- Understanding F1 Labelling
- What Does F1 Mean on a Seed Packet?
- The Meaning of F1
- Advantages of F1 Hybrid Plants
- Understanding F1 Labels
- Decoding the Meaning of F1 in Seed Labelling
- What does F1 stand for?
- What are the characteristics of F1 plants?
- How are F1 plants bred?
- Why are F1 plants popular?
- Are there any drawbacks to F1 plants?
- Conclusion
- Benefits of F1 Hybrid Seeds
- 1. Vigorous Growth
- 2. Disease and Pest Resistance
- 3. Improved Quality
- 4. Consistency
- 5. Early Maturity
- 6. Hybrid Vigor
- Factors to Consider When Choosing F1 Hybrid Seeds
- Understanding the Genetic Makeup of F1 Hybrid Seeds
- Genetic Characteristics of F1 Hybrid Seeds
- Benefits of F1 Hybrid Seeds
- Understanding F1 Hybrid Seed Labels
- Conclusion
- How to Properly Use F1 Hybrid Seeds in Your Garden
- 1. Understand the Basics
- 2. Choose the Right Seeds
- 3. Follow Sowing Instructions
- 4. Use Good Quality Soil
- 5. Plant at the Right Depth
- 6. Provide Adequate Water and Sunlight
- 7. Monitor for Pests and Diseases
- 8. Harvest and Save Seeds
- Common Misconceptions About F1 Hybrid Seeds
- 1. F1 hybrid seeds are genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
- 2. F1 hybrid seeds are sterile
- 3. F1 hybrid seeds are less nutritious
- 4. F1 hybrid seeds are more expensive
- 5. F1 hybrid seeds are unnatural
- “Question-Answer”
- What is F1 labelling on a seed packet?
- What does F1 stand for?
- Why is F1 labelling important?
- What does F1 hybrid mean?
- What are the advantages of growing F1 hybrid plants?
- “Video” How To Grow Morning Glory From Seed (FULL INFORMATION)
When purchasing seeds for your garden, you may come across the term “F1 labelling.” But what does it mean? F1 stands for “first filial generation” and refers to the result of crossbreeding two different parent plants. It is a common practice in the seed industry to create new and improved varieties by breeding plants with desirable traits.
The F1 labelling on a seed packet signifies that the seeds inside are from the first-generation offspring of a controlled cross between two distinct parent plants. This controlled cross ensures that the resulting plants have specific characteristics, such as disease resistance, improved yield, or better flavor. The F1 labelling is an assurance of uniformity and predictability in the plants grown from these seeds.
When a plant breeder performs a controlled cross, they carefully select the parent plants based on their desired traits and characteristics. By crossbreeding these two plants, they aim to combine the best qualities of both parents into their offspring. The F1 generation usually exhibits traits that are superior to those of the parent plants, such as increased vigor, uniformity, or adaptability.
It’s important to note that F1 hybrid seeds are different from open-pollinated seeds. Open-pollinated seeds result from natural pollination, where plants are pollinated by wind, insects, or other means. This can lead to genetic variation, resulting in plants with different characteristics. In contrast, F1 hybrid seeds are bred for consistency, as they are derived from controlled crosses that produce offspring with predictable traits.
Understanding F1 Labelling
When you pick up a seed packet, you will often see the term “F1” on it. This label might not mean much to you at first, but it has an important significance in the world of gardening and plant breeding.
What does F1 mean?
The term “F1” stands for the first filial generation. In plant breeding, the first filial generation is the result of cross-pollinating two parent plants with distinct traits. F1 hybrids are created to obtain desirable characteristics from both parent plants, such as disease resistance, high yield, or improved taste.
Why are F1 hybrids popular?
F1 hybrids have gained popularity among gardeners and farmers for several reasons:
- Uniformity: F1 hybrids tend to be very consistent in their growth habits, producing plants that are similar in size, shape, and color.
