- What is Ammonium Sulphate?
- Ammonium Sulphate Composition and Formula
- Chemical Properties of Ammonium Sulphate
- Benefits of Applying Ammonium Sulphate Fertilizer
- Ammonium Sulphate as a Nitrogen Source
- Ammonium Sulphate as a Source of Sulphur
- Advantages of Using Ammonium Sulphate as a Source of Sulphur:
- When to Apply Ammonium Sulphate Fertilizer?
- 1. Pre-plant or Pre-seeding Application
- 2. Side-Dressing Application
- 3. Top-Dressing Application
- 4. Split Application
- Ammonium Sulphate Application Timing
- Pre-planting
- Top-dressing
- Split Applications
- Soil Testing
- Ammonium Sulphate Application Rates and Methods
- Application Rates
- Application Methods
- Timing of Application
- “Question-Answer”
- What is ammonium sulphate?
- How does ammonium sulphate help plants?
- When should I apply ammonium sulphate?
- How should I apply ammonium sulphate?
- What are the benefits of using ammonium sulphate as a fertilizer?
- Are there any precautions or potential drawbacks when using ammonium sulphate?
- “Video” Lawn fertilizer and calculation guide, add nitrogen and reduce soil PH with Ammonium Sulfate
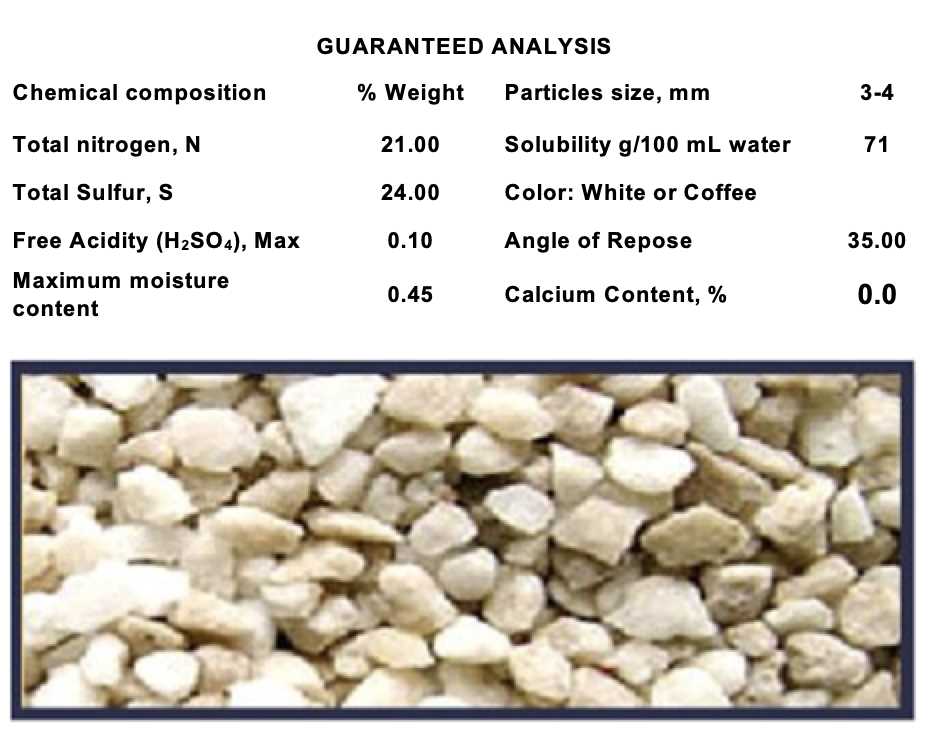
Ammonium sulphate is a common nitrogen fertilizer that is widely used in agriculture to promote healthy plant growth. It is a white crystalline solid that contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulphur, making it an excellent source of these essential nutrients for plants.
One of the key properties of ammonium sulphate is its high solubility in water. This means that it can be easily dissolved and absorbed by the plant roots, providing a quick and efficient source of nitrogen and sulphur. Additionally, ammonium sulphate has a slightly acidic pH, which can help to lower the soil pH in alkaline soils, making it more suitable for growing certain types of plants.
When it comes to application, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, the timing of application is important. Ammonium sulphate is typically applied in the early stages of plant growth, as it provides an immediate boost of nitrogen and sulphur, which are crucial for early plant development. However, it is important to avoid over-application, as excessive nitrogen can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution.
