- Urea in Vegetable Gardening: Benefits and Tips
- Benefits of Using Urea:
- Tips for Using Urea in Vegetable Gardening:
- Enhancing Soil Fertility
- The Role of Urea in Soil Fertility
- The Benefits of Urea in Enhancing Soil Fertility
- Best Practices for Using Urea in the Vegetable Garden
- Promoting Growth and Productivity
- 1. Nitrogen Source
- 2. Increased Nutrient Uptake
- 3. Enhanced Root Development
- 4. Improved Plant Metabolism
- 5. Increased Fruit and Vegetable Yields
- Improving Nitrogen Uptake
- 1. Applying Urea at the Right Time
- 2. Proper Application Method
- 3. Water Management
- 4. Nutrient Balancing
- 5. Organic Matter and Soil Health
- 6. Considerations for Nitrogen-Loving Crops
- Reducing Nitrogen Losses
- 1. Timing
- 2. Incorporation
- 3. Irrigation
- 4. Split Applications
- 5. Soil Testing
- 6. Organic Matter
- Dosage and Application Methods
- 1. Determining the Right Dosage
- 2. Applying Urea
- 3. Time of Application
- 4. Safety Precautions
- Precautions and Safety Measures
- Complementing Organic Fertilizers
- 1. Side-dressing
- 2. Broadcasting
- 3. Composting
- 4. Liquid fertilization
- 5. Combination with organic soil amendments
- Consultation and Expert Advice
- “Question-Answer”
- What is urea and why is it used in the vegetable garden?
- How should urea be applied in the vegetable garden?
- What are the benefits of using urea in the vegetable garden?
- Is urea safe to use in the vegetable garden?
- Can urea be used on all types of vegetables?
- Are there any alternatives to urea for fertilizing the vegetable garden?
- “Video” Triple14 and Urea epektibong Combo Meal for your Plants,, Paano?
Urea is a nitrogen-rich fertilizer commonly used in agriculture and gardening. It is a versatile fertilizer that can provide numerous benefits when used in the vegetable garden.
One of the main advantages of using urea in the vegetable garden is its high nitrogen content. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and urea provides a readily available source of this nutrient. By using urea, gardeners can ensure that their vegetable plants have an adequate supply of nitrogen to promote healthy growth and development.
Urea is also known for its ability to promote lush and green foliage in vegetable plants. Nitrogen plays a crucial role in the production of chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. By applying urea, gardeners can enhance the production of chlorophyll and ensure that their vegetable plants have vibrant and healthy leaves.
“Another benefit of using urea in the vegetable garden is its long-lasting effects. Urea is a slow-release fertilizer, which means that it provides a steady supply of nitrogen over an extended period. This makes it an ideal choice for gardeners looking to nourish their vegetable plants throughout the growing season.”
It is important to note that while urea offers many benefits for the vegetable garden, it should be used with caution. Excessive use of urea can lead to nitrogen burn, a condition where plant tissues become damaged due to excess nitrogen. Gardeners should follow recommended application rates and ensure that urea is properly diluted before use.
In conclusion, urea can be a valuable fertilizer for the vegetable garden, providing a readily available source of nitrogen, promoting lush foliage, and offering long-lasting effects. By using urea responsibly, gardeners can enjoy the benefits of this versatile fertilizer and help their vegetable plants thrive.
Urea in Vegetable Gardening: Benefits and Tips

Urea is a commonly used fertilizer in vegetable gardening due to its numerous benefits. It is a rich source of nitrogen, which is essential for the growth and development of plants. When used correctly, urea can greatly enhance the productivity and health of your vegetable garden. Here are some benefits and tips for using urea in vegetable gardening:
Benefits of Using Urea:
- High Nitrogen Content: Urea is a concentrated source of nitrogen, with around 46% nitrogen content. Nitrogen is a vital nutrient for plants, promoting leafy growth, strong stems, and vibrant color.
- Rapid Nutrient Release: Urea quickly converts to ammonia in the soil, making it readily available for plant uptake. This ensures rapid nutrient absorption, leading to faster growth and improved yields.