- Vigor: F1 hybrids often exhibit vigorous growth, resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
- Disease resistance: F1 hybrids are often bred for specific disease resistance, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
- Improved traits: F1 hybrids can have improved taste, shelf life, or other desirable characteristics, making them more attractive to consumers.
How are F1 hybrids produced?
Producing F1 hybrids involves controlled pollination. Breeders carefully select the parent plants and manually transfer pollen from the male parent’s flower to the female parent’s flower. This ensures that the desired traits from both parents are passed on to the offspring.
How to interpret F1 labelling on a seed packet?
When you see “F1” on a seed packet, it indicates that the seeds inside have been produced from a controlled cross between two genetically distinct parent plants. This means that the resulting plants should exhibit the desired traits associated with the F1 hybrid, ensuring a higher chance of success in the garden.
It’s important to note that F1 hybrids are usually designated by a specific name or code, which helps in identifying the characteristics they possess. This information is often provided on the seed packet or in accompanying catalogues.
In conclusion, understanding F1 labelling is essential for gardeners and farmers who want to make informed choices when selecting seeds. F1 hybrids offer the benefits of uniformity, vigor, disease resistance, and improved traits, making them an attractive option for successful gardening and farming.
What Does F1 Mean on a Seed Packet?

When you see the term “F1” on a seed packet, it refers to the first generation offspring resulting from a controlled cross between two different parent plants. This term is commonly used in the field of plant breeding and hybridization.
The Meaning of F1
The “F” stands for “filial” in Latin, which means “son” or “daughter.” The number “1” represents the first generation of offspring. Therefore, “F1” represents the first generation resulting from the cross between the parent plants.
Plant breeders carefully select the parent plants to create desired characteristics in the resulting offspring. The goal is to combine the best traits of both parents, resulting in improved quality, yield, disease resistance, or other desirable traits.
Advantages of F1 Hybrid Plants
F1 hybrid plants have several advantages:
- Vigour: F1 hybrids often exhibit increased vigour compared to their parent plants. They tend to be more vigorous in terms of growth, producing larger and healthier plants.
- Uniformity: F1 hybrids also tend to show high uniformity in terms of characteristics such as size, shape, and color. This helps growers predict and plan for consistent results.
- Disease Resistance: Breeders select parent plants with increased resistance to diseases, allowing F1 hybrids to inherit this desirable trait. It helps in reducing the need for pesticides and contributes to better plant health.
- Improved Yield: F1 hybrids are often bred to have higher yield potential, resulting in increased productivity for farmers and gardeners.
Understanding F1 Labels
When you see F1 on a seed packet, it is an indication that the seeds you are purchasing are first-generation hybrid seeds resulting from a controlled cross. It means that the plants grown from these seeds will have a combination of traits from both parent plants, resulting in improved characteristics.
It is worth noting that F1 hybrids are created through controlled breeding processes and cannot be replicated by simply saving and replanting their seeds. The seeds produced by F1 plants will not consistently produce plants with the same desirable traits. If you want to grow F1 hybrid plants, you will need to purchase new seeds for each growing season.
In summary, F1 on a seed packet signifies that the seeds are first-generation hybrids resulting from a controlled cross between two parent plants. These hybrids offer advantages, such as increased vigour, uniformity, disease resistance, and improved yield. If you choose to grow F1 hybrid plants, make sure to purchase fresh seeds each year for consistent results.
Decoding the Meaning of F1 in Seed Labelling
When shopping for seeds for your garden, you may come across the term F1 on the seed packet label. To understand what F1 means, it’s important to decode its meaning.
What does F1 stand for?

F1 stands for the first filial generation, which is the result of crossing two different parent plants. This method is known as hybridization.
What are the characteristics of F1 plants?
F1 plants typically exhibit certain characteristics that make them desirable to gardeners:
- Vigor: F1 plants often display vigorous growth, resulting in healthy and vigorous seedlings.
- Uniformity: F1 plants tend to be uniform in appearance and growth, producing consistent results.
- High yields: F1 plants are bred for increased productivity and are known for producing high yields of fruits, vegetables, or flowers.
