- Tips for Preventing Diseases in Seedlings
- 1. Start with Quality Seeds
- 2. Clean and Disinfect Containers
- 3. Use Sterilized Seed Starting Mix
- 4. Provide Proper Drainage
- 5. Water Wisely
- 6. Avoid Overcrowding
- 7. Practice Crop Rotation
- 8. Monitor for Symptoms
- 9. Remove Infected Plants
- 10. Provide Proper Ventilation
- Essential Preparations for Disease Prevention
- 1. Clean and disinfect equipment
- 2. Choose disease-resistant seed varieties
- 3. Use sterilized soil and growing media
- 4. Practice proper sanitation
- 5. Provide adequate spacing
- 6. Monitor and control environmental conditions
- 7. Avoid cross-contamination
- 8. Implement crop rotation
- 9. Apply preventive treatments
- Choosing Healthy Seeds
- 1. Buy from reputable sources
- 2. Check for certification
- 3. Examine the packaging
- 4. Check the expiration date
- 5. Look for seeds with a good germination rate
- 6. Consider disease-resistant varieties
- Proper Seedbed Preparation
- Implementing Sterilization Techniques
- 1. Clean Equipment and Tools Regularly
- 2. Use Sterilized Soil and Compost
- 3. Disinfect Seed Starting Trays
- 4. Practice Crop Rotation
- Applying Adequate Drainage Methods
- 1. Using Well-Draining Soil
- 2. Providing Proper Watering Techniques
- 3. Creating Adequate Drainage Holes
- 4. Using Raised Beds or Containers with Drainage Systems
- 5. Avoiding Overcrowding
- 6. Regularly Inspecting and Cleaning Containers
- Using Disease-Resistant Varieties
- Benefits of using disease-resistant varieties
- Choosing disease-resistant varieties
- Rotating crops and resistant varieties
- Conclusion
- Monitoring and Removing Infected Plants
- 1. Regular inspection
- 2. Record keeping
- 3. Isolation
- 4. Removal of infected plants
- 5. Sanitization
- Maintaining Proper Watering Practices
- Implementing Crop Rotation
- Benefits of Crop Rotation
- Implementing Crop Rotation
- “Question-Answer”
- What are some common diseases that affect seedlings?
- How can I prevent damping-off in seedlings?
- What are some natural methods for preventing diseases in seedlings?
- What are some signs that seedlings may be infected with a disease?
- Can seedlings be saved if they are infected with a disease?
- How can I prevent the spread of diseases from infected seedlings?
- “Video” 10 Organic Ways to Control Pests in the Garden
Seedlings are delicate and vulnerable to various diseases, which can greatly impact their growth and development. To ensure healthy and robust seedlings, it is crucial to take essential precautions to prevent diseases from taking hold. In this article, we will share some valuable tips and preparations that you can implement to minimize the risk of diseases in your seedlings.
Clean and Sterilize: Before you even start sowing your seeds, it is important to clean and sterilize all your gardening tools, trays, and containers. This will help eliminate any pathogens or disease-causing organisms that may be present. Soak your tools in a solution of bleach and water, or use a commercial sterilizing agent, to ensure they are free from harmful contaminants.
High-Quality Seeds: Use high-quality seeds that are disease-resistant, if possible. These varieties are bred to withstand common diseases and have a better chance of producing healthy seedlings. Additionally, make sure to purchase seeds from a reputable source to ensure their quality and authenticity.
Air Circulation: Good air circulation is essential for preventing diseases in seedlings. Proper ventilation helps to control humidity levels and prevents the growth of fungal spores that lead to diseases like damping off. Place fans or open windows to maintain a gentle airflow around your seedlings.
Hygiene Practices: Practicing good hygiene is crucial when handling seedlings. Always wash your hands thoroughly before and after working with seedlings to prevent the spread of diseases. Ensure that your working area is clean and sanitized, and avoid over-crowding seedlings, as this can lead to increased moisture and disease development.
Proper Watering: Overwatering can create a damp environment that encourages the growth of fungal diseases. Water seedlings properly, allowing the soil to dry out between watering sessions. Avoid wetting the leaves, as this can also create a favorable environment for diseases to thrive.