- Cost-Effective: Urea is a cost-effective fertilizer option compared to other nitrogen sources. It provides a high concentration of nitrogen at an affordable price, making it an ideal choice for large vegetable gardens.
- Increases Crop Yield: The high nitrogen content of urea stimulates plant growth, resulting in increased crop yields. It helps the plants to produce more foliage, flowers, and fruits, leading to a bountiful harvest.
- Improves Soil Fertility: Urea not only provides essential nutrients to the plants but also enhances soil fertility. Nitrogen promotes the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, improving the overall health and structure of the soil.
Tips for Using Urea in Vegetable Gardening:
- Proper Application: Apply urea fertilizer according to the recommended dosage for your specific vegetables. Over-application can lead to nitrogen burn and damage the plants, while under-application may result in nutrient deficiency.
- Timing: Apply urea fertilizer during the active growing stage of your vegetables. This is usually when the plants are actively producing foliage and before the flowering and fruiting stages.
- Uniform Distribution: Spread the urea fertilizer evenly across the vegetable garden to ensure uniform nutrient distribution. This helps prevent uneven growth and nutrient imbalances.
- Watering: After applying urea fertilizer, water the vegetable garden thoroughly. This helps dissolve the urea granules and facilitates nutrient absorption by the plants.
- Do Not Mix with Seeds: Avoid direct contact between urea fertilizer and seeds as it may damage or kill the germinating seeds. Apply the fertilizer away from the planting rows or wait until after seed germination.
- Monitor Plants: Regularly monitor the health and growth of your vegetable plants after applying urea fertilizer. Adjust the fertilization schedule and dosage if necessary based on the plant’s response and nutrient needs.
Using urea in vegetable gardening can greatly benefit your plants and improve overall yields. By following these tips and guidelines, you can ensure successful and productive vegetable gardening with the help of urea fertilizer.
Enhancing Soil Fertility
Soil fertility is a crucial factor in the success of any vegetable garden. Without fertile soil, plants may struggle to grow, produce healthy yields, and resist pests and diseases. Fortunately, there are several ways to enhance soil fertility, and one effective approach is the use of urea.
The Role of Urea in Soil Fertility
Urea, a compound that contains nitrogen, plays a vital role in enhancing soil fertility. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants, as it is a key component of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll. By providing plants with an adequate supply of nitrogen, urea promotes healthy growth and development.
When urea is applied to the soil, it undergoes a process known as hydrolysis, which converts it into ammonia and carbon dioxide. The ammonia is then transformed into ammonium ions, a form of nitrogen that plants can readily absorb and utilize for their growth. This conversion process makes urea a valuable source of nitrogen for plant nutrition.
The Benefits of Urea in Enhancing Soil Fertility
- Improved Plant Growth: Urea provides plants with a readily available source of nitrogen, which is essential for their growth and development. By promoting healthy plant growth, urea enhances overall soil fertility.
- Increase in Yield: The application of urea can lead to higher yields in vegetable gardens. Nitrogen is a key nutrient that plants need in large quantities, and by providing an adequate supply of nitrogen, urea can contribute to increased crop production.
- Enhanced Nutrient Uptake: Urea improves the availability of other nutrients in the soil. Nitrogen is known to enhance the uptake of other essential nutrients by plants, such as phosphorus and potassium. This improved nutrient availability can further enhance soil fertility.
- Cost-Effective: Urea is a cost-effective option for enhancing soil fertility. It is widely available and relatively affordable compared to other nitrogen fertilizers.
Best Practices for Using Urea in the Vegetable Garden
When using urea to enhance soil fertility in the vegetable garden, it’s important to follow these best practices:
- Proper Application: Apply urea evenly across the soil, following the recommended application rate for the specific crop or plant type.
- Timing: Apply urea at the appropriate time, considering the plant’s growth stage and the soil temperature. Early spring or fall applications are often recommended.
