- Preventing Black Foot Disease on Seedlings
- 1. Proper Sanitation
- 2. Soil Sterilization
- 3. Improved Drainage
- 4. Crop Rotation
- Essential Conditions for Permanent Elimination
- Understanding Black Foot Disease
- Causal agents
- Symptoms
- Transmission and spread
- Prevention and control
- Importance of Proper Seedling Management
- 1. Disease Prevention:
- 2. Optimal Growing Conditions:
- 3. Early Detection and Treatment:
- 4. Proper Disposal of Infected Plants:
- Implementing Effective Sanitation Measures
- 1. Clean and Disinfect Tools and Equipment
- 2. Disinfect Growing Areas
- 3. Practice Crop Rotation
- 4. Monitor and Remove Infected Plants
- 5. Maintain Proper Hygiene Practices
- Choosing Resistant Plant Varieties
- Enhancing Soil Health and Fertility
- Managing Environmental Factors
- Regular Monitoring and Early Detection
- Methods of Monitoring
- Early Detection
- Regular Monitoring Plan
- Conclusion
- “Question-Answer”
- What is black foot disease?
- How can black foot disease be prevented in seedlings?
- Why is proper sanitation important in preventing black foot disease?
- What does it mean to use disease-free substrate?
- Why is proper drainage important in preventing black foot disease?
- Why is regular monitoring and early detection necessary to prevent black foot disease?
- What are some other diseases that can affect seedlings?
- “Video” Doctor explains DIABETIC FOOT COMPLICATIONS – PLUS 12 TIPS FOR PREVENTION!
In the world of horticulture, black foot disease is a common issue that affects the growth and development of seedlings. This fungal disease can cause significant damage to young plants, leading to stunted growth, wilting, and even death. However, there are several essential conditions that can be implemented to permanently eliminate the threat of black foot disease on seedlings.
First and foremost, proper sanitation practices are crucial in preventing the spread of black foot disease. This includes cleaning and disinfecting all gardening tools, pots, and trays before and after each use. Additionally, removing and discarding any diseased or infected plants will help prevent the disease from spreading to other seedlings.
Secondly, implementing a strict crop rotation schedule can greatly reduce the risk of black foot disease. This involves rotating the location of seedlings each growing season, as the fungal pathogens that cause the disease tend to build up in the soil over time. By moving seedlings to different areas, the disease-causing pathogens are less likely to infect new plants.
Furthermore, maintaining proper drainage in the growing area is essential for preventing black foot disease. Excess moisture can create an ideal environment for fungal growth, so ensuring that the soil has proper drainage and avoiding overwatering the seedlings is crucial. This can be achieved by using well-draining soil mixes and providing adequate spacing between plants to promote airflow.
Lastly, implementing biological control methods can help to permanently eliminate black foot disease on seedlings. This includes introducing beneficial microbes and fungi into the soil, which can outcompete the disease-causing pathogens. Additionally, incorporating organic matter into the soil can improve its overall health and create a more hospitable environment for beneficial microorganisms.
By following these four essential conditions – practicing proper sanitation, implementing crop rotation, ensuring proper drainage, and utilizing biological control methods – it is possible to permanently eliminate the threat of black foot disease on seedlings. By doing so, growers can ensure the healthy growth and development of their plants, improving overall crop yield and quality.
Preventing Black Foot Disease on Seedlings
Black Foot Disease is a serious fungal disease that affects seedlings in nurseries and can cause stunted growth or even death of the plants. It is important to take preventive measures to eliminate this disease and ensure healthy seedlings. Here are four essential conditions for permanent elimination of Black Foot Disease:
1. Proper Sanitation
One of the key steps in preventing Black Foot Disease is maintaining proper sanitation practices in the nursery. This includes regularly cleaning and disinfecting all equipment, tools, and containers used for seedlings. It is also important to remove and destroy any infected or dead plants to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Soil Sterilization

The soil used for seedlings should be sterilized to eliminate any pathogens that may be present. This can be done through various methods such as steam sterilization or chemical treatments. It is essential to follow the recommended guidelines for soil sterilization to ensure effective elimination of Black Foot Disease.
3. Improved Drainage
Black Foot Disease thrives in wet and poorly drained soil conditions. To prevent the disease, it is important to improve the drainage in the nursery by ensuring proper soil composition and implementing drainage systems if necessary. This will help to prevent excessive moisture and create an environment that is less favorable for the growth of the fungus.
4. Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an effective strategy to prevent the buildup of pathogens in the soil. By rotating the crops grown in the nursery, the likelihood of reinfection with Black Foot Disease can be reduced. It is important to choose crops that are not susceptible to the disease and to carefully plan the rotation schedule to maximize its effectiveness.
By following these four essential conditions, it is possible to permanently eliminate Black Foot Disease on seedlings in nurseries. Implementing proper sanitation practices, soil sterilization, improved drainage, and crop rotation will help create a healthy and disease-free environment for seedling growth.
Essential Conditions for Permanent Elimination
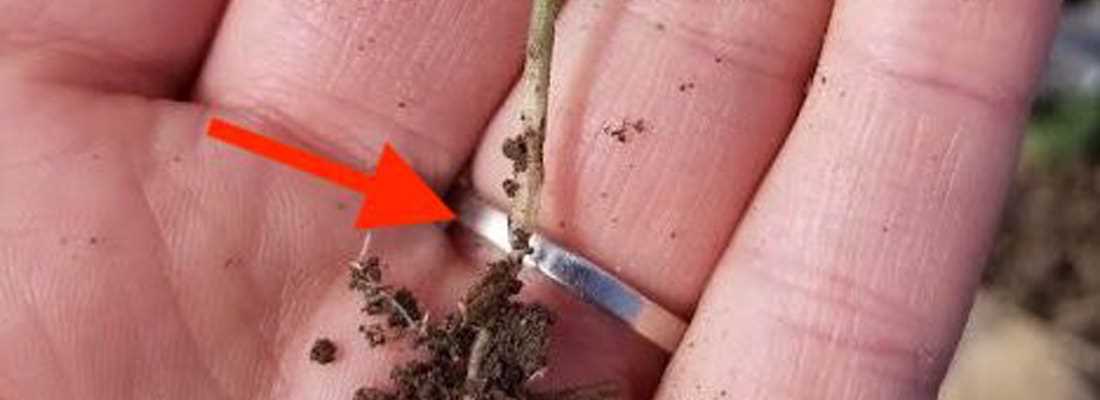

To permanently eliminate black foot disease on seedlings, it is crucial to establish and maintain the following essential conditions:
High-Quality Soil
Using high-quality soil is the first step towards preventing black foot disease. The soil should be well-draining and have good structure to avoid waterlogged conditions that favor disease development. It should also be free from any pathogens or contaminants that can contribute to disease spread.
Proper Seedling Handling
Proper handling of seedlings is vital in preventing black foot disease. It is essential to ensure that seedlings are healthy and disease-free before planting. Inspecting seedlings for any signs of infection, such as darkened roots or stunted growth, is crucial. Infected seedlings should be discarded to prevent disease spread.
Sterilization and Disinfection
Sterilizing and disinfecting tools, equipment, and containers is essential to prevent the introduction and spread of black foot disease. Tools should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected between uses, especially if they have come into contact with infected plants or soil. Containers and trays should also be sterilized before use to eliminate any potential sources of contamination.
Appropriate Cultural Practices
Implementing appropriate cultural practices can help prevent black foot disease. These practices include proper spacing between seedlings, adequate ventilation to prevent high humidity, and regular irrigation to maintain optimal soil moisture levels. Avoiding overwatering and excessive use of nitrogen-containing fertilizers can also help reduce the risk of disease development.
By establishing and maintaining these essential conditions, growers can greatly minimize the risk of black foot disease on seedlings and ensure a healthy and productive crop.
Understanding Black Foot Disease
Black Foot Disease is a fungal disease that affects the roots of seedlings, leading to stunted growth or death of the plants. It is caused by several species of fungi, including Chalara elegans and Thielaviopsis basicola.
The disease is most commonly found in nursery production systems, particularly in young seedlings that are grown in containers or beds. It can be a significant problem in nurseries and can cause considerable economic losses.
Causal agents
Chalara elegans is a fungus that primarily attacks the roots of plants, causing dark brown lesions. The lesions may girdle the roots, resulting in rot and death of the plant. This fungal species can produce spores that remain viable for several years in the soil, making it difficult to eradicate.
