- Optimal Timing for Seed Sowing: Ensuring Healthy Seedling Growth
- Understanding the Importance of Timing
- Researching Plant-Specific Timing
- Considering Local Climate Conditions
- Using Tools and Resources
- Keeping a Gardening Journal
- Conclusion
- Importance of Proper Timing
- Understanding Seedling Growth
- The Life Cycle of a Plant
- Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
- Optimal Timing for Sowing Seeds
- Caring for Seedlings
- Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
- Determining the Ideal Sowing Time
- 1. Frost Dates
- 2. Planting Zone
- 3. Seed Packet Instructions
- 4. Germination Time
- 5. Climate and Weather Conditions
- 6. Crop Rotation
- Preparing Seeds for Sowing
- 1. Seed Selection
- 2. Seed Storage
- 3. Seed Treatment
- 4. Seed Soaking
- 5. Seed Scarification
- 6. Seed Stratification
- 7. Seed Sowing Depth
- 8. Moisture and Temperature
- 9. Light Requirements
- 10. Seedling Care
- Creating the Perfect Sowing Environment
- 1. Clean and Sterile Environment
- 2. Good-Quality Soil
- 3. Proper Moisture
- 4. Optimal Temperature
- 5. Sufficient Light
- 6. Adequate Air Circulation
- Monitoring and Adjusting Sowing Time
- Observation
- Comparison
- Environmental Factors
- Thinning
- Record Keeping
- Adjusting Sowing Time
- Consult Experts
- Flexibility
- Post-Sowing Care for Seedlings
- 1. Watering
- 2. Light
- 3. Temperature
- 4. Ventilation
- 5. Fertilization
- 6. Transplanting
- “Question-Answer”
- When is the best time to sow seeds for summer vegetables?
- What are the consequences of sowing seeds too early?
- Can seeds be sown directly into the ground instead of starting them indoors?
- Is it necessary to have a greenhouse or grow lights for starting seeds indoors?
- What is the best way to determine the proper timing for sowing seeds?
- Can seeds be sown too late?
- What are some signs that indicate seedlings are overgrown?
- “Video” 5 Tips on Seed Sowing and Seedling Growing in Trays
Knowing when to sow seeds is crucial for successful gardening. The timing of seed sowing plays a vital role in the development and growth of seedlings. Seeds that are sown too early or too late can result in overgrown or stunted plants. To prevent these issues, it is important to understand the ideal timing for sowing different types of seeds.
Each plant species has specific requirements for germination and growth. Some seeds thrive in warm soil and need to be sown in early spring or late summer, while others prefer cooler temperatures and should be sown in early spring or early fall. By carefully researching the optimal conditions for each type of plant, gardeners can ensure that their seeds are sown at the right time.
When seeds are sown too early, they may face challenges such as frost, low soil temperatures, or insufficient sunlight. These conditions can result in slow or failed germination, weak seedlings, and poor growth. On the other hand, sowing seeds too late may result in a shorter growing season, as the plants may not have enough time to mature before the arrival of unfavorable weather conditions.
By following gardening guides or consulting with local experts, gardeners can determine the best time to sow their seeds based on their specific geographical location and climate. Collecting data on average temperatures, precipitation, and frost dates can also be helpful in determining the optimal timing for seed sowing. With proper timing and planning, gardeners can maximize the potential of their seeds and ensure healthy, thriving plants.
Optimal Timing for Seed Sowing: Ensuring Healthy Seedling Growth
Proper timing for seed sowing is crucial to ensure healthy seedling growth and maximize the success of your gardening endeavors. By sowing seeds at the right time, you can prevent the development of overgrown or stunted seedlings, leading to stronger and more productive plants in the long run.
Understanding the Importance of Timing
Each plant has its own ideal timing for seed sowing, which is determined by factors such as the plant’s growth requirements, climate conditions, and the intended time of harvest. Sowing seeds too early can result in seedlings that are vulnerable to frost or unfavorable weather conditions, while sowing seeds too late can lead to a delayed harvest or poor growth due to insufficient time for the plant to mature.
Researching Plant-Specific Timing
Before sowing seeds, it is important to research the specific timing requirements for each plant variety. This information can usually be found on the seed packet or through reputable gardening resources. Plant-specific timing guidelines often include instructions on optimal sowing dates based on the average last frost date in your area or the number of weeks before or after a specific event, such as transplanting or the start of the growing season.
