the right kind of fertilizer. While chemical fertilizers may work, many gardeners are now turning to mineral-organic fertilizers for a more natural and sustainable option.
One of the best sources of mineral-organic fertilizer is manure. Manure is rich in essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth. Additionally, it contains organic matter that improves soil structure, retains moisture, and promotes beneficial microbial activity.
To prepare mineral-organic fertilizer from manure, start by collecting fresh manure from a reliable source. Cow, horse, or poultry manure are commonly used types. Next, allow the manure to decompose and age for several weeks. This process helps to break down any harmful pathogens and reduces the risk of burning your plants.
After the manure has aged, it can be mixed with other organic materials such as compost, leaves, or straw to create a nutrient-rich fertilizer. This mixture should then be applied to your garden beds or pots before planting. During the growing season, you can continue to apply the mineral-organic fertilizer every few weeks to provide your plants with a steady supply of nutrients.
By using mineral-organic fertilizer from manure, you can not only improve the health and productivity of your garden but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening. So start preparing your own mineral-organic fertilizer and enjoy the benefits of year-long gardening success!
Why use mineral-organic fertiliser?
Mineral-organic fertiliser is a combination of mineral and organic substances that provide essential nutrients to plants. It offers several benefits that make it an excellent choice for gardening:
Improved soil fertility: Mineral-organic fertiliser enriches the soil by replenishing essential nutrients that may be lacking. It contains a balanced combination of macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (such as iron, zinc, and manganese), which are crucial for plant growth.
Slow-release of nutrients: Unlike synthetic fertilisers that release nutrients rapidly, mineral-organic fertiliser provides a gradual and sustained release of nutrients. This helps to prevent nutrient leaching and ensures that plants receive a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period.
Increased organic matter: Organic components in mineral-organic fertiliser, such as composted manure, help improve the soil structure and increase its water-holding capacity. This enhances root development and enables plants to withstand periods of drought or heavy rainfall.
Environmentally-friendly: Mineral-organic fertiliser minimises the risk of groundwater contamination and reduces the environmental impact compared to synthetic fertilisers. It promotes sustainable gardening practices by utilising natural and renewable resources.
Promotion of beneficial soil microorganisms: Mineral-organic fertiliser fosters a healthy soil ecosystem by encouraging the growth of beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms help break down organic matter, improve nutrient availability, and suppress harmful pests and diseases.
By using mineral-organic fertiliser, gardeners can provide their plants with the necessary nutrients while promoting soil health and sustainability. Its numerous advantages make it an essential component of year-long gardening success.
Benefits of manure for gardening
Manure is a valuable source of nutrients for plants and can provide several benefits for gardening. Here are some key advantages of using manure in your garden:
- Nutrient-rich: Manure is rich in essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth. These nutrients help in the development of strong roots, healthy foliage, and abundant flowers or fruits.
- Improved soil structure: When manure is added to the soil, it helps improve its structure by increasing its water-holding capacity and promoting better drainage. This means that plants can access water and nutrients more easily, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
- Organic matter: Manure is an excellent source of organic matter, which is important for building and improving soil fertility. Organic matter helps retain moisture in the soil, enhances microbial activity, and improves soil texture, making the soil more productive and conducive to plant growth.
- Natural soil amendment: Using manure as a natural soil amendment can help balance pH levels and provide micronutrients that are often lacking in synthetic fertilizers. It can also help neutralize acidic or alkaline soils and create a more favorable pH for plant growth.
- Sustainable and cost-effective: Manure is a sustainable and cost-effective option for gardeners as it can be obtained from various sources, such as livestock farms or backyard composting. Using manure as a fertilizer reduces the dependence on synthetic chemicals and promotes the use of natural and organic resources.
It’s important to note that not all types of manure are suitable for gardening, as some may contain weed seeds or high levels of salts. It’s recommended to compost or age manure before using it in the garden to reduce the risk of potential issues.
In conclusion, incorporating manure into your gardening practices can offer numerous benefits, including increased nutrient content, improved soil structure, and enhanced overall plant health. It’s a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to promote successful gardening year-round.
Preparing Mineral-Organic Fertiliser
Mineral-organic fertiliser can be prepared from manure to provide your garden with year-long success. By combining the nutrients found in manure with mineral components, you can create a balanced and nutrient-rich fertiliser that will promote the healthy growth of your plants.