Thielaviopsis basicola is another common fungus associated with Black Foot Disease. It infects the roots of seedlings, causing dark brown or black discoloration. The fungus can survive in the soil for long periods, and its spores can be easily spread through contaminated soil, water, or infected plant material.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Black Foot Disease can vary depending on the affected plant species and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Stunted growth
- Wilting or yellowing of leaves
- Root rot
- Dark brown or black discoloration of the roots
Severely infected seedlings may die before reaching maturity.
Transmission and spread
Black Foot Disease can be transmitted through contaminated soil, water, or infected plant material. It can also spread via contaminated tools, containers, or equipment used in nurseries.
The fungus can survive in the soil for extended periods, making it difficult to eliminate. It can be introduced into nurseries through infected seeds, contaminated soil, or infected plant material brought from other locations.
Prevention and control
Preventing and controlling Black Foot Disease requires a multi-faceted approach. Some key measures include:
- Using disease-free planting material: It is crucial to start with healthy seedlings that are free from any signs of infection. Inspecting the roots and stems of seedlings for any discoloration or lesions can help identify potentially infected plants.
- Sanitation practices: Ensuring cleanliness in the production area is essential. This includes regularly cleaning tools, containers, and equipment used in the nursery, as they can be potential sources of contamination.
- Proper irrigation: Overwatering can create favorable conditions for fungal growth. Implementing appropriate irrigation practices, such as using well-draining soil and avoiding waterlogged conditions, can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Crop rotation: Avoid planting susceptible species or varieties in the same area repeatedly. Rotating crops can help break the disease cycle and reduce the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
Implementing these measures, along with regular monitoring and early detection of any signs of infection, can help in the prevention and control of Black Foot Disease in nurseries.
Importance of Proper Seedling Management
Proper seedling management is crucial in preventing the occurrence and spread of black foot disease. By following best practices in seedling production and care, growers can effectively eliminate the risk of this devastating disease on their crops.
1. Disease Prevention:
Proper seedling management plays a vital role in preventing the initiation and spread of black foot disease. By implementing strict hygiene practices, such as sterilizing tools and equipment, growers can minimize the chances of disease transmission. Additionally, ensuring that seedlings are grown in disease-free media and using pathogen-free seeds can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
2. Optimal Growing Conditions:
Providing seedlings with optimal growing conditions is essential for their overall health and vigor. This includes ensuring proper irrigation, temperature control, and nutrient supply. By maintaining a balanced and consistent growing environment, growers can enhance seedling development and strengthen their resistance against diseases, including black foot.
3. Early Detection and Treatment:
Regular monitoring of seedlings is crucial in detecting the early signs of black foot disease. By identifying and isolating infected plants in their initial stages, growers can prevent the spread of the disease to healthy seedlings. Prompt treatment with appropriate fungicides can also help in controlling the disease and minimizing its impact on the crop.
4. Proper Disposal of Infected Plants:
Once black foot disease is detected, it is crucial to properly dispose of infected plants. This helps to prevent the disease from spreading to other areas and contaminating healthy seedlings. Disposal methods may include deep burial or incineration, depending on local regulations and practices.
In conclusion, proper seedling management is essential for effective prevention and elimination of black foot disease. By following best practices in disease prevention, providing optimal growing conditions, practicing early detection and treatment, and ensuring proper disposal of infected plants, growers can safeguard their crops and achieve successful seedling production.
Implementing Effective Sanitation Measures
To prevent the spread of black foot disease on seedlings, it is crucial to implement effective sanitation measures. By maintaining a clean and hygienic environment, you can eliminate the conditions that promote the growth and spread of the disease. Here are some essential sanitation measures to consider:
1. Clean and Disinfect Tools and Equipment
Regularly clean and disinfect all tools and equipment used in the seedling production process. This includes tools such as pruning shears, transplanting tools, and pots. Use a disinfectant solution that is effective against fungal pathogens, and make sure to thoroughly clean all surfaces.
2. Disinfect Growing Areas
Fungal pathogens can remain in the soil and infect new seedlings. To prevent this, disinfect the growing areas before planting new seedlings. Remove any infected debris and thoroughly clean the area. You can use a disinfectant solution or solarization techniques to kill any remaining pathogens.
3. Practice Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an effective technique to reduce the risk of black foot disease. Avoid planting seedlings in the same area or using the same containers consecutively. Rotate the crops to different areas or use fresh containers to prevent the build-up of fungal pathogens in the soil.
4. Monitor and Remove Infected Plants

Regularly monitor the seedlings for any signs of black foot disease. If any plants show symptoms of the disease, remove them immediately to prevent the spread of the infection. Dispose of the infected plants properly and avoid contaminating other healthy seedlings.