Considering Local Climate Conditions

Local climate conditions play a significant role in determining the optimal timing for seed sowing. Understanding your region’s climate, including the average last frost date, first frost date, and the length of the growing season, can help you make informed decisions about when to sow seeds. In colder climates, starting seeds indoors or using protective measures, such as row covers or tunnels, can extend the growing season and allow for successful seedling growth.
Using Tools and Resources
Various online tools and resources are available to assist gardeners in determining the optimal timing for seed sowing. These tools take into account factors such as your location, desired plantings, and local climate data to provide personalized sowing recommendations. Additionally, gardening books, local gardening clubs, and extension services can offer valuable insights into timing techniques specific to your area.
Keeping a Gardening Journal
Maintaining a gardening journal can be a valuable tool for tracking the success of various seed sowing times and methods. By recording the dates of sowing, germination, and transplanting, as well as any environmental factors or observations, you can assess which timing methods have yielded the best results for specific plant varieties in your garden. Over time, this knowledge can be used to refine your sowing schedule and optimize seedling growth.
Conclusion
Optimal timing for seed sowing is paramount in ensuring healthy seedling growth and maximizing the potential of your garden. By researching plant-specific timing, considering local climate conditions, utilizing tools and resources, and keeping a gardening journal, you can make informed decisions and achieve optimal results in your gardening endeavors.
Importance of Proper Timing
Proper timing is crucial when it comes to sowing seeds as it greatly affects the growth and development of seedlings. Planting seeds at the right time ensures that they have enough time to grow and mature before unfavorable weather conditions arrive. Whether you’re planting in a garden or starting seeds indoors, understanding the importance of proper timing is essential for successful seedling establishment.
1. Optimal Growing Conditions
Sowing seeds at the appropriate time allows them to take advantage of the optimal growing conditions. Different plant species have specific environmental requirements, such as temperature, sunlight, and moisture levels. By sowing seeds at the right time, you can ensure that the seedlings will have access to the necessary resources for healthy growth.
2. Disease Prevention
Planting seeds at the right time helps prevent the occurrence of diseases in seedlings. When seeds are sown too early, they may be exposed to cold and damp conditions that can promote the growth of pathogens. On the other hand, sowing seeds too late may expose them to high temperatures and dry conditions, making them more susceptible to stress and disease. By timing the sowing correctly, you can minimize the risk of diseases affecting your seedlings.
3. Avoid Overgrown or Stunted Seedlings
If seeds are sown too early, the seedlings may become overgrown before they can be transplanted outside or before they have enough space to grow indoors. This can result in overcrowded and weakened seedlings. Conversely, if seeds are sown too late, the seedlings may not have enough time to grow and develop adequately, resulting in stunted and underdeveloped plants. Proper timing ensures that seedlings are at their optimal size for transplantation or outdoor growth.
4. Maximize Plant Productivity
By sowing seeds at the right time, you can maximize the productivity of your plants. Once the seedlings are mature and transplanted or moved outdoors, they will have a head start in their growth and development. This allows them to establish their root systems and start producing fruits, flowers, or vegetables earlier in the season. Early planting can also extend the growing season, giving your plants more time to thrive and yield a bountiful harvest.
Conclusion
Proper timing is essential for successful seed sowing and the establishment of healthy seedlings. By understanding the importance of timing, you can ensure optimal growing conditions, prevent diseases, avoid overgrown or stunted seedlings, and maximize the productivity of your plants. Take the time to research the specific requirements for each plant species, and plan your seed sowing accordingly to set yourself up for gardening success.
Understanding Seedling Growth
Seedling growth is an essential stage in the life cycle of plants. It is the process by which a seed transforms into a young plant capable of surviving on its own. Understanding the factors that influence seedling growth can help gardeners and farmers make informed decisions about when to sow their seeds and how to care for their seedlings.
The Life Cycle of a Plant
Before we dive into seedling growth, let’s briefly review the life cycle of a plant. It typically begins with the germination of a seed, followed by the emergence of a seedling from the soil. The seedling then grows into a mature plant, which eventually produces flowers or fruits. These flowers or fruits contain seeds, completing the cycle.
Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
Several factors can influence the growth of a seedling. These factors include:
- Temperature: Seeds have specific temperature requirements for germination. If the temperature is too low or too high, it can affect the growth of the seedling.
- Light: Light is essential for seedlings to undergo photosynthesis, a process that converts light energy into chemical energy. Insufficient or excessive light can hinder seedling growth.