Steps to Prepare Mineral-Organic Fertiliser:
- Collect Manure: Start by collecting manure from organic sources such as cows, horses, or chickens. It is important to ensure that the manure is well-aged and decomposed to avoid any potential harmful pathogens.
- Mix with Organic Materials: In a large container or compost bin, mix the collected manure with organic materials such as straw, leaves, or compost. This mixture will help enhance the nutrient content of the final fertiliser.
- Add Mineral Components: To create a mineral-organic fertiliser, you will need to incorporate mineral components into the mixture. These minerals can include rock phosphate, bone meal, green sand, and kelp meal. Be sure to add these minerals in the recommended ratios for optimal plant growth.
- Mix and Compost: Thoroughly mix the manure, organic materials, and mineral components together to ensure an even distribution of nutrients. This mixture should be composted for several weeks or months to allow for the decomposition of the organic materials and to activate the mineral components.
- Test and Adjust: After the composting process, test the nutrient content of the fertiliser using a soil testing kit or by sending a sample to a laboratory. This will help determine the exact nutrient composition and allow you to make any necessary adjustments by adding more organic or mineral components.
- Store and Use: Once the mineral-organic fertiliser is ready, store it in a dry and cool place to maintain its nutrient content. When using the fertiliser, follow the recommended application rates for different plants and apply it evenly to the soil or use it as a side dressing during the growing season.
By preparing mineral-organic fertiliser from manure, you can ensure that your garden receives the essential nutrients it needs for healthy plant growth. This homemade fertiliser is not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective, making it an excellent choice for year-long gardening success.
Choosing the right manure

When it comes to preparing a mineral-organic fertilizer from manure, it is important to choose the right type of manure that will provide the necessary nutrients for your plants. Here are some common types of manure that you can consider:
- Cow manure: Cow manure is one of the most popular types of manure due to its balanced nutrient content. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth. Additionally, cow manure also improves soil structure and moisture retention.
- Chicken manure: Chicken manure is high in nitrogen and phosphorous, making it an excellent choice for promoting vigorous plant growth. However, it can be quite potent and should be composted before use to prevent burning or damaging plants.
- Horse manure: Horse manure is another good option for fertilizing your garden. It is rich in nitrogen and can improve soil structure. However, horse manure may contain weed seeds, so it is recommended to compost it thoroughly to prevent weed growth.
- Sheep manure: Sheep manure is a well-balanced fertilizer, providing a good mix of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. It also helps to improve soil structure and moisture retention.
- Pig manure: Pig manure is high in nitrogen and organic matter, making it a valuable fertilizer. However, it can be quite odorous and should be composted properly to minimize odor and prevent nutrient loss.
It is important to note that fresh manure can be too strong and may burn or damage plants, so it is recommended to compost it before using it as a fertilizer. Composting helps to break down the organic matter and reduce any potential pathogens or weed seeds present in the manure.
Before applying manure to your garden, consider conducting a soil test to determine the nutrient needs of your plants. This will help you adjust the application rates accordingly and avoid over or under fertilization.
Composting process
Composting is a natural process that converts organic materials, such as manure, into a rich and nutrient-packed fertiliser. It can be done in a compost bin or a designated composting area in your garden.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to compost:
1. Collect organic materials

Collect a mixture of brown and green organic materials. Brown materials include dry leaves, straw, and woodchips, while green materials include fresh grass clippings, kitchen scraps, and manure. Aim for a ratio of 3 parts brown to 1 part green.
2. Prepare composting area
Select a well-drained area for composting. You can use a compost bin or create a compost pile directly on the ground. Make sure the area is easily accessible for turning and watering the compost.
3. Layer the organic materials
Start by layering a few inches of brown materials at the bottom of the composting area. Then add a layer of green materials. Continue alternating layers until you have used all your organic materials. Aim for a compost pile that is about 3 feet high and 3 feet wide.
4. Ensure moisture and aeration
Moisten the compost pile as you layer the materials to ensure it is evenly damp but not soaking wet. The compost pile should have the consistency of a damp sponge. Turn the pile every few weeks with a garden fork or shovel to aerate it, allowing oxygen to reach the microorganisms that decompose the organic materials.
5. Monitor the compost
Monitor the compost pile regularly. It should feel warm to the touch, indicating that decomposition is occurring. If the pile is too dry, add water. If it is too wet, add more brown materials. The composting process typically takes several months to a year, depending on the environmental conditions and the size of the materials.
