- The Importance of Urea Application
- 1. Nitrogen Source
- 2. Increased Crop Productivity
- 3. Nutrient Recycling
- 4. Cost-Effective
- 5. Environmental Considerations
- Conclusion
- Factors Affecting Urea Efficiency
- Soil pH:
- Temperature:
- Moisture:
- Application Technique:
- Other Nutrients:
- Crop Uptake:
- Conclusion:
- Best Practices for Urea Application
- 1. Use the Right Equipment
- 2. Timely Application
- 3. Proper Calibration
- 4. Incorporate into Soil
- 5. Consider Split Applications
- 6. Avoid Excessive Application
- 7. Monitor Soil Moisture
- 8. Consider Environmental Factors
- Timing and Rate of Urea Application
- Timing
- Rate
- Urea Application Methods
- 1. Broadcasting
- 2. Side-Dressing
- 3. Top-Dressing
- 4. Injection
- 5. Fertigation
- 6. Controlled-Release Fertilizers
- Minimizing Potential Losses from Urea Application
- Monitoring Urea Application Effects
- Soil Nutrient Levels
- Crop Growth and Yield
- Environmental Impact
- Timing and Frequency
- Visual Scouting
- Consulting Experts
- “Question-Answer”
- What is urea and how is it used in agriculture?
- What are the benefits of urea application?
- How should urea be applied to maximize soil benefits?
- Can urea be used in all types of soil?
- Are there any precautions to take when using urea as a fertilizer?
- “Video” STOP OVERSEEDING! There’s a Cheaper Way!!

Urea is a commonly used nitrogen fertilizer that can greatly improve soil health and plant growth. However, to maximize its benefits, it is important to understand how to properly apply urea to the soil. This article will provide an overview of the best practices for urea application, including the timing, rate, and placement of the fertilizer.
Timing is an important factor in urea application. It is best to apply urea when the soil is moist but not waterlogged. This allows the urea to dissolve and be absorbed by the plants more effectively. Additionally, it is recommended to apply urea before or during periods of expected rainfall, as this helps to further facilitate nutrient uptake by the plants.
The rate of urea application is also crucial to maximizing its benefits. It is important to follow the recommended application rates provided by soil testing labs or agronomists. These recommendations are based on factors such as soil fertility, crop nutrient requirements, and expected yield goals. Applying too much urea can result in nutrient imbalance and environmental pollution, while applying too little may not provide sufficient nutrients for optimal plant growth.
Lastly, the placement of urea fertilizer is another key consideration. Urea can be applied as a top-dressing, where the fertilizer is broadcasted on the soil surface and then incorporated into the soil through irrigation or rainfall. This method works well for crops with an established root system. Alternatively, urea can be applied as a side-dressing, where the fertilizer is placed in a band near the plant roots. This method is particularly effective for row crops and helps to minimize nutrient loss through volatilization.
In conclusion, proper urea application is essential for maximizing soil benefits and promoting healthy plant growth. By considering factors such as timing, rate, and placement, farmers and gardeners can ensure that the urea fertilizer is used efficiently and effectively. Following best practices for urea application not only benefits the plants, but also helps to protect the environment by reducing nutrient runoff and pollution.
The Importance of Urea Application
Urea application is essential for optimizing soil health and crop productivity. Urea, a common nitrogen fertilizer, provides vital nutrients to plants, promoting their growth and development. This article will discuss the importance of urea application in maximizing soil benefits.
1. Nitrogen Source
Urea is a rich source of nitrogen, a crucial nutrient required by plants for various physiological processes. Nitrogen is an essential component of proteins, enzymes, chlorophyll, and DNA. By applying urea to the soil, farmers can ensure that plants receive an adequate supply of nitrogen, which is necessary for optimal growth and yield.
2. Increased Crop Productivity
Urea application plays a significant role in enhancing crop productivity. Nitrogen stimulates chlorophyll production, improving the photosynthesis process. This, in turn, leads to increased plant growth, higher yields, and improved crop quality. With the proper application of urea, farmers can maximize their agricultural output and achieve better profitability.
3. Nutrient Recycling
Urea application promotes nutrient recycling in the soil. When plants absorb nitrogen from urea, they utilize it for growth. Eventually, when plants decompose or are harvested, the nitrogen is returned to the soil, making it available for future crops. This recycling process helps maintain soil fertility and reduces the need for excessive nitrogen fertilizer application.
4. Cost-Effective
Urea is a cost-effective nitrogen fertilizer compared to other forms, such as ammonium nitrate or ammonium sulfate. Its relatively low cost per unit of nitrogen makes it an attractive option for farmers looking to optimize their fertilizer budgets. Using urea efficiently can help reduce expenses while still achieving desired crop yields.
5. Environmental Considerations
Proper urea application techniques can minimize the negative environmental impacts associated with nitrogen fertilizer use. By applying urea at the right time and in the right amounts, farmers can reduce the risk of nitrogen runoff into water bodies, which can lead to water pollution and ecosystem damage. Careful management of urea application ensures efficient nutrient utilization while minimizing environmental harm.
Conclusion
Urea application is crucial for maximizing soil benefits and crop productivity. Its role as a nitrogen source, ability to increase crop yields, promotion of nutrient recycling, cost-effectiveness, and environmentally friendly aspects make urea an essential tool in modern agricultural practices. By understanding the importance of urea application, farmers can make informed decisions to optimize their farming operations and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices.
Factors Affecting Urea Efficiency
The efficiency of urea application in soil can be affected by several factors. Understanding these factors can help farmers maximize the benefits of urea application and improve crop yield. Here are some of the key factors that can impact urea efficiency:
Soil pH:
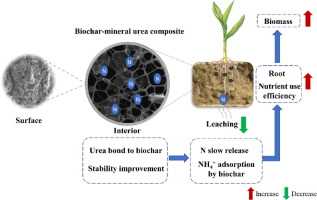