- Water: Adequate water supply is crucial for seedling growth. Too much or too little water can lead to stunted or overgrown seedlings.
- Nutrients: Seedlings require nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium for healthy growth. Soil quality and the availability of nutrients play a significant role in seedling development.
- Air: Proper air circulation is necessary for seedlings to exchange gases and regulate transpiration. Inadequate air circulation can lead to weak, leggy seedlings.
Optimal Timing for Sowing Seeds
Timing is crucial when sowing seeds to ensure optimal seedling growth. Different plants have different temperature and light requirements for germination. Some plants thrive in cool-season conditions, while others prefer warmer temperatures. Additionally, understanding the growing season and frost dates in your region can help you determine the best time to sow your seeds.
Caring for Seedlings
Proper care is essential for promoting healthy seedling growth. This includes providing the right amount of water, light, nutrients, and air circulation. Overwatering or underwatering can lead to root rot or dehydration, respectively. Insufficient or excessive light can cause weak or leggy seedlings. Applying appropriate fertilizers and ensuring good soil quality can provide the necessary nutrients for seedling development.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Water correctly | Provide adequate moisture to prevent drying out or waterlogging. |
| Provide sufficient light | Ensure seedlings receive the right amount of light for photosynthesis. |
| Use appropriate fertilizers | Apply fertilizers based on the specific nutrient needs of your seedlings. |
| Ensure good air circulation | Provide proper ventilation to prevent the buildup of moisture and fungal diseases. |
| Protect from pests | Take measures to prevent pests from damaging or feeding on your seedlings. |
By understanding seedling growth and providing the optimal conditions for their development, gardeners and farmers can ensure healthy and vigorous plants that will thrive throughout their life cycle.
Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
There are several factors that can significantly impact the growth of seedlings. It is important to consider these factors to ensure healthy and vigorous growth. Some of the key factors affecting seedling growth include:
- Temperature: Temperature plays a crucial role in seedling growth. Different plant species have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth. Inadequate or extreme temperatures can hinder germination or lead to stunted growth.
- Light: Light is essential for photosynthesis, a process through which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Insufficient or excess light can affect the growth and development of seedlings. Some plants require full sunlight, while others thrive in partial shade.
- Moisture: Adequate moisture is vital for seed germination and seedling growth. Lack of water can lead to wilting and even death, while excessive moisture can cause root rot and other fungal diseases.
- Nutrients: Seedlings require an adequate supply of nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, for proper growth. Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances can result in stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and other nutritional disorders.
- Soil Quality: The quality of the soil significantly impacts seedling growth. Good soil structure, proper drainage, and the presence of organic matter promote healthy root development and nutrient uptake.
- Oxygen: Adequate oxygen supply is crucial for seedling growth. Oxygen is necessary for root respiration, and insufficient oxygen levels in the soil can lead to poor root development and overall stunted growth.
By considering these factors and providing the optimal conditions for seedling growth, you can ensure successful germination and healthy, vigorous plants.
Determining the Ideal Sowing Time
Choosing the right time to sow your seeds is crucial for achieving healthy and well-developed seedlings. The ideal sowing time varies depending on the specific plant species and climate conditions. Here are some factors to consider when determining the ideal sowing time:
1. Frost Dates
Frost dates play an important role in determining when to sow your seeds. Knowing the last expected frost date in your area can help you avoid planting too early, which can result in the damage or death of your seedlings. On the other hand, planting too late can lead to shorter growing seasons and reduced yields. Check with your local agricultural extension office or use online resources to find out the frost dates for your region.
2. Planting Zone
Understanding your planting zone can provide valuable information about the suitable sowing time for different plant species. Planting zones are determined based on factors such as average temperatures, frost dates, and climate conditions. By knowing which planting zone you are in, you can determine the best sowing time for your seeds.
3. Seed Packet Instructions
Seed packets often provide specific instructions on when to sow the seeds. They may include information on the best time to sow indoors or outdoors, as well as the optimal germination temperature. Always refer to the instructions on the seed packet for accurate sowing timing.
4. Germination Time
Consider the germination time required for your specific plant species. Some seeds may take longer to germinate, while others may have a shorter germination period. If you know the average time it takes for your seeds to sprout, you can count back from the desired planting date to determine the ideal sowing time.
5. Climate and Weather Conditions
The climate and weather conditions in your area can greatly affect the growth and development of seedlings. Some plants prefer warmer temperatures, while others thrive in cooler climates. Take into consideration the average temperature and weather patterns when determining the ideal sowing time for your seeds.