- Disease resistance: F1 plants are often bred for increased resistance to common diseases, making them more resilient and easier to grow.
How are F1 plants bred?
F1 plants are created through a controlled breeding process called hybridization. This process involves cross-pollinating two different parent plants with desirable traits to create a new plant with a combination of these traits.
Why are F1 plants popular?
F1 plants have gained popularity among gardeners due to their superior characteristics. The advantages of growing F1 plants include:
- Uniformity: F1 plants produce consistent results, making it easier for gardeners to plan and manage their gardens.
- Vigor and High Yields: F1 plants tend to have vigorous growth and higher productivity, resulting in a bountiful harvest.
- Disease Resistance: F1 plants offer increased resistance to diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and making them a healthier option for both gardeners and the environment.
- Improved Traits: F1 plants are often bred to have improved traits such as improved flavor, color, or size.
Are there any drawbacks to F1 plants?
While F1 plants have many advantages, it’s important to consider some potential drawbacks:
- Higher Cost: F1 seeds are often more expensive than non-hybrid seeds due to the time and effort involved in their production.
- Less Adaptability: F1 plants may be less adaptable to different growing conditions compared to non-hybrid varieties.
- Seed Saving: F1 plants do not produce true-to-type seeds, meaning the seeds saved from F1 plants will not result in plants with the same characteristics as the parent plant.
Conclusion
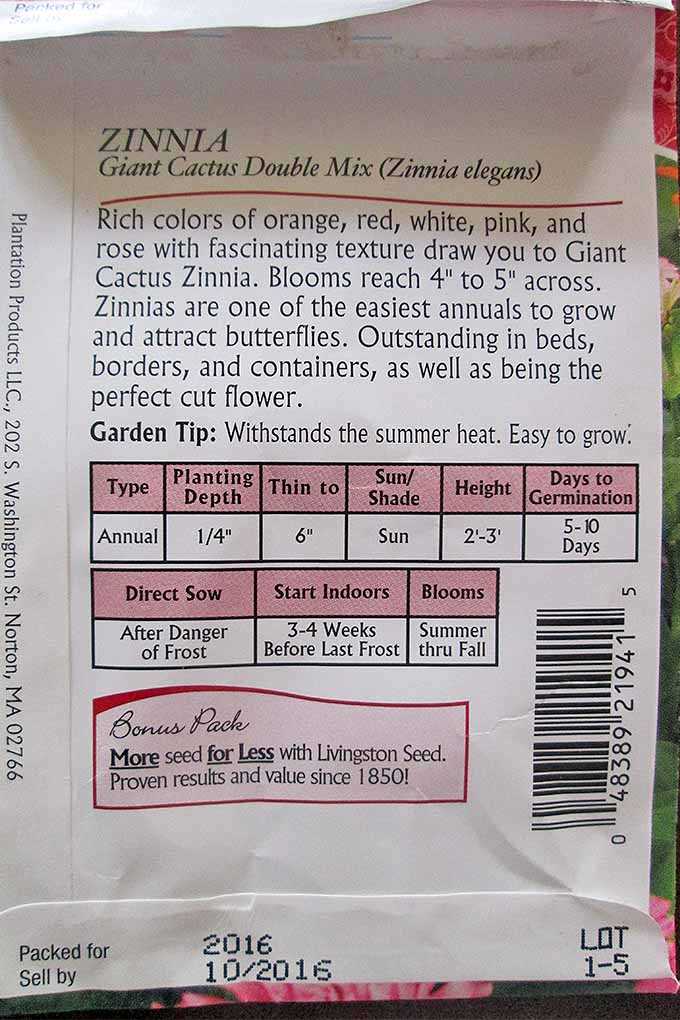

Understanding the meaning of F1 on seed packets can help you make informed decisions when selecting seeds for your garden. F1 plants offer a range of benefits, but it’s important to weigh the advantages against any potential drawbacks before making a choice.