Quarantine: If you notice any signs of disease in your seedlings, remove them immediately to prevent the spread of the disease to healthy plants. Quarantine the affected seedlings and treat them separately to avoid contaminating the rest of your garden or seedlings.
By implementing these essential preparations and following these tips, you can significantly reduce the risks of diseases in your seedlings. Taking proactive measures will not only promote the growth of healthy seedlings but also contribute to the overall success of your garden.
Tips for Preventing Diseases in Seedlings
When starting seedlings, it’s important to take necessary precautions to prevent diseases that could harm your plants. Here are some essential preparations for disease prevention:
1. Start with Quality Seeds
Using high-quality seeds from reputable sources is the first step in preventing diseases in seedlings. Look for seeds that are certified disease-free and have been tested for germination rates.
2. Clean and Disinfect Containers
Before planting your seeds, make sure to clean and disinfect your planting containers. Use a mild detergent and warm water to wash away any dirt or debris. Then, soak the containers in a solution of 1 part bleach to 9 parts water for at least 10 minutes to disinfect them.
3. Use Sterilized Seed Starting Mix
Using sterilized seed starting mix can help prevent the introduction of diseases into your seedlings. Look for a mix that is labeled as sterilized or pasteurized to ensure it is free from harmful pathogens.
4. Provide Proper Drainage
Good drainage is essential for preventing soil-borne diseases in seedlings. Make sure your containers have drainage holes to allow excess water to escape and prevent waterlogging.
5. Water Wisely
Overwatering can create a favorable environment for disease-causing fungi and bacteria. Water your seedlings from the bottom or use a watering can with a fine rose to avoid splashing water onto the leaves.
6. Avoid Overcrowding
Overcrowding seedlings can lead to poor air circulation and create a humid environment, which is ideal for disease development. Thin out seedlings as they grow to provide adequate space between each plant.
7. Practice Crop Rotation
Rotate your crops every year to prevent the buildup of disease-causing pathogens in the soil. Avoid planting seedlings from the same family in the same location year after year.
8. Monitor for Symptoms
Regularly inspect your seedlings for any signs of diseases, such as wilting, yellowing leaves, or unusual spots. If you notice any symptoms, take immediate action to prevent the spread of the disease.
9. Remove Infected Plants
If any of your seedlings become infected with a disease, promptly remove them to prevent the spread of the pathogens to healthy plants. Dispose of the infected plants in a sealed bag or burn them to eliminate the risk of further contamination.
10. Provide Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial for reducing humidity and preventing the development of diseases in seedlings. Place your seedlings in a well-ventilated area or use fans to improve air circulation.
By following these tips and taking necessary precautions, you can greatly reduce the risk of diseases in your seedlings and ensure healthy plant growth.
Essential Preparations for Disease Prevention
Preventing diseases in seedlings starts with taking the necessary precautions and implementing proper preparations. By following these essential steps, you can greatly reduce the risk of diseases affecting your seedlings and ensure healthy growth.
1. Clean and disinfect equipment
Before starting any seedling activity, it is crucial to clean and disinfect your equipment properly. This includes tools, trays, pots, and any other items that come into contact with the seedlings. Cleaning removes any dirt or debris, while disinfection kills any potential pathogens. Use a mild bleach solution or a commercial disinfectant to ensure thorough cleaning.
2. Choose disease-resistant seed varieties
When selecting seeds for your seedlings, opt for disease-resistant varieties whenever possible. These seeds have been bred to withstand common diseases and are less likely to be affected. Consult with local gardening experts or seed catalogs to identify the best disease-resistant options for your region and crop type.
3. Use sterilized soil and growing media
The soil and growing media you use for seedling cultivation should be sterilized to eliminate any potential disease-causing organisms. Sterilization can be done through heat treatment or by using commercially available sterilized soil or potting mixes. Avoid using soil from your garden or reusing old potting mixes, as they may contain pathogens.