6. Use the finished compost
Once the organic materials have decomposed into a dark, crumbly substance, the compost is ready to use. It will be rich in nutrients and beneficial microorganisms. Use the compost to fertilise your plants, mix it with potting soil for container gardening, or spread it as a top dressing in your garden beds.
Composting is a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to recycle organic materials and create a nutrient-rich fertiliser for your garden. By following these steps, you can harness the power of composting to promote healthy plant growth and enhance the productivity of your garden.
Adding minerals for optimal fertility
While manure is rich in organic matter, it may lack certain essential minerals that are necessary for optimal plant growth and fertility. Adding minerals to your mineral-organic fertilizer can help ensure that your plants receive a balanced and complete nutrient supply. Here are some key minerals to consider adding:
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is crucial for promoting leaf and stem growth. It is responsible for the green color in plants and helps to enhance photosynthesis. Adding nitrogen to your fertilizer can be accomplished by including materials such as blood meal, feather meal, or fish meal. These materials provide a slow-release source of nitrogen that will be gradually released to your plants over time.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is necessary for promoting root development, flowering, and fruit production. Adding phosphorus to your fertilizer can be done by incorporating materials such as bone meal or rock phosphate. These materials are rich in phosphorus and will slowly release this essential nutrient to your plants.
Potassium (K)
Potassium is vital for overall plant health and helps with disease resistance, water regulation, and overall nutrient uptake. Including potassium in your fertilizer can be achieved by using materials such as wood ash or kelp meal. These materials provide a natural source of potassium that will gradually become available to your plants.
Secondary nutrients and micronutrients
In addition to the primary macronutrients mentioned above, it is also important to consider adding secondary nutrients such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), as well as micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn). These nutrients are vital for various physiological processes in plants and can be included in your fertilizer blend by using materials such as gypsum, dolomite lime, or trace mineral supplements.
By adding these essential minerals to your mineral-organic fertilizer, you can ensure that your plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and productivity. Remember to follow the recommended application rates and consider testing your soil to determine any specific nutrient deficiencies that may need to be addressed. With a well-balanced mineral-organic fertilizer, you’ll be well on your way to year-long gardening success!
Application in Year-Long Gardening
The mineral-organic fertiliser prepared from manure offers several benefits for year-long gardening success. Here are some ways to effectively use this fertiliser:
1. Preparing the Soil
- Mix the mineral-organic fertiliser into the soil before planting your crops. This will enrich the soil with essential nutrients and promote healthy plant growth.
- Ensure that the fertiliser is evenly distributed throughout the soil to provide a consistent nutrient supply to the plants.
2. Seedlings and Transplants
- When starting seedlings or transplanting young plants, mix a small amount of the fertiliser into the potting mix or the hole where the plant will be placed. This will give the plants a nutrient boost to support their initial growth.
3. Top Dressing

- Apply a thin layer of the mineral-organic fertiliser around the base of established plants, taking care not to let it touch the stems or leaves. This top dressing will slowly release nutrients into the soil, providing a continuous supply for the plants.
4. Composting
- Use the leftover organic matter after extracting the fertiliser to create compost. Composting is a sustainable way to recycle garden and kitchen waste and can further enhance the nutrient content of the soil.
- Apply the compost to the garden as a mulch or mix it into the soil to improve overall fertility and soil structure.
5. Testing and Monitoring
- Regularly test the soil to monitor its nutrient levels and pH. This will help determine if any adjustments or additional fertiliser applications are needed.
- Keep a record of the fertiliser application and its impact on plant growth. This will allow for fine-tuning of the fertiliser dosage and application methods in the future.
By following these practices, you can maximize the benefits of mineral-organic fertiliser in year-long gardening and enjoy healthier and more productive plants.
Preparing the garden bed
Before planting your garden, it is important to prepare the garden bed to provide a healthy environment for your plants to grow. Here are the steps to prepare your garden bed:
1. Clear the area
- Remove any weeds, rocks, or debris from the garden bed.
- Make sure the area is free from any obstructions that may hinder plant growth.
2. Loosen the soil
- Use a garden fork or tiller to loosen the soil in the garden bed.
- Break up any clumps of soil and create a loose, crumbly texture.
3. Amend the soil
- Add compost or organic matter to improve soil quality and fertility.