- Watering: After applying urea, ensure that the garden receives adequate irrigation to help incorporate the urea into the soil and prevent nitrogen loss through volatilization.
- Combining with Organic Matter: To further enhance soil fertility, consider incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, along with urea. This combination can provide a balanced source of nutrients for plants.
Conclusion
Enhancing soil fertility is essential for a successful vegetable garden, and urea can play a crucial role in achieving this goal. By providing plants with an accessible source of nitrogen, urea promotes healthy growth, increases yield, and enhances overall soil fertility. By following best practices for urea application, gardeners can maximize the benefits of this valuable fertilizer.
Promoting Growth and Productivity
Using urea in the vegetable garden can greatly promote growth and productivity. Here are some key ways urea benefits plants:
1. Nitrogen Source
Urea is a rich source of nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth. Nitrogen promotes lush, green foliage and helps plants produce chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis. Urea provides a readily available source of nitrogen, ensuring that plants have enough of this crucial element for optimal growth.
2. Increased Nutrient Uptake
By providing plants with a concentrated source of nitrogen, urea helps improve their ability to absorb other essential nutrients. Nitrogen is necessary for the uptake and utilization of other nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium. By promoting nutrient uptake, urea ensures that plants have access to all the necessary elements they need to thrive.
3. Enhanced Root Development
Urea stimulates root growth and development in plants. This is important for overall plant health and vigor as strong, well-developed roots can efficiently absorb water and nutrients from the soil. With enhanced root development, plants are better equipped to withstand environmental stresses and establish themselves effectively in the garden.
4. Improved Plant Metabolism
Urea plays a vital role in the metabolism of plants. It is involved in various biochemical processes, including the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. By supplying plants with urea, you can help boost their metabolism, leading to enhanced growth, productivity, and overall plant health.
5. Increased Fruit and Vegetable Yields
One of the main benefits of using urea in the vegetable garden is increased yields. With its ability to promote plant growth, nutrient uptake, root development, and overall plant metabolism, urea can significantly boost the production of fruits and vegetables. This means you’ll be able to harvest a larger quantity and obtain better-quality crops.
Incorporating urea into your vegetable gardening routine can be a valuable tool for promoting growth and productivity. However, it’s important to follow proper application rates and timing guidelines to avoid overfertilizing or damaging your plants. Consult with a gardening expert or reference the product label for specific instructions on using urea in your garden.
Improving Nitrogen Uptake
One of the main benefits of using urea in the vegetable garden is its high nitrogen content. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth and is often a limiting factor in plant productivity. Urea provides a readily available source of nitrogen that can be easily taken up by plants.
1. Applying Urea at the Right Time

To improve nitrogen uptake, it is important to apply urea at the right time. Ideally, urea should be applied when plants are actively growing and in need of nitrogen. This is typically during the early stages of plant development or when plants are showing signs of nitrogen deficiency, such as slow growth and yellowing leaves.
2. Proper Application Method

Urea can be applied to the vegetable garden in various ways, including broadcasting, banding, or side-dressing. Broadcasting involves spreading urea evenly over the soil surface, while banding and side-dressing involve placing the urea in a concentrated band or trench near the plants. The chosen application method should ensure that the urea is evenly distributed and in close proximity to the plant roots for efficient nitrogen uptake.
3. Water Management
Water management is crucial for optimal nitrogen uptake. Adequate soil moisture is required for the urea to dissolve and be taken up by plants. However, excessive moisture can lead to leaching of nitrogen beyond the reach of plant roots. It is important to maintain proper soil moisture levels through irrigation practices that provide sufficient water without causing waterlogging.
4. Nutrient Balancing
While urea is a valuable source of nitrogen, it is important to maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the vegetable garden. Nitrogen must be accompanied by other essential nutrients, such as phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients, to support overall plant health and productivity. Regular soil testing can help identify any nutrient deficiencies and guide appropriate fertilizer application.