4. Practice proper sanitation
Maintaining a clean and sanitized growing area is vital for disease prevention. Remove any dead or diseased plant materials promptly. Keep the surrounding area free from weeds and debris that could harbor diseases. Additionally, ensure you wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling the seedlings to avoid spreading pathogens.
5. Provide adequate spacing
Overcrowded seedlings are more susceptible to diseases due to reduced airflow and increased humidity. Provide adequate spacing between the seedlings to allow for proper ventilation. This will help prevent the spread of fungal and bacterial diseases that thrive in moist conditions.
6. Monitor and control environmental conditions
Regularly monitor and control the environmental conditions in your seedling area. Proper air circulation, temperature, and humidity levels are vital for disease prevention. Avoid overwatering, which can create a favorable environment for diseases to develop. Use fans or ventilation systems to ensure adequate airflow.
7. Avoid cross-contamination
Prevent cross-contamination between healthy and infected plants by carefully cleaning and disinfecting your tools and equipment between uses. Avoid touching healthy plants after handling diseased seedlings without properly washing your hands or sanitizing your gloves. This will help prevent the spread of diseases to healthy seedlings.
8. Implement crop rotation
If you plan to grow seedlings in the same location year after year, implement crop rotation to reduce the risk of disease buildup in the soil. Planting different crops or rotating between unrelated plant families helps disrupt disease cycles and prevents pathogens from establishing themselves.
9. Apply preventive treatments
In addition to the above precautions, consider applying preventive treatments such as biofungicides or beneficial microbes to the seedlings. These can help increase the plant’s natural defense mechanisms and protect against potential diseases. Consult with local gardening experts or specialists to identify suitable preventive treatments for your specific crop and growing conditions.
By implementing these essential preparations for disease prevention, you can give your seedlings a better chance of thriving and avoid potential disease setbacks.
Choosing Healthy Seeds
When starting seedlings, one of the most important factors for disease prevention is using healthy seeds. Here are some tips to help you choose the best seeds for your seedlings:
1. Buy from reputable sources
Purchasing seeds from reliable and reputable sources is an essential step in ensuring their quality. Look for reputable seed companies or nurseries that specialize in selling high-quality seeds. These companies often have strict quality control measures in place to ensure that their seeds are disease-free.
2. Check for certification
Look for certified organic or certified disease-free seeds. These certifications indicate that the seeds have been tested and meet specific standards for quality. You can usually find this information on the seed packaging or on the company’s website.
3. Examine the packaging
Inspect the seed packaging for any signs of damage or tampering. Avoid seeds that have opened or torn packaging, as this may indicate poor handling or storage conditions, increasing the risk of disease transmission.
4. Check the expiration date
Seeds have a shelf life, and using expired seeds can reduce the germination rate and increase the risk of disease. Always check the expiration date on the seed packet or container before purchasing or using the seeds.
5. Look for seeds with a good germination rate
Some seed packets include information about the germination rate. Choosing seeds with a high germination rate increases the chance of successful seedling growth and reduces the risk of diseases caused by weak or slow-growing plants.
6. Consider disease-resistant varieties
Some seed varieties are naturally resistant to certain diseases. When choosing seeds, consider selecting varieties that are known for their resistance to common seedling diseases in your area. This can help reduce the risk of disease outbreaks and increase the overall health of your seedlings.
Remember, starting with healthy seeds is a crucial step in preventing diseases in your seedlings. By following these tips, you can increase your chances of successful germination and produce stronger, disease-resistant plants.
Proper Seedbed Preparation
Proper seedbed preparation is essential for preventing diseases in seedlings. A well-prepared seedbed creates an optimal environment for seed germination and growth, while minimizing the risk of disease introduction and spread. Here are some important tips for preparing the seedbed:
- Clear the area: Start by removing any existing vegetation or debris from the planting area. This will help eliminate potential sources of disease and provide a clean slate for the new seedlings.
- Break up the soil: Use a garden fork or a tiller to break up the soil and create a loose, well-aerated seedbed. This will ensure that the roots can penetrate easily and nutrients are more accessible to the emerging seedlings.