In terms of application methods, ammonium sulphate can be applied either as a dry granular fertilizer or as a liquid solution. The choice of application method depends on factors such as soil type, crop type, and equipment available. Dry granular fertilizers are commonly broadcasted or applied in rows during planting, while liquid solutions can be sprayed directly onto the foliage or applied through irrigation systems.
In conclusion, ammonium sulphate is a versatile fertilizer that provides an immediate source of nitrogen and sulphur for plants. Its high solubility, acidity, and timing of application make it a valuable tool for promoting healthy plant growth. However, it is important to use this fertilizer judiciously and follow recommended application rates to avoid nutrient imbalances and environmental issues.
What is Ammonium Sulphate?

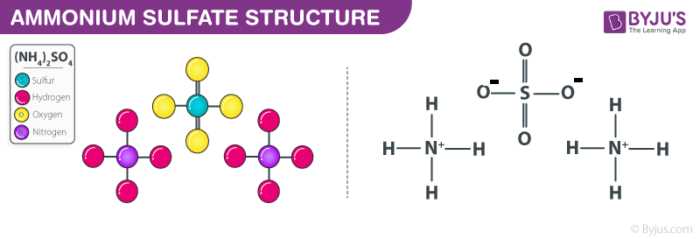
Ammonium sulphate is a type of fertilizer that contains both nitrogen and sulfur. It is often used in agriculture to provide essential nutrients to plants. The chemical formula of ammonium sulphate is (NH4)2SO4. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water.
Ammonium sulphate is a source of both nitrogen and sulfur, two important nutrients for plant growth. Nitrogen is a key component of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, which are essential for plant growth and development. Sulfur is important for the formation of certain amino acids and proteins, as well as for the synthesis of vitamins and enzymes in plants.
Ammonium sulphate can be manufactured synthetically or derived from natural sources, such as volcanic deposits or the byproducts of certain industrial processes. The synthetic production of ammonium sulphate involves combining ammonia gas with sulphuric acid. The resulting product is then further processed to obtain the desired form, such as powdered or granular ammonium sulphate.
Ammonium sulphate is commonly used as a fertilizer in agricultural practices, especially in crops that require high levels of nitrogen and sulfur, such as corn, wheat, and soybeans. It is often applied to soil before planting or as a top dressing during the growing season. Ammonium sulphate can be applied directly to the soil or dissolved in water and applied as a foliar spray.
One of the benefits of using ammonium sulphate as a fertilizer is its quick-release nature. The nitrogen and sulfur present in ammonium sulphate are readily available for plant uptake, providing immediate nutrition and promoting rapid growth. However, it is important to note that excessive use of ammonium sulphate can lead to nitrogen leaching and soil acidification, which may negatively impact the environment and plant health.
Overall, ammonium sulphate is a valuable fertilizer that provides essential nutrients to plants, particularly nitrogen and sulfur. It is commonly used in agricultural practices to promote healthy plant growth and enhance crop yields.
Ammonium Sulphate Composition and Formula

Ammonium sulphate is a type of inorganic chemical compound that is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture. Its chemical formula is (NH4)2SO4, which indicates that each molecule of ammonium sulphate contains two ammonium ions (NH4+) and one sulphate ion (SO42-).
The ammonium ions in ammonium sulphate are a source of nitrogen, one of the essential nutrients required by plants for growth and development. The sulphate ion, on the other hand, provides plants with sulphur, which is important for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and vitamins.
Ammonium sulphate is often added to soil to provide a readily available source of nitrogen and sulphur to plants. Its composition of nitrogen and sulphur can be advantageous in certain agricultural practices where these nutrients are required in specific quantities.
It is important to note that ammonium sulphate has a slightly acidic pH, which can be beneficial for certain crops that prefer acidic soil conditions. However, it is advisable to use the fertilizer in moderation and monitor soil pH levels to avoid creating an overly acidic environment that may negatively impact soil health.
In summary, the composition and formula of ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4 indicate its rich content of nitrogen and sulphur, making it a versatile fertilizer for a range of crops. Understanding its composition can help in determining the appropriate application rates and timing for optimal plant growth and yield.
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Sulphate
Ammonium sulphate, also known as diammonium sulphate or sulfuric acid diammonium salt, is a chemical compound with the formula (NH4)2SO4. It is a white, crystalline solid with a characteristic ammoniacal odor. Here are the chemical properties of ammonium sulphate:
- Chemical formula: (NH4)2SO4
- Molecular weight: 132.14 g/mol
- Solubility: Ammonium sulphate is highly soluble in water. Approximately 70 grams of ammonium sulphate can dissolve in 100 milliliters of water at room temperature (25°C).