6. Crop Rotation
If you practice crop rotation in your garden, it can affect the timing for sowing certain plants. Some plants may require specific intervals between plantings to prevent disease and nutrient depletion. Consider your crop rotation schedule when determining the ideal sowing time for different plant species.
By taking these factors into account, you can determine the ideal sowing time for your seeds and set your seedlings up for success.
Preparing Seeds for Sowing
Properly preparing your seeds is crucial for successful sowing. By taking the necessary steps to prepare your seeds, you can increase their chances of germination and ensure healthy growth.
1. Seed Selection

Choose high-quality seeds from a reputable supplier. Look for seeds that are fresh, well-formed, and free from damage or disease. Check the expiration date on the seed packet to ensure they are still viable.
2. Seed Storage
Store your seeds in a cool, dry place to maintain their viability. Keep them in airtight containers or seed envelopes that are labeled with the seed variety and date of collection.
3. Seed Treatment
Some seeds may require special treatment to break their dormancy and improve germination rates. This can include scarification, stratification, or soaking in water. Follow the specific instructions for each seed variety to ensure proper treatment.
4. Seed Soaking
Soaking seeds before sowing can help promote germination. Place the seeds in a container of room temperature water and let them soak for the recommended time specified on the seed packet. Drain the water before sowing.
5. Seed Scarification
Scarification involves nicking or scratching the seed coat to help water penetrate the seed and promote germination. This can be done by gently filing or rubbing the seed coat with sandpaper or a small knife. Be careful not to damage the embryo inside.
6. Seed Stratification
Some seeds require a period of cold stratification to simulate winter conditions before they can germinate. This can be achieved by placing the seeds in a moist paper towel or sphagnum moss and storing them in the refrigerator for the recommended stratification period.
7. Seed Sowing Depth
It is important to sow the seeds at the correct depth. The general rule of thumb is to sow the seeds at a depth equal to two times their diameter. However, some seeds may have specific depth requirements, so refer to the seed packet for guidance.
8. Moisture and Temperature

After sowing the seeds, keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Provide the seeds with the appropriate temperature conditions for germination, as different seeds have different temperature requirements. Refer to the seed packet for the ideal temperature range.
9. Light Requirements
Some seeds require light to germinate, while others prefer darkness. Ensure you are providing the appropriate light conditions for your seeds. The seed packet should indicate whether light or darkness is necessary.
10. Seedling Care
Once the seeds have germinated and seedlings have emerged, provide them with proper care. This includes regular watering, adequate sunlight or artificial light, and protection from pests or extreme weather conditions.
By taking the time to properly prepare your seeds for sowing, you can increase their chances of successful germination and ensure the healthy growth of your seedlings.
Creating the Perfect Sowing Environment
Creating the perfect sowing environment is crucial for the successful growth of your seedlings. By providing the right conditions, you can ensure that your seeds germinate properly and develop into healthy, vigorous plants. Here are some tips for creating the perfect sowing environment:
1. Clean and Sterile Environment
Before sowing your seeds, it is important to clean and sterilize the sowing containers and tools. This helps prevent the spread of diseases and reduces the chances of seedling damping off. Use a mild bleach solution or a commercial sterilizing agent to clean your containers and tools thoroughly.
2. Good-Quality Soil
Choose a good-quality seed starting mix or potting soil for sowing your seeds. Avoid using garden soil, as it may contain weed seeds, pests, and diseases. The soil should be well-draining and lightweight, allowing the seeds to germinate and roots to grow freely.
3. Proper Moisture
Seedlings need consistent moisture to germinate and grow. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to damping off and root rot. Keep the soil evenly moist but not soggy. Use a spray bottle or water from the base to avoid disturbing the delicate seeds.
4. Optimal Temperature
Most seeds have a preferred temperature range for germination. Consult the seed packet or reference guide to find out the optimal temperature range for your specific seeds. You can use a seedling heat mat or place your containers near a heat source to maintain the desired temperature.
5. Sufficient Light
Provide sufficient light to your seedlings to ensure proper growth. If you are sowing indoors, place your containers near a sunny window or use artificial grow lights. Adjust the distance between the light source and seedlings to prevent them from getting leggy.
6. Adequate Air Circulation
Proper air circulation is essential for preventing disease and promoting strong seedling growth. Avoid overcrowding your seedlings, as it can lead to increased humidity and disease issues. Use a small fan or open a window occasionally to improve air circulation.