- Improve soil drainage: If the soil in the planting area is heavy or poorly drained, consider adding organic matter or sand to improve drainage. Excess moisture can create favorable conditions for diseases to develop.
- Amend the soil: Test the soil pH and nutrient levels to determine if any amendments are needed. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can help improve soil fertility and create a favorable environment for seedling growth.
- Level the seedbed: After preparing the soil, use a rake or a leveling tool to create a smooth and even surface. This will facilitate proper seed placement and ensure uniform growth of the seedlings.
By following these guidelines for proper seedbed preparation, you can greatly reduce the risk of seedling diseases and give your plants the best start possible.
Implementing Sterilization Techniques
Sterilization is an essential step in preventing diseases in seedlings. By eliminating harmful pathogens and microorganisms, you can ensure the health and wellness of your plants. Here are some important techniques to implement:
1. Clean Equipment and Tools Regularly
Before starting any seeding or transplanting process, it is crucial to clean all your gardening tools and equipment. This includes pots, trays, watering cans, and any other supplies you use. Use a mild bleach solution or a commercial disinfectant to thoroughly clean and sterilize these items. Rinse them well with water and allow them to air dry before using them.
2. Use Sterilized Soil and Compost
The soil and compost you use for seedlings should be free from pathogens and pests. To ensure this, it is recommended to sterilize the soil and compost before use. You can do this by baking the soil in the oven at a temperature of 180°F (82°C) for 30 minutes. This will kill any potential pathogens and weed seeds. Make sure to let the soil cool down before using it for seeding.
3. Disinfect Seed Starting Trays
Seed starting trays are prone to harboring pathogens and diseases. To prevent this, disinfect the trays before each use. Soak them in a solution of one part bleach to nine parts water for at least 10 minutes. Rinse them thoroughly with clean water and allow them to air dry before adding the soil and seeds.
4. Practice Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an effective technique for preventing the buildup of soil-borne diseases. By rotating the location of your crops each year, you can disrupt the life cycle of pathogens and reduce their impact on your plants. This technique is especially important if you are growing the same type of seedlings year after year.
By implementing these sterilization techniques, you can greatly reduce the risk of diseases affecting your seedlings. This will result in healthier plants and a higher success rate in your gardening endeavors. Remember to regularly clean and disinfect your tools and equipment, use sterilized soil and compost, disinfect seed starting trays, and practice crop rotation to ensure optimal plant health.
Applying Adequate Drainage Methods
Proper drainage is essential for preventing diseases in seedlings. Excess water can lead to waterlogged soil, which creates a perfect breeding ground for fungal and bacterial pathogens. By implementing adequate drainage methods, you can ensure the health and vitality of your seedlings.
1. Using Well-Draining Soil
Start by using well-draining soil mixtures that allow excess water to move away from the roots of the seedlings. Consider adding organic matter such as compost or perlite to improve soil structure and drainage. Avoid compacted soils, as they tend to retain water and promote disease development.
2. Providing Proper Watering Techniques

Watering seedlings correctly is vital for preventing diseases. Overwatering can lead to waterlogged soil, while underwatering can result in stressed and weak seedlings. Water the seedlings when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Use a technique that allows for slow, deep watering, such as bottom watering or using a soaker hose.
3. Creating Adequate Drainage Holes
Ensure that your seedling containers have sufficient drainage holes at the bottom. These holes allow excess water to escape and prevent the accumulation of water in the container. If necessary, you can drill additional holes to improve drainage.
4. Using Raised Beds or Containers with Drainage Systems
Raised beds and containers with built-in drainage systems can provide excellent drainage for seedlings. These options elevate the seedlings above the ground, allowing water to flow away from the roots. Additionally, containers with drainage systems prevent water from pooling, reducing the risk of disease.
5. Avoiding Overcrowding

Overcrowding seedlings can lead to poor airflow and high humidity, creating a favorable environment for diseases. Space out your seedlings adequately to allow for proper air circulation and reduce moisture buildup. This will help prevent the spread of pathogens and keep your seedlings healthy.