The pH of the soil plays a crucial role in urea efficiency. Urea hydrolyzes in the soil to release ammonium ions, and this hydrolysis process is affected by soil pH. Urea hydrolysis is favored in slightly acidic to neutral soils, with a pH range of 6 to 7.5. In alkaline soils, the hydrolysis process is slower, reducing urea efficiency.
Temperature:

Temperature also affects the efficiency of urea application. Warm temperatures favor the microbial activity responsible for urea hydrolysis, resulting in faster release of ammonium ions. In cold temperatures, the hydrolysis process is slower, which can lead to a delay in nutrient availability to the crops.
Moisture:
Soil moisture content is another important factor that affects urea efficiency. Optimal soil moisture levels allow for proper dissolution and hydrolysis of urea granules, ensuring efficient nutrient release. In dry soil conditions, urea may not dissolve and hydrolyze effectively, reducing its efficiency.
Application Technique:
The technique used for urea application can significantly impact its efficiency. Broadcasting urea on the soil surface without proper incorporation can lead to nitrogen loss through volatilization. Incorporating urea into the soil, either through tillage or irrigation, enhances contact with soil particles and reduces the risk of nitrogen loss.
Other Nutrients:
The presence of certain nutrients in the soil can influence urea efficiency. Urea requires the enzyme urease to hydrolyze into ammonium ions. If the soil lacks sufficient levels of urease or other essential nutrients, such as sulfur or phosphorus, the hydrolysis process might be compromised, reducing the efficiency of urea application.
Crop Uptake:
The efficiency of urea application also depends on the ability of crops to uptake and utilize the released ammonium ions. Factors such as crop type, growth stage, and root development can affect the uptake efficiency. Ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth, such as proper irrigation and nutrient management, can enhance urea efficiency.
Conclusion:
To maximize the soil benefits of urea application, it is essential to consider these factors that can impact urea efficiency. Farmers should carefully manage soil pH, temperature, moisture levels, and application techniques. Additionally, addressing other nutrient deficiencies and promoting crop uptake can further enhance the effectiveness of urea application and improve overall crop yield.
Best Practices for Urea Application
Urea is a commonly used nitrogen fertilizer that can greatly benefit soil health and plant growth when applied correctly. Here are some best practices for urea application:
1. Use the Right Equipment
It is important to use the right equipment when applying urea to maximize its efficacy. A spreader or sprayer specifically designed for urea application will help ensure an even and accurate distribution of the fertilizer.
2. Timely Application

Urea should be applied at the appropriate time to avoid nutrient losses and optimize plant uptake. Consider the specific crop’s growth stage and the soil conditions before determining the best time to apply urea. Consulting with local agricultural experts can provide valuable insights.
3. Proper Calibration
Calibrate the urea application equipment to ensure accurate and consistent fertilizer application rates. Incorrect calibration can lead to over or underapplication, which can negatively affect plant growth and soil health.
4. Incorporate into Soil
Urea should be incorporated into the soil shortly after application to reduce nitrogen losses due to volatilization. This can be achieved through irrigation, cultivation, or incorporating the fertilizer into the soil during planting.
5. Consider Split Applications
In some cases, it may be beneficial to split the urea application into multiple doses throughout the growing season. This helps prevent nutrient losses and ensures a continuous and steady supply of nitrogen to the plants.
6. Avoid Excessive Application
Overapplication of urea can result in nitrogen runoff, which can contribute to water pollution and harm the environment. It is important to follow recommended application rates and adjust them based on soil nutrient levels and crop needs.
7. Monitor Soil Moisture