By creating the perfect sowing environment, you can give your seeds the best chance of germinating and growing into healthy seedlings. Pay attention to the cleanliness, soil quality, moisture, temperature, light, and air circulation, and you will be rewarded with strong, vibrant plants.
Monitoring and Adjusting Sowing Time
Monitoring the progress of your seedlings is crucial to ensure they are growing at the optimal rate and are not becoming overgrown or stunted. Regularly checking on the development of your seedlings will help you determine if any adjustments need to be made to the sowing time.
Observation
Start by observing the growth of your seedlings. Look for signs of overgrowth or stunted growth, including extremely tall or spindly seedlings, or small and underdeveloped ones. Take note of any variations in height or size among seedlings within the same batch.
Comparison
To determine if your seedlings are growing at the expected rate, compare their progress to established growth charts or guidelines specific to the plant species you are growing. This will help you identify any deviations from the expected growth pattern and allow you to make necessary adjustments.
Environmental Factors
Consider the environmental conditions in which your seedlings are growing. Factors such as temperature, light intensity, humidity, and air circulation can significantly affect their growth. If your seedlings are growing too quickly, it may be necessary to decrease the temperature or reduce the amount of light they receive. On the other hand, if your seedlings are growing slowly or appear weak, increasing the temperature or providing more light may be necessary.
Thinning
If you notice that your seedlings are overcrowded or competing for resources, thinning them out may be necessary. Remove the weakest seedlings, leaving only the strongest and healthiest ones. This will allow the remaining seedlings to grow more vigorously and prevent them from becoming stunted.
Record Keeping
Keep a record of the dates and conditions under which you sow your seeds. This will help you track the growth progress of your seedlings over time and identify any trends or patterns. By reviewing your records, you can make more informed decisions when adjusting the sowing time for future plantings.
Adjusting Sowing Time
If you consistently find that your seedlings are either overgrown or stunted, it may be necessary to adjust the sowing time for future plantings. Bringing forward or delaying the sowing date by a few days can make a significant difference in the growth and development of your seedlings.
Consult Experts
If you are unsure about the proper timing for sowing specific plant species, consult gardening experts, local agricultural extension offices, or reputable online sources for guidance. They can provide valuable insights and advice tailored to your specific gardening conditions.
Flexibility
Finally, be open to experimenting and adjusting your sowing time. Every plant species and environment is unique, so it may require some trial and error to determine the optimal sowing time for your specific circumstances. Don’t be discouraged by setbacks and be willing to adapt your approach as needed.
Post-Sowing Care for Seedlings
Once you have sown your seeds, it is important to provide proper care to ensure the healthy growth of your seedlings. Here are some post-sowing care tips to follow:
1. Watering
After sowing, the soil should be kept moist but not waterlogged. Watering should be done gently, using a watering can or a spray bottle to avoid damaging the delicate seedlings. It is essential to water regularly, especially during dry periods, to prevent wilting and dehydration.
2. Light
Place the seed trays or containers in a well-lit area, such as a sunny windowsill or under grow lights. Adequate light is crucial for photosynthesis and the development of strong, healthy seedlings. If the seedlings appear leggy or stretched, it indicates a lack of light, and you may need to adjust their position or provide additional artificial light.
3. Temperature
Seedlings require the right temperature for optimal growth. Most seeds germinate best in a warm environment, typically between 65°F and 75°F (18°C – 24°C). However, be sure to check the specific requirements for the seeds you are sowing, as some may have different temperature preferences.
4. Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is essential to prevent diseases and ensure healthy seedling growth. Once the seedlings have emerged, remove any plastic covers or domes to allow proper air circulation. This will help prevent fungal diseases and mold from developing.