- pH: A 0.1 M solution of ammonium sulphate has a pH value of around 5.5. It is slightly acidic.
- Hygroscopicity: Ammonium sulphate is hygroscopic, meaning it has a tendency to absorb moisture from the air.
- Combustibility: Ammonium sulphate is non-combustible.
Ammonium sulphate is commonly used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content. It is also used in various industrial applications, such as in flame retardants, in the production of food additives, and as a pH buffer in laboratories.
Benefits of Applying Ammonium Sulphate Fertilizer
Ammonium sulphate fertilizer offers several benefits when applied to plants and crops. Its unique composition and properties make it an effective source of essential nutrients for healthy plant growth and development. Some of the key benefits of using ammonium sulphate fertilizer include:
- High nitrogen content: Ammonium sulphate fertilizer contains a high percentage of nitrogen, typically around 21%. Nitrogen is one of the essential macronutrients required by plants for various physiological processes, including protein synthesis, leaf growth, and chlorophyll production.
- Quick-release nitrogen: The nitrogen in ammonium sulphate fertilizer is readily available for plant uptake, making it a fast-acting fertilizer. This means that plants can quickly absorb and utilize the nitrogen, resulting in faster growth and improved yield.
- Acidifies soil: Ammonium sulphate has an acidic pH, which can help lower the pH of alkaline soils. This is particularly beneficial for plants that prefer acidic soil conditions, such as blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons.
- Source of sulphur: Apart from nitrogen, ammonium sulphate also provides a significant amount of sulphur, another important nutrient for plants. Sulphur is vital for the formation of amino acids, enzymes, and vitamins, and plays a crucial role in plant growth and development.
- Inexpensive: Ammonium sulphate fertilizer is relatively inexpensive compared to other nitrogen fertilizers. Its cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice among farmers and gardeners looking for an affordable option to meet their plant nutritional requirements.
In summary, ammonium sulphate fertilizer offers the benefits of high nitrogen content, quick-release nitrogen, soil acidification, sulphur supplementation, and cost-effectiveness. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a valuable fertilizer for promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing crop yield.
Ammonium Sulphate as a Nitrogen Source
Ammonium sulphate is commonly used as a nitrogen fertilizer in agriculture due to its high nitrogen content. It provides plants with readily available nitrogen in the form of ammonium ions (NH4+), which can be easily absorbed and used by plants for growth and development.
Benefits of Ammonium Sulphate as a Nitrogen Source:
- High nitrogen content: Ammonium sulphate typically contains around 21% nitrogen, making it a concentrated nitrogen source.
- Quick release: The nitrogen in ammonium sulphate is readily available for plant uptake, making it an effective fertilizer for providing a quick boost to plant growth.
- Acidifying effect: Ammonium sulphate is an acidifying fertilizer, which can help lower soil pH levels in alkaline soils.
Optimal Application of Ammonium Sulphate as a Nitrogen Source:
Ammonium sulphate can be applied as a broadcast fertilizer or incorporated into the soil prior to planting. The appropriate application rate will depend on factors such as soil type, crop requirements, and nutrient management goals. It is important to follow recommended guidelines for the specific crop being grown to avoid over-application and potential negative impacts on the environment.
Considerations when Using Ammonium Sulphate as a Nitrogen Source:
- Volatilization: Ammonium sulphate is prone to volatilization, especially in warm and humid conditions. To minimize nitrogen loss, it is recommended to incorporate the fertilizer into the soil soon after application or to apply it just before rainfall.
- Acidic soils: Due to its acidifying effect, caution should be exercised when using ammonium sulphate on already acidic soils, as excessive acidity can have detrimental effects on plant growth.
- Nitrogen management: Ammonium sulphate should be used as part of a comprehensive nutrient management plan, taking into account the nitrogen requirements of the crop, soil testing results, and other nutrient sources.
Conclusion:
Ammonium sulphate is a valuable nitrogen fertilizer for agricultural applications. Its high nitrogen content, quick release, and acidifying effect make it a versatile option for boosting plant growth. However, proper application and nutrient management practices are essential to maximize its effectiveness and minimize potential negative impacts on the environment.
Ammonium Sulphate as a Source of Sulphur
Ammonium Sulphate is not only a commonly used fertilizer for providing nitrogen to plants, but it also serves as an excellent source of sulphur.