5. Organic Matter and Soil Health

Improving soil health through the addition of organic matter can also enhance nitrogen uptake. Organic matter improves soil structure, increases nutrient availability, and promotes microbial activity. Incorporating compost, manure, or other organic materials into the soil can improve overall nutrient cycling and enhance plant uptake of nitrogen from urea and other sources.
6. Considerations for Nitrogen-Loving Crops
Some vegetable crops, such as corn, tomatoes, and leafy greens, have high nitrogen requirements. For these nitrogen-loving crops, it may be necessary to provide additional nitrogen beyond what is supplied by urea. This can be accomplished by incorporating nitrogen-rich amendments, like blood meal or fish emulsion, into the soil or through regular foliar feeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
Overall, improving nitrogen uptake in the vegetable garden is essential for maximizing plant growth and productivity. By applying urea at the right time, using proper application methods, managing water effectively, balancing nutrients, promoting soil health, and considering the needs of specific crops, gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the nitrogen they need for optimal performance.
Reducing Nitrogen Losses
When using urea in the vegetable garden, it’s important to take steps to reduce nitrogen losses. Nitrogen can easily be lost through volatilization, leaching, and denitrification. Here are some tips to minimize these losses:
1. Timing
Apply urea at the right time to maximize nitrogen uptake by plants and minimize losses. This is especially important for nitrogen-hungry vegetables like leafy greens and corn. Apply urea before planting or side dress it during the growing season to provide a steady supply of nitrogen.
2. Incorporation
After applying urea, make sure to incorporate it into the soil. This will help prevent nitrogen from volatilizing into the atmosphere. Use a rake, cultivator, or tiller to mix the urea into the top few inches of soil.
3. Irrigation
Water the vegetable garden immediately after applying urea. This will help move the nitrogen into the soil and reduce the risk of leaching. Additionally, make sure to water the garden regularly throughout the growing season to keep the soil moist and promote proper nutrient uptake.
4. Split Applications
Instead of applying all the urea at once, consider splitting the application into multiple doses. This can help avoid excessive nitrogen availability at one time, reducing the risk of leaching and denitrification. Spread out the urea applications throughout the season to provide a steady supply of nitrogen.
5. Soil Testing
Regularly test the soil in the vegetable garden to determine its nutrient content, including nitrogen levels. This will help you make informed decisions about urea application rates and timings. Excess nitrogen can harm plants and contribute to water pollution, so it’s important to adjust your fertilizer practices based on actual soil conditions.
6. Organic Matter
Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil. Organic matter helps improve soil structure and fertility, allowing plants to better utilize nitrogen. It also helps retain moisture and reduce the risk of nitrogen leaching.
By following these tips, you can make the most of urea in the vegetable garden while minimizing nitrogen losses. Proper nitrogen management not only benefits your plants but also protects the environment by reducing water pollution.
Dosage and Application Methods
1. Determining the Right Dosage
When it comes to using urea in your vegetable garden, it’s important to determine the right dosage to avoid over-fertilization and potential damage to your plants. The dosage will depend on factors such as the type of vegetables you’re growing, the nutrient requirements of the specific vegetables, and the current nutrient levels in your soil.
A general guideline for urea application is to use 1 to 2 pounds (0.45 to 0.9 kg) of urea per 1000 square feet (93 square meters) of garden area. However, it’s recommended to conduct a soil test to determine the exact nutrient levels and adjust the dosage accordingly. The soil test will provide valuable information about the nitrogen content and pH levels, allowing you to make more precise calculations.
2. Applying Urea
Urea can be applied to the soil in various ways, depending on your preferences and the tools available:
- Broadcast spreading: This method involves spreading the urea evenly over the soil surface. You can use a handheld spreader or a mechanical spreader for larger areas. After spreading, lightly rake the urea into the top few inches of soil to prevent nutrient runoff.
- Banding: Banding involves placing the urea in rows or bands near the plant roots. This method is especially useful for row crops. Dig a trench or furrow, place the urea in the trench, and cover it with soil. Ensure that the urea is placed a few inches away from the plant stems to avoid direct contact.