Benefits of F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds offer several advantages over traditional open-pollinated seeds. These benefits make them a popular choice among both home gardeners and commercial farmers:
1. Vigorous Growth
F1 hybrid seeds are the result of a controlled cross between two purebred parent plants. This controlled breeding leads to plants with greater vigor and uniformity. F1 hybrids tend to grow faster, produce more uniform and healthy plants, and have higher yields compared to their open-pollinated counterparts.
2. Disease and Pest Resistance
One of the key advantages of F1 hybrid seeds is their improved resistance to diseases and pests. Through careful selection and breeding, F1 hybrids exhibit enhanced resistance to common diseases and pests that can compromise plant health and reduce yields. This resistance can help reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and fungicides, making F1 hybrids a more sustainable choice.
3. Improved Quality
F1 hybrid seeds often produce fruits and vegetables with superior flavor, texture, and appearance. The controlled cross-breeding process allows breeders to select for desirable traits, such as sweeter fruits, crunchier vegetables, or more vibrant colors. This results in produce that is not only more visually appealing but also more enjoyable to eat.
4. Consistency
With F1 hybrid seeds, you can expect more consistency in plant performance and yield. The offspring of F1 hybrids tend to inherit the best traits from their parents, resulting in more predictable outcomes. This consistency makes F1 hybrids particularly attractive to commercial farmers who rely on uniform crops for efficient harvesting, packaging, and transportation.
5. Early Maturity
F1 hybrid seeds often have a shorter time to maturity compared to open-pollinated seeds. This means that you can expect to harvest your crops earlier, allowing for multiple plantings in a season or extending the growing season in colder climates. Early maturity is especially beneficial for home gardeners who want to enjoy their homegrown produce as soon as possible.
6. Hybrid Vigor
F1 hybrid seeds exhibit hybrid vigor, also known as heterosis. This is the phenomenon where the offspring of two different parent plants display enhanced traits compared to both parents. Hybrid vigor can manifest as increased plant size, improved disease resistance, and higher yields. This makes F1 hybrids a preferred choice for farmers looking to optimize their crop production.
In conclusion, F1 hybrid seeds offer a range of benefits, including vigorous growth, disease and pest resistance, improved quality, consistency, early maturity, and hybrid vigor. These advantages make F1 hybrids a valuable tool for both home gardeners and commercial farmers seeking to maximize their crop yields and produce high-quality, reliable plants and produce.
Factors to Consider When Choosing F1 Hybrid Seeds
- Plant Characteristics: Consider the specific characteristics of the plant you want to grow. Look for F1 hybrid seeds that are known for traits like disease resistance, yield potential, growth habit, and fruit quality. Make sure the seeds will suit your specific growing conditions and preferences.
- Quality and Reputation of the Seed Company: Choose F1 hybrid seeds from reputable seed companies that have a proven track record of producing high-quality seeds. Research the company’s reputation, read customer reviews, and look for any certifications or awards that demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- Availability: Check if the F1 hybrid seeds you are interested in are readily available. Some varieties may be in high demand and sell out quickly, especially if they are popular or have recently been introduced to the market. Ensure that you can easily and reliably purchase the seeds you need.
- Price: Compare prices of F1 hybrid seeds from different sources but remember that the cheapest option may not always be the best. Consider the overall value of the seeds, taking into account the quality, reputation, and availability factors mentioned above.
- Intended Use: Consider the purpose for which you are growing the plants. If you are growing vegetables for personal consumption, choose F1 hybrid seeds that are known for their taste and nutritional value. If you are growing flowers for aesthetic purposes, select seeds that will produce blossoms with desirable colors, shapes, and fragrances.
- Climate and Growing Conditions: Take into account the climate and growing conditions in your area. Look for F1 hybrid seeds that are adapted to your region’s temperature, soil type, and other environmental conditions. This will increase the likelihood of success and maximize your yield.
- Growing Requirements: Consider your own gardening skills and available resources. Choose F1 hybrid seeds that align with your ability to provide proper care, such as watering, fertilizing, and pest control. Some varieties may require more intensive care or specific growing techniques.