5. Fertilization
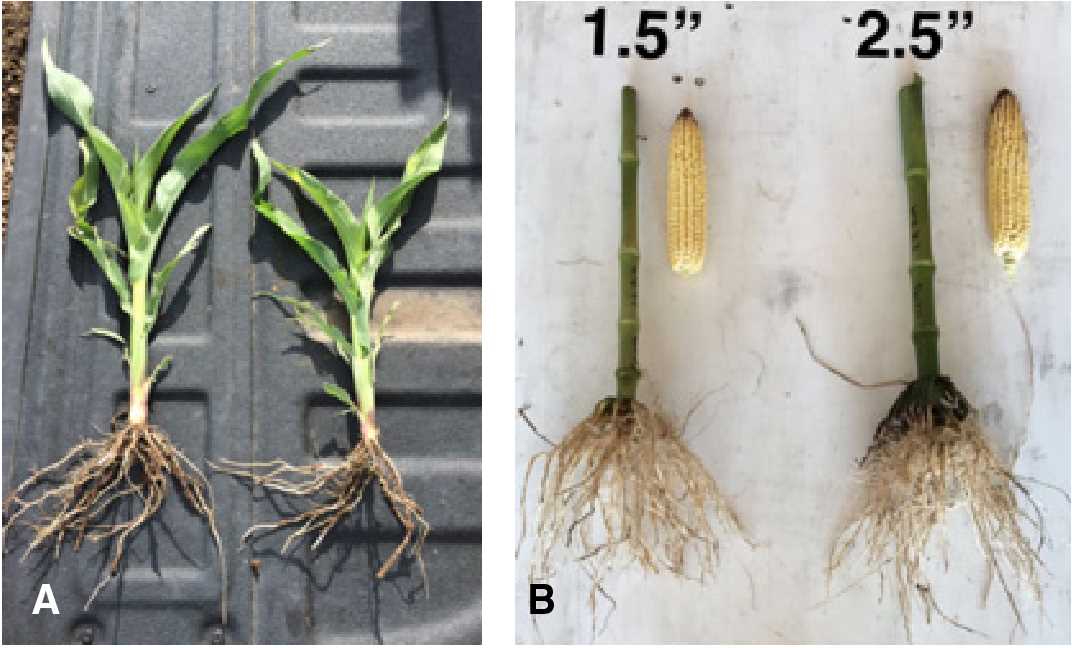

After the seedlings have developed their first true leaves, you can start applying a diluted liquid fertilizer, following the package instructions. This will provide them with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Be careful not to use too much fertilizer, as it can damage the delicate seedlings.
6. Transplanting
Once the seedlings have grown to a suitable size and have developed a strong root system, they can be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the garden. Be gentle when handling the seedlings to avoid damaging the roots. Gradually acclimate them to outdoor conditions by placing them outside for increasing periods each day before transplanting them into the garden.
By providing proper post-sowing care, you can ensure that your seedlings grow into healthy, robust plants ready for transplantation into the garden.
“Question-Answer”
When is the best time to sow seeds for summer vegetables?
The best time to sow seeds for summer vegetables is typically in the early spring, around 4-6 weeks before the last frost date. This allows the seedlings enough time to grow and develop before being transplanted into the garden.
What are the consequences of sowing seeds too early?
If seeds are sown too early, they may become overgrown and leggy by the time they are ready to be transplanted. This can result in weak or stunted seedlings that may struggle to survive once planted in the garden. It’s important to follow the recommended sowing times for each type of plant to ensure healthy growth.
Can seeds be sown directly into the ground instead of starting them indoors?
Yes, certain seeds can be sown directly into the ground instead of starting them indoors. These are typically seeds that can tolerate cooler soil temperatures and have a shorter growing season. Examples of seeds that can be directly sown include radishes, carrots, and lettuce. However, starting seeds indoors and transplanting them later can provide better control over the growing conditions and give the seedlings a head start.
Is it necessary to have a greenhouse or grow lights for starting seeds indoors?
While having a greenhouse or grow lights can be beneficial for starting seeds indoors, they are not necessary. Seeds can be started in a sunny window or under fluorescent lights. The most important factors for successful seed starting are providing adequate moisture, maintaining the right temperature, and ensuring the seedlings receive enough light.
What is the best way to determine the proper timing for sowing seeds?
The best way to determine the proper timing for sowing seeds is to consult a seed packet or gardening guide specific to the type of plant you are growing. These resources often provide recommended sowing dates based on the average last frost date in your area. Additionally, experienced gardeners and local gardening extension offices can provide valuable insight and advice.
Can seeds be sown too late?
Yes, seeds can be sown too late in the season. If seeds are sown too close to the end of the growing season, they may not have enough time to mature before the first frost. In such cases, the plants may produce a limited or no harvest. It’s important to sow seeds early enough to give the plants sufficient time to grow and mature.
What are some signs that indicate seedlings are overgrown?
Some signs that indicate seedlings are overgrown include tall and spindly stems, small and pale leaves, and a weak or wilted appearance. Overgrown seedlings may also have a difficult time supporting themselves and may require additional support or staking. To prevent overgrowth, it’s important to provide adequate spacing and proper lighting for the seedlings.