- Topdressing: Topdressing involves applying urea directly around the base of the plants. It’s commonly used for smaller plants or container-grown vegetables. Sprinkle the urea around the plants, making sure to avoid contact with the foliage. Lightly water the area to help the urea dissolve and reach the roots.
3. Time of Application
The timing of urea application is crucial for optimal results:
- Pre-planting: You can apply urea a few weeks before planting to provide a slow-release nitrogen source for the developing vegetables.
- Side-dressing: Side-dressing with urea can be done during the growing season to supply additional nutrients. Apply urea around the base of the plants, avoiding contact with the leaves.
- Foliar application: Urea can also be diluted with water and sprayed onto the foliage of the plants. This method provides a quick nitrogen boost and is often used when plants show signs of deficiency.
4. Safety Precautions
When handling and applying urea, it’s important to take some safety precautions:
- Wear gloves and protective clothing to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Avoid inhaling urea dust by wearing a mask or respirator.
- Store urea in a cool and dry place, away from moisture and sunlight.
- Keep urea out of reach of children and pets.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for proper handling and storage.
By following these dosage and application methods, you can effectively incorporate urea into your vegetable garden, promoting healthy plant growth and bountiful yields.
Precautions and Safety Measures
When using urea in the vegetable garden, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure safety and prevent any negative effects on plants, humans, and the environment. Here are some key precautions and safety measures to keep in mind:
- Wear protective clothing and equipment: When handling urea, it is important to wear gloves, goggles, and a mask to protect yourself from any potential harm. This is especially important when working with concentrated urea solutions or when applying urea in windy conditions.
- Store urea safely: Urea should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and any sources of ignition. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers and stored out of reach of children and pets.
- Follow application instructions: It is crucial to carefully read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer when applying urea in the garden. Over-application of urea can lead to excessive nitrogen levels in the soil, which can damage plants and contribute to pollution of water sources.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes: Urea should not come into direct contact with the skin or eyes, as it can cause irritation and discomfort. In case of contact, rinse the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Keep urea away from water sources: Urea should not be applied near water bodies, such as ponds, lakes, or streams, as it can contribute to water pollution. Be cautious when applying urea near these areas and avoid excessive run-off.
- Do not use urea on sensitive plants: Some plants, such as legumes, are sensitive to high nitrogen levels and can be harmed by the application of urea. Make sure to research the specific needs of your plants and avoid using urea on those that are sensitive to it.
- Be mindful of environmental impact: Urea, like any nitrogen fertilizer, can contribute to environmental pollution if not used responsibly. Use urea sparingly and avoid excessive application. Consider alternative organic fertilizers and practices, such as composting and crop rotation, to minimize the use of synthetic fertilizers.
Following these precautions and safety measures will help ensure that urea is used safely and effectively in the vegetable garden, promoting healthy plant growth and minimizing any potential negative impacts.
Complementing Organic Fertilizers

In addition to using organic fertilizers in your vegetable garden, you can also complement them with urea to maximize the benefits. Urea is a synthetic fertilizer that contains high levels of nitrogen, making it an excellent supplement to organic fertilizers. Here are some ways to use urea alongside organic fertilizers:
1. Side-dressing
Side-dressing refers to the application of fertilizer alongside the plants after they have been planted. To side-dress with urea, you can sprinkle a small amount of granular urea around the base of the plants, making sure to keep it away from the stem. This will provide a quick source of nitrogen for the plants, helping them to grow and produce more abundant harvests.
2. Broadcasting
Broadcasting involves spreading fertilizer evenly over the entire garden bed. You can incorporate urea into organic fertilizers and broadcast the mixture over the soil surface. This will ensure that all the plants in the garden receive a balanced supply of nutrients, including nitrogen from the urea.
3. Composting
Another way to use urea in conjunction with organic fertilizers is by incorporating it into your compost pile. Urea can speed up the decomposition process by providing a source of nitrogen for the beneficial microorganisms that break down organic matter. This will result in nutrient-rich compost that can be used to enrich the soil in your vegetable garden.