Sulphur is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. It plays a vital role in various plant processes, including protein synthesis, enzyme activity, and the formation of chlorophyll. Despite its importance, sulphur is often neglected in fertilizer formulations, as many soils naturally contain sufficient amounts of this element. However, certain crops, such as brassicas (cabbage, broccoli, etc.), legumes, and onions, have a higher sulphur requirement and may benefit from additional supplementation.
Ammonium Sulphate contains approximately 24% sulphur in its chemical composition. This means that when this fertilizer is applied, it can provide a significant amount of sulphur to the soil and subsequently to the plants.
Advantages of Using Ammonium Sulphate as a Source of Sulphur:
- High sulphur content: Ammonium Sulphate contains a relatively high concentration of sulphur, making it an effective source of this nutrient for sulphur-demanding crops.
- Quick release: As ammonium sulphate dissolves in the soil, it readily releases both nitrogen and sulphur ions, which can be rapidly taken up by plant roots.
- Acidifying effect: Ammonium Sulphate has an acidifying effect on the soil, which can be beneficial for crops that prefer acidic growing conditions.
- Compatibility: Ammonium Sulphate can be used in combination with other fertilizers and soil amendments without any compatibility issues.
It is important to note that while Ammonium Sulphate is an effective source of sulphur, its use should be tailored to the specific sulphur requirements of the crops being grown. Soil testing and nutrient management plans can help determine the appropriate amount of Ammonium Sulphate needed to meet the sulphur needs of the plants without causing any nutrient imbalances.
Overall, Ammonium Sulphate offers a convenient and efficient way to supplement sulphur in the soil and promote healthy plant growth.
When to Apply Ammonium Sulphate Fertilizer?
Applying ammonium sulphate fertilizer at the right time is crucial for optimal plant growth and maximum crop yields. The timing of application depends on several factors such as the type of crop, soil conditions, and climate. Here are some general guidelines to help you determine when to apply ammonium sulphate fertilizer:
1. Pre-plant or Pre-seeding Application
Ammonium sulphate can be applied before planting or seeding to provide the necessary nutrients for the initial growth of the crops. This helps to kick-start their development and establish a strong root system.
2. Side-Dressing Application

Side-dressing refers to the practice of applying fertilizer along the rows of growing plants. For crops that require additional nitrogen during their growing season, such as corn or wheat, side-dressing with ammonium sulphate can be done when the plants are at a certain stage of growth. This ensures that the plants receive a timely supply of nitrogen to support their growth and development.
3. Top-Dressing Application
Top-dressing involves applying the fertilizer on the soil surface after the crops have emerged. This method is commonly used for crops like vegetables or fruits that need a continuous supply of nutrients throughout their growth cycle. Ammonium sulphate can be top-dressed periodically during the growing season to provide a steady source of nitrogen.
4. Split Application
In some cases, it may be beneficial to split the application of ammonium sulphate fertilizer into multiple doses. This can help prevent nutrient leaching and ensure a steady supply of nitrogen to the plants. Split application is often done by applying a portion of the fertilizer at pre-planting or pre-seeding and the remaining amount at a later stage of growth.
It is important to note that the exact timing and rate of application may vary depending on specific crop requirements, soil conditions, and local recommendations. Therefore, it is always recommended to consult with agricultural experts or refer to soil test results for precise fertilizer application recommendations.
Ammonium Sulphate Application Timing

Timing is crucial when it comes to applying ammonium sulphate fertilizer. The right time to apply this fertilizer depends on several factors including the crop you are fertilizing, soil conditions, and climate. Here are some general guidelines for the application timing of ammonium sulphate:
Pre-planting
If you are planning to use ammonium sulphate as a pre-planting fertilizer, it is best to apply it a few weeks before planting. This will give the fertilizer enough time to break down and release the nutrients into the soil, making them available for the plants when they are ready to grow.
Top-dressing

For established crops, top-dressing with ammonium sulphate can be done during the growing season. The exact timing will depend on the specific crop and growth stage. Generally, it is recommended to apply the fertilizer when the plants are actively growing and in need of additional nutrients.
Split Applications
In some cases, it may be beneficial to split the application of ammonium sulphate into multiple doses. This can help provide a steady supply of nutrients to the plants throughout the growing season. Split applications are particularly useful for crops with a long growing season or high nutrient requirements.
Soil Testing
It is important to conduct regular soil testing to determine the nutrient levels in your soil. This will help you determine the appropriate timing and application rate of ammonium sulphate fertilizer. Soil testing can also help identify any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances that need to be corrected.