- Mix the compost thoroughly into the soil using the garden fork or tiller.
4. Level the bed
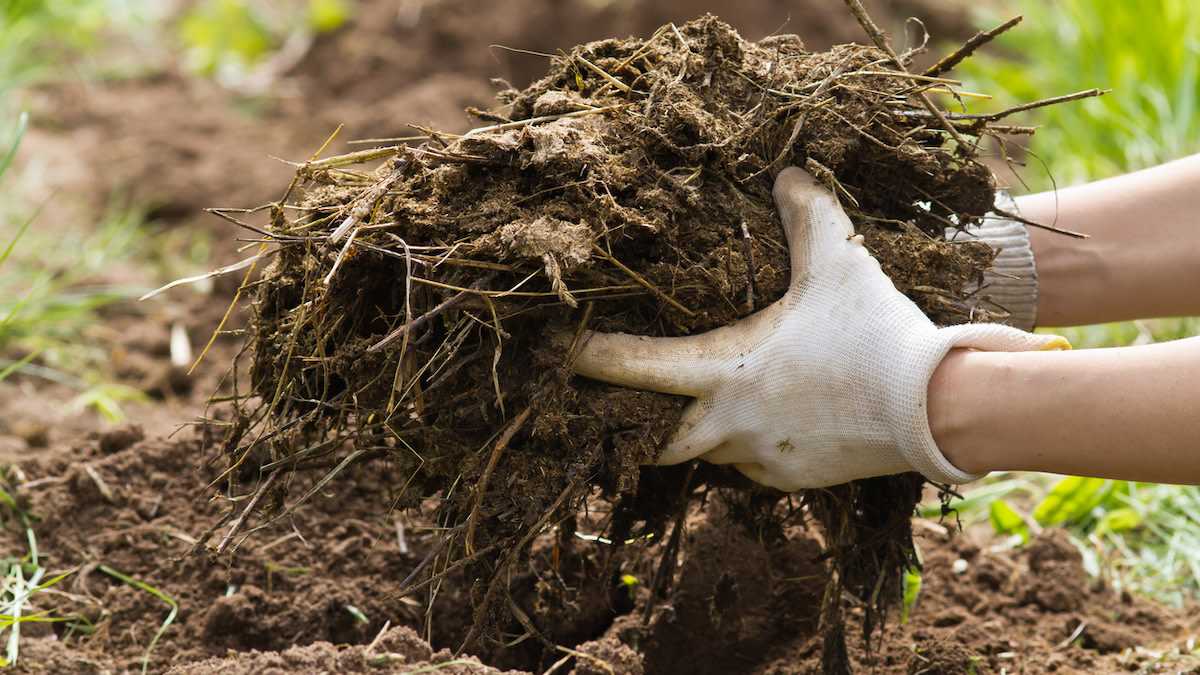

- Use a rake or garden hoe to level the soil surface of the garden bed.
- Smooth out any uneven areas to ensure an even planting surface.
5. Create rows or planting areas

- Determine the spacing and layout for your plants.
- Create rows or designated planting areas in the garden bed.
6. Add mulch
- Spread a layer of mulch over the soil surface to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Choose organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, for best results.
By following these steps, you will have a well-prepared garden bed that provides a fertile and ideal environment for your plants to thrive.
Applying the fertiliser throughout the year
For year-long gardening success, it is important to apply the mineral-organic fertiliser derived from manure correctly and at the right time. Here is a guide on how to apply the fertiliser throughout the year to maximize its benefits:
Spring
- Pre-planting: Before planting any crops or flowers, apply a layer of the mineral-organic fertiliser to the soil. This will provide essential nutrients to the growing plants and help them establish strong root systems.
- Top-dressing: As the plants begin to grow, you can apply a thin layer of the fertiliser around the base of the plants. This will provide a continuous supply of nutrients as the plants continue to grow.