4. Liquid fertilization
Urea can also be used to make liquid fertilizers that can be applied directly to the plants. You can dissolve urea in water and use the solution to water your plants, ensuring that they receive a steady supply of nitrogen. This method is especially useful for plants that have a high demand for nitrogen, such as leafy vegetables or plants that are in the growth stage.
5. Combination with organic soil amendments
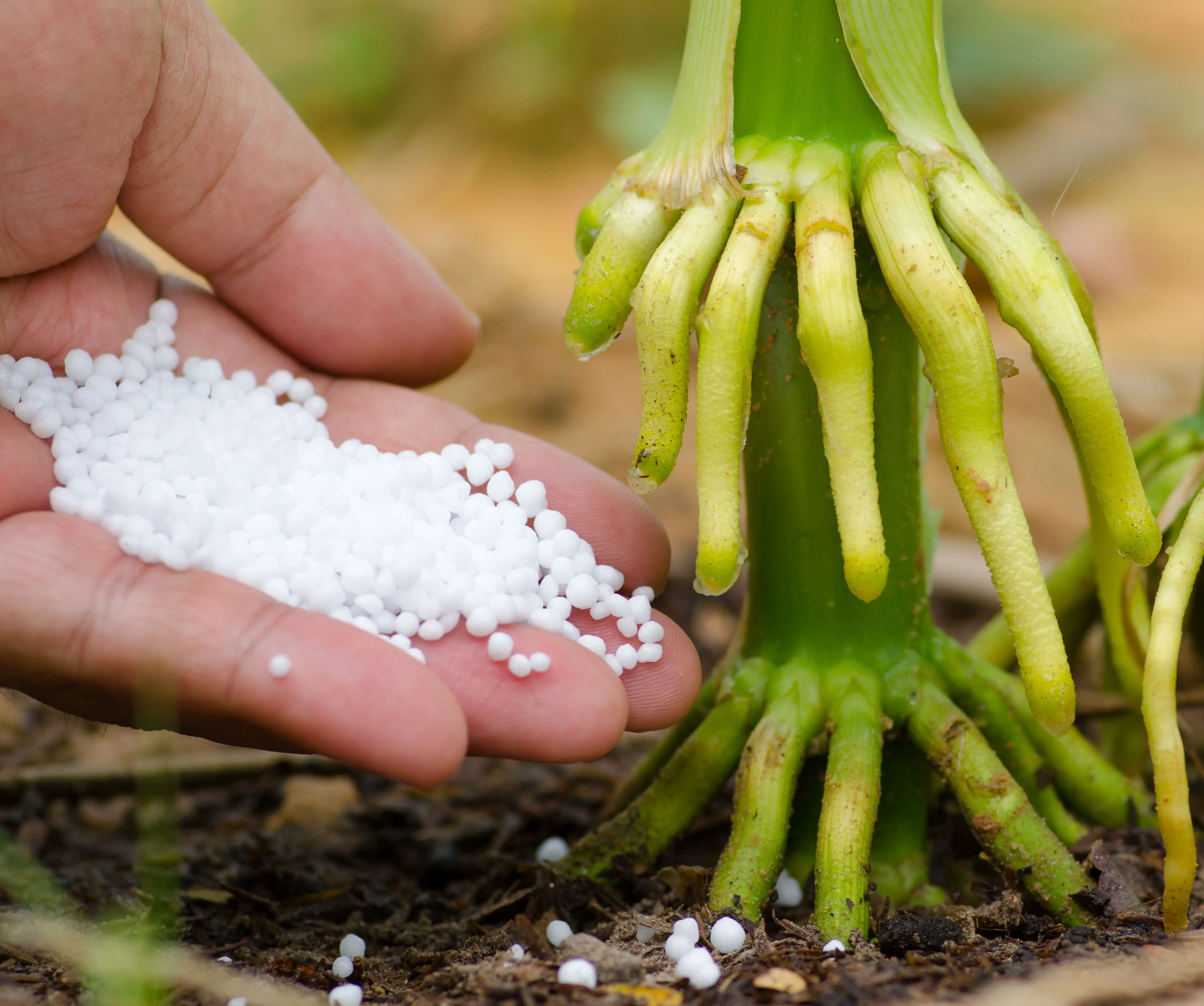

Lastly, you can mix urea with organic soil amendments, such as compost or aged manure, before applying them to the garden. This will provide a balanced nutrient profile for the plants, as organic amendments may not always contain sufficient nitrogen. By combining urea with organic fertilizers, you can ensure that your plants receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and productivity.