5. Maintain Proper Hygiene Practices
Personal hygiene is essential to prevent the spread of diseases. Make sure to wash your hands thoroughly before and after working with seedlings. Additionally, avoid introducing external contaminants by wearing clean clothing and using clean tools.
By implementing these effective sanitation measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of black foot disease on seedlings. Regularly practice these measures to maintain a healthy and disease-free seedling production environment.
Choosing Resistant Plant Varieties
One of the key strategies in preventing the spread of black foot disease on seedlings is to choose plant varieties that have resistance to the disease. By selecting resistant varieties, growers can significantly reduce the risk of infection and minimize the need for chemical treatments.
When selecting resistant plant varieties, there are several factors to consider:
- Disease susceptibility: Different plant varieties have varying levels of susceptibility to black foot disease. It is important to choose varieties that have been bred or selected for resistance to the disease.
- Proven performance: Look for plant varieties that have a track record of performing well in your particular geographic region. Varieties that have shown resistance to black foot disease in other areas may not perform as well in your specific climate and soil conditions.
- Diversity: Planting a diverse range of resistant varieties can further reduce the risk of disease spread. By mixing different resistant varieties, you can decrease the chance of the disease becoming established in your crop.
- Availability: Make sure that the resistant plant varieties you choose are readily available through reputable nurseries or seed suppliers. Availability can vary depending on the region and the specific crop you are growing.
It is also important to note that resistance to black foot disease may not provide complete immunity. Even resistant varieties can still be infected, albeit at a lower rate, under certain conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to combine the use of resistant varieties with other preventive measures, such as proper sanitation and crop rotation.
By carefully selecting resistant plant varieties and maintaining good cultural practices, growers can greatly reduce the impact of black foot disease on their seedlings.
Enhancing Soil Health and Fertility
Enhancing soil health and fertility is crucial in preventing black foot disease on seedlings. By ensuring that the soil is rich in nutrients and has the right balance of minerals, you can create an environment that is unfavorable for the growth and spread of the disease-causing pathogens.
Here are some essential practices to enhance soil health and fertility:
- Organic Matter – Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil. Organic matter helps improve soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient availability for the plants. It also encourages the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, which can help suppress pathogens.
- Crop Rotation – Implement a crop rotation system where you alternate the type of crops grown in a specific area. This practice helps break the disease cycle by reducing the pathogens’ host availability. It also helps to replenish the soil with different nutrients, as different crops have different nutrient requirements.
- Cover Crops – Planting cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, during the fallow season can provide numerous benefits. Cover crops help protect the soil from erosion, improve soil structure, and add organic matter when they are incorporated into the soil. They also capture atmospheric nitrogen and make it available to other crops, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Proper Nutrient Management – Regularly test your soil to determine its nutrient content and pH level. Based on the results, adjust the nutrient inputs accordingly to meet the plants’ needs. It is important to use balanced fertilizers, avoiding over-fertilization, which can lead to nutrient imbalances and create an environment suitable for the development of diseases.
Additionally, it is essential to practice good irrigation management and avoid overwatering, as excess moisture can contribute to the development of black foot disease. Adequate drainage is also crucial to prevent waterlogging, which can suffocate the roots and make them more susceptible to pathogens.
By implementing these practices, you can create a healthy soil environment that promotes the growth of strong and disease-resistant seedlings, reducing the risk of black foot disease and ensuring the long-term success of your planting endeavors.
Managing Environmental Factors

Environmental factors play a crucial role in the prevention and elimination of black foot disease on seedlings. By managing these factors effectively, growers can create an environment that is unfavorable for the disease to thrive. Here are four essential conditions that need to be controlled:
- Temperature:
- Humidity:
- Drainage:
- Sanitation:
Maintaining the right temperature is vital in reducing the risk of black foot disease. The optimal temperature range for seedling growth is between 18°C and 25°C (64°F and 77°F). Temperatures outside of this range can create stress on the plants, making them more susceptible to the disease. Monitoring and controlling the temperature in the nursery is critical to prevent the disease from spreading.
High humidity levels provide an ideal environment for the growth and spread of black foot disease. To prevent the disease, growers should ensure proper ventilation in the nursery and avoid overcrowding the seedlings. Good air circulation and maintaining humidity levels below 70% will help minimize the risk of infection.