Proper soil moisture is crucial for urea conversion and plant uptake. Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation practices as needed to maintain optimal conditions for urea transformation and nutrient availability.
8. Consider Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can affect urea conversion and nutrient uptake. It is important to consider these factors when determining the timing and rate of urea application.
By following these best practices, you can maximize the benefits of urea application, promote soil health, and optimize plant growth.
Timing and Rate of Urea Application
Proper timing and rate of urea application are crucial to maximize its soil benefits and ensure optimal crop growth. Here are some guidelines to follow:
Timing
- Split applications: It is often recommended to split the urea application into multiple timings throughout the growing season. This helps to provide a continuous supply of nitrogen to the plants and prevents excessive leaching or volatilization.
- Early application: It is generally advised to apply urea early in the growing season, ideally before the onset of heavy rainfall or irrigation. This allows for better nutrient uptake and utilization by the plants.
- Top-dressing: Urea can also be top-dressed during the crop’s active growth stage. This ensures that the plants receive nitrogen when they have the highest nutrient demand.
Rate
- Soil testing: Conduct a soil test to determine the nitrogen requirements of the crop. This will help determine the appropriate rate of urea application.
- Crop type and growth stage: Different crops have varying nitrogen requirements and growth stages. Consider these factors when determining the rate of urea application.
- Nitrogen loss considerations: Take into account potential nitrogen losses due to leaching or volatilization when deciding the rate of urea application. Applying higher rates may be necessary to compensate for these losses.
It is important to note that the timing and rate of urea application may vary depending on specific soil and crop conditions. Consulting with a local agricultural expert or agronomist can provide more personalized recommendations for your specific situation.
Urea Application Methods
Urea is a commonly used nitrogen fertilizer in agriculture due to its high nitrogen content and affordability. However, to maximize its benefits, it is important to apply urea in the right way. Here are some common methods of urea application:
1. Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the most common method of urea application. In this method, urea is spread evenly over the surface of the soil. It can be done manually or using machinery such as broadcast spreaders. Broadcasting is suitable for crops that are not sensitive to nitrogen burn.
2. Side-Dressing
Side-dressing involves applying urea to the soil near the base of the plants. This method is commonly used for row crops such as corn or vegetables. Side-dressing allows plants to have a direct access to nitrogen as they grow, promoting better growth and development.
3. Top-Dressing
Top-dressing is similar to side-dressing, but it involves applying urea on the soil surface around the plants. This method is commonly used for established crops with dense canopies where it is difficult to apply urea through broadcasting. Top-dressing ensures that urea is not intercepted by the crop foliage.
4. Injection
Injection is a method of applying urea below the soil surface using special equipment. This method helps to reduce nitrogen losses through volatilization and improve nitrogen use efficiency. It is commonly used for high-value crops or in areas with high rainfall.
5. Fertigation
Fertigation involves applying urea through irrigation systems. Urea is dissolved in water and applied directly to the root zone of plants. Fertigation allows for precise application of urea and efficient nutrient uptake by plants. This method is commonly used in drip irrigation systems.
6. Controlled-Release Fertilizers