6. Regularly Inspecting and Cleaning Containers
Frequent inspections and cleaning of seedling containers are crucial for disease prevention. Remove any dead plant matter or debris from the containers, as they can harbor disease-causing organisms. Sanitize the containers between seedlings to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
By applying these adequate drainage methods, you can significantly reduce the risk of diseases in your seedlings. Remember to monitor your seedlings regularly for signs of disease and take prompt action if any issues arise.
Using Disease-Resistant Varieties
One of the most effective ways to prevent diseases in seedlings is by choosing disease-resistant varieties. These varieties have been specifically bred to be resistant to certain diseases, making them less likely to become infected.
Benefits of using disease-resistant varieties
- Reduced disease risk: Disease-resistant varieties have built-in resistance mechanisms that make them less susceptible to infection. This significantly reduces the risk of disease outbreaks in your seedlings.
- Decreased need for chemical treatments: By planting disease-resistant varieties, you can reduce the need for chemical treatments and pesticides. This not only saves you money but also promotes environmentally friendly gardening practices.
- Better overall plant health: Disease-resistant varieties are generally healthier and more vigorous than susceptible varieties. They are better equipped to withstand diseases and other environmental stresses, resulting in stronger and more productive plants.
Choosing disease-resistant varieties
When selecting disease-resistant varieties for your seedlings, it’s essential to consider the specific diseases that pose a threat in your area. Consult with local gardening experts and extension offices to identify the prevalent diseases and recommended resistant varieties.
Look for seed packets or plant labels that indicate disease resistance. The labeling usually includes abbreviations or codes for specific diseases. For example, “VFN” may refer to resistance against Verticillium wilt, Fusarium wilt, and nematodes.
Rotating crops and resistant varieties
Rotating your crops and planting different disease-resistant varieties each year can help prevent the buildup of pathogens in the soil. This practice disrupts the life cycle of diseases and reduces their ability to spread and persist.
Keep a record of your crops and their disease resistance traits to ensure proper rotation. Proper crop rotation can help maintain soil health and minimize the risk of disease outbreaks in your seedlings.
Conclusion
Using disease-resistant varieties is an effective strategy for preventing diseases in seedlings. By selecting and planting varieties that have built-in resistance, you can significantly reduce the risk of disease outbreaks and promote overall plant health. Remember to consult local experts and consider crop rotation to maximize the benefits of using disease-resistant varieties.
Monitoring and Removing Infected Plants
Monitoring your seedlings regularly is an essential step in preventing the spread of diseases. By observing your plants closely, you can identify any signs of infection early on and take immediate action. Here are some tips for effectively monitoring your seedlings:
1. Regular inspection
- Examine your plants daily or at least every few days.
- Check for any abnormal growth, spots, discoloration, wilting, or other signs of disease.
- Focus on the undersides of leaves, stems, and fruits, as diseases often start in these hidden areas.
2. Record keeping
- Maintain a record of your observations, including the date, location, and specific symptoms observed.
- This information can help you track disease patterns and make informed decisions for disease prevention in future seasons.
3. Isolation
- If you notice one or more infected plants, isolate them from healthy ones immediately.
- Place the infected plants in a separate area or container where they won’t come into contact with the healthy plants.
- This will prevent the spread of pathogens to the rest of your seedlings.
4. Removal of infected plants
- Once you have identified infected plants, remove and destroy them as soon as possible.
- Do not compost infected plants, as the pathogens can survive and spread.
- You can either bag the plants and dispose of them in the trash or burn them to eliminate the pathogens.
5. Sanitization
- After removing infected plants, thoroughly clean your hands, tools, and any surfaces that came into contact with the infected plants.
- Use a disinfectant or a solution of water and bleach to sanitize your equipment.
- This will help prevent the spread of pathogens to other plants.
By diligently monitoring your seedlings and taking prompt action, you can effectively prevent the spread of diseases and ensure the health and vitality of your plants.