Remember, timing is just one aspect of proper fertilizer application. It is also important to take into consideration the crop’s nutrient requirements, soil conditions, and other factors that may affect the effectiveness of the fertilizer. Consulting with a local agricultural expert or soil specialist can provide valuable guidance for optimizing the timing and application of ammonium sulphate fertilizer.
Ammonium Sulphate Application Rates and Methods

Ammonium sulphate is a versatile fertilizer that can be applied to various crops and soil types. The application rate and method of this fertilizer depend on several factors, including the crop type, soil condition, and nutrient requirements.
Application Rates
The recommended ammonium sulphate application rates typically range from 50 to 100 kg per hectare, depending on the specific crop and soil conditions. It is important to consider the current nutrient levels in the soil and the crop’s nutrient requirements to determine the appropriate application rate.
Soil testing is crucial in determining the nutrient content and pH level of the soil. This information helps in determining the appropriate dosage of ammonium sulphate to achieve optimal results.
Application Methods
There are several application methods for ammonium sulphate:
- Broadcasting: This method involves spreading the ammonium sulphate evenly over the entire field using a mechanical spreader or by hand. It is suitable for crops that have wide row spacing or are grown as a cover crop.
- Side-dressing: In this method, the ammonium sulphate is applied in bands or rows alongside the plants. It is commonly used for row crops such as corn, cotton, and vegetables.
- Fertigation: Fertigation involves applying the fertilizer through an irrigation system. Ammonium sulphate can be dissolved in water and applied directly to the soil, providing a uniform distribution of nutrients.
- Foliar application: This method involves spraying a dilute solution of ammonium sulphate directly onto the leaves of the plant. It is commonly used for crops that require quick nutrient uptake or have nutrient deficiencies.
It is important to follow the recommended application method for each specific crop and consult with agronomists or fertilizer specialists to ensure proper application and avoid over-application, which can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution.
Timing of Application
The timing of ammonium sulphate application depends on the specific crop’s growth stage and nutrient requirements. Generally, it is advisable to apply the fertilizer before or during the early growth stages to meet the crop’s nutrient demands.
For annual crops, the first application is typically made at planting or before seed germination. Additional applications may be required during the growing season, especially for crops with high nutrient demands.
Perennial crops such as orchards or vineyards may require annual or biennial applications during the dormant season or before active growth resumes.
Overall, the correct timing, application rate, and method of ammonium sulphate fertilizer application are crucial for maximizing crop yields and maintaining soil fertility. Consult with local agricultural experts and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the best results.
“Question-Answer”
What is ammonium sulphate?
Ammonium sulphate is a type of fertilizer that contains nitrogen and sulphur in a form that is readily available for plants to absorb and use for their growth.
How does ammonium sulphate help plants?
Ammonium sulphate provides plants with a source of nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for their growth and development. It also provides sulphur, which is needed for the production of certain proteins and enzymes in plants. In addition, ammonium sulphate helps to lower the pH of alkaline soils, making it easier for plants to absorb other nutrients from the soil.
When should I apply ammonium sulphate?
Ammonium sulphate can be applied to plants at various stages of their growth, depending on their specific nutrient needs. It is commonly used as a side dressing or top dressing for crops such as corn, wheat, and soybeans during their early growth stages. It can also be applied as a pre-planting fertilizer or as a maintenance fertilizer for established plants.
How should I apply ammonium sulphate?
Ammonium sulphate can be applied to the soil either by broadcasting it evenly over the entire area or by banding it near the roots of the plants. It should be applied at the recommended rate for the specific crop and soil conditions. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and methods.
What are the benefits of using ammonium sulphate as a fertilizer?
Some benefits of using ammonium sulphate as a fertilizer include its high nitrogen content, its ability to provide readily available nitrogen to plants, its relatively low cost compared to other nitrogen fertilizers, and its ability to lower pH in alkaline soils. It is also a non-volatile source of nitrogen, meaning it does not easily evaporate into the air, reducing the risk of nitrogen loss.
Are there any precautions or potential drawbacks when using ammonium sulphate?
While ammonium sulphate can be an effective fertilizer, there are some precautions and potential drawbacks to consider. It is important to avoid over-application, as excessive nitrogen can harm plants and contribute to water pollution. It should not be used on crops that are sensitive to high levels of sulphur. In addition, it is recommended to wear appropriate protective gear when handling ammonium sulphate, as it can be irritating to the skin and eyes.