Controlled-release fertilizers are coated with materials that regulate the release of nutrients over time. These fertilizers can be applied using any of the above-mentioned methods. Controlled-release urea releases nitrogen slowly, providing a sustained supply of nutrients to plants and reducing the risk of nitrogen loss.
It is important to consider factors such as crop type, soil conditions, and weather when choosing the appropriate urea application method. Consulting with agricultural experts or soil testing services can help determine the most suitable method for maximizing the soil benefits of urea.
Minimizing Potential Losses from Urea Application
Although urea is a valuable source of nitrogen for plants, it can be subject to potential losses if not properly managed. Here are some strategies to consider in order to minimize these losses:
- Timely application: Applying urea at the right time ensures that the nutrients are available to plants when they need them the most. It is important to consider the crop growth stage and weather conditions to determine the optimal time for application.
- Incorporation into the soil: Urea should be incorporated into the soil as soon as possible after application. This helps to reduce the chance of nitrogen loss through volatilization. Incorporation can be done through tillage or irrigation.
- Split applications: Instead of applying all the urea at once, splitting the applications can help reduce potential losses. This allows for a more efficient use of the nitrogen by the plants and decreases the risk of nitrogen leaching or denitrification.
- Proper dosage: Applying the correct dosage of urea is essential to minimize the potential for nutrient losses. Applying too much urea can lead to excess nitrogen leaching or runoff, while applying too little may result in insufficient nitrogen availability for the plants.
- Use of urease inhibitors: Urease inhibitors can be used to reduce urea hydrolysis and subsequent ammonia volatilization. These inhibitors help to retain nitrogen in the ammonium form for a longer period, increasing the nitrogen use efficiency by plants.
By following these strategies, farmers can minimize the potential losses associated with urea application, ensuring that the nitrogen is effectively utilized by plants and protecting the environment from nitrogen pollution.
Monitoring Urea Application Effects


The application of urea fertilizer can have various effects on soil health and crop growth. It is important to monitor these effects to ensure that the desired benefits are achieved. Here are some key aspects to consider when monitoring urea application effects:
Soil Nutrient Levels
- Regularly test the soil to monitor the nutrient levels, especially nitrogen (N) content, after urea application. This will help determine if the fertilizer has been effectively absorbed by the soil.
- Sampling should be done at different depths to understand nutrient distribution within the soil profile.
- Use appropriate laboratory techniques to analyze the soil samples and quantify the nutrient levels accurately.
Crop Growth and Yield
- Monitor the growth and development of the crops after urea application. Keep track of factors such as plant height, leaf color, and overall plant health.
- Regularly assess the crop yield to evaluate the effectiveness of urea fertilization. Compare the yield with previous seasons or control plots to determine the extent of improvement.
Environmental Impact
- Monitor the environmental impact of urea application, particularly nitrogen runoff or leaching into nearby water bodies. Assess water quality and measure nitrogen concentrations in the surrounding ecosystem.
- Consider implementing best management practices to minimize environmental impacts, such as following recommended application rates, timing, and methods.
Timing and Frequency
- Record the timing and frequency of urea application to understand the long-term effects on soil health and crop growth. This information can help optimize fertilization schedules.
- Keep a log of application rates, weather conditions, and any other relevant factors that may influence the effectiveness of urea fertilization.
Visual Scouting
- Regularly observe the field for any visual changes or symptoms that may indicate issues related to urea application. These could include nutrient deficiencies, leaf burning, or excessive plant growth.
- Note any unusual patterns or areas of poor crop performance and investigate further to identify potential causes.
Consulting Experts
In complex cases or for more accurate analysis, consider consulting experts such as agronomists, soil scientists, or crop consultants. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise and experience.
By monitoring the effects of urea application, farmers can optimize fertilizer management practices, improve soil health, and maximize crop yields.
“Question-Answer”
What is urea and how is it used in agriculture?
Urea is a white crystalline substance that contains high levels of nitrogen. It is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture to provide plants with the essential nutrient for growth. Urea can be applied to the soil directly or dissolved in water for foliar application.
What are the benefits of urea application?
Urea application offers several benefits to the soil and plants. It provides a readily available source of nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth and development. It also helps increase crop yield, improve soil fertility, and promote healthy plant growth.
How should urea be applied to maximize soil benefits?
To maximize soil benefits, it is important to apply urea correctly. Urea should be applied at the right time and in the right amount. It is best to apply urea before planting or during the early stages of plant growth. It should be evenly distributed across the soil surface and incorporated into the soil to prevent nitrogen loss through volatilization. Split applications can also be used to ensure a continuous supply of nitrogen to the plants.
Can urea be used in all types of soil?
Yes, urea can be used in all types of soil. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on the soil type. Sandy soils, for example, have a higher leaching potential, so urea may need to be applied in smaller and more frequent doses. Clay soils, on the other hand, have a higher retention capacity, so larger doses of urea may be required.
Are there any precautions to take when using urea as a fertilizer?
Yes, there are a few precautions to consider when using urea as a fertilizer. Firstly, it is important to follow the recommended application rates to avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to environmental pollution and plant damage. Secondly, urea should not be applied to frozen or waterlogged soils, as it can increase the risk of nitrogen losses. Lastly, it is important to store urea properly to prevent moisture absorption, which can reduce its effectiveness.