- Consider Trial and Error: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different F1 hybrid seeds to find the ones that work best for you. Gardening is a learning process, and what works well in one garden may not work as effectively in another. Keep a record of your experiences and make adjustments as needed.
Understanding the Genetic Makeup of F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds are a popular choice among gardeners and horticulture enthusiasts due to their superior characteristics and performance. These seeds are created by cross-pollinating two different parent plants with desired traits. Understanding the genetic makeup of F1 hybrid seeds can help gardeners make informed decisions when selecting and growing plants.
Genetic Characteristics of F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds are the result of a controlled breeding process where two different parent plants of the same species are cross-pollinated. This process combines the desirable traits of both parent plants and creates offsprings with improved characteristics. The genetic makeup of F1 hybrid seeds is referred to as “heterozygous,” meaning they have two different alleles for each trait.
The first generation resulting from the cross-pollination is known as the F1 generation. The F1 hybrid seeds exhibit traits that are a combination of the parent plants, often displaying enhanced qualities like disease resistance, improved yield, or specific coloration.
Benefits of F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds offer several advantages over other types of seeds:
- Vigorous Growth: F1 hybrids tend to have stronger and more vigorous growth compared to open-pollinated or heirloom varieties.
- Uniformity: F1 hybrids have a high degree of uniformity in terms of traits, size, and maturity, making it easier for gardeners to plan and maintain their gardens.
- Increased Yield: F1 hybrids often have higher yields compared to their parent plants, making them a popular choice for commercial farming.
- Disease Resistance: F1 hybrids are bred to be resistant to specific diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and increasing plant longevity.
Understanding F1 Hybrid Seed Labels

When purchasing F1 hybrid seeds, it is important to understand the information provided on the seed packet label. The label typically includes the following details:
- Variety Name: The name given to the hybrid variety.
- Parentage: The parent plants used in the cross-pollination process.
- Traits: The specific traits that the hybrid variety possesses, such as disease resistance or coloration.
- Instructions: Guidelines for planting, care, and harvesting the seeds.
- Expiration Date: The date until which the seeds are guaranteed to retain their viability.
Gardeners should carefully read and understand the information on the seed packet to ensure they select the right F1 hybrid seeds for their needs and to maximize their chances of successful growth and cultivation.
Conclusion
Understanding the genetic makeup of F1 hybrid seeds can significantly impact a gardener’s success in growing plants with desired characteristics. The controlled breeding process and the combination of desirable traits make F1 hybrid seeds an excellent choice for both commercial cultivation and home gardening. By knowing how to interpret seed packet labels and the benefits of F1 hybrid seeds, gardeners can make informed choices and achieve outstanding results in their gardens.
How to Properly Use F1 Hybrid Seeds in Your Garden
Using F1 hybrid seeds in your garden can be a great way to get reliable and high-quality plants. Here are some tips on how to properly use these seeds in your garden:
1. Understand the Basics
Before using F1 hybrid seeds, it’s important to understand what they are. F1 hybrid seeds are the result of cross-breeding two different parent plants to create a new hybrid variety. They are known for their uniformity, vigor, and productivity.
2. Choose the Right Seeds
When selecting F1 hybrid seeds for your garden, read the seed packet carefully. Look for information on the specific characteristics of the plant, such as its size, color, and disease resistance. Choose seeds that are well-suited to your growing conditions and gardening goals.
3. Follow Sowing Instructions
Each seed packet comes with sowing instructions that provide guidance on the best time and method for planting the seeds. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure successful germination and growth.
4. Use Good Quality Soil
Prepare your garden soil by adding compost or organic matter to improve its fertility and drainage. F1 hybrid seeds perform best in well-draining soil that is rich in nutrients.
5. Plant at the Right Depth
Plant your F1 hybrid seeds at the recommended depth. If planted too shallow, they may dry out, and if planted too deep, they may struggle to reach the surface. Follow the seed packet instructions for the best results.
6. Provide Adequate Water and Sunlight
Water your F1 hybrid seeds regularly, especially during dry periods, to keep the soil evenly moist. Additionally, provide them with adequate sunlight according to their specific requirements.