Summer
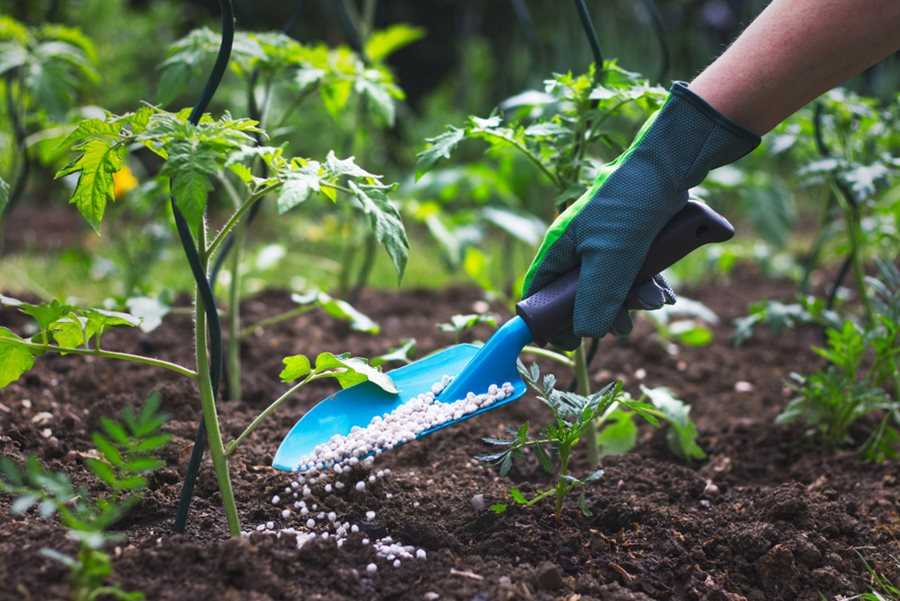

- Side-dressing: When the plants are in full growth, side-dressing can be done by applying a small amount of the fertiliser alongside the rows of plants. This will provide additional nutrients to support their growth during the summer months.
Fall
- Top-dressing: As the growing season comes to an end, it is beneficial to apply another layer of the mineral-organic fertiliser to the soil. This will replenish any nutrients that may have been depleted throughout the growing season and provide a nutrient reserve for the following year.
Winter
During the winter months, it is best to refrain from applying the fertiliser to the soil. Instead, focus on preparing the soil for the next growing season by adding organic matter, such as compost or mulch, to improve its structure and fertility.
By following these guidelines and applying the mineral-organic fertiliser at the appropriate times, you can ensure that your plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth throughout the year. Happy gardening!
“Question-Answer”
What is mineral-organic fertiliser?
Mineral-organic fertiliser is a type of fertiliser that combines mineral nutrients and organic matter. It is made from decomposed manure and other organic materials, which provide essential nutrients for plants, and mineral additives, such as phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen.
How can I prepare mineral-organic fertiliser from manure?
To prepare mineral-organic fertiliser from manure, you will need to mix decomposed manure with mineral additives. Start by collecting the manure and allowing it to decompose naturally. Once it has decomposed, mix it with mineral additives like bone meal, rock phosphate, and potassium sulfate. The ratio of manure to mineral additives can vary depending on the nutrient requirements of your plants.
What are the benefits of using mineral-organic fertiliser?
The use of mineral-organic fertiliser offers several benefits. First, it provides a balanced combination of essential nutrients for plants to grow and thrive. Second, it improves soil fertility and structure, enhancing water and nutrient retention. Third, it promotes the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, which help break down organic matter and release nutrients. Finally, mineral-organic fertiliser is environmentally friendly, as it reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilisers and minimizes the risk of water pollution.
Can I use mineral-organic fertiliser for all types of plants?
Yes, mineral-organic fertiliser can be used for all types of plants, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and ornamental plants. The nutrients provided by the fertiliser are essential for the growth and development of various plant species. However, it is essential to adjust the nutrient composition of the fertiliser based on the specific requirements of different plants.
How often should I apply mineral-organic fertiliser?
The frequency of applying mineral-organic fertiliser depends on various factors, such as the nutrient requirements of the plants, the composition of the fertiliser, and the condition of the soil. In general, it is recommended to apply the fertiliser 2-4 times during the growing season. It is important to monitor the plants’ health and growth to determine if any additional fertiliser is needed.
Are there any alternatives to mineral-organic fertiliser?
Yes, there are alternatives to mineral-organic fertiliser. Some common alternatives include synthetic fertilisers, compost, and other organic fertilisers. Synthetic fertilisers are chemical-based and provide quick nutrient release. Compost is made from organic waste and improves soil structure. Other organic fertilisers, such as seaweed extract and fish emulsion, provide natural nutrients for plants. The choice of fertiliser depends on personal preference, plant requirements, and environmental considerations.