Maintaining Proper Watering Practices
Proper watering is essential for the health and vitality of seedlings. Overwatering or underwatering can both lead to stress and disease development. Here are some tips for maintaining proper watering practices:
- Observe the seedlings: Monitor the seedlings closely and look for signs of dehydration or overhydration. Wilting, yellowing leaves, or waterlogged soil are indicators that adjustments need to be made.
- Watering frequency: Determine the watering frequency based on the specific needs of the seedlings. Factors such as humidity, temperature, and type of growing medium can influence how often seedlings require watering.
- Watering method: Use a gentle watering method to avoid damaging the delicate seedlings. Pouring water directly onto the soil or using a spray bottle are good options. Avoid using a hose or a high-pressure watering system that may disturb the seedlings.
- Watering technique: Apply water evenly throughout the growing medium, ensuring that it reaches the root zone. Avoid applying too much water at once, as it can lead to water accumulation and the development of diseases.
- Drainage: Ensure that the containers or trays used for seedlings have proper drainage holes to allow excess water to escape. Standing water can quickly lead to root rot and other diseases.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent watering schedule to provide a stable environment for the seedlings. Avoid fluctuations in soil moisture, as it can stress the seedlings and make them more susceptible to diseases.
By maintaining proper watering practices, you can help prevent the development of diseases in seedlings and promote their healthy growth.
Implementing Crop Rotation
Implementing crop rotation is an important step in preventing diseases in seedlings. By rotating different crops in your garden, you can disrupt the life cycle of diseases and pests, reducing their populations and preventing the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
Benefits of Crop Rotation
- Disease control: Crop rotation can help control the spread of diseases by interrupting the cycle of pathogens. Different crops have different susceptibility to diseases, so rotating crops can reduce the risk of infection.
- Pest management: Crop rotation can also help manage pests. Some pests are specific to certain crops, so by rotating crops, you can help break their life cycles and reduce their populations.
- Soil health: Different crops have different nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, you can prevent depletion of specific nutrients in the soil and improve overall soil health.
- Weed control: Crop rotation can also help control weeds. Different crops may require different weed management strategies, and by rotating crops, you can disrupt the growth cycle of weeds and reduce their populations.
Implementing Crop Rotation
Here are some tips for implementing crop rotation in your garden:
- Plan your rotation: Before planting, create a rotation schedule that includes a variety of crops from different plant families. Rotate crops every year or every few years to maximize the benefits.
- Diversify your crops: Choose a variety of crops with different growth habits, root structures, and nutrient requirements. This will increase the effectiveness of crop rotation in preventing diseases and improving soil health.
- Keep records: Keep track of the crops you have planted in each bed or section of your garden. This will help you remember which crops were grown in each area, making it easier to plan your rotation schedule in future seasons.
- Manage residues: Remove and dispose of crop residues properly to prevent the spread of diseases and pests. Do not add infected plant material to your compost pile.
- Consider cover crops: Include cover crops in your rotation schedule. Cover crops can help improve soil fertility and structure, control weeds, and break pest and disease cycles.
By implementing crop rotation, you can create a more resilient and disease-resistant garden, leading to healthier seedlings and better overall plant growth.
“Question-Answer”
What are some common diseases that affect seedlings?
Common diseases that affect seedlings include damping-off, powdery mildew, and various fungal and bacterial infections.
How can I prevent damping-off in seedlings?
To prevent damping-off in seedlings, ensure proper air circulation, use sterile soil or growing medium, water seedlings from the bottom, and avoid overcrowding.
What are some natural methods for preventing diseases in seedlings?
Some natural methods for preventing diseases in seedlings include using compost or organic matter to improve soil health, practicing crop rotation, and using beneficial insects or plants to control pests.