Waterlogged soil is a breeding ground for black foot disease. Ensuring proper drainage in the nursery is essential to prevent the disease. Growers should use well-draining potting mixes and containers with adequate drainage holes. Regularly monitoring and adjusting irrigation practices will help maintain optimal soil moisture levels and prevent waterlogging.
Proper sanitation practices are crucial to prevent the spread of black foot disease. Infected seedlings and debris should be promptly removed and destroyed. Tools, equipment, and nursery surfaces should be regularly disinfected to eliminate any potential sources of infection. Implementing strict sanitation protocols will help minimize the risk of disease outbreaks.
By effectively managing these environmental factors, growers can significantly reduce the risk of black foot disease on seedlings. Regular monitoring, adjustment, and implementation of appropriate control measures will contribute to the permanent elimination of the disease from the nursery.
Regular Monitoring and Early Detection
Regular monitoring and early detection are crucial in preventing the spread of Black Foot disease on seedlings. By closely monitoring the health of the seedlings, potential signs of the disease can be identified early on, allowing for prompt action to be taken.
Methods of Monitoring
There are several methods that can be used to monitor the seedlings for signs of Black Foot disease:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the seedlings for any visible symptoms such as wilting, stunted growth, or discoloration of the roots or stems.
- Root Examination: Carefully remove the seedlings from the containers and examine the roots for any signs of black discoloration or decay.
- Microscopic Analysis: Take samples of the roots and examine them under a microscope to detect the presence of the disease-causing pathogens.
Early Detection
Early detection of Black Foot disease is crucial for preventing its spread to other seedlings. Once the disease is detected, immediate action should be taken to prevent its further development. This may include:
- Isolation: Remove and isolate any infected seedlings to prevent the spread of the disease to healthy plants.
- Sanitation: Clean and disinfect all tools, containers, and surfaces that have come into contact with the infected seedlings to prevent the transmission of the disease.
- Appropriate Treatment: Depending on the severity of the disease, appropriate treatment methods, such as fungicide application or cultural practices, may be implemented to control and eliminate the disease.
Regular Monitoring Plan
Developing a regular monitoring plan is essential in preventing the recurrence of Black Foot disease. Here are some steps to consider when developing a monitoring plan:
- Frequency: Determine how often the seedlings need to be monitored. This will depend on factors such as the growth stage of the seedlings and the prevalence of the disease in the area.
- Monitoring Techniques: Decide on the specific monitoring techniques that will be used, such as visual inspection, root examination, or microscopic analysis.
- Record Keeping: Keep detailed records of the monitoring results, including the date of inspection, the symptoms observed, and any actions taken.
- Action Plan: Develop a clear action plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event that Black Foot disease is detected.
Conclusion
Regular monitoring and early detection are essential components of a comprehensive strategy for preventing the spread of Black Foot disease on seedlings. By closely monitoring the health of the seedlings and taking prompt action when signs of the disease are detected, growers can minimize the risk of infection and ensure the long-term health and productivity of their plants.
“Question-Answer”
What is black foot disease?
Black foot disease is a fungal infection that affects the roots of seedlings, leading to stunted growth and eventually death.
How can black foot disease be prevented in seedlings?
Preventing black foot disease in seedlings requires four essential conditions: proper sanitation, use of disease-free substrate, proper drainage, and regular monitoring and early detection.
Why is proper sanitation important in preventing black foot disease?
Proper sanitation is important because the fungus that causes black foot disease can survive in soil and plant debris, so keeping the growing area clean and free of potential sources of contamination is crucial to preventing the disease.
What does it mean to use disease-free substrate?
Using disease-free substrate means using a growing medium that has been sterilized or treated to kill any potential fungal pathogens, reducing the risk of black foot disease in seedlings.
Why is proper drainage important in preventing black foot disease?
Proper drainage is important because excessive moisture can create a favorable environment for the growth of the fungus that causes black foot disease. Good drainage helps to prevent the roots from sitting in water and becoming susceptible to infection.
Why is regular monitoring and early detection necessary to prevent black foot disease?
Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of any signs or symptoms of black foot disease, such as stunted growth or discoloration of the roots. Early detection allows for prompt action to be taken to prevent the spread of the disease and save the affected seedlings.
What are some other diseases that can affect seedlings?
Some other diseases that can affect seedlings include damping off, root rot, and powdery mildew.