7. Monitor for Pests and Diseases
Regularly inspect your F1 hybrid plants for any signs of pests or diseases. Take appropriate steps to prevent and treat any issues before they can cause significant damage.
8. Harvest and Save Seeds

If you want to save seeds from your F1 hybrid plants for future use, make sure you follow the correct techniques and protocols. Keep in mind that saved seeds may not produce plants with the same characteristics as the parent plant.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your F1 hybrid seeds thrive in your garden, providing you with healthy and productive plants.
Common Misconceptions About F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds are a popular choice among gardeners due to their improved performance and characteristics. However, there are several common misconceptions associated with F1 hybrid seeds that need to be addressed.
1. F1 hybrid seeds are genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
One common misconception is that F1 hybrid seeds are genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This is not true. F1 hybrid seeds are created through traditional breeding methods, where two different parent plants with desirable traits are cross-pollinated to create a new variety. No genetic modification techniques are involved in the production of F1 hybrid seeds.
2. F1 hybrid seeds are sterile
Another misconception is that F1 hybrid seeds are sterile, meaning they cannot produce viable seeds for future planting. While it is true that saving seeds from F1 hybrid plants may not result in the same characteristics as the original plant, it does not mean that the seeds are completely sterile. In fact, F1 hybrid seeds can still produce plants with desirable traits, although they may exhibit some variation.
3. F1 hybrid seeds are less nutritious
Some people believe that F1 hybrid seeds are less nutritious compared to open-pollinated or heirloom varieties. However, the nutritional content of a plant is determined by its genetic makeup and growing conditions, not whether it is an F1 hybrid or an open-pollinated variety. Therefore, there is no inherent difference in nutritional value between F1 hybrid seeds and other types of seeds.
4. F1 hybrid seeds are more expensive
While it is true that F1 hybrid seeds may be more expensive than open-pollinated or heirloom varieties, this is not always the case. The cost of seeds can vary depending on factors such as the seed company, variety, and demand. It is important to compare prices and consider the overall value and performance of the seeds before making a purchasing decision.
5. F1 hybrid seeds are unnatural
Some people have concerns about F1 hybrid seeds being “unnatural” or not in line with traditional plant breeding practices. However, F1 hybrid seeds are produced through controlled and purposeful cross-pollination, a process that has been used for centuries to improve plant characteristics. While the specific breeding methods may have evolved over time, the principles of selective breeding remain the same.
In conclusion, it is important to dispel misconceptions about F1 hybrid seeds. They are not genetically modified organisms, they are not completely sterile, their nutritional value is not inherently different, their pricing varies, and their breeding methods are not unnatural. Understanding the true nature of F1 hybrid seeds can help gardeners make informed choices and maximize their gardening success.
“Question-Answer”
What is F1 labelling on a seed packet?
F1 labelling on a seed packet indicates that the seeds are the first-generation offspring resulting from the crossbreeding of two different parent plants.
What does F1 stand for?
F1 stands for “first filial generation”. It refers to the first generation of offspring resulting from the crossbreeding of two different parent plants.
Why is F1 labelling important?
F1 labelling is important because it indicates that the seeds are the result of controlled crossbreeding, ensuring certain desirable traits in the offspring. It helps gardeners and farmers choose seeds that are more likely to exhibit specific characteristics.
What does F1 hybrid mean?
F1 hybrid refers to the breeding technique that involves crossbreeding two genetically distinct parent plants to produce seeds with desired traits in the first generation. These F1 hybrid seeds, when planted, will result in plants that are more uniform and consistent in their characteristics.
What are the advantages of growing F1 hybrid plants?
Growing F1 hybrid plants has several advantages. Firstly, F1 hybrid plants tend to be more uniform, meaning they have consistent characteristics such as color, size, and disease resistance. They also tend to have higher yields and better performance compared to open-pollinated varieties. Additionally, F1 hybrid plants can exhibit hybrid vigor, which results in plants that are more robust and productive.