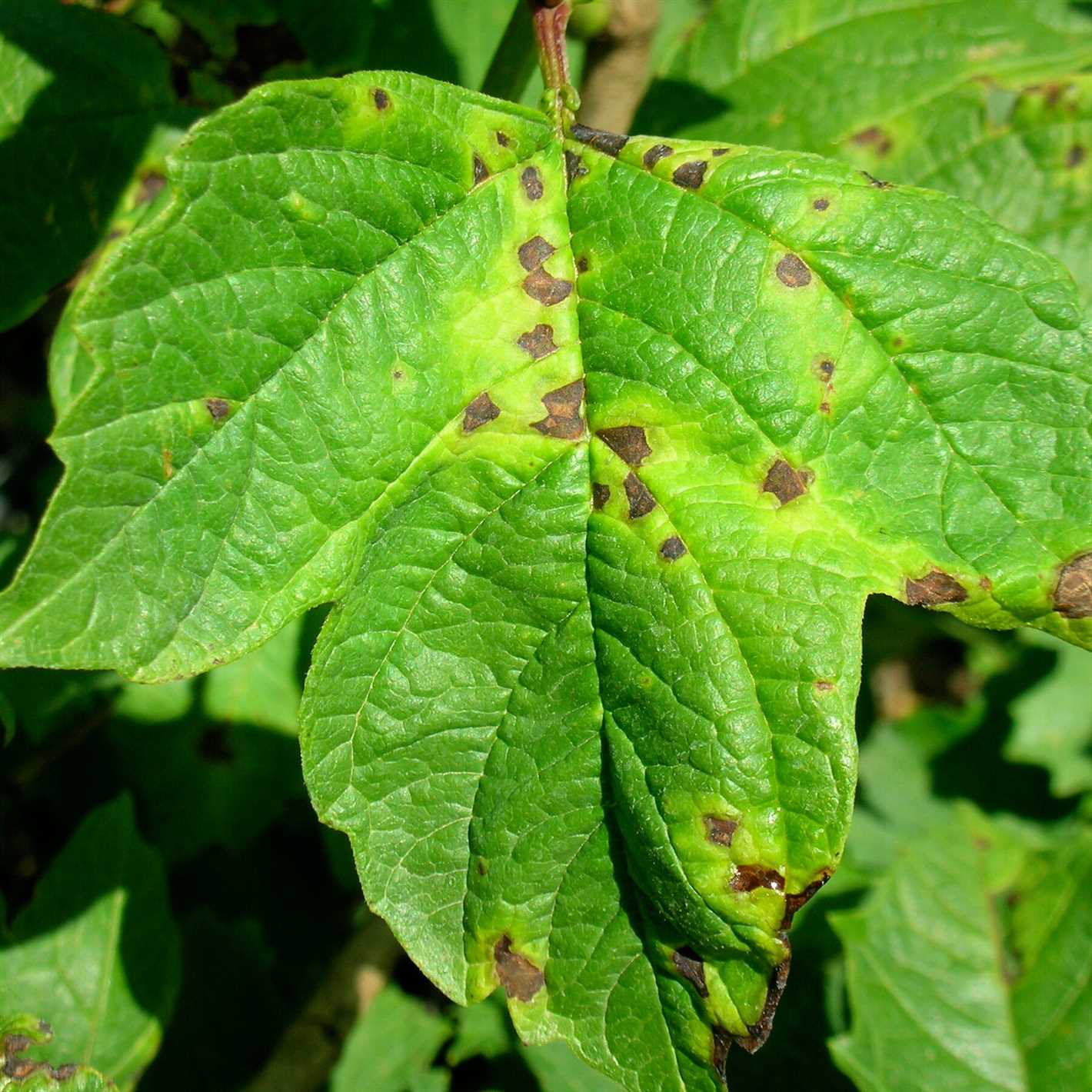
What are some signs that seedlings may be infected with a disease?
Signs that seedlings may be infected with a disease include stunted growth, yellowing or wilting leaves, spots or lesions on leaves or stems, and a general decline in plant health.
Can seedlings be saved if they are infected with a disease?
It is possible to save infected seedlings if the disease is caught early and appropriate steps are taken. This may include removing and disposing of infected plants, treating the remaining seedlings with fungicides or other treatments, and providing optimal growing conditions.
How can I prevent the spread of diseases from infected seedlings?
To prevent the spread of diseases from infected seedlings, avoid using contaminated tools or equipment, wash hands thoroughly after handling infected plants, and quarantine or remove infected seedlings from healthy plants.