Remember to always follow the instructions and recommended dosage when using urea or any other fertilizer in your vegetable garden. It is also essential to monitor the plants’ response and make adjustments as necessary to achieve the best results.
Consultation and Expert Advice

If you have any questions or concerns about using urea in your vegetable garden, it is always advisable to seek consultation and expert advice. This will ensure that you are using urea correctly and in a way that is safe for your plants and the environment.
One source of expert advice is your local agricultural extension office. These offices are staffed with knowledgeable professionals who can provide guidance on fertilizers, including urea, and answer any specific questions you may have. They can also provide information on soil testing and offer recommendations based on the specific needs of your garden.
Another option for expert advice is to consult with a professional gardener or horticulturist. These individuals have in-depth knowledge and experience in gardening and can provide personalized recommendations for your vegetable garden. They can help you determine the appropriate application rate of urea, as well as any additional fertilizers or soil amendments that may be beneficial for your specific crops.
Additionally, there are many online resources available that offer expert advice on gardening and the use of urea. You can find forums, blogs, and websites dedicated to vegetable gardening where you can ask questions and receive advice from experienced gardeners. However, it is important to ensure that the information you find online is from a reliable and reputable source.
When seeking consultation and advice, be sure to provide specific details about your garden, such as the types of vegetables you are growing, the soil conditions, and any past fertilizer applications. This will help the expert tailor their advice to your specific situation and provide you with the most accurate recommendations.
By consulting with experts and seeking advice, you can ensure that you are using urea effectively in your vegetable garden and maximizing its benefits without causing harm to your plants or the environment. Remember, proper application and understanding of urea is crucial for achieving optimal growth and yield in your vegetable crops.
“Question-Answer”
What is urea and why is it used in the vegetable garden?
Urea is a type of nitrogen fertilizer that is commonly used in the vegetable garden. It provides plants with a readily available source of nitrogen, which is essential for their growth and development. Urea can help promote healthy foliage, increased fruit and vegetable production, and overall plant vigor.
How should urea be applied in the vegetable garden?
Urea can be applied to the vegetable garden by either broadcasting it over the soil surface or by diluting it in water and using it as a foliar spray. It is important to follow the instructions on the packaging for the specific application rates for your particular plants.
What are the benefits of using urea in the vegetable garden?
Using urea in the vegetable garden offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides plants with a quick and efficient source of nitrogen, which promotes fast growth and healthy foliage. Secondly, urea helps increase fruit and vegetable production, resulting in a higher yield. Finally, urea can also improve overall plant vigor and help plants withstand stressors such as disease and environmental changes.
Is urea safe to use in the vegetable garden?
Yes, urea is generally safe to use in the vegetable garden when used according to the instructions on the packaging. However, it is important to handle urea with care and avoid direct contact with the skin or eyes. It is also important to keep urea out of reach of children and pets.
Can urea be used on all types of vegetables?
Yes, urea can be used on all types of vegetables. However, it is important to follow the application rates specified on the packaging for each specific type of vegetable. Some vegetables may have different nutrient requirements, so it is important to do your research and adjust the application rates accordingly.
Are there any alternatives to urea for fertilizing the vegetable garden?
Yes, there are several alternatives to urea for fertilizing the vegetable garden. Organic fertilizers such as compost, manure, and bone meal can be used to provide plants with a slow-release source of nutrients. Additionally, there are also other synthetic fertilizers available on the market that provide a similar nutrient profile to urea.







